Access to a variety of AP Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Question Paper March 2017 allows students to familiarize themselves with different question patterns.
AP Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Question Paper March 2017
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 75
Note:
This question paper consists of THREE sections A, B and C.
Section – A
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt ALL questions.
- Each question carries TWO marks.
Question 1.
Find the equation of circle with centre (1, 4) and radius 5.
Solution:
Here (h, k) = (1,4) and r = 5
∴ (x – 1)2 + (y – 4)2 = 52
i.e; x2 + y2 – 2x – 8y – 8 = 0
Question 2.
Find the value of K if the points (1, 3) and (2, K) are conjugate with respect to the circle x2 + y2 = 35.
Solution:
Given circle is S = x2 + y2 – 35 = 0
the point (1, 3) (2, k) are conjugate w.r.t S = 0
⇒ S12 = 0
⇒ x1x2 + y1y2 – 35 = 0
⇒ (1) (2) + (3) (k) – 35 = 0
⇒ 2 + 3k – 35 = 0 ⇒ 3k – 33 = 0
∴ k = 11
![]()
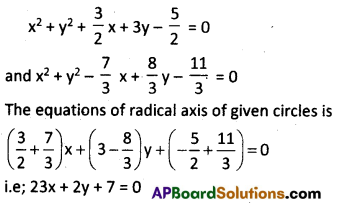
Question 3.
Find the equation of the radical axis of the circles
2x2 + 2y2 + 3x + 6y – 5 = 0 and 3x2 + 3y2 – 7x + 8y – 11 = 0.
Solution:
2x2 + 2y2 + 3x + 6y – 5 = 0 ……… (1)
3x2 + 3y2 – 7x + 8y – 11 = 0 …….. (2)
Here is given equations of the circles are not in the general form. Reducing them into general form.
We get
Question 4.
Find the coordinates of the points on the parabola y2 = 8x whose focal distance is 10.
Solution:
The focal distance of a point on the parabola y2 = 4ax is |x1 + a |
Here a = 2
∴ |x1 + 2| = 10
⇒ x1 = 8 ⇒ \(\mathrm{y}_1^2\) = 64 ⇒ y1 = + 8
∴ Coordinates of the points (8, + 8)
Question 5.
If the eccentricity of a hyperbola is \(\frac{5}{4}\), then find the eccentricity of its conjugate hyperbola.
Solution:
Let e and e be the eccentricities of the hyperbola and its conjugate respectively
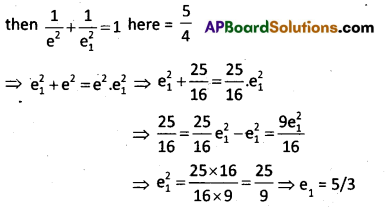
Question 6.
Evaluate ∫ex sin ex dx on R.
Solution:
Let t = ex
then dt = ex dx
∴ ∫ex sinexdx = ∫sint dt = -cos t + c = – cos (ex) + c
Question 7.
Evaluate ∫e<sup.x (sin x + cos x) dx on R.
Solution:
∫ex (sin x + cos x) dx, x ∈ R
take f(x) = sin x then f'(x) = cos x
So by using formula ∫ex [f(x) + f'(x) dx = ex f(x) + c we have
∫ex (sin x + cos x) dx = ex sin x + c.
Question 8.
Evaluate \(\int_2^3 \frac{2 x}{1+x^2} d x\)
Solution:
Let 1 + x2 = t
then 2x dx = dt,
∴ Upper limit t = 1 + 9 = 10 when x = 3
Lower limit = 1 + 4 = 5 when x = 2
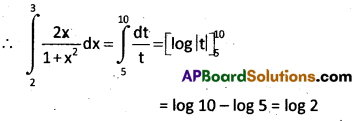
Question 9.
Find \(\int_0^{\pi / 2} \sin ^7 x\)dx
Solution:
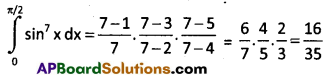
Question 10.
Find the general solution of \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{2 y}{x}\)
Solution:
The given equation can be written variable separable form as
\(\frac{d y}{2 y}\) = \(\frac{d x}{x}\)
⇒ log |y| = 2 log |x| + log c
⇒ log y = log x2 + log c
⇒ log (y/x2) = log c
⇒ y = cx2
⇒ x2 = \(\frac{1}{c}\)y
⇒ x2 = c1y where c1 is a constant is the general solution.
Section – B
(5 × 4 = 20)
II. Short Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt ANY FIVE questions.
- Each question carries FOUR Marks.
Question 11.
Find the pole of x + y + 2 = 0 with respect to the circle
x2 + y2 – 4x + 6y – 12 = 0.
Solution:
Given equation of the circle is x2 + y2 – 4x + 6y – 12 = 0
Comparing this equation with x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
We get g = – 2; f = 3; c = -12
Radius r = \(\sqrt{g^2+f^2-c}\) = \(\sqrt{4+9+12}\) = \(\sqrt{25}\) = 5
Given equation of the straight line is x + y + 2 = 0
Comparing this equation with lx + my + n = 0 we get l = 1; m = 1; n = 2
The pole of lx + my + n = 0, w.r.t x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is
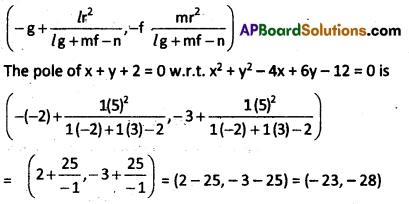
![]()
Question 12.
Find the equation and length of the common chord of the circles
x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y + 1 = 0, x2 + y2 + 4x + 3y + 2 = 0.
Solution:
Given equations of the circles are
S ≡ x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y + 1 = 0
S’ ≡ x2 + y2 + 4x + 3y + 2 = 0
The equation of the common chord of the circles S = 0 and S’ = 0 is S – S’ = 0
(x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y + 1) – (x2 + y2 + 4x + 3y + 2) = 0
x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y + 1 – x2 – y2 – 4x – 3y – 2 = 0
2x + 2y + 1 – 4x – 3y – 2 = 0
-2x – y – 1 = 0
2x + y + 1 = 0
Centre of the circle S = 0 is C = (-1, – 1)
Radius of the circle S = 0 is
r = \(\sqrt{(1)^2+(1)^2-1}\) = \(\sqrt{1+1-1}\) = \(\sqrt{1}\) = 1
Now d = the perpendicular distance from the centre C (-1, -1) to the common chord 2x + y + 1 = 0.
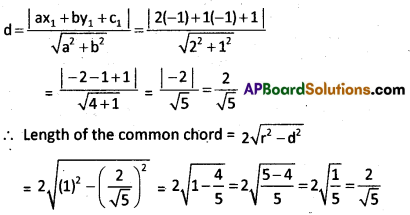
Question 13.
Find the length of latus rectum, eccentricity, coordinates of centre and foci of the ellipse 9x2 + 16y2 = 144.
Solution:
Given equation of ellipse is 9x2 + 1y2 = 1
Writing this in the standard form we get \(\frac{x^2}{16}\) + \(\frac{y^2}{9}\) = 1
and comparing with S = 0
we get a2 = 16; and b2 = 9 ⇒ a = 4 and b = 3.
Here a > b
- Length of the latus rectum = \(\frac{2 b^2}{a}\) = \(\frac{2(9)}{4}\) = \(\frac{9}{2}\)
- Eccentricity = \(\sqrt{\frac{a^2-b^2}{a^2}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{16-9}{16}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\)
- Coordinates of centre = (0, 0)
- Foci = ±(ae, 0) = (±\(\sqrt{7}\) ; 0)
Question 14.
Show that the locus of the feet of the perpendiculars drawn from foci to any tangent of the ellipse is the auxiliary circle.
Solution:
Let S = \(\frac{x^2}{a^2}\) + \(\frac{y^2}{b^2}\) – 1 = 0 be the equation of ellipse.
Let (x1, y1) be any point on the locus the equation of tangent to the ellipse.
S = 0 having slope ‘m’ is
y = mx ± \(\sqrt{a^2 m^2+b^2}\)
⇒ y – mx = ±\(\sqrt{a^2 m^2+b^2}\)
The equation to the perpendicular from either foci (±ae, 0) on the tangent (1) is
y – 0 = –\(\frac{1}{m}\) (x ± ae) ⇒ my + x = ± ae ……… (2)
Since P (x1, y1) is a point of intersection of (1) and (2) we have
y1 – mx1 = ±\(\sqrt{a^2 m^2+b^2}\) ……… (3)
and my1 + x1 = ± ae ……… (4)
Eliminating m from the equation by squaring and adding (3) and (4).
(y1 – mx1}2 + (my1 + x1)2 = a2m2 + b2 + a2e2
= a2m2 + a2(1 – e2) + a2e2
= a2m2 + a2 = a2(m2 + 1)
∴ \(y_1^2\)(1 + m2) + \(x_1^2\)(1 + m2) = a2 (1 + m2)
⇒ x2 + y2 = a2
∴ Locus of P (x1, y1) is x2 + y2 = a2 which is the equation of auxiliary circle of ellipse.
Question 15.
Find the equations of the tangents to the hyperbola 3x2 – 4y2 = 12 which are
i) parallel and
ii) perpendicular to the line y = x – 7.
Solution:
Given equation of the hyperbola is 3x2 – 4y2 = 12
\(\frac{x^2}{4}\) – \(\frac{y^2}{3}\) = 1. Here a2 = 4, b2 = 3
Given equation of the straight line is y = x – 7 ⇒ x – y – 7 = 0
i) The equation of the tangent parallel to the line x – y – 7 = 0 is
x – y + k = 0 …….. (1)
y = x + k
Comparing with y = mx + c, we get m = 1, c = k
Since equation (1) is a tangent to the given hyperbola then
c2 = a2m2 – b2
k2 = 4(1)2 – 3 ⇒ k2 = 1 ⇒ k = ±1
Substitute the value of k in equation (1).
∴ The required parallel tangents are x – y ± 1 = 0
ii) The equation of the tangent perpendicular to the line x – y – 7 = 0 is x + y + k = 0 …….. (2)
⇒ y = -x – k
Comparing with y = mx + c, we get m = -1, c = – k
Since equation (2) is a tangent to the given hyperbola then
c2 = a2m2 – b2
(-k)2 = 4(-1)2 – 3
k2 = 4 – 3 ⇒ k2 = 1 ⇒ k = ±1
Substitute the value of k in equation (2).
∴ The required perpendicular tangents are x + y ± 1 = 0.
Question 16.
Evaluate
\(\int_0^{\pi / 2} \frac{\sin ^5 x}{\sin ^5 x+\cos ^5 x}\)dx
Solution:
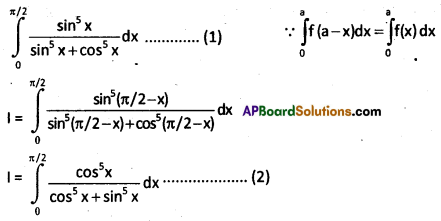
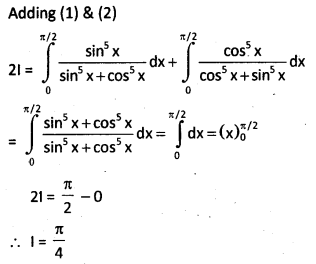
![]()
Question 17.
Solve the differential equation : \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + y tan x = cos3x
Solution:
Given \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + y tan x = cos3x
which is of the form \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + Py = Q where P = tanx and Q = cos3 x
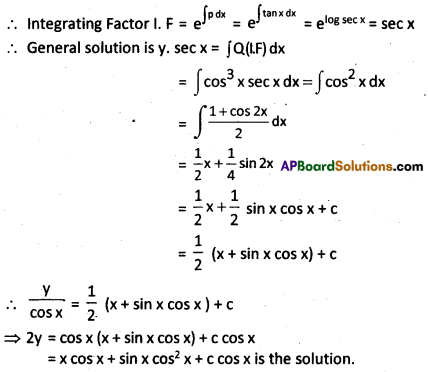
Section – C
III. Long Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt ANY FIVE questions.
- Each question carries SEVEN marks.
Question 18.
If (2, 6), (0, 1), (4, 5) and (0, C) are concyclic, then find C.
Solution:
Let, the equation of the required circle is
x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 ……. (1)
Since equation (1) passes through the point (2, 0) then
(2)2 + (0)2 + 2g(2) + 2f(0) + c = 0
4 + 4g + c = 0
4g + c = -4 ………. (2)
Since equation (1) passes through the point (0, 1) then
02 + 12 + 2g(0) + 2f(1) + c = 0
⇒ 2f + c = -1 ……… (3)
Since equation passes through the point (4, 5) then
(4)2 + (5)2 + 2g(4) + 2f(5) + c = 0
16 + 25 + 8g + 10f + c = 0
⇒ 8g + 10f + c = -41 …….. (4)
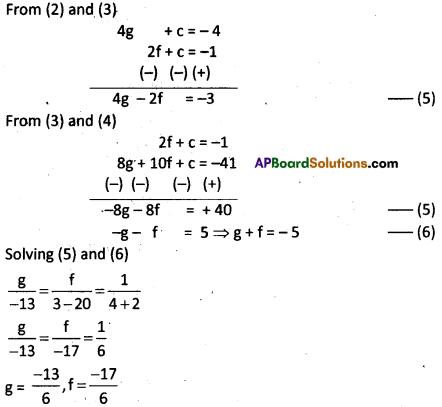
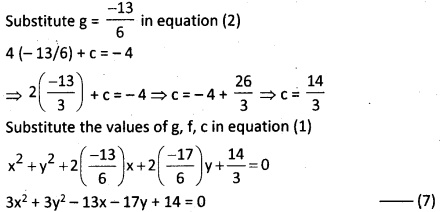
Since the given points are concyclic, then the point (0, c) lies on (7).
3(0)2 + 3c2 – 13(0) – 17c + 14 = 0
⇒ 3c2 – 17c + 14 =0
⇒ 3c2 – 3c – 14c + 14 = 0
⇒ 3c(c – 1) – 14(c – 1) = 0
⇒ (c – 1)(3c – 14) = 0 ⇒ c = 1; c = \(\frac{14}{3}\)
∴ c = 14/3
Question 19.
Show that the circles x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y – 12 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 6x + 18y + 26 = 0 touch each other. Also find the point of contact and common tangent at this point of contact.
Solution:
Given equations of the circles are
x2 + y2 – 4x – 6y – 12 = 0 ……… (1)
x2 + y2 + 6x + 18y + 26 = 0 …….. (2)
For the circle (1)
Centre C1 = (2, 3)
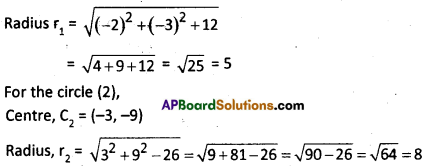
C1C2 = \(\sqrt{(2+3)^2+(3+9)^2}\) = \(\sqrt{5^2+12^2}\) = \(\sqrt{25+144}\) = \(\sqrt{169}\) = 13
Now, r1 + r2 = 8 + 5 = 13
∴ C1C2 = r1 + r2
∴ The given circles touch each other externally.
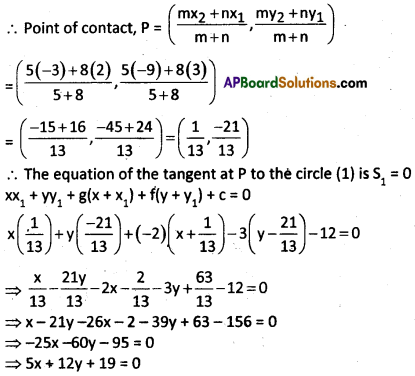
Let P be the point of contact.
Now, the point of contact divides C1C2 in the ratio r1: r2 (5 : 8) internally.
Question 20.
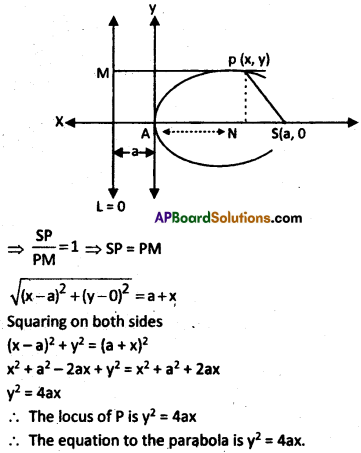
Show that the equation of the parabola in the standard form is y2 = 4ax.
Solution:
The equation of a parabola in the standard form is y2 = 4ax
Let ‘S’ be the focus and L = 0 be the directrix of the parabola.
Let ‘P’ be a point on the parabola.
Let M, Z be the projections of P, S on the directrix, L = 0 respectively
Let N be the projection of P and SZ.
Let ‘A’ be the mid point of SZ.
Since SA = AZ, ‘A’ lies on the parabola
Let As = a
take As, the principal axis of the parabola as x – axis and AY perpendicular to SZ as y – axis, then S = (a, 0) and the parabola is in the standard form.
Let P = (x, y)
Now, PM = NZ = AN + AZ = x + a
P lies on the parabola
![]()
Question 21.
Evaluate the integral \(\int \frac{x+1}{x^2+3 x+12}\)dx
Solution:
\(\int \frac{x+1}{x^2+3 x+12} d x\)
We write x + 1 = A\(\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) (x2 + 3x + 12) + B = A (2x + 3) + B dx
On comparing the coefficients of like powers of x on both sides of the above equation, we get
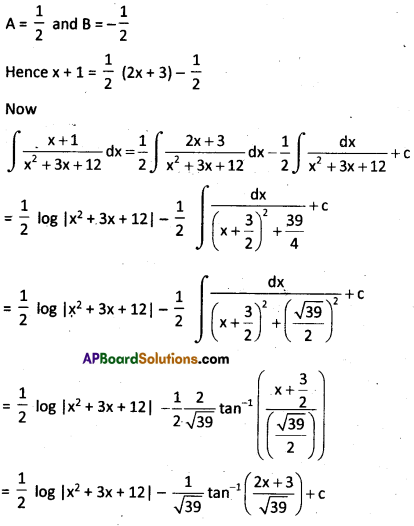
Question 22.
Obtain the reduction formula for ∫sinnx dx for an integer n ≥ 2 and deduce the value of ∫sin4x dx.
Solution:
Let In = ∫sinnx dx = ∫sinn-1x.sin x dx
Using Integration by parts.
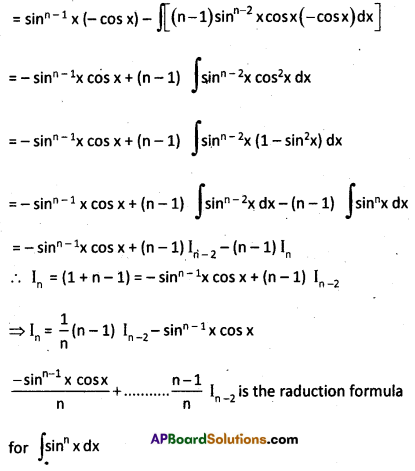
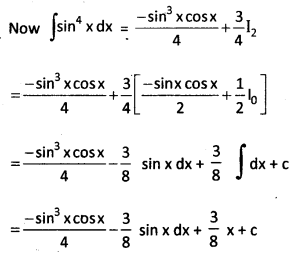
Question 23.
Evaluate \(\int_0^{\pi / 4} \frac{\sin x+\cos x}{9+16 \sin 2 x} d x\)
Solution:
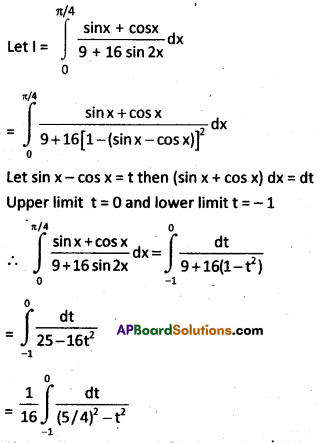
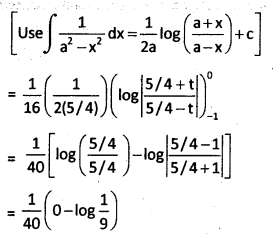
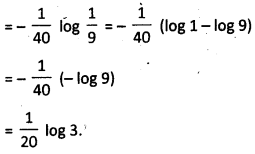
Question 24.
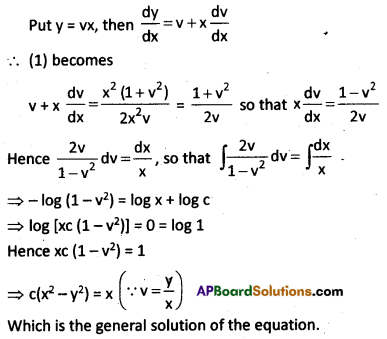
Solve the differential equation (x2 + y2) dx = 2xy dy.
Solution:
(x2 + y2) dx = 2xy dy
The given equation can be written as
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{x^2+y^2}{2 x y}\)
Which is a homogeneous equation, since the numerator and denominator on the right are homogeneous functions each of degree 2.