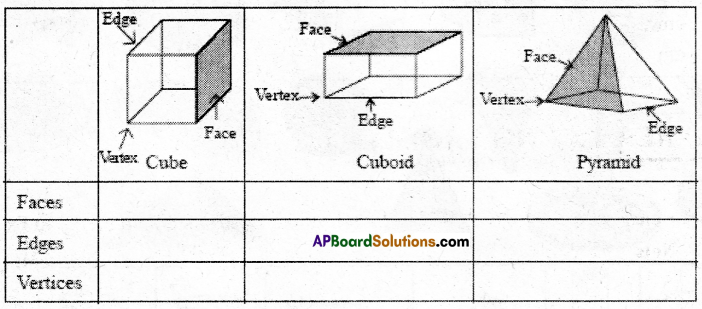
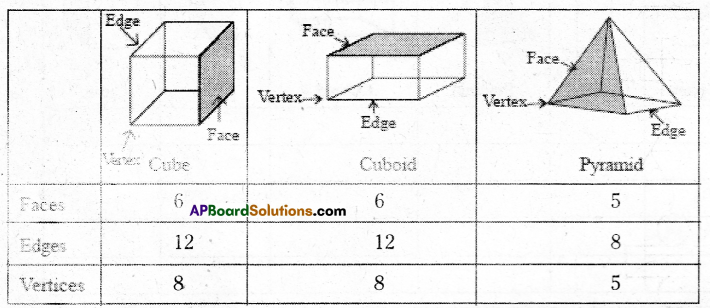
AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Data Handling Ex 1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Maths Solutions 7th Lesson Data Handling Exercise 1

Question 1.
Maximum day time temperatures of Hyderabad in a week (from 26th February to 4th March, 2011) are recorded as 26°C, 27°C, 30°C, 30°C, 32°C, 33°C and 32°C.
(i) What is the maximum temperature of the week?
(ii) What is the average temperatures of the week?
Solution:
i) Maximum temperature = 33C
ii) Average temperature = \(\frac{\text { Sum of the temperatures }}{\text { No. of observations }}\)
= \(\frac{26+27+30+30+32+33+32}{7}=\frac{210}{7}\)
∴ The average temperature of the week 30°C.
Question 2.
Rice consumed in a school under the mid-day meal program for 5 consecutive days is 15.750 kg, 14.850 kg, 16.500 kg, 14.700 kg, and 17.700 kg. Find the average rice consumption for the 5 days.
Solution:
Rice consumed for 5 days in kg = 15.750, 14.850, 16.500 14.700, 17.700
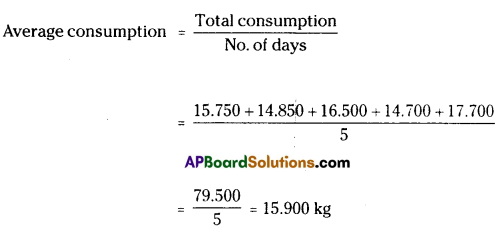
∴ The average rice consumption for the 5 days = 15.900 kg.

Question 3.
In a village three different crops are cultivated in four successive years. The profit (in rupees) on the crops, per acre is shown in the table below-
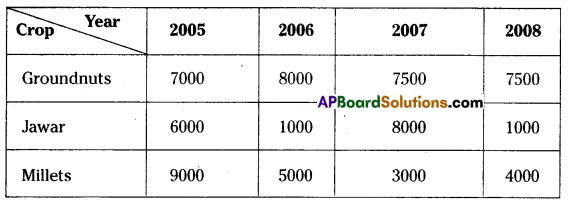
(i) Calculate the mean profit for each crop over the 4 years.
(ii) Based on your answers, which crop should be cultivated in the next year?
Solution:
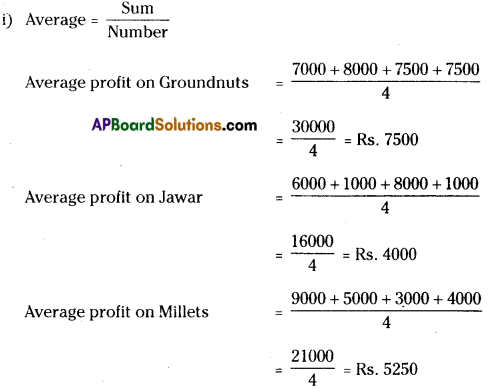
(ii) As the mean profit on Groundnuts is more than the other two crops, Groundnuts may be cultivated for the next year.
Question 4.
The number of passengers who travelled in APSRTC bus from Adilabad to Nirmal in 4 trips in a day are 39, 30, 45 and 54. What is the occupancy ratio (average number of passengers travelling per trip) of the bus for the day?

Solution:
Passengers travelled in 4 days 39. 30, 45 and 54
Average / Occupancy ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum }}{\text { Number }}=\frac{\text { Total passengers travelled }}{\text { Number of days }}\)
= \(\frac{39+30+45+54}{4}=\frac{168}{4}=42\)
∴ The occupancy ratio of the bus for the day = 42

Question 5.
The following table shows the marks scored by Anju, Neelesh and Lckhya in four unit tests of English.
(i) Find the average marks obtained by Lekhya.
(ii) Find the average marks secured by Anju. Will you divide the total marks by 3 or 4?Why?
(iii) Neelesh has given all four tests. Find the average marks secured by him. Will you divide the total marks by 3 or 4? Why?
(iv) Who performed best in the English?
Solution:
Average = \(\frac{\text {Sum of the observations }}{\text { Number of observations }}\)
i) Average marks obtained by Lekhya = \(\frac{20+24+24+24}{4}=\frac{92}{4}\) = 23
ii) Anju has given only three tests. So to find the average marks we divide by 3.
(i.e.) average = \(\frac{19+23+21}{3}=\frac{63}{3}\) = 21
iii) Neelesh has given 4 tests. So to find the average marks we divide by 4.
(i.e.) average = \(\frac{0+20+22+24}{4}=\frac{66}{4}\) = 16.5
iv) As the average marks of Lekhya is greater than the other two, we conclude that Lekhya
performed best in English.
Question 6.
Three friends went to a hotel and had breakfast to their taste, paying 16, 17 and 21 respectively
(i) Find their mean expenditure.
(ii) If they have spent 3 times the amount that they have already spent, what would their mean expenditure be?
(iii) If the hotel manager offers 50% discount, what would their mean expenditure be?
(iv) Do you notice any relationship between the change in expenditure and the change in mean expenditure.
Solution:
i) Mean expenditure = \(\frac{\text { Total expenditure }}{\text { No. of persons }}\)
= \(\frac{16+17+21}{3}=\frac{54}{3}\) = Rs. 18

ii) Amount spent = 3 times I.e., 3 × 16; 3 × 17; 3 × 21
= Rs. 48; Rs. 51; Rs. 63
Now the average = \(\frac{48+51+63}{3}=\frac{162}{3}\) = Rs. 54 = 3 x original average
iii) After 50% discount the amount spent is Half of the actual amount = \(\frac{16}{2}, \frac{17}{2}, \frac{21}{2}\)
= Rs.8; Rs. 8.50; Rs. 10.50
Now the average = \(\frac{8+8.50+10.50}{3}=\frac{27.00}{3}\) = Rs .9 = \(\frac{\text { Original average }}{2}\)
iv) The change In the observations is also carried out in the mean.
Question 7.
Find the mean of the first ten natural numbers.
Solution:
First ten natural numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10
∴ Average = \(\frac{\text { Sum of the numbers }}{\text { Number }}\)
= \(\frac{1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10}{10}=\frac{55}{10}\) = 5.5
∴ The mean of the first ten natural numbers = 5.5.

Question 8.
Find the mean of the first five prime numbers.
Solution:
First five prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7 and 11
Average of first five prime numbers = \(\frac{\text { Sum of the numbers }}{\text { Number of primes }}\)
= \(\frac{2+3+5+7+11}{5}=\frac{28}{5}\) = 5.6
Question 9.
In a set of four integers, the average of the two smallest integers is 102, the average of the three smallest integers is 103, the average of all four is 104. Which is the greatest of these integers?
Solution:
Given that
The average of four lntegers = 104 = \(\frac{\text { Sum of the four integers }}{\text { Number of integers }}\)
∴ The sum of the four integers = average × number
= 104 × 4
= 413
Also the average of the three smallest integers = 103 = \(\frac{\text { Sum of the three smallest integers }}{\text { Number of integers }}\)
∴ The sum of the smallest three integers = average × number
= 103 × 3
= 309
∴ The greatest integer / fourth number (Sum of four Integers) – (Sum of three integers)
=416 – 309 = 107

Question 10.
Write at least two questions to find the mean, giving suitable data.
Solution:
Q – 1: The daily income of a shop-keeper during 6 days are Rs. 350, Rs. 325, Rs, 400, Rs. 450, Rs. 600, Rs. 120. Find his average daily income.
Q – 2: The number of eggs sold by a poultry during 5 days are 480, 512, 680, 720 and 1026. Find the average daily sales.
![]()
![]()
![]()