AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Science Solutions Chapter 6 Fun with Magnets Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Science Solutions 6th Lesson Fun with Magnets
6th Class Science 6th Lesson Fun with Magnets Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Fill in the Blanks.
1. The materials which are attracted towards a magnet are called ——–.
Answer:
Magnetic material.
2. Paper is not a ——– material.
Answer:
magnetic
3. In the olden days, sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of ——–.
Answer:
natural magnet with thread.
4. A magnet always has ——– poles.
Answer:
two
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
1. Which of the following object is attracted by magnet?
A) wooden piece
B) plain pins
C) eraser
D) a piece of paper
Answer:
B) plain pins
2. A freely suspended magnet always comes to rest in the direction
A) North – East
B) South – West
C) East-West
D) North-South
Answer:
D) North-South
3. Magnets lose their properties when they are
A) used
B) stored
C) heated
D) cleaned
Answer:
C) heated
Answer the Following Questions.
Question 1.
List the magnetic and non-magnetic materials in your classroom.
Answer:
| S.No. | Material | Magnetic / Non-magnetic |
| 1. | Wooden benches | Non-magnetic |
| 2. | Two iron benches | Magnetic |
| ‘3. | Teacher’s wooden chair | Non-magnetic |
| 4. | Teacher’s wooden table | Non-magnetic |
| 5. | Wooden blackboard | Non-magnetic |
| 6. | Metal box attached to the blackboard for putting chalk pieces | Magnetic |
| 7. | Plastic dust bin | Non-magnetic |
| 8. | Nail in the wall for hanging maps | Magnetic |
Question 2.
If you have two similar bars, one a magnet and another a piece of iron. Can you find out which one of these is a magnet? Explain the process.
Answer:
- We will take a bar magnet. We have to identify two identical bars A and B. One as a magnet and the other as a simple bar.
- To identify, we have to bring our magnet to both the ends of bars A and B one after another.
- It is easy to locate the magnet. It attracts the bar magnet when pointed to its one end and repels if pointed to the other end.
- The iron bar will be attracted by the magnet in both situations.
Question 3.
The teacher said that the Earth is a magnet. But Sreevidya has some doubts and she asked her teacher some questions. What may be the questions?
Answer:
- Is there any big magnet present inside the Earth?
- Who has put that magnet inside the Earth?
- Where are the South and North poles of Earth’s magnet?
- How is this magnet inside the earth discovered?
- Is the magnet inside the earth there from the time of formation of the earth?
Such questions are likely to be asked by Sreevidya.
![]()
Question 4.
Does the Earth behave as a magnet? How do you prove it?
Answer:
- A bar magnet is placed on the table.
- Another bar magnet is suspended very close to the first one kept on the table.
- It is observed that the N – pole of the suspended bar magnet points towards the S – pole of the magnet placed on the table.
- The S – pole of the suspended bar magnet points towards the N – pole of the bar magnet kept on the table.
- Later the first bar magnet is removed from the table.
- Now the suspended bar magnet aligns itself in the North-South directions of the earth.
- This is because the earth influenced the Suspended bar magnet as the first magnet done.
- With this, it is evident that the earth behaves as a magnet.
Question 5.
Predict which of the following materials are magnetic and non-magnetic. Test with a bar magnet and check your predictions. What do you say after testing all materials? Plastic, Iron, Stainless steel, Wood, Aluminum, Gold, Silver, Copper, Paper, Cloth.
Answer:
My predictions and tests are recorded in the table given below.
| S.No. | Material | Prediction | Test with a bar magnet |
| 1. | Plastic | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 2. | Iron | Magnetic | Magnetic |
| 3. | Stainless steel | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 4. | Wood | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 5. | Aluminium | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 6. | Gold | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 7. | Silver | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 8. | Copper | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 9. | Paper | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| 10. | Cloth | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
Question 6.
Draw a bar magnet and locate the poles.
Answer:

Question 7.
Surya was wonderstruck to know that Earth is a big magnet and appreciated the efforts of scientists to discover this. Do you notice any such things in magnets to appreciate? Explain.
Answer:
I found the following things in magnets to appreciate.
- Every magnet has two poles. If we break a magnet into two pieces, each piece develops two poles and act as individual magnets.
- A freely suspended magnet always rests in the north-south direction. This helps in identifying the directions in new places.
- Iron nail kept near magnet act as magnet due to magnetic induction.
- Magnetic levitation helps to run electro-magnetic trains.
- The attraction property of magnets helps in the separation of magnetic materials from their mixtures.
- Electrical cranes are used to lift the huge weight of magnetic materials using this attraction property.
- Magnets are useful in various equipment such as motors, speakers, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Mention some situations where you use magnets in your day-to-day life?
Answer:
A magnet finds its use at a number of places.
| S.No. | Uses | S.No. | Uses |
| 1. | Refrigerator doors | 6. | Pin stand |
| 2. | Some pencil boxes | 7. | Fans |
| 3. | Many toys | 8. | Automobile dynamos |
| 4. | Magnetic stickers | 9. | Loud speaker |
| 5. | Soap stand | 10. | Microphones |
In addition, magnets are used in audio and videotapes and computer hard disks to store information. Magnets are also used for magnetotherapy.
Activities and Projects
6th Class Science Textbook Page No. 69
Question 1.
Think and say, in which directions your house is facing? Use the compass and find out the exact direction of your house and compare it with your prediction. Similarly predict and find out in which direction you keep your head while sleeping at night, the directions you face while you are reading, eating etc.
Answer:
- I felt my house is facing towards east.
- By using compass I found that it is very slightly towards north east.
- I predicted that I keep my head towards east while sleeping but found it is also very slightly towards north east.
- I predicted that I face towards east while reading and eating also. But I found it also same as above.
Question 2.
Prepare a toy using magnets and write the procedure of preparation briefly.
Answer:
- Secure a plastic toy car. Fix a small bar magnet in it by using tape.
- Now, keep the car on a table and hold it in your hand.
- Keep the N-pole of the magnet facing the S-pole of the magnet in the toy car.
- The car moves forward as your gradually draw the magnet in your hand backwards. (∵ unlike poles of magnets attract each other)
Question 3.
Think and say where the poles will be located in a ring magnet? Try to find out its poles using a bar magnet and check your prediction.
Answer:
Prediction: Magnetic poles are located on the upper and lower surfaces of a ring magnet.
Check:
- When I bring south pole of a bar magnet near the upper surface of the ring magnet they repel each other indicating that the upper surface of the ring magnet is its south pole.
- When I bring south pole of a bar magnet near the lower surface of the ring magnet they attract each other indicating that the lower surface of the ring magnet is its north pole.
- But I came to know from my teacher that there are three possibilities of having poles position basing on their mode of preparation.
i) Upper & lower surfaces( Axial)

ii) Parallel to the Height ( side by side )( Diametral)

iii) Inner and outer surfaces. (Radial)

![]()
Question 4.
Magnetize a needle using a bar magnet. Make a compass with that needle by following the process explained in activity.
Answer:
- Take a bar magnet and place one of its poles near to sharp edge of needle.
- Move the bar magnet along the length of the needle till we reach the other end.
- Then the bar magnet is lifted from the other end and brought to the same pole of the bar magnet.
- On repeating the process for at least 20 to 30 times the needle will became magnetized.

- Tape the magnetized needle to a light cork.
- Float the cork in a glass of soap water as shown in fig.
- The needle points in North-South direction. Thus it acts as a magnetic compass.
Question 5.
Kiran wants to prepare a toy using some magnets to make people understand the slogan “Reject bad food and accept only good food”. Can you help him to prepare the toy? If yes, how?
Answer:
- The toy can be prepared like this.
- Take a plate. Put good food on one side and bad food on the opposite side in the plate and label accordingly.
- A magnet is attached at the bottom of this plate with its N-pole pointing towards good food and S-pole pointing towards bad food.
- A magnet is fitted in the bottom of a duck where its S-pole points towards the mouth and N-pole points towards the tail of the duck.
- When good food portion of the plate is brought closer to the duck, the duck placed in a tub of water moves towards the plate because unlike poles of the magnets attract each other.
- When the bad food portion of the plate is brought closer to the duck, the duck moves away because like poles of the two magnets repel each other.
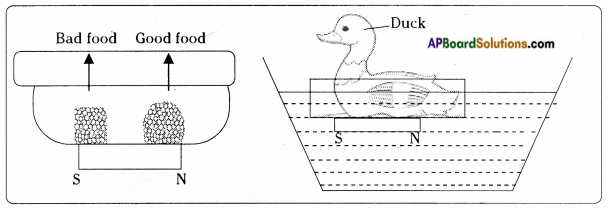
6th Class Science 6th Lesson Fun with Magnets Activities
Activity – 1
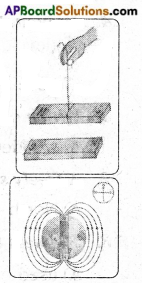
1. Take a steel glass. Put a magnet in it. Take a needle through which thread is passed. Press the thread with a finger near the eye of the needle as shown in figure 2 and raise the glass upward slowly. (Page No. 60)
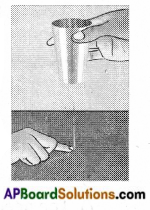
i) What happens?
Answer:
The needle stand vertically up without touching the glass.
ii) Does the needle stand vertically up without touching the glass? Why does this happen?
Answer:
Yes. This is because the magnet in the glass is attracting the needle.
Activity – 2
Finding Materials attracted by Magnets. (Page No. 61)
2. Take a bar magnet, nail, jump-clip, plastic scale, a piece of glass, key, paper, iron bolt, pen, blade, pencil, knife, stainless steel spoon, piece of chalk, wood, and touch the magnet to each item. Does the magnet attract every object? Observe and record your observations duly mentioning the name of the material of which the object is made in the table.

Answer:
| S.No. | Name of the object | Material of which the object is made | Attracted by Magnet (Yes / No) |
| 1. | Jump clip | Iron | Yes |
| 2. | Scale | Plastic | No |
| 3. | Nail | Iron | Yes |
| 4. | A piece of glass | Glass | No |
| 5. | Key | Iron | Yes |
| 6. | Paper | Paper | No |
| 7. | Iron bolt | Iron | Yes |
| 8. | Pen | Plastic | No |
| 9. | Blade | Iron | Yes |
| 10. | Pencil | Wood | No |
| 11. | Knife | Iron | Yes |
| 12. | Stainless steel spoon | Alloy | No |
| 13. | Piece of chalk | Mineral of Calcium | No |
| 14. | Wood | Wood | No |
i) Which materials are attracted by a magnet?
Answer:
Nail, jump-clip, key, iron bolt, blade, knife.
![]()
ii) Which materials are not attracted by a magnet?
Answer:
Plastic scale, a piece of glass, paper, pen, pencil, stainless steel spoon, piece of chalk, wood.
iii) Give your own examples for magnetic materials.
Answer:
Iron, cobalt, nickel.
iv) Give your own examples for non-magnetic materials.
Answer:
Gold, Silver, Copper, wood, paper, plastic.
Activity – 3
3. Spread some iron fillings uniformly on a sheet of paper. Place a bar magnet below this sheet. (Page No. 62)

i) What do you observe?
Answer:
I observe that the uniformly spread iron filings come close and get concentrate at two points of the paper sheet. At some distance, I found some scattered iron filings between these two points.
ii) Does the property of attracting iron filings remain the same for all parts of a bar magnet?
Answer:
No. the ends of the bar magnet attract more iron filings than the middle part of the magnet.
iii) Do you observe any change in the pattern of iron filings spread over the sheet?
Answer:
Yes, uniformly spread iron filings changed their pattern and concentrated more at endpoints of the bar magnet. Scattered iron filings between these two points are somehow in some lines from one point to other.
Activity – 4
4. Attraction and Repulsion between Two Magnets. Take two similar magnets, place them in four different ways as shown in Figure, and record your observations. (Page No. 63)
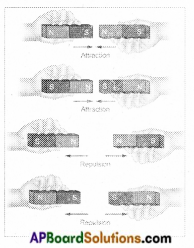
i) What do you observe?
Answer:
I observe that magnets not only attracts but also repel each other
ii) When do the magnets attract each other?
Answer:
In the first two situations, they attract each other. That means when unlike poles come close to each other they attract.
iii) When do the magnets repel each other?
Answer:
In the last two situations, they repel each other. That means when like poles come close to each other they repels.
![]()
Activity – 5
Finding directions with a bar magnet. (Page No. 63)
5. Suspend the bar magnet freely with the help of a thread tied around its center as shown in figure.
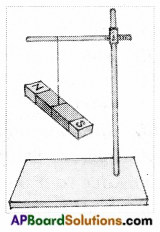
i) Does the magnet remain stationary?
Answer:
After some time it becomes stationary.
ii) Wait for some time. What do you find now?
Answer:
I found that the magnet rests in a north-south direction.
You will notice that the magnet finally takes a position in the North-South direction. Mark the endpoints towards the North with some color. Now disturb the magnet and again wait for some time.
iii) Where does the colored portion come to rest?
Answer:
The colored portion comes to rest towards the north.
iv) Repeat this experiment at another place. What do you observe?
Answer:
I observed that the magnets always come to rest in the North-South direction.
Activity – 6
Making Magnet (Page No. 64)
6. Aim: To make a magnet
What do you need? (Materials required): Iron nail/ piece of iron. Bar magnet, pin/ iron fillings.
What to do? (Procedure):
- Take a nail /a piece of Iron and place it on a table.

- Now take a bar magnet and place one of its poles near one edge of the nail / piece of iron and rub from one end to another end without changing the direction of the pole of the magnet.
- Repeat the process for 30 to 40 times.
- Bring a pin or some iron filings near the nail / piece of iron to check whether if has become a magnet.
What do you see?(Observation): The nail/ piece of iron attract the pin / iron filings. What do you learn? (Result): Iron nail,/ piece become a magnet.
![]()
Activity – 7
Making your own Magnetic Compass. (Page No. 65)
7. Aim: To make a magnetic compass
What you need? (Materials required: magnetized needle, tape, water, detergent.
What to do? (Procedure):
- Take a magnetized needle.
- Attach the needle with a tape to a light cork.
- Float the cork in a glass of water.
- Add a little detergent to the water to help the cork float freely.
What do you see? (Observation): The magnetized needle points in North- South direction.
What do you learn? (Result): This acts as a magnetic compass.
Activity – 8
Magnetic Induction (Page No. 65)
8. Aim: To observe and understand magnetic induction.
What you need? (Materials required): safety pin, alpin, bar magnet
What to do? (Procedure):
- Take a safety pin and bring it close to an alpin.
- Bring the safety pin close to one pole of a bar magnet and see how it gets attached to the magnet.
- Now bring an alpin and touch it to the safety pin.
What do you see?(Observation):
- Safety pin does not attract the Alpin when it is not in contact with magnet.
- But when it is in contact with a magnet it attracts the alpin.
- From the above two cases, we notice that the safety pin acts as a magnet when it is in contact with another magnet.
What do you learn? (Result): Magnetic property is induced in the safety pin due to the bar magnet. The magnetic property possessed by a magnetic substance due to the presence of a magnet near it, is called magnetic induction.
![]()
Activity – 9
9. Finding out whether the given object is a magnet or not. (Page No. 66)
You have been given three objects of the same size, shape and colour and a bar magnet. You have to decide which one among them is a magnet, which is not a magnet but made up of magnetic material or a non-magnetic material Bring three objects one after the other close to one pole of the bar magnet and observe whether they get attracted, repelled or not attracted. Record your observation in table 2. After that bring those objects close to the other pole of the bar magnet in the same way and record your observations.
Answer:
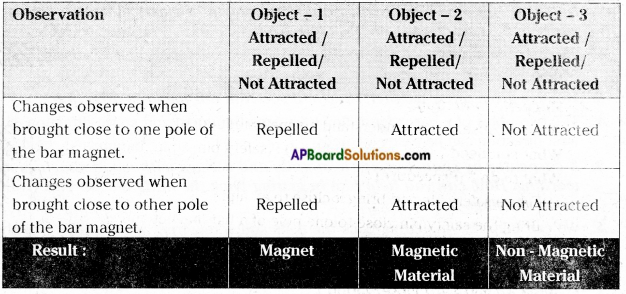
If an object is attracted by one pole of the bar magnet and repelled by its other pole, then it is a magnet. So object -1 is magnet.
If an object is attracted by both the poles of a bar magnet and not repelled by any pole, then it is not a magnet but a magnetic substance. So object -2 is made up of magnetic material.
If an object is neither attracted by a magnet nor repelled by it, then it is a non-magnetic substance. So object – 3 is made up of non- magnetic material.