Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 4 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 4 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Distinguish between Home trade and Foreign trade.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Home trade and Foreign trade.
| Home Trade | Foreign Trade | |
| 1. Trade | Trade carries within the country. | Trade carried with other countries. |
| 2. Currency | It does not Involve any exchange of currency. | It involves the exchange of currencies. |
| 3. Restrictions | It is not subjected to any restrictions. | It is subject to many restrictions. |
| 4. Risk | Transport costs and risks are less. | Transport costs and risks are higher. |
| 5. Nature | It consists of sales, transfer, or exchange of goods within the country. | It involves the import and export of goods. |
| 6. Transport of Goods | The movement of goods depends on the internal transport systems, e.g: Roads and railways. | The movement of goods takes place usually by sea wherever possible. |
| 7. Specialisation | It helps to derive benefits of specialization within the country. | It helps all trading countries to derive the benefits of specialization. |
| 8. Volume of Trade | The volume of trade depends upon the size of the population, the volume of production, development of banking facilities. | There are restrictions imposed on the free entry of goods and duties and taxes are to be paid. |
| 9. Suitable | It facilitates the movement of goods from the point of production to the areas where they are consumed. | It facilitates countries to specialize in the production of goods for which they have maximum advantage. |
Question 2.
What do you understand by the word transport?
Answer:
Transport is the physical means of moving goods and persons from one place to another. Transport creates place utility of goods by moving them from different centers of production to places of consumption. Goods are” now produced thousand miles away from places where the consumer resides. Transportation only helps businessmen reach consumers. Not only does transport give place utility, but it also renders time utility in various ways. Transportation, in simple language can be defined as “a means through which goods are transferred from one place to another”.
Benefits of Functions of Transport:
- Movement of goods: The first and most important function of transport is the movement of goods. The raw materials have to move from their sources to the factory. The manufactured goods have to move from the factory to the consuming areas.
- Transport enhances the mobility of labour and capital: An efficient network of transport services encourages the movement of people from one place to another labour can migrate to the place where they can get better job opportunities which reduces the exploitation of labour.
- Creation of place utility: It moves goods from places where they are abundant to places where they are scarce and thus creates place utility.
- Specialization and division of labour: Transportation facilitates the optimum utilization of the natural resources of a country. For example, the petroleum resources of Arab countries, watches of Switzerland, etc.
- Creation of time utility: With the advancement of technology, transportation time is being shortened. So, it creates time utility.
- Stability in prices: Goods can be transported from the place where the goods are abundant, to the places where scarcity exists. In this way, prices are equalized throughout the country.
- Contribution to national income: Transportation also contributes national income of a nation. For example, our railways.
- Economies of large-scale production: Transport has helped the development of large-scale industries. Transport procures raw materials, and labor and sells the finished goods.
- Improve the standard of living: Availability of a wide variety of goods at reasonable prices improves the standard of living.
- National defense: Transport strengthens the national defense transport system. During the war period, all the personnel, materials, and equipment can be moved rapidly to the border areas.
Limitations of Transport:
- Cottage and small-scale industries lost their glory: With the development of transport, labor is showing interest in working in big factories. This has led to a shortage of workers in tiny and small-scale industries.
- Accidents: Improvement in transport facilities has given rise to new problems viz. accidents.
- High urbanization: Improved means of transport have helped in creating big cities, which have further resulted in the concentration of the population in these cities. This has given rise to many new problems such as housing, health, and pollution.
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by the financial market? Briefly explain its functions and classification.
Answer:
A financial market is a broad term describing any marketplace where buyers and sellers participate in the trade of financial assets such as equities, bonds, currencies, and derivatives. Investors have access to a large number of financial markets and exchanges representing a vast range of financial products. Some of these markets have always been open to private investors; Others remained the exclusive domain of major international banks and financial professionals until the very end of the twentieth century. Specifically, financial markets play an important role in the allocation of scarce resources in an economy by performing the following four important functions.
1. Mobilisation of Savings and Channelling them into most Productive Uses:
A financial market facilitates the transfer of savings from savers to investors. It gives savers to choice of different investments and thus helps to channel surplus funds into the most productive use.
2. Facilitating Price Discovery:
It is known that the forces of demand, and supply help to establish a price for a commodity or service in the market. In the financial markets, households are suppliers of funds and business firms represent the demand. The interaction between them helps to establish a price for the financial asset that is being traded in that particular market.
3. Providing Liquidity to Financial Assets:
Financial markets facilitate the easy purchase and sale of financial assets. In doing so, they provide liquidity to financial assets, so that they can be easily converted into cash whenever required. Holders of assets can readily sell their financial assets through the mechanism of their financial market.
4. Reducing Cost of Transaction:
Financial markets provide valuable information about securities being traded in the market. It helps to save time, effort, and money that both buyers and sellers of financial assets would have to otherwise spend to try and find each other. The financial market is thus, a common platform where buyers and sellers can meet for fulfilment of their individual needs.
Financial markets are classified, based on the maturity of financial instruments traded in them, into the money market and capital market. Financial instruments with a maturity of less than one year are traded in the money market and those with long maturity are traded in the capital market. Further, the money market is classified primarily into the call money market, acceptance market, bill market, and collateral loan market, whereas the capital market may include both primary market and secondary market.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Role of entrepreneurship in economic development.
Answer:
- Entrepreneurship promotes capital formation by mobilizing the idle savings of the public.
- It provides large-scale employment and helps to reduce the unemployment problem.
- Entrepreneurship promotes balanced regional development.
- It helps to reduce the concentration of economic power.
- Entrepreneurship stimulates the equitable distribution of wealth, income, and even political power in the interest of the country.
- Entrepreneurship encourages effective resource mobilization of capital and skill which might otherwise remain unutilized and idle.
- It also induces backward and forward linkages which stimulate the process of economic development.
- Entrepreneurship also promotes the country’s export trade. It is an important ingredient to economic development.
Question 5.
Objectives of SEZ.
Answer:
Objectives: The following are the objectives of special economic zones.
- To create employment opportunities.
- To generate additional economic activity.
- To promote the export of goods and services.
- To develop infrastructural facilities.
- To promote investment from domestic and foreign sources.
- To import capital goods and raw materials duty-free.
- To create a foreign territory for trade operations and tariffs.
- To allow 100% foreign direct investment for developing townships.
- To exempt import duties and service tax.
- To get a wide range of income tax benefits.
Question 6.
Explain the features of fire insurance.
Answer:
According to Asbury, Fire insurance is defined as “It is a contract of insurance by which the insurer agrees for consideration to indemnify the insured upto a certain extent and subject to certain terms and conditions against loss or damage by fire which may happen to the property of the insured during a specified period”.
Features of Fire Insurance:
- Contract of indemnity: The fire insurance contract is a contract of indemnity and the insured cannot claim more than the value of goods lost or damaged by fire or the amount of the policy whichever is less.
- Lawful consideration: There must be a consideration in the fire insurance contract. The consideration is paid by the insured, which is called the premium. Thus the essential element of a fire insurance contract is the premium received from the insured.
- Insurable interest: The insured must have an insurable interest in the property or goods insured against fire. He must have an insurable interest at the time of taking the policy and also at the time when the loss occurs and the claim is filed for compensation.
- Claim over residue: The scrap or damaged goods after the fire accident automatically pass on to the insurer after the payment of the claim under fire insurance.
- Cause of accident: The loss must be the outcome of fire or ignition. No other reason for loss of property is accepted for settlement of claim.
- Utmost good faith: In a fire insurance contract, both the insured and insurer must have utmost good faith in each other.
![]()
Question 7.
Disadvantages of Railway transportation.
Answer:
- The railways require a large investment of capital. The cost of construction, maintenance, and overhead expenses are very high compared to other modes of transport.
- Railway transport is not flexible. The routes and timings cannot be adjusted to the individual requirements.
- Rail transport cannot provide door-to-door service as it is tied to a particular track.
- Railway transport is unsuitable and uneconomical for short distances and small tariffs on goods.
- It involves much time and labour for booking and taking delivery of goods through railways.
Question 8.
Write the regulating functions of SEBI.
Answer:
- Registration of brokers, sub-brokers, and other players in the market.
- Registration of collective investment schemes and mutual funds.
- Regulation of stock brokers, portfolio exchanges, underwriters, and merchant bankers and the business of stock exchange and any other securities market.
- Regulation of takeover bids by companies.
- Calling for information by undertaking inspections, conducting inquiries, and audits of stock exchanges and intermediaries.
- Levying fee or other charges for carrying out the purposes of the Act.
- Performing and exercising such power under the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, as may be delegated by the Government of India.
Question 9.
Explain about depositing.
Answer:
Depository:
Just like a bank keeps money in safe custody for customers, a depository is also like a bank and keeps all securities in electronic form on behalf of the investor. In the depository, a securities account can be opened, all shares can be deposited, they can be withdrawn/sold at any time, and instruction to deliver or receive shares on behalf of the investor can be given. It is a technology-driven electronic storage system. It has no paperwork relating to share certificates, transfer forms, etc. All investors’ transactions are settled with greater speed and efficiency and all securities are entered in a book entry.
Dematerialisation:
All trading in securities is now done through computer terminals. Since all systems are computerized, the buying and selling of securities are settled through an electronic book entry form. This is mainly done to eliminate problems like theft, fake/forged transfers, transfer delays, and paperwork associated with share certificates or debentures held in physical form. In this process securities held by the investor in physical form are canceled and the investor is given an electronic entry or number so that he can hold it as an electronic balance in an account. The process of holding securities in an electronic form is called dematerialization. For this, the investor has to open a Demat account with an organization called a depository. Now all initial public offers are issued in dematerialized form.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Explain any one function of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
An entrepreneur performs all the functions necessary right from the generation of an idea and upto setting up an enterprise. The following are the functions of an entrepreneur.
Decision Making:
An entrepreneur as a decision maker takes various decisions regarding the following:
- Ascertaining the objective of the enterprise
- Sources of finance
- Product mix
- Pricing policies
- Promotion strategies
- Appropriate technology or new equipment etc.
Question 11.
Entrepot trade.
Answer:
When goods are imported into a country, not for consumption in that country, but for exporting them to a third country, it is known as ‘Entrepot trade’.
e.g.: India importing wheat from the U.S. and exporting the same to Sri Lanka.
Question 12.
Electronic banking.
Answer:
The concept of E-banking will enable anyone to transact with the bank from anywhere such as home or office at any time convenient to him, which can be beyond banking hours. Electronic banking is banking with the use of electronic tools and facilities and through electronic delivery channels.
Question 13.
What is the proximate cause?
Answer:
According to this principle, if the loss is caused by a nearest and direct factor, then only the insurer will have to bear the loss. The principle is useful in deciding the actual cause of loss when several causes have contributed to the occurrence of loss.
Question 14.
What is freight insurance?
Answer:
If the cargo does not reach the destination due to damage or loss in transit, the shipping company is not paid freight charges. Freight insurance is for reimbursing the loss of freight to the shipping company i.e., insured.
![]()
Question 15.
Cash credit.
Answer:
A cash credit is an agreement where by a bank agrees to lend money to the borrower upto a certain limit. The amount is credited to the account of the borrower. The borrower draws money as and when he needs it. Interest is charged on the amount drawn.
Question 16.
Primary market.
Answer:
It is also known as the new issue market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time. The essential function of the primary market is to facilitate the transfer of investible funds from savers to entrepreneurs.
Question 17.
What is consumerism?
Answer:
Consumerism is defined as a social force designed to protect consumer interest in the marketplace by organizing consumer pressure on businesses. By consumerism, we mean the process of realizing the rights of the consumer as entries in the Consumer Protection Act, of 1986, and ensuring the right standards for the goods and services for which one makes payment.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
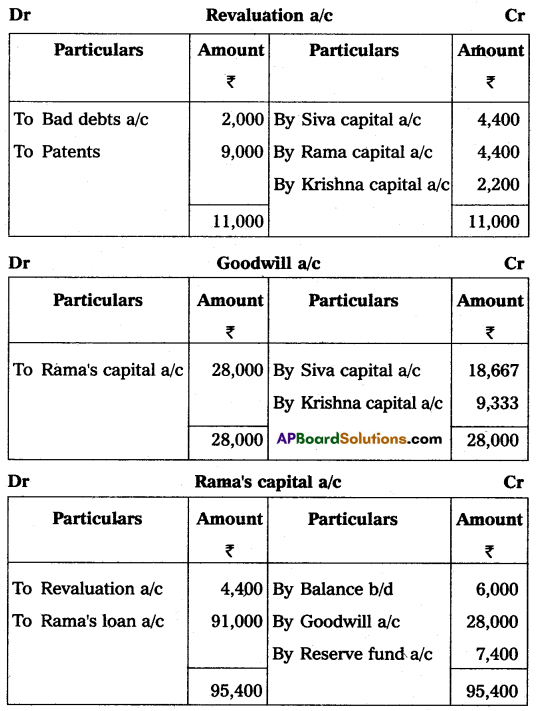
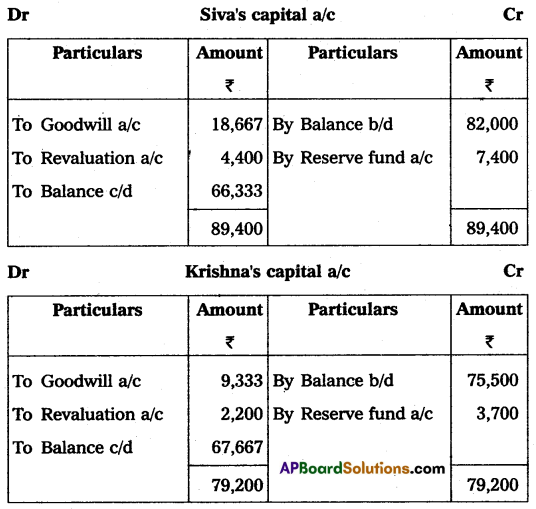
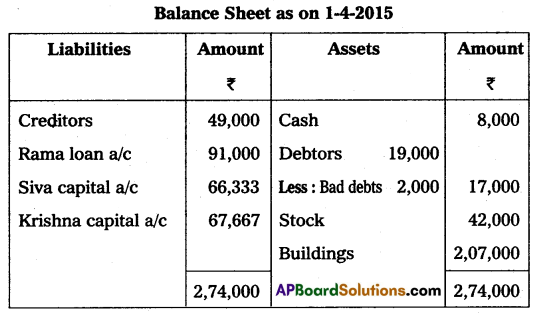
Siva, Rama, and Krishna were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. Their Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2015, was as follows:
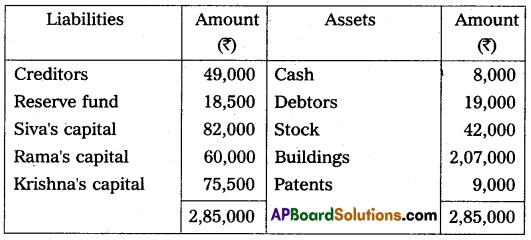
Rama retired on 31st March 2015 on the following terms:
(i) The firm’s goodwill was valued at ₹ 70,000 and was not to appear in the books.
(ii) Bad debts amounting to ₹ 2,000 were to be written off.
(iii) Patents were considered as valueless.
Prepare the Revaluation account, partners’ capital accounts, and the Balance sheet.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
On 1st April 2011, Rajesh Transport Company purchased 4 trucks at ₹ 6,00,000 each. The company writes off depreciation @ 10% per annum on the original cost. On 1st July 2013, one of the trucks was involved in an accident and destroyed. The insurance company paid ₹ 3,00,000 in full settlement of the claim. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Prepare truck account for three years.
Answer:
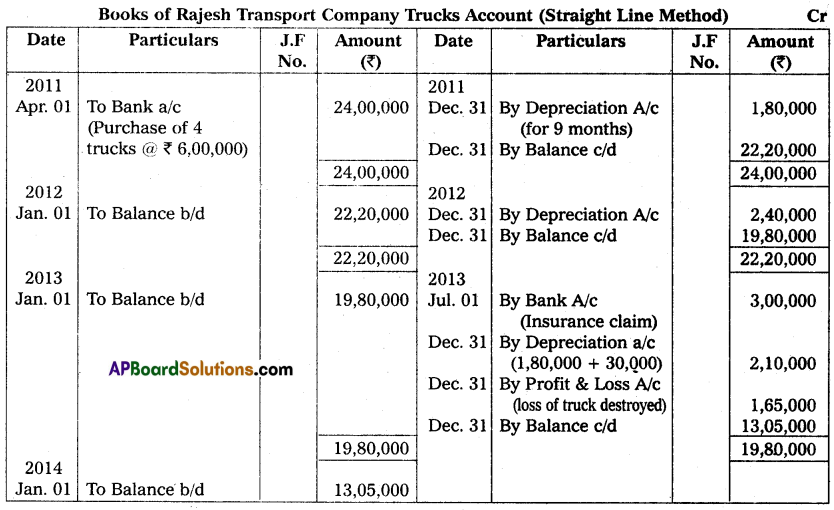
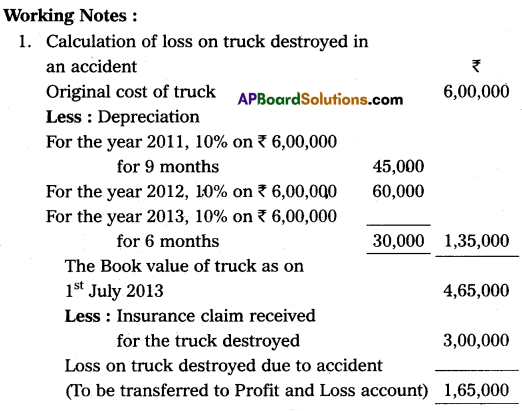
(Or)
Question 20.
Visakha Sports Association extracts the following receipts and payments A/c for the year ended 31-Dec-2014. From the particulars given, prepare income and expenditure a/c.
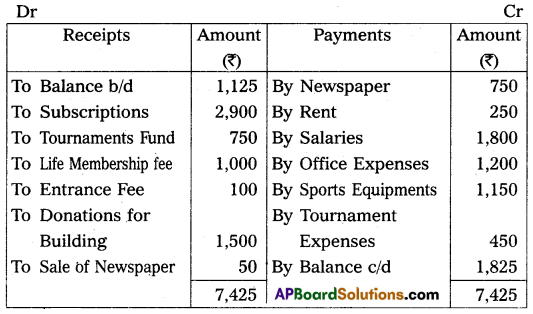
Adjustments:
(a) Subscriptions outstanding on 31, Dec., 2013 – ₹ 450, and on 31, Dec., 2014 – ₹ 400. Subscriptions received include ₹ 100 on account of the year 2015.
(b) Sports equipment was valued on 31, Dec., 2013 – ₹ 550, and on 31, Dec., 2014 – ₹ 1,090.
(c) Office expenses include ₹ 150, for the year 2013 whereas ₹ 200 is still payable on this account for 2014.
Answer:
Income and Expenditure of Visakha Sports Association for the year ended 31st Dec. 2014
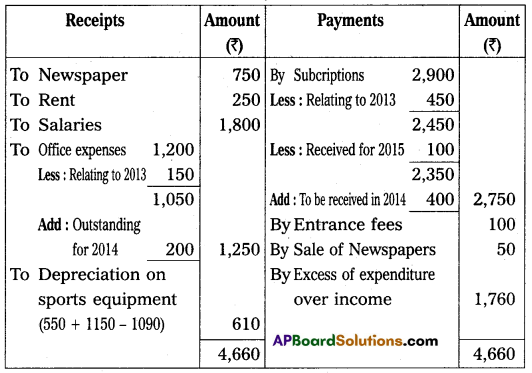
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
Difference between receipts and payments account and income and expenditure account.
Answer:
| Basis of Distinction | Receipts and Payment Account | Income and Expenditure Account |
| 1. Type of Account | Real Account | Nominal Account |
| 2. In Lieu of | It is prepared in lieu of a cash book. | It is prepared in lieu of a profit and loss account. |
| 3. Sides | Debit side receipts and credit side payments. | Debit side payments and Credit side receipts. |
| 4. Opening | There can be an opening balance which represents cash in hand/cash at the bank. | No opening balance. |
| 5. Closing Balance | This shows cash in hand/cash at the bank at the end of the accounting period. | There is no closing balance but the difference represents either surplus or deficit. |
| 6. Capital and Revenue | All items are taken irrespective of capital and revenue. | Only revenue items are taken. Capital items are excluded. |
| 7. Period | All receipts and payments whether relating to current succeeding or preceding periods are taken into consideration. | Only current-period incomes and expenditures are taken into consideration. Preceding and Succeeding period items are excluded. |
| 8. Balance Sheet | It is not necessary to prepare a Balance sheet along with this account. | The balance sheet must be prepared along with this account. |
| 9. Adjustments | No adjustments are required to be made at the end of the year. | All adjustments are made at the end of the year. |
| 10. Non-Cash Items | It does not record non-cash items such as depreciation etc. | It records non-cash items. |
| 11. Basis of Accountancy Balance | It is prepared on cash baste. | It is prepared on an accrual basis. |
Question 22.
Viswanadh sold goods to Srinivas on 1st April 2014 for ₹ 4,000 and drew a bill for 3 months on Srinivas for the same amount. Srinivas accepted the bill and returned it to Viswanadh. On the due date, Srinivas requested Viswanadh to draw a new bill for 3 months. Srinivas agreed to pay interest in cash @ 9% p.a. immediately. Viswanadh agreed to this proposal. The new bill was honored on the due date. Pass the necessary journal entries in the books of Viswanadh and Srinivas.
Answer:
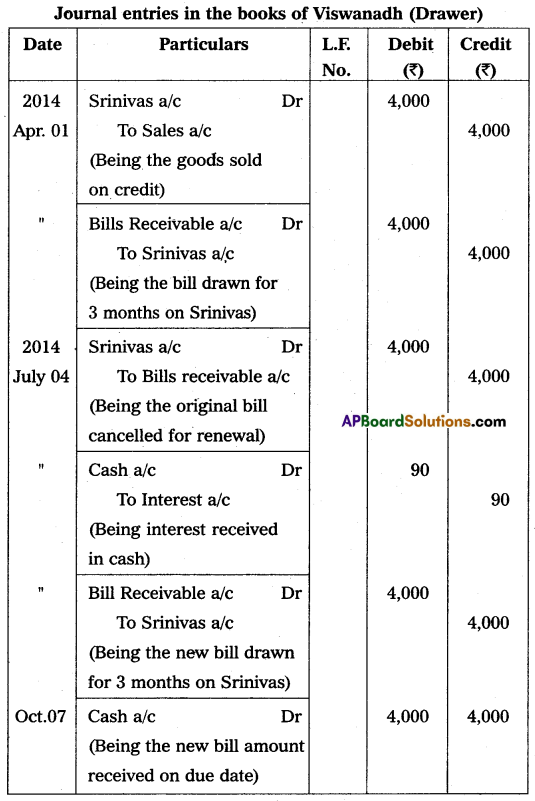
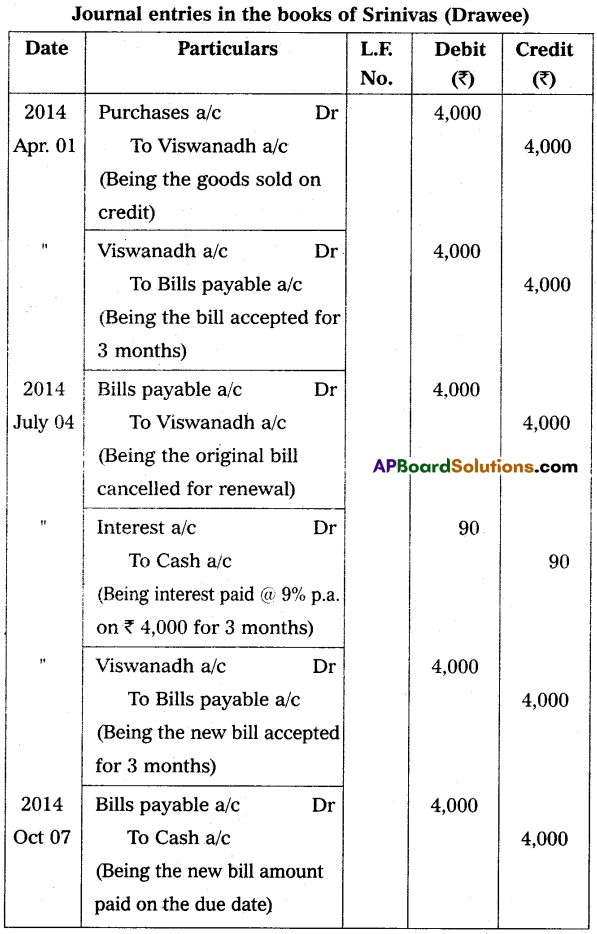
![]()
Question 23.
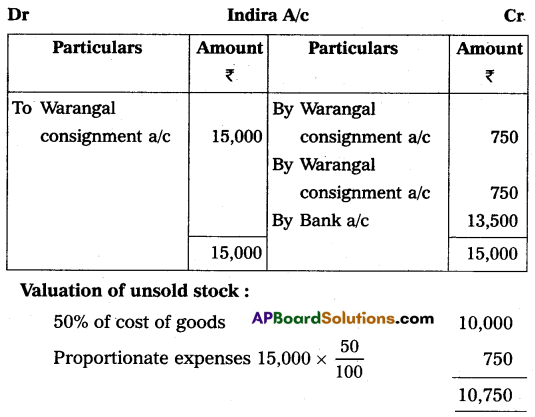
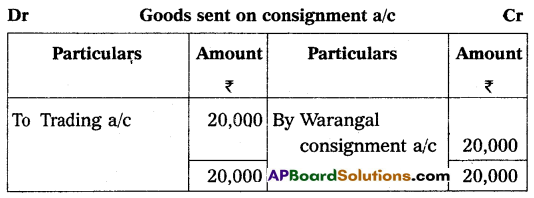
On 1st January 2009, Sudha of Srinagar consigned goods valued at ₹ 20,000 to Indira of Warangal. Sudha paid cartage and other expenses ₹ 1,500. On 1st April 2009, Indira sent on account sales with the following information.
(a) 1/2 of the goods sold for ₹ 15,000
(b) Indira incurred expenses of ₹ 750
(c) Indira is entitled to receive commission @ 5% on sales.
The bank draft was enclosed for the balance due. Prepare consignment account in the books of Sudha.
Answer:
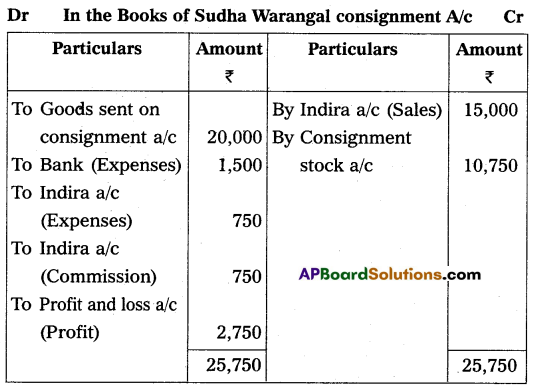
Question 24.
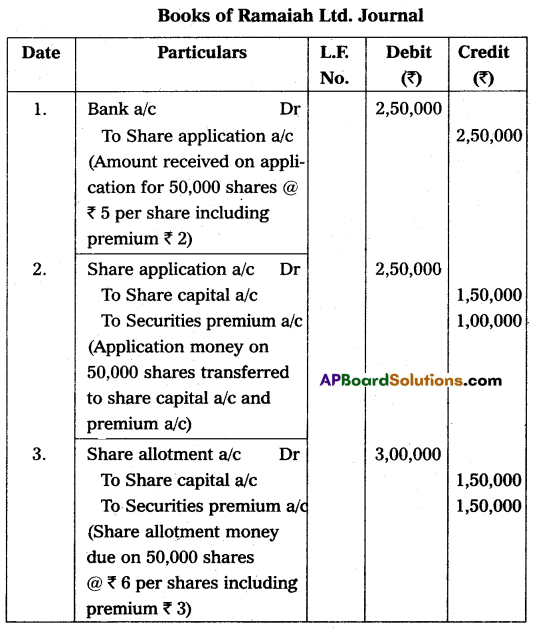
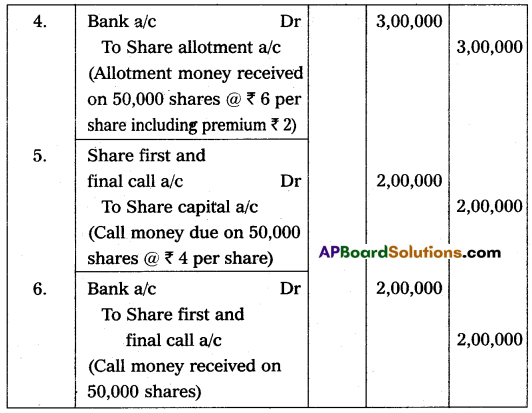
Ramaiah Ltd. issued 50,000 shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 5 per share, payable as follows, on application ₹ 5 (including premium ₹ 2) per share, on allotment ₹ 6 (including premium ₹ 3) per share, the remaining balance ₹ 4 on first and final call, the issue was fully subscribed. All the money was duly received. Make Journal entries.
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is a retirement bill of exchange?
Answer:
When the drawee makes the payment of the bill before its due date it is called ‘retirement of bill’. In such a case, the holder of the bill usually allows a certain amount as a rebate to the drawee.
Question 26.
What is the Reducing balance method?
Answer:
This method is also known as written down value method. Under this method, depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage on the book value of the asset. Since the book value keeps on reducing by the annual charge of depreciation, it is known as the reducing balance method.
Question 27.
Explain the term normal loss.
Answer:
In the case of some goods, even after taking all the precautions, some loss of quantity is bound to take place. Therefore, the loss that is unavoidable, natural, and due to the inherent nature of goods is called normal loss. For example, if coal is consigned a small portion of coal is bound to be lost while loading and unloading. Similarly, in the case of oil and petroleum products, a portion may last due to evaporation and leakage when they are stored.
Question 28.
What is deferred revenue expenditure?
Answer:
It is like revenue expenditure. But when a huge amount is paid, the benefit of which may be for more than one year, a portion will be debited to P&L A/c and the balance is shown as an asset in the balance sheet, e.g. for differed revenue expenditure is a huge amount spent on advertisement.
Question 29.
The capitals of A and B are ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 30,000. Interest on capital is agreed @ 6% p.a. Calculate interest on capital.
Answer:
Calculation of interest capital:
A = 50,000 × \(\frac{6}{100}\) = ₹ 3,000
B = 30,000 × \(\frac{6}{100}\) = ₹ 1,800
Question 30.
What do you understand by a Gaining ratio?
Answer:
The ratio in which the share of the retiring partner is taken over by other partners is called the ‘Gaining Ratio’. To calculate the new profit sharing ratio, the share of profit of the retiring partner taken over by each continuing partner is added to his respective share of profit before the retirement of the outgoing partner.
∴ Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
![]()
Question 31.
Explain the issue of shares at a discount.
Answer:
When the company issues its shares at a price less than the face value, it is said to be an issue at a discount. The difference between the face value and issue price is called ‘Discount’.
Ex: If the face value of the share is ₹ 100 and it is issued at ₹ 90.
Question 32.
Write any three differences between a statement of Affairs and a Balance sheet.
Answer:
| Basis | Statement of Affairs | Balance Sheet |
| 1. Purpose | It shows the financial position as well as to find out capital in ascertaining profit/loss. | It shows the financial position on a particular date. |
| 2. Source | It is prepared from ledger balances and partly from other particulars and estimates etc. | It is prepared from balances only. |
| 3. Accounting Method | It is prepared when accounts are prepared under a single entry. | It is prepared when accounts are maintained double-entry system. |