Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 5(a) Immune System which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 5(a) Immune System
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Where are the testes located in man? Name the protective coverings of each testes.
Answer:
- Testes in man are located in a pouch outside the abdomen called scrotal sacs(scrotum).
- Each testis is enclosed in a fibrous envelope the tunica albuginea.
- The testis is also covered by an outer peritoneal layer called tunica veginalis.
Question 2.
Name the canals that connect the cavities of scrotal sac and abdominal cavity. Name the structures that keep the testes in their position.
Answer:
- Inguinal canal connects the scrotal sac to the abdminal cavity.
- The testis are held in position by gubemaculum, a fibrous cord. It connects the testis to the bottom of scrotal sac.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the functions of Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules and the Levdig cells in man? [AP MAY-22] [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
- Sertoli cells are nourishing cells. They nourish the spermatozoa and also produce a hormone called inhibin. It stops the production of FSH. They are present along with sperm mother cells.
- Leydig cells are interstitial cells present between columns of seminiferous tubules. They secrete androgens (male hormones) of which Testosterone is important.
Question 4.
Name the copulatory structure of man. What are the three columns of tissues in it?
Answer:
- The copulatory organ of man is penis.
- It has three columns of tissues. Thd two upper (dorsal) columns are corpora cavernosa and the single ventral column is corpus spongiosum.
Question 5.
Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer:
- Spermiogenesis is the process in which spermatids transform into spermatozoa.
- Spermiation is the process in which spermatozoa (sperm heads) are released from seminiferous tubules.
Question 6.
Name the yellow mass of cells accumulated in the empty follicle after ovulation. Name the hormone secreted by it and what is its function. [AP MAR 16,20]
Answer:
- After ovulation, the empty follicle is filled with yellow mass of glandular cells called corpus luteum.
- It secretes progesterone which maintains pregnancy.
Question 7.
Define gestation period. What is the duration of gestation period in the human beings?
Answer:
- The period (time) of development of an embryo inside the uterus is called gestation period.
It is the time between inception (fertilization) and delivery (parturition). - Human pregnancy (gestation) is about 38 weeks from fertilization or 40 weeks from the last menstrual cycle.
Question 8.
What is implantation, with reference to embryo?
Answer:
Implantation: It is an event that occurs early in human pregnancy (after 6th day of fertilisation.) in which the human embryo (blastocysts) adheres to the wall of the uterus.
![]()
Question 9.
Distinguish between epiblast and hypoblast.
Answer:
| Epiblast | Hypoblast |
| 1) After implantation, the outer layer of cells of germinal disc of blastocyst forms the epiblast. 2) It is future ectoderm. |
1) After implantation, the inner cell layer facing the blastocyst cavity forms the Hypoblast, 2) It is future extraembryonic endoderm. |
Question 10.
Write two major functions, each of testis and ovary.
Answer:
- The Testis produces sperms and male hormones(Testosterone) called androgens.
- The ovary produces ova and female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Question 11.
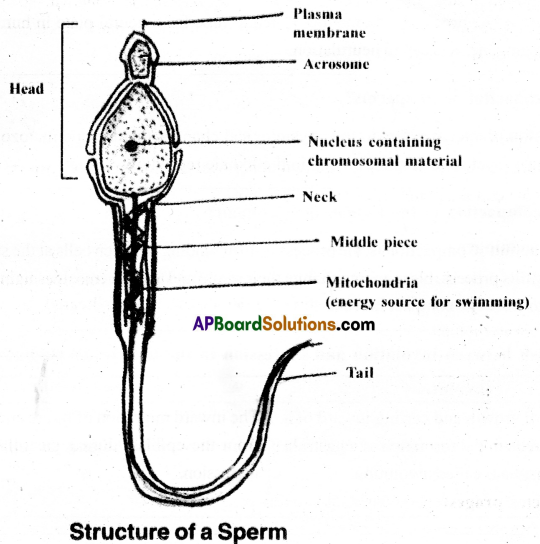
Draw a labelled diagram of a sperm
Answer:
Question 12.
What are the major components of the seminal fluid?
Answer:
- Major components of the seminal fluid: Fructose, proteins, citric acid, inorganic phosphorous, potassium and prostglandins.
- The secretion is contributed by Seminal vesicles, prostate gland and cowpers glands.
Question 13.
What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Answer:
- The reproductive cycle in the human, female primates is called Menstrual cycle.
- One ovum is released in the middle of each cycle.The endometrium of uterus develops and breaks down. In female humans, cyclic changes occur in uterus for every 28/29 days.
- The cycle is regulated mainly by four hormones:
(i) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
(ii) Lutinizing hormone(LH) from pituitary
(iii) estrogen
(iv) progesteron from ovary.
Question 14.
What is parturition? Which homones are involved in inducing parturition?
Answer:
- Parturition: It is the process of delivery of child birth.
- Oxytocin induces parturition.
Question 15.
How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave | birth to six puppies?
Answer:
For the formation of six puppies six eggs(ova) are released, unless there are no identical twins.
Question 16.
What is neurulation?
Answer:
Neurulation: The process of formation of neural tube from neural plate in human embryo, as part of organogenesis is called neurulation.
Question 17.
What is the capacitation of sperms? (TS MAR-19)
Answer:
Capacitation of sperm refers to the physiological changes that the spermatozoa undergoes to be able to penetrate and fertilize an egg in the female reproductive tract.
![]()
Question 18.
What is compaction in the human development? [AP MAR-15]
Answer:
- Compaction: Compaction is the process of firm binding between cells at the stage of morula.
- During this process, blastomeres change their shape and align themselves tightly against each other to form the compact morula.
Question 19.
Distinguish between involution and ingression in the human development.
Answer:
| Involution | Ingression |
| The inward grow th and curling inward of a group of cells in the formation of a gastrula from a blastula is called involution. | The inward migration of future endodermal cells from the epiblast during gastrulation is called ingression. |
Question 20.
What are the four extra embryonic membranes?
Answer:
The four extra embryonic membranes are Amnion, allantois, yolk sac and chorion. Those animals having extra embryonic membranes are called amniotes. Ex: Reptiles, Aves and Mammals. .
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe microscopic structure of testis of man.
Answer:
- Testes of man are present in scrotal sac outside the abdomen because tests cannot produce sperms at abdominal body temperature.
- Each testis is covered by a fibrous envelope called tunica albuginea.
- This tunic extends inside the testis and forms septa.
- In between septa there are about 250 lobules.
- Each lobule contains two or three highly coiled seminiferous tubules.
- Each seminiferous tubule is lined by germinal epithelium which has spermatogoneal mother cells and sertoli cells.
- Spermatogonia produce primary spermatocytes, which undergo meiotic division to produce spermatids.
- Spermatids form into spermotozoa or sperms by spermiogenesis.
- Sertolicells provide nourishment to spermatozoa and also produce a hormone inhibin which inhibits the secretion of FSH
- In between seminiferous tubules there are interstitial cells called ley dig cells (endocrine cells) which produce androgens (testosterone)
- Testosterone is essential for the developement of male secondary sexual characters.
- Seminiferous tubules open into rete testis which intum opens into vasa efferentia.
- Vasa efferentia open into epididymis which is divided into caput, corpus and cauda parts. Epididymis is highly and tightly coiled. It stores the sperms which mature here.
Question 2.
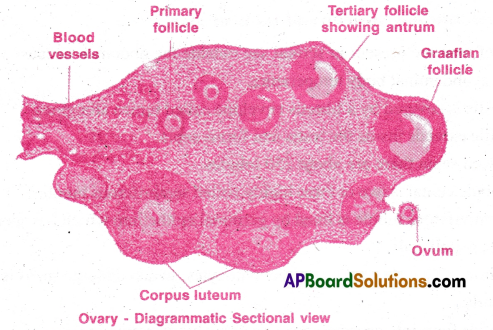
Describe the microscopic structure of ovary of woman.
Answer:
- Ovary: Ovaries are primary female sex organs. They produce ova and female hormones.
- The two ovaries are located in lower part of abodomen.
- Ovaries are connected to dorsal body wall by double layered peritoneum, the mesovarium.
- Ovaries are covered by simple cuboidal epithelium (germinal epithelim).
- Below the germinal epithelium there is tunica albuginea (a dense connective tissue capsule).
- The main body of ovary or stoma is divided into outer cortex and inner medulla.
- The medulla has loose connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphaties and nerve fibres.
- The cortex is granular due to the presence of ovarian follicles at different stages.
- Graafian follicles, corpusiuteum and corpus albicans are also found in ovary.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the Graaian follicle in woman.
Answer:
- The well developed and to be released follicle is called Graafian follicle.
- Graafian follicle is mature ovarian follicle.
- The oocyte is surrounded by zona pellucida a homogenous membrane.
- Outside zona pellucida there are are granulosa cells.
- The inner layer of granulosa cells close to zona pellucida, form corona radiata.
- Outside the oocyte, coronoradiata and granulosa cells a cavity called antrum is present.
- The antrum is surrounded by granulosa cells.
- The outer wall of graafian follicle is formed by outer theca exterma and inner theca interna.
- In between these two theca there are interstitial cells, connective tissue and blood capillaries.
- The egg to be released is at the secondary oocyte stage.
- The rupture of the follicle and release of ovum (ovulation) are induced by LH.
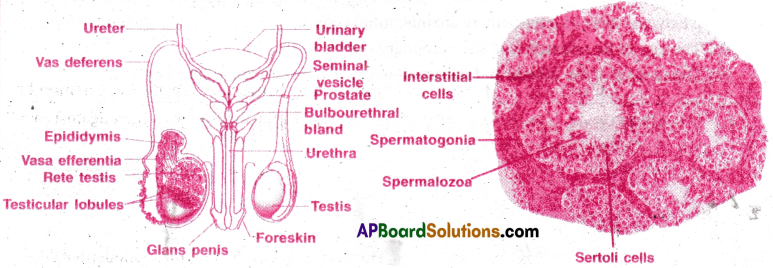
Question 4.
Draw a labelled diagram of the male reproductive system.
Answer:
Question 5.
Draw a labelled diagram of the female reproductive system.
Answer:
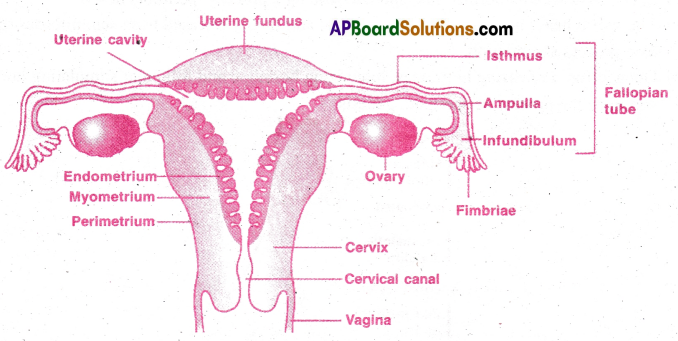
Question 6.
Describe the structure of seminiferous tubule.
Answer:
Seminiferous tubules:
- Seminiferous tubules are present in the. testicular lobules of the testis.
- The lobules are present in partitions formed by septa of tunica albugnea in testis.
- Each seminiferous tubule is highly coiled.
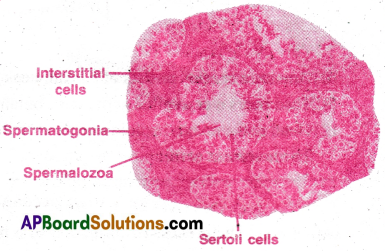
- The seminiferous tubule is lined by germinal epithelium.
- The germinal epithelium consists spermatogonial mother cells and sertoli cells.
- The spermatogonial mother cells produce primary spermatocytes which undergo meiotic division to produce spermatids.
- Spermatids transform into spermatozoa by spermiogenesis.
- Sertoli cells provide nourishment to spermatozoa.
- In between seminiferous tubules there are interstitial space containing leydig cells.
- Leydig cells secrete androgen hormones of which Testosterone is important. Seminiferous tubules open into retetestis (a network).
![]()
Question 7.
What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis in man.
Answer:
- Spermatogenesis The process of formation of sperms is spermatogenesis. In human males spermatogenesis begins at puberty.
- Spermatogonial stem cells are present in seminiferous tubules. They multiply by mitosis.
- Some of these cells develop into primary- spermatocytes (46 chromosomes).
- These primary spermatocytes undergo first meiotic division and produce secondary spermatocytes (23 chromosomes).
- The second spermatocytes undergo second meiotic division to produce spermatids.
- Each primary spermatocytes produces four equal sized haploid spermatids.
- Spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa by a process spermiogenesis.
- The sperm heads are embeded in sertolicells and finally released from seminiferous tubules by a process spermiation.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormones, luteinizing hormone and follicular stimulating hormone stimulate the process of spermato genesis.
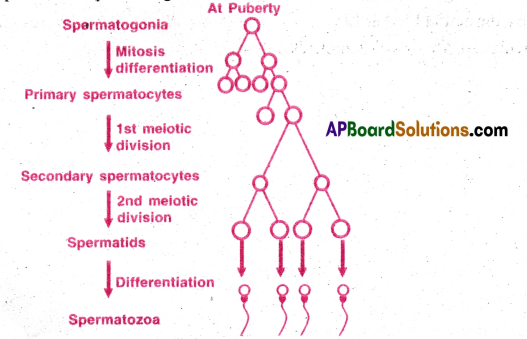
- A mature sperm consists of a head, neck, middle piece and tail.
- Head bears a cap called acrosome containing penetrating enzymes (Hyaluronidase).
- Head also contains haploid nucleus middle piece contains mitochondria which provide energy for movement of tail.
Question 8.
What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis in a woman.
Answer:
Oogenesis: The process of formation of a mature female gamete is called oogenesis.
- The female foetus has about two million oogonia in each ovary.
- Their development stops at prophase 1 ofmeiosis 1.
- At this stage they are called primary oocytes. Each primary oocyte is enclosed in flat follicular cells. It is called primordial follicle.
- Many of the priordial follicles degenerate before puberty.
- After reaching puberty the flat follicular cells become cuboidal and increase in number to form granulosa cells, (membrana granulosa)
- The primary oocyte with granulosa cells is called a primary follicle.
- A membrane is formed around primary oocyte called zona pellucida (between primary oocyte and membrana granulosa)
- The layer of granulosa cells close to zonapellucida firmly attach to it to form corona radiata.
- A cavity called antrum appears in granulosa cells and enlarge pushing the primary oocyte to one side.
- The granulosa cells surround the primary oocyte and maintain contact with granulosa cells outside the antrum by cumulus oophorus.
- The stroma cells of ovary condense around membrana granulosa to form theca interna.
- Fibrous tissue around theca interna condense to form theca externa.
- At this stage the follicle is called secondary follicle.
- The primary oocyte completes meiosis to form a large secondary oocyte (haploid) and first polar body.
- Second meiotic division begins and stops at metaphase-II.
- At this stage the follicle is called graafian follicle.
- By the action FSH & LH the folloicle grows in size and ruputures releasing the ovum. It is ovulation. Meiosis-II completes only when sperm enters ovum.
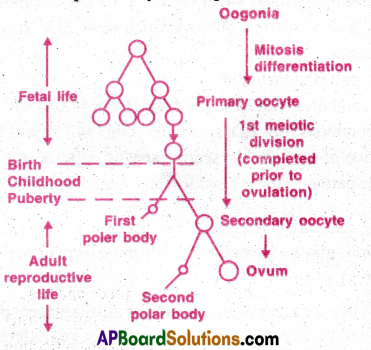
![]()
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Answer:
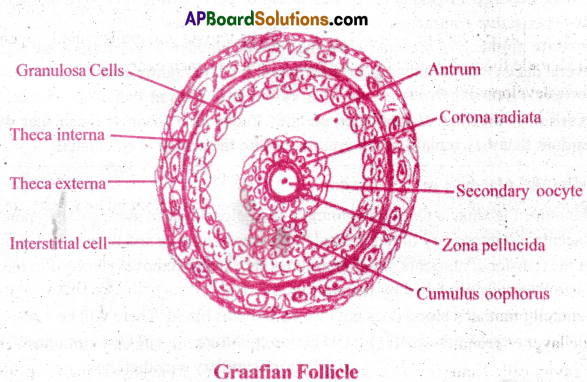
Question 10.
In our society women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Answer:
- A child develops from a zygote.
- A zygote is formed by the union of ovum from mother and sperm from father.
- Human female is homogametic i.e., she produces only one type of egges (ova).
- Her chromosomal configuration is 44XX (X is sex chromosome).
- She produces ova with 22X configuration only. So all the ova will have 22X chromosomes.
- Human male is heterogametic. He produces two types of sperms.
- His chromosomal configuration is 44XY (X and Y are sex chromosomes).
- He produces two types of sperms, 50% of which have 22X chromosomes and other 50% A have 22Y chromosomes.
- Fertilization is always a random union.
- When 22X ovum combines with 22X sperm the child (44XX) will be female.
- When 22X ovum combines with 22Y sperm the child (44XY) will be male.
- So the determination of sex is by the sperm carrying either X or Y chromosome.
- So it is by the male partner. So it is unethical and foolish to blame female partner for the sex of the child.
Question 11.
Describe the accessory glands associated with male reproductive system of man.
Answer:
Accessory glands of M.R.S:
a) Seminal vesicles: They are a pair of simple tubular glands present posterio-interior to urinary bladder. Each seminal vesicle opens into corresponding Vas deferens.
Their secretion constitute 60% total seminal fluid. It is alkaline, viscous fluid. It contains – fructose, proteins, citric acid, inorganic phosphorus, potassium and prostaglandins. Fructose provides energy. Prostaglands makes lining of cervix more receptive to sperms. They also cause peristaltic contraction of uterus and fallopian tubes.
b) Prostate gland: It is’present below the urinary bladder. The seretions are released through several ducts. It constitutes 15-30% seminal fluid. It is slightly acidic and activates the sperms.
c) Cowper’s glands (Bulbo urethral glands): It is present below the prostate glands. The secretion is alkaline. It lubricates urethra. It acts as a flushing agent that washes out the residues that may remain in the urethra, before the semen is ejaculated.
Question 12.
Describe the placenta in a woman.
Answer:
I) Placenta: Placenta is found in mammals and helps the intra uterine development of embryo.
Placenta is a temporary’ organ formed by tissues of mother and tissues of developing embryo for the transfer of nutrients, gases, hormones etc., It also removes carbon dioxide and excretory waste materials produced by the embryo.
Generally mother’s blood does not mix with foetus blood. There will be some barriers.
A) The maternal tissues are
- Uterine epithlium
- Uterine connective tissue
- Uterine capillary endothelium
B) The foetal tissues are
- Foetal capillary endothelium
- Foetal connective tissue
- Foetal chorionic epithelium
The human placenta is chorioallantoic placenta because chorion fuses with allantois.
The placenta is described as haemochoreal placenta because the chorionic villi directly come into contact with maternal blood.
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe female reproductive system of a woman with the help of a labelled diagram.
[AP MAY-22] [AP,TS MAR-15,19] [TS MAY-17]
Answer:
Human Female reproductive system:
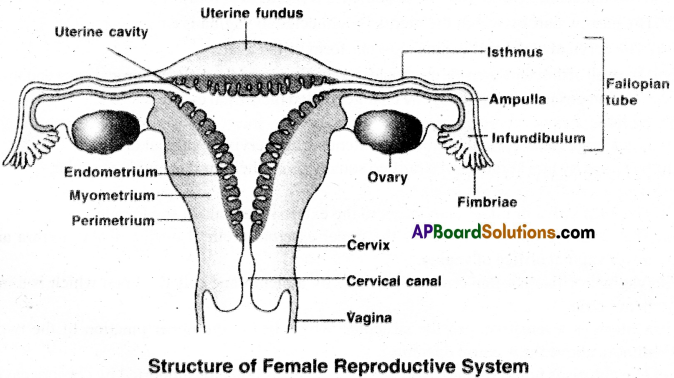
The female reproductive organs present in the pelvic region are as follows:
- Ovaries
- Fallopian tubes
- Uterus
- Vagina
- Vulva
1) Ovaries:
- Ovaries are the primary female sex organs that produce female gametes (ova) and also several steroid hormones.
- A pair of ovaries are located one on each side of the lower abdomen.
- Ovary is connected with the wall of abdominal cavity by a fold of peritoneum called mesovarium.
- Each ovary has 3 distinct regions.
(a) The ovaries are covered on the outside by a layer called germinal (ovarian) epithelium.
(b) Underneath this layer, there is a dense connective tissue capsule called tunica albuginea.
(c) The main body of ovary is called stroma. The outer part of stroma is cortex and inner part is medulla. This is made up of blood vessels, lymphatics and nerve fibres.
2) Fallopian tubes:
- Each fallopian tube extends from the periphery of each ovary to the uterus. .
- Each fallopian tube has funnel shaped infundibulum.
- The edge of infundibulum has finger like folds called fimbriae.
- Fimbriae collect ovum after ovulation.
- Infundibulum leads to wide ampulla.
- Isthmus is the last part which joins the uterus.
- Fallopian tube is the site of fertilization. It conducts the ovum towards the uterus by peristalsis.
- Fallopian tube is attached to body wall by mesosalpinx (fold of peritoneum).
3) Uterus:
- Uterus is single and is also called womb.
- It is present between urinary bladder and rectum.
- It is a large pear shaped sac. It is highly muscular and vascular.
- It is connected to body wall by mesometrium (peritoneal fold).
- The narrow part by which the uterus is connected to vagina is cervix.
- The cervical canal and vagina together form birth canal.
- The wall of the uterus is made up of outer perimetrium, middle myometrium and inner endometrium.
- Endometrium undergoes cyclic changes called menstrual cycle.
4) Vagina:
- It is a large fibro muscular tube that extends from cervix to vaginal orifice.
- It is lined by non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.lt is highly vascular.
5) Vulva or External genitalia :
- The term vulva or pudendum refers to the external genitals of the female.
- The vestibule has two apertures the upper external urethral orifice of the urethra and the lower vaginal orifice of vagina.
- Vaginal orifice is often covered partially by a membrane called hymen which is a mucous membrane.
- Clitoris is a sensitive, erectile structure, which lies at the upper junction of the two labia minora above the urethral opening.
- The clitoris is homologous to the penis of a male as both are supported by corpora cavernosa internally.
- There is a cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hair present above the labia majora It is known as mons pubis.
Accessory reproductive glands of female:
These glands include (a) Bartholin’s glands (b) Skene’s glands and (c) Mammary glands
a) Bartholin’s glands:
- The Bartholin’s glands (Greater vestibular glands) are two glands located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina
- They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina and are homologous to the bulbourethral glands of the male reproductive system.
![]()
b) Skene’s glands:
- The Skenes glands (Lesser Vestibular glands) are located on the anterior wall of the vagina, around the lower end of the urethra.
- They secrete a lubricating fluid when stimulated
c) Mammary glands:
- The mammary glands are paired structures (breasts) that contain glandular tissue and variable amount of fat.
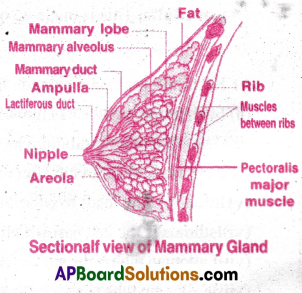
- Mammary glands contain alveoli which secrete milk after the birth of child.
- The Alveoli open into mammary tubules. The tubules of each lobe join to form a mammary duct.
- Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla which is connected to lactiferous duct through which milk is sucked out by the baby.
Question 2.
Describe male reproductive system of a man. Draw a labelled diagram of it.
Answer:
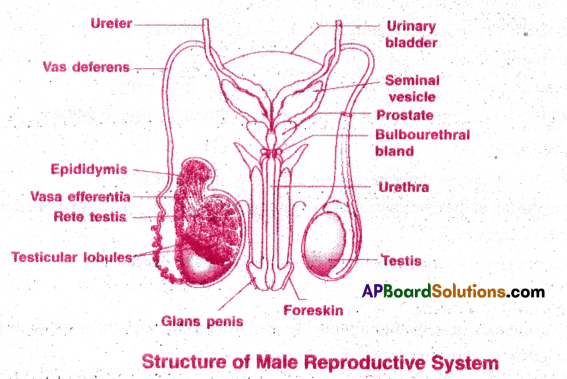
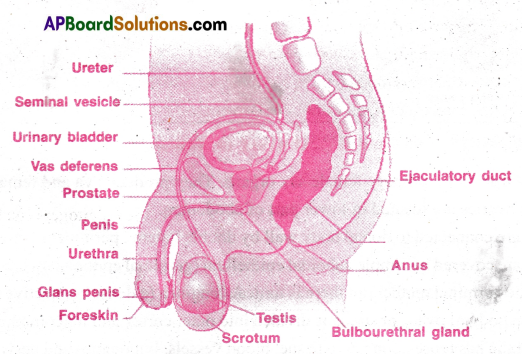
The male reproductive organs present in the pelvic region are as follows:
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Vasa deferentia
- Urethra
- Penis
- Accessory glands
I) Testes:
- Testes or testicles are a pair of oval pinkish male primary sex organs.
- They are suspended outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
- Sperms do not develop at body (abdominal) temperature so they descend into scrotum.
- The scrotum is connected to abdominal cavity through inguinal canal.
- Inside the scrotum, testis is held by gubemaculum. This connects testis to the bottom of scrotum and also by a spermatic cord that connects testis to abdominal wall.
- Spermatic cord is formed by the blood vessels, nerve and vas deferens. This cord runs from abdomen to each testis through inguinal canal.
- Tunica albuginea project inside the testis as septa. There are about 250 testiscular lobules in each testis. Each lobule contains 2 or 3 highly coiled seminiferous tubules.
- Each seminiferous tubules consists of germinal epithelium and sertoli cells. Germinal epithelium produces sperms. Sertoli cells nourish the sperms. The regions outside the seminiferous tubules called interstitial spaces contain Leydig cells. They produce male hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone .
- Testosterone controls the development of secondary sexual characters and spermatogenesis.
- Seminiferous tubules open in rete testis. Rete testis opens into vasa efferentia. Vasa efferential open into a highly coiled epididymis.
![]()
2) Epididymis :
- It is a narrow tightly coiled tube located along posterior surface of each testis.
- Vasa deferentia leave the testis and open into epididymis .
- Epididymis provides space for maturation and storage of spenns.
- Epididymis is divided into 3 regions
(a) caput epididymis (b) corpus epididymis and (c) cauda epididymis. - Caput epididymis receives the sperms from the testis through vasa efferentia.
3) Vasa deferentia:
- The vas deferens or ductus deferens is a long, narrow, muscular tube.
- It starts from the tail of the epididymis, passes through the inguinal canal into the abdomen and loops over the urinary bladder.
- The two ducts open into urethra at the centre of the prostate gland.
4) Urethra:
- The urethra originates from the urinary bladder and extends through the penis to its external opening called urethral meatus.
- The urethra provides an exit for urine as well as semen during ejaculation
- Urethra is shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary systems.
- Urethra is the urinogenital duct of man passes through penis to open outside.
5) Penis:
- The penis serves as a urinal duct and also intromittent organ that transfers spermatozoa to the vagina of a female.
- It has 3 columns of tissue. Two upper corpora cavernosa and one ventral corpus spongiosum.
- The terminal enlarge part is glans penis covered by loose skin(fore skin) called prepuce.
- Skin and a subcutaneous layer enclose all three columns, which consist of special tissue that helps in erection of the penis to facilitate insemination.
6) Male accessory genital glands: These glands include the following:
(a) a pair of seminal vesicles, (b) a prostate and (c) bulbourethral glands.
(a) Seminal vesicles.
- A pair of simple tubular glands is present below the urinary bladder. Each seminal vesicle opens into the corresponding vas deference.
- Its secretion constitutes 60% of total seminal fluid. It is alkaline and viscous fluid containing fructose, proteins, citric acid, inorganic phosphorous, potassium and prostaglandins.
- Fructose acts as the main energy source of the sperm.
(b) Prostate gland:
- It is present below the urinary bladder. Its contribution to seminal fluid is 15-30%.
- Its secretion is slightly acid. It activates the sperms and provides nutrition,
(c) Bulbourethral glands(Cowper’s glands):
- These are present below the prostate gland.
They add an alkaline fluid to semen during the process of ejaculation. - The fluid secreted by these glands lubricates the urethra.
Question 3.
Write an essay on diferent events that occur during development of a human.
Answer:
Human embryonic development:
1) Fertilization: Fertilization takes place in ampullary-isthmic junction of fallopian tube.
The sperm nucleus mixes with ovum nucleus forming zygote. This process is called syngamy. The calcium released in ovum stops the entry of other sperms. Corona radiata disappears.
2) Cleavage: It is holoblastic and indeterminate. First division occurs at 36 hours after fertilization. All the cells are equal in size. The solid ball of cell with 16-32 cells is Morula. Compaction takes place by tight juctions and gap junctions. A cavity is formed inside the ball and grows in size pushing the cells to the periphery. This cavity is blastocoel. The outer layer of cells form trophectoderm.
3) Blastocyst: The embryo with trophectoderm, inner cell mass and blastocoel filled with fluid is called blastocyst. The inner cell mass (formative cells) gives rise to embryo proper and extra embryonic membranes.
4) Implantation: Blastocyst reaches uterus. The zona pellucida disappears. Trophoblast cells stick to endometrium. It begins on 6th day after fertilization. Trophoblast invades uterus and forms villi and differentiates into two layers.
5) Embryonic disc: The inner cells mass transforms into two layered embryonic disc the outer layer epiblast (primitive ectoderm) and inner layer is hypoblast (extra embryonic endoderm).
6) Gastrulation: In this process the cells from epiblast migrate to their destinations. These movements are called morphogenic movements. Primitive streak marks the begining of gastrulation.
7) Notochord: The chorda mesodermal cells converge and involute over primitive knot and reach anteriorly ventral to epiblast and become notochordal rudiment which becomes notochord.
8) Neural tube: The notochordal cells induce the overlying epiblast cells to form a longitudinal ribbon like strip of cells. It is neuralplate ectoderm. It changes into a groove and lateral folds lateral unite dorsally to form a tube, the neural tube which later transform into brain and spinal chord.
![]()
9) Mesoderm: It is transformed into (a) epimere (b) hypomere and (c) mesomere
Epimere produces vertebral column, voluntary muscles, skin and other connective tissues, mesomere forms the urinogenital organs and their ducts.
Hypomere splits in splanchnic and somatic layer between which coelom is formed.
10) Extra embryonic membranes: They protect the embryo from desiccation, shock and helps in absorption of nutrients. They are ammion, allantois, chorion and yolksac
11) Placenta: The placenta is chorio allantoic placenta and hemochoreal placenta.
The chorionic villi directly come into contact with maternal blood.
12) Gestation period: Human pregnancy averages 266 days or 38 week from fertilization or another two weeks from last menstruation.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Variations are possible in
1. Multiple fission
2. Sexual reproduction
3. Budding
4. Schizogony
Answer:
2. Sexual reproduction
Question 2.
The ovaries are covered by
1. Germinal epithelium
2. Ciliated epithelium
3. Columnar epithelium
4. Mesovarium
Answer:
1. Germinal epithelium
Question 3.
Cleavage in man is
1. Holoblastic
2. Equal
3. Meroblastic
4. Determinate
Answer:
1. Holoblastic
Question 4.
The function of epididymis is
1. Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
2. Temporary storage of the sperms until they mature
3. Nourishing of the sperms only
4. Activation of the sperms only
Answer:
2. Temporary storage of the sperms until they mature
Question 5.
The fundamental feature of sexual reproduction is
1. Fusion of gametes produced by mitosis
2. Fusion of male and female haploid gametes produced by mitosis
3. Fusion of male and female gametes produced by meiosis
4. Fusion of two adult individuals
Answer:
3. Fusion of male and female gametes produced by meiosis
Question 6.
The testes are connected posterior to scrotal sacs by
1. Spermatic cords
2. Dartos muscle
3. Rachis
4. Gubenaculum
Answer:
4. Gubenaculum
![]()
Question 7.
Meiosis occurs in
1. Primary and secondary spermatocytes
2. Primary and secondary oocytes
3. Spermatogonia and oogonia
4. Both (1) and (2)
Answer:
4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 8.
The seminal plasm is secreted by
1. Prostate gland
2. Bulbourethral glands
3. Seminal vesicles
4. All the above
Answer:
4. All the above
Question 9.
The part of fallopian tube close to the ovary is
1. Ampulla
2. Cervix
3. Isthmus
4. Infundibulum
Answer:
4. Infundibulum
Question 10.
The enzyme essential for penetration of sperm through corona radiata and zona pcllueida is
1. Protease
2. Hyaluronidase
3. Hydrochloric acid
4. Citric acid
Answer:
2. Hyaluronidase
Question 11.
The day of implantation in human is .
1. 6th day after ovulation
2. 6th day after menstruation
3. 6th day after fertilization
4. 12th day after copulation
Answer:
3. 6th day after fertilization
Question 12.
The enzyme essential for implantation
1. Progesterone
2. Proteases
3. Lipases
4. Amylases
Answer:
2. Proteases
Question 13.
The foetal heart beat starts from
1. 14th day
2. End of I trimester
3. 4th week
4. 2nd month
Answer:
3. 4th week
Question 14.
Secretion of which gland has high percentage of fructose
1. Prostate gland
2. Cowper’s gland
3. Seminal vesicle
4. Tyson
Answer:
3. Seminal vesicle
Question 15.
In mammals, failure of testes to descend into scrotum is known as
1. Paedogenesis
2. Castration
3. Cryptorchidism
4. Impotency
Answer:
3. Cryptorchidism
Question 16.
Vasdeferens arises from
1. Cauda-epididymis
2. Caput epididymis
3. Corpus epididymis
4. Rete testis
Answer:
1. Cauda-epididymis
![]()
Question 17.
Which accessory genital gland occurs only in male mammal
1. Bartholin’sgland
2. Perineal gland
3. Prostate gland
4. All
Answer:
3. Prostate gland
Question 18.
Seminal vesicle is present at the junction of
1. Prostate and urethra
2. Prostate and vas-deferens
3. Prostate and cowper’s gland
4. vas-deferens and testis
Answer:
2. Prostate and vas-deferens
Question 19.
Spermatozoa are nourished during their development by
1. Sertoli cells
2. Interstitial cells
3. Connective tissue cells
4. None
Answer:
1. Sertoli cells
Question 20.
Eggs liberated from ovary in human is called
1. Secondary oocyte stage
2. Primary oocyte stage
3. Oogonial stage
4. Mature ovum stage
Answer:
1. Secondary oocyte stage
Question 21.
The Endocrinal structure formed after ovulation (release of ovum from graafian follicle is
1. Corpus albicans
2. Corpus callosum
3. Corpus luteum
4. Corpus striatum
Answer:
3. Corpus luteum
Question 22.
A female gland corresponding to prostrate of males is
1. Bartholin’sgland
2. Bulbourethral gland
3. Clitoris
4. None
Answer:
4. None
Question 23.
Luteal phase is the other name of
1. Follicular phase
2. Proliferative phase
3. Menstrual flow phase
4. Secretory phase
Answer:
4. Secretory phase
Question 24.
Which extraemhryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus?
1. Chorion
2. Allantois
3. Yolk sac
4. Amnion
Answer:
4. Amnion
Question 25.
Which is common regarded as urinary bladder of embryo?
1. Amnion
2. Allantois
3. Chorion
4. Yolk sac
Answer:
2. Allantois
Question 26.
Spermatogenesis is under the regulatory influence of
1. ADH
2. FSH
3. LH
4. STH
Answer:
2. FSH
![]()
Question 27.
Which is wrong about oogenesis?
1. Unequal meiotic division
2. Growth phase
3. Formation of polar bodies
4. Equal meiotic division
Answer:
4. Equal meiotic division
Question 28.
Prostaglandins are derived from
1. amino acids
2. steroid
3. fatty acids
4. carbohydrate
Answer:
3. fatty acids
Question 29.
Embryo at 16-cclled stage is called
1. Morula
2. Blastula
3. Blastomere
4. Gastrula
Answer:
1. Morula
Question 30.
The phase of menstrual cycle in human that lasts for 7-8 days, is
1. follicular phase
2. ovulatory phase
3. luteal phase
4. menstruation
Answer:
1. follicular phase
Question 31.
Both corpus lutea and macula lutea arc
1. Found in human ovaries
2. Source of hormones
3. Characterised by yellow colour
4. Contributory in maintaining pregnancy
Answer:
3. Characterised by yellow colour
Question 32.
Fertilizin is present and synthesized by
1. sperm head tip
2. egg surface
3. testes
4. epididymis
Answer:
2. egg surface
Question 33.
The secretory phase in the human menstrual cycle is also called
1. luteal phase and lasts for about 6 days
2. follicular phase and lasts for about 6 days
3. luteal phase and lasts for about 13 days
4. follicular phase and lasts for about 13 days
Answer:
3. luteal phase and lasts for about 13 days
Question 34.
The signals for parturition originate from
1. placenta only
2. placenta as well as fully developed foetus
3. oxytocin released from maternal pituitary
4. fully developed foetus only
Answer:
2. placenta as well as fully developed foetus
Question 35.
Second maturation division of mammalian ovum occurs
1. Until after sperm has penetrated into ovum
2. Until nuclei of sperm and ovum fuse
3. In Graafian follicle soon after first maturation division
4. Shortly after ovulation before entry into fallopian tube
Answer:
1. Until after sperm has penetrated into ovum
![]()
Question 36.
After ovulation, follicles converted into
1. Corpus luteum
2. Corpus albicans
3. Corpus cavernosa
4. Corpus callosum
Answer:
1. Corpus luteum
Question 37.
Bartholin’s glands are situated
1. on the sides of the head of some amphibians
2. at the reduced tail end of birds
3. on either side of vagina in humans
4. on either side of vas deferens in humans
Answer:
3. on either side of vagina in humans
Question 38.
What would happen if vasa deferentia of man are cut?
1. Sperms are non-nucleate
2. Spermatogenesis does not occur
3. Semen is without sperms
4. Sperms are nonmotile
Answer:
3. Semen is without sperms
Question 39.
The functional maturation of sperms takes place in
1. Oviduct
2. Epididymis
3. Vagina
4. All of these
Answer:
2. Epididymis
![]()
Question 40.
Accessory sexual character in female is promoted by
1. Androgen
2. Progesterone
3. Estrogen
4. Testosterone
Answer:
3. Estrogen