Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 6 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Classify and describe each type of economic activities.
Answer:
All human activities are directed towards satisfying human wants. Depending upon the nature of wants, human activities may be categorised as economic and non-economic. Economic activities are undertaken to create utilities. Non-economic activities do not have economic values and these primarily tend to satisfy social, religious, cultural or sentimental requirements of human beings.
Classification of Economic activities : Economic activities are broadly classified into three types. They are :
1. Business
2. Profession
3. Employment
1) Business : The business is an activity which is primarily pursued with the object of earning profit. A business activity involves production, exchange of goods and services to earn profit or to earn a living. The word business literally means a state of being busy. Every person is engaged in some kind of occupation, a farmer works in the field, a worker works in the factory, a clerk does his work in the office, a teacher teaches in the class, a salesman is busy in selling the goods and entrepreneur is busy in running his factory. The primary aim of all these persons is to earn their livelihood while doing some work.
2) Profession : Profession is an occupation involving a provision of personal services of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional service of specialised nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc. The specialised service is provided for a professional fees charged from the clients. For instance, a doctor helps his patients through his expert knowledge of the science and medicine and charges a fee for the service. Minimum education qualifications are prescribed for entry into profession and profession requires a high degree of formal education and specialised training in a particular field. Ex : Chartered Accountant needs to be member of the ICAI. A person entered into profession of law has to acquire LL.B degree to become a lawyer.
3) Employment or Service: Employment or service involves working under someone known as employer in a contract of employment in return for a wage or salary. The person engaged under employment works as per the directions of the employer. There is an employer – employee relationship. A professional may also work under the contract of employment. A Chartered Accountant may be employed by the company. The service may be of government department or in a private organisation.
Question 2.
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Joint Stock Company.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Joint Stock Company.
- Large financial services : As there is no limit on the number of shareholders in public company, it can collect large amount of capital.
- Limited liability : The liability of the shareholders is limited to the face value of the shares held by them. If a member pays entire amount on shares, he will not be called upon to pay even a single rupee.
- Perpetual succession : A company has continuous existence. It does not come to an end with the death, lunacy or insolvency of members.
- Transfer of shares : Transferability of shares acts as an added incentive to investors. The shares of public company are traded easily in stock exchange.
- Economies of large scale production : A company has large amount of capital. It can organise production on large scale. It will result in economies in production, purchase, marketing, management etc.
- Efficient professional management : A company has large resources at its disposal. So, it can appoint highly qualified persons and secure their services.
- Diffused risk : In case of companies, there are large number of shareholders. So risk is shared by large number of persons and risk is reduced to each member.
- Tax benefits : Although the companies are required to pay tax at higher rates, their tax burden is low as they enjoy many tax exemptions under Income tax Act.
The following are the disadvantages of Joint Stock Company :
- Difficulty in formation : Promotion of company is not an easy task. There are so many legal formalities are to be compiled with. Large amount is to be spent.
- Lack of motivation : A company is managed by Board of Directors and paid officials. They do not have share in profits. They do not have any incentive to work hard.
- Economic oligarchy : The management of the company is supposed to carried on in according to the collective will of its members. But there is rule by few often the directors try to mislead the members and manipulate voting power to maintain their control.
- Fradulent (corrupt) management: In companies, there is often danger of fraud and misuse of property by dishonest management. Unscrupulous person may manipulate annual accounts to show artificial profits or losses for their personal gain.
- Delay in decisions : Quick decisions cannot be taken as all important decisions are taken either by the Board of Directors or referred to general house.
- Unhealthy speculation : As the liability of the members is limited, the management is tempted to get into speculative business activities.
- Excessive government control : At every stage, the management of the company has to follow several legal provisions and reports are to filed. A lot of time and money is wasted.
- Social evils : The growth of companies encouraged monopolies. It may be become a cause of political corruption. The Company influence the policies of the government by giving donations to the political parties.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the various factors that determine the selection of sources of finance ?
Answer:
The following factors should be considered for selecting the sources of finance.
- Cost factor: While deducting the sources of funds that is utilised by the business concern, the cost of procuring the funds and the cost of utilising are to be considered.
- Sound financial position: In the choice of source funds, the business should be financially sound so that it can repay the principle amount together with interest.
- Form of business organisation : The form of business organisation influences the choice of source raising money. Ex: A partnership firm cannot raise money by issue of equity shares.
- Purpose and period of time: While selecting the sources of finance, purpose and period of time is to be taken into account. A short term need can be met by borrowing funds through trade credit, commercial paper etc., with low rates of interest. For long term finance, sources like issue of shares and debentures are more appropriate.
- Risk factor: Business should evaluate each of the sources of finance in terms of risk involved. Ex: If equity shares are issued, they are to be repaid only at the time of winding up and dividends are not paid if the profits are not available. There is little risk involved. On the other hand, a loan is to be repaid as per the schedule and the interest is to be paid whether firm earns profits or not.
- Control : A particular sources of funds may affect the control and power of the owners on the management of the firm. As the equity shareholders enjoy voting rights, by the issue of equity shares the financial institutions may take control of the assets or may impose conditions as per loan agreement.
- Effect on credit worthiness : Depending on certain sources of finance may affect the credit worthiness in the market. Ex : Issue of secured debentures may affect the interests of the creditors and they may not be willing to extend furthur loans to the company.
- Flexibility and ease : Another factor which may affect the choice of sources of finance is flexibility and ease of obtaining funds. In order to secure loans from banks, they may impose restrictions and documentation is necessary. If other sources are available, traders may not prefer approaching banks and financial institutions.
- Tax benefits : Tax is not deducted on dividend on preference shares. Interest paid on loans and debentures is tax deductable. In order to take advantage of tax benefits, firms may issue debentures of take loans.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Social objectives of business.
Answer:
According to Henry Ford “The primary aim of business should be service and subsidiary aim should be earning profit”.
The social objectives are as follows.
- Availability and supply of quality goods : The business should ensure the supply of goods to meet the requirements of the society. It is social obligation on the part of the business to supply quality goods at a reasonable prices.
- Fair remuneration to employees : In addition to wages and salary, a reasonable part of the profits should be distributed among employees by way of bonus. It is the duty of the employer to provide hygenic working conditions to workers.
- Creation of more employment: The expansion of busi-ness can help the society by creating more and more job opportu-nities. Provision Of full employment is a significant service to the society.
- Co-operation with the government : Business should co-operate with the government in helping to achieve the objectives of the nation. They should pay the taxes honestly and at right time. These taxes provide revenue to government for spending on public welfare.
- Social welfare : Business should support to social, cul-tural and religious organisations. They should build schools, hos-pitals, libraries, sports bodies research institutions.
Question 5.
Distinction between sole trader and partnership.
Answer:
The following are the differences between partnership and sole trader.
| Basis of Comparison | Partnership | Sole trader |
| 1. Formation | Easy-only agreement is required. | Easy. No legal formalities are required |
| 2. Registration | Registration is optional | Not necessary. |
| 3.Membership | Minimum – 2, Maximum – 10 in banking and 20 in others. | Single ownership. |
| 4. Liability | Unlimited, joint and several. Risk shared. | Unlimited. Full risk |
| 5. Capital | Capital can be pooled from two or more persons. | Limited capital. |
| 6. Suitability | Suitable for medium size business. | Suitable for small size business. |
| 7. Sharing of profits | As per the agreement | All to the owner |
| 8. Business secrets | Secrets limited to partners | Perfect secrecy |
| 9. Transferability of interest | Partners can transfer shares with mutual consent. | A sole trader can transfer at will. |
Question 6.
What are different types of promoters ?
Answer:
The following are the different types of promoters.
- Professional promoters : The professional promoters are specialised persons or agencies and promotion is their whole time occupation.
- Accidental promoters : Accidental promoters are not spe-cialists in company formation. They promote their own firms as promoters.
- Occassional promoters : The promoters take interest in floating some companies. They are not in promotional work on regular basis, but takeup promotion of some companies and then go to their earlier promotion. Ex : Engineers, lawyers etc.
- Financial promoters : Financial promoters float new en-terprises during favourable conditions in the securities market.
- Technical promoters: Technical promoters promote new companies on the basis of their specialised knowledge and training in technical fields.
- Institutional promoters : IDBL, NIDC and other specialised institutions promote technical, managerial and technical assistance in the promotion of a company.
Question 7.
Discuss the Privileges enjoyed by MSMEs.
Answer:
MSMED Act, 2006 provides the following privileges to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
1. Buyers liability to make timely payment : Section 15 envisages to ensure timely receipt of payment for their goods and services by Micro and Small Enterprises. It casts an obligation upon the buyer of any goods or services, to make payment to supplier, by the specified as follows :
a) When there is an agreement in writing : On or before the date agreed upon between them in writing. Furthur, in no case the period so agreed shall exceed 45 days from the date of acceptance.
b) When there is no agreement: Before the appointed day, which means the day following immediately after the expiry of 15 days from the day of acceptance or day of deemed acceptance.
Buyer means a person buying goods or receiving service, from a supplier means a Micro or Small Enterprise and the day of acceptance is the day of acutal delivery of goods or rendering service.
2) Interest for delayed payment by buyer: When a buyer fails to make as required above, he shall be liable to pay interest on the outstanding amount which is three times the bank rate and compounded at monthly rates.
3) Reference of dispute: Any dispute relating to the payment of any goods and services and any interest. Thereon may be referred to any party by Micro and Small Enterprises.
![]()
Question 8.
Briefly outline the risks faced while involving E-business transactions.
Answer:
The following are the risks involved in E-business transactions.
- Risk of unauthorised alteration of information while travelling the internet.
- Risk related to confidentiality of personal information and banking information like credit card details, password etc.
- Risk relating to legal enforceability of the transactions entered through E-Commerce.
- Risk of failure of electronic communications which may result closure of business.
- Risk to the management in controlling and clearing E-Commerce transactions and in selecting the best suitable communication techniques to transact.
- Risks relating to technology, like viruses and banking.
Question 9.
Explain the inter relationship between trade commerce and industry.
Answer:
Industry, trade and commerce are inter related to each other. Industry is related to the production of goods and providing of services. No commercial activities are possible without industry and production. Commerce is connected with the distribution of goods and services. Industry and production cannot survive in the absence of commerce. The goods produced must reach the consumers.
Commerce helps in the distribution of goods to the users and this, in turn helps industry. But industry and commerce are dependent upon each other. Industry provides a base to commerce and commerce helps industry in its development. Trade involves buying and selling of goods. It is the media for transfer of goods from producers to consumers. Trade provides a foundation for the development of commerce. The development of trade at international level has helped the industry in increasing the scale of operations. On the other hand, the increased production of goods will require more trading activities. There is a link and dependence of industry, trade and commerce on one another.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Home trade
Answer:
Home trade refers to a trade where buying and selling of goods takes place between the persons who belong to the. same country. So, home trade is carried within the boundaries of the nation. Home trade is also called as internal trade or domestic trade. For movement of goods internal transport system is used.
Question 11.
Co-operative society
Answer:
Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interests. It works on the principle of self help and mutual help. The motto of cooperative society is “Each for all and all for each”. People come forward as a group, pool their individual resources, utilise them in the best possible manner and derive some common benefits out of it.
Question 12.
Criminal liability for mis-statements in prospectus.
Answer:
Along with the civil liability, the company is also liable for criminal action for the fraud committed by it. Every person who is responsible for mis-statements in prospectus and deceiving the public, is imprisoned for two years or imposed a fine of ₹ 5,000 or both. Apart from this, persons who induce people and wilfully commit fraud are imprisoned upto 5 years or fine upto ₹ 10,000 or both.
Question 13.
Short term finance
Answer:
The finance required for a period of not exceeding one year is called short-term finance. Short-term finance is utilised for meeting working capital requirements of the business. The amount required for short-term funds depends on the nature of business, delivery time, volume of business and operating cycle. The sources of short-term finance are trade credit, bank credit, installment credit, customers, advance, commercial paper.
Question 14.
State financial corporation
Answer:
The State Financial Corporation was established by the government of India in 1951 with a view to provide financial assistance to small and medium scale industries which are beyond the scope of IFCI. Its share capital is subscribed by respective state governments, RBI, LIC and commercial banks.
Question 15.
Equity shares
Answer:
These shares are also known as ordinary shares and equity shareholders are the real owners of the company, because these shares carry voting rights. Equity shareholders are paid dividend after paying it to the preference shares. The rate of dividend depends on the profits of the company. They may get higher rate or may not get anything. So these shareholders take more risk than the preference shareholders. They will get their capital after all other claims are met.
Question 16.
Define service enterprises as per MSMEs Act, 2006.
Answer:
These enterprise involve in providing or rendering service. Service sector may be defined interms of investment made in equipment.
- A micro enterprise is one where the investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
- A small enterprise is one where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 2 crores.
- A medium enterprise is one where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2 crores but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
![]()
Question 17.
E-Auctioning
Answer:
The internet enables people to participate in auction without sacrificing their personal time. In E-Auctioning, the people who want to participate in auction, visit the website with a click and go through the details of goods offered or kept in auction in concerned web pages and participate in auction. Ex: Bank auctioners tenders.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
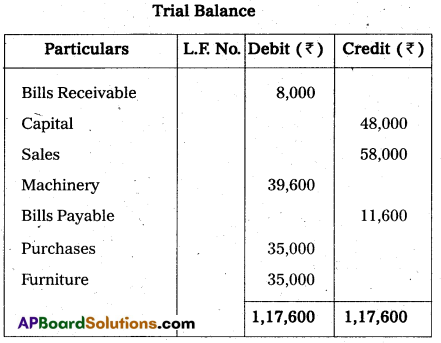
From the following Trial Balance of Vishnu Traders prepare final accounts for the year ended 31.03.2014.
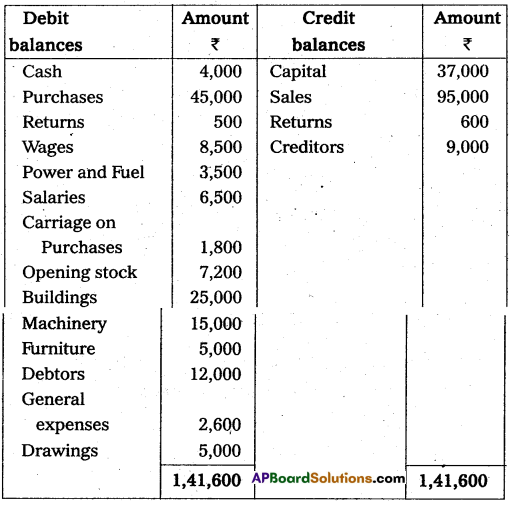
Adjustments :
- Closing stock value : ₹ 14,000.
- Depreciation on Furniture ₹ 250, Machinery ₹ 750.
- Outstanding Wages ₹ 500.
- Bad debts ₹ 400.
- Interest on drawings 5%.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss Account of Vishnu Traders for the year ended 31-03-2014
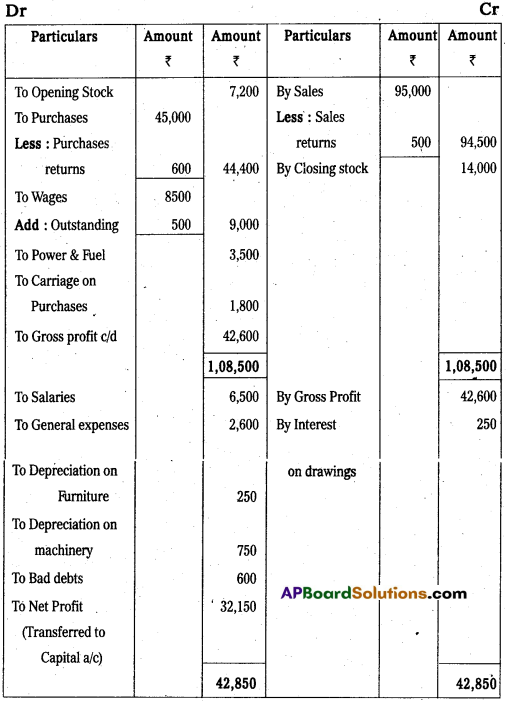
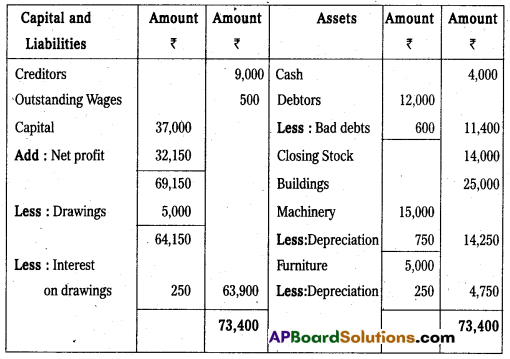
Balance Sheet of Vishnu Traders as on 31-03-2014
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
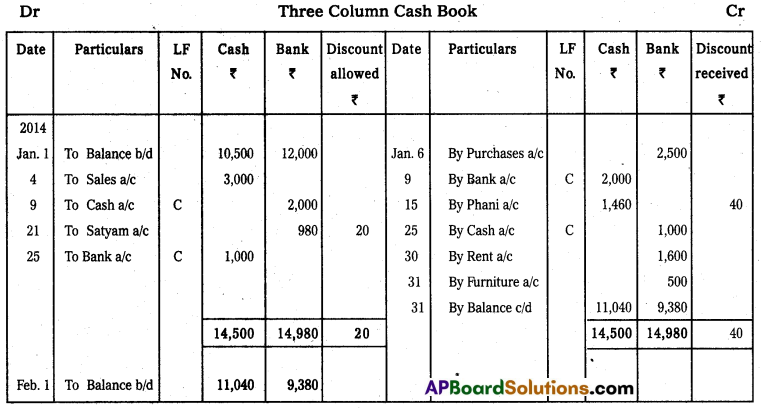
Question 19.
Prepare triple column cash book from the following information.


Answer:
Question 20.
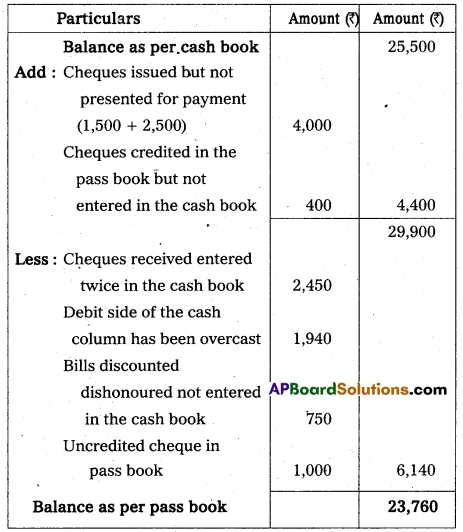
Reddy’s Cash Book shows a favourable balance of ₹ 25,500 as on 31st Decemebet, 2013. On comparing the same with his Pass Books following differences were noticed. Calculate bank balance as per Pass Book.
a) A Cheque for ₹ 2,450 received from Saritha & Co. was entered twice in the Cash Book.
b) The receipt column of the cash book has been over added by ₹ 1.940.
c) Several cheques, totalling ₹ 6,000 were issued to different suppliers. Of these, cheques worth ₹ 1,500 were debited in the Pass Book on 2nd January, 2014 and ₹ 2,500 on 4th January The balance of cheques were debited before 31st December, 2013.
d) Bill discounted got dishonoured ₹ 750
e) A cheque for ₹ 400 was credited in pass book, but was not recorded in cash book.
f) Uncredited cheque ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Reddy as on 31.12.2013
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Define double entry system of book-keeping and explain its features.
Answer:
In book-keeping, all the business transactions are recorded in the books of accounts and a transaction involves transfer of money or money’s worth. It is clear that every business transaction involves a transfer and as such consists of two aspects.
1) The receiving aspect
2) The giving aspect. It is necessary to note that these aspects go together, because receiving necessarily implies giving and vice-versa. The record of any business transaction will be complete only when both these aspects are recorded. The recording of two aspects of each transaction is known as “Double entry system of book-keeping”.
Features:
- Every transaction has two aspects i.e., receiving the benefit and giving the benefit.
- Every transaction affects two accounts.
- Double entry system is based upon the principles and concepts of accounting.
- It helps in the preparation of trial balance which is a test for arithimetical accuracy in accounts.
- If facilitates the preparation of final accounts with the help of trial balance.
![]()
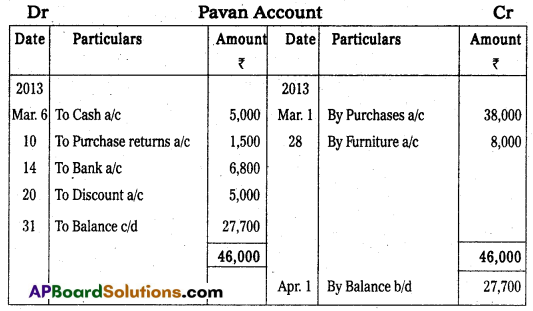
Question 22.
Prepare Pavan account from the following.


Answer:
Question 23.
Enter the following transactions in proper subsidiary books.

Answer:
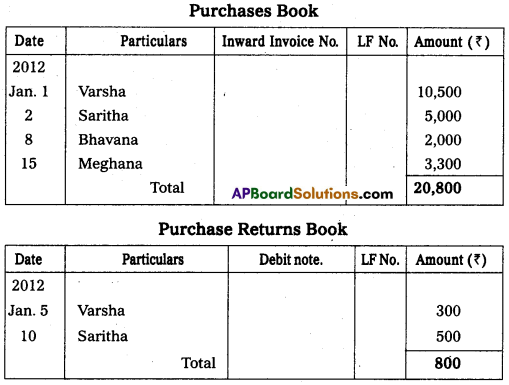
Question 24.
Pass journal entries to rectify the following.
a) Commission of ₹ 200 received was wrongly credited to interest account.
b) Return outwards book was undercast by ₹ 100.
c) Furniture worth ₹ 600 purchased debited to purchases account.
d) An amount of ₹ 300 received from Bhim Raj was wrongly credit to Ram Raj a/c.
Answer:
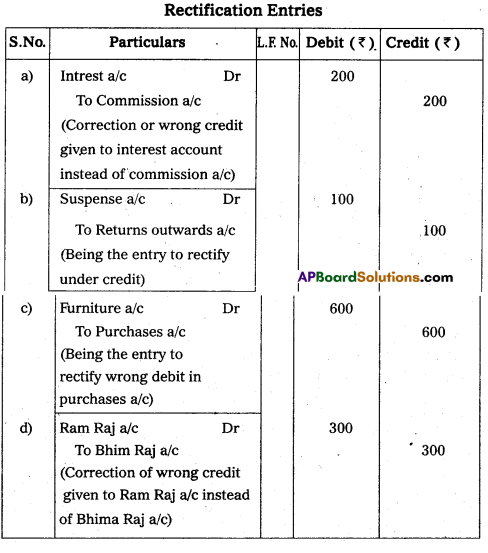
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 1o)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is an account?
Answer:
Every transaction has two aspects and each aspect has an account. An account is a summary of relevant transactions at one place relating to a particular head. An account has three parts.
- A title describes the name of the account.
- A left side or debit side.
- A right side or credit side.
Question 26.
Invoice
Answer:
It is a statement sent by the supplier along with the goods or in advance, to the trader, stating that the goods are supplied along with the price, discount offered and other terms and conditions. The document is called ‘Inward Invoice”, as it is received by the trader from the supplier.
Question 27.
Closing entries
Answer:
Closing entries are used at the end of the accounting year for closing all accounts relating to expenses and revenues. These accounts are closed by transferring their balances to trading account and Profit and Loss account.
![]()
Question 28.
Cash discount
Answer:
If a debtor clears his debt before or on the date specified, he may receive some rebate in the form of cash from the creditor. This is treated as cash discount received by the debtor. In the same way, the rebate given by the creditor is treated as discount allowed. The discount column is maintained on both sides of the cash book.
Question 29.
What do you mean by favourable balance ?
Answer:
When the cash book shows the debit balance and the pass book shows credit balance, it is called favourable balance. Favourable indicate that the businessman has got money in his account with the bank.
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions.

Answer:
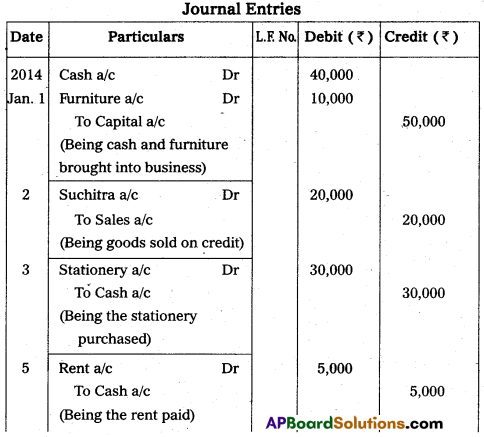
Question 31.
Rama and Co. started business on 1st January 2014 with the following assets and liabilities.
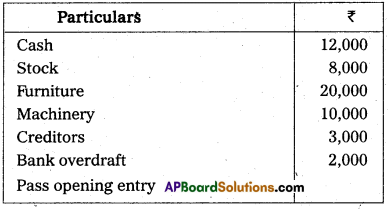
Answer:
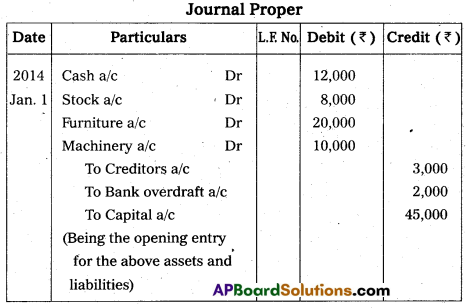
Question 32.
Prepare Trial Balance of Rohita.
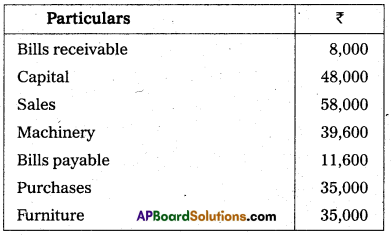
Answer: