Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 3 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Explain the characteristics of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
The following are some of the important characteristics that every successful entrepreneur must possess.
1. Innovation:
Innovation is an important characteristic of an entrepreneur in modem business. The entrepreneur makes arrangements for introducing innovations that help in increasing production on the one hand and reducing costs on the other.
2. Risk-taking:
Risk-taking is another feature of an entrepreneur. He has to pay for all the other factors of production in advance. There are chances that he may be rewarded with a handsome profit or he may suffer a heavy loss. Therefore, risk-bearing is the final responsibility of an entrepreneur.
3. Decision Making:
An entrepreneur has to make decisions about the establishment of a business its management and the coordination of various resources. Every activity of the business requires decision-making. The entrepreneur has to make decisions every day which have an impact on the working of the enterprise.
4. Leadership:
An entrepreneur has to be a leader because he is such a person who organizes directly and controls the functions of the organization. His personality will influence the working of his subordinates who can praise and appreciate him. An entrepreneur in his role as a leader, not only guides and counsels his people but he motivates them to achieve goals quickly and efficiently.
5. Organisation of Production:
An entrepreneur procures various factors of production like land, labor, capital, raw materials, etc. For manufacturing a product or bringing out a service. He assesses the viability of different production processes and selects one which is most suitable.
6. Planning:
An entrepreneur is a person who plans everything in the business. Planning is a process that involves thinking before an entrepreneur decides the following:
- What to do?
- When to do it?
- How to do?
- Who does a particular task?
7. Work Hard:
The willingness to work hard distinguishes a successful entrepreneur from an unsuccessful one. Most successful entrepreneurs work hard endlessly, especially in the beginning and the same becomes their whole life.
8. Desire for High Achievement and Highly Optimistic:
Entrepreneurs should have a strong desire to achieve high goals in business. Successful entrepreneurs are not disturbed by present problems and are optimistic for future that the situation will become favorable to business in the future.
9. Independence:
Successful entrepreneurs do not like to be guided by others and like to be independent in the matters of their business.
10. Foresight:
Entrepreneurs should have good foresight i.e., they visualize the likely changes to take place in the market, consumer attitude, technological developments, etc., and take timely action accordingly.
![]()
Question 2.
Define life Assurance policy. What are the kinds of life assurance policies?
Answer:
A life insurance contract may be defined as “a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of premium paid either in lumpsum or in periodical installments, undertakes to pay an annuity or a certain sum of money, either on the death of the insured or on the expiry of the certain number of years”.
Kinds of Life Assurance Policies:
The following are some of the popular life assurance policies.
1. Whole Life Policy:
Under this policy, the premium is paid throughout the life of the insured. The sum assured is payable only after the death of the assured. The premium payable is low and it is meant for the family.
2. Endowment Policy:
This policy is taken up for a specific period called the endowment period. The policy will mature at the end of the specified period or the attainment of a particular age or on the death of the insured, whichever is earlier. This policy offers the advantage of both protection and investment.
3. With or Without Profits Policies:
When the policy is insured with profits, the policyholders share the profits of the company. The profit is called Bonus. The amount of the policy and bonus is paid on the maturity of the policy. When the policy is insured without profits, the insured does not share any profits and the amount of the policy only is paid on maturity.
4. Joint Life Policies:
A policy may be taken jointly on the lives of two or more persons. On the death of any one person, the policy is paid to another surviving policyholder as the case may be. This type of policy may be taken by husband and wife.
5. Convertible Whole Life Policy:
The policy is insured for a whole life policy with a provision to convert it into an endowment policy after a specified period. The conversion is done at the request of the assured. The rate of premium is increased after conversion.
6. Janata Policy:
Janata policy was introduced by the Life Insurance Corporation of India in May 1957. This policy was introduced for the benefit of lower-income group people. It can be issued for a term of 5,10,15,20 and 25 years subject to the condition that it should mature at the age of 60 years. No loans are granted on such policies.
7. Annuity Policy:
Under this policy, the insured would deposit a lumpsum amount with the insurance company. The amount of the policy would be paid to the insured for a specified number of years or until the death of the insured.
8. Children Endowment Policy:
This policy is taken by a person for his/her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age.
9. Group Insurance Policy:
Members of a family or the employees of a business concern can take this insurance policy.
Question 3.
Describe the rights of consumers as per CPA 1986.
Answer:
Although business man is aware of their social responsibilities even then we come across many cases of consumer protection. Hence Government of India provided the following six rights to all the Consumers under Consumer Protection Act.
1. Right to Safety:
According to this right, the consumers have the right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services that are hazardous to life and property. The right is important for a safe and secure life.
2. Right to Information:
According to this right, the consumer has the right to get information about the quality, quantity, purity standard, and piece of goods or services. The producer must supply all the relevant information at a suitable place.
3. Right to Choice:
According to this right, every consumer has a right to choose the goods or services of his or her liking. The supplier should not force the consumer to buy a particular brand only. Consumers should be free to choose the most suitable product from their viewpoint.
4. Right to Consumer Education:
According to this right, it is the right of the consumer to acquire knowledge and skills to be informed to the customer. It is easier for literate consumers to know their rights and take action.
5. Right to Seek Redressal:
According to this right, the consumer has the right to get compensation or seek redressal against unfair trade practices or any other exploitation. The right assures justice to consumers against exploitation.
6. Right to Heard/Right to Represent:
According to this right, the consumer has the right to represent himself or to be heard or the right to advocate his interest. In case a consumer has been exploited or has any complaint against the product or service then he has a right to be heard.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Explain any one function of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
An entrepreneur performs all the functions necessary right from the generation of an idea and upto setting up an enterprise. The following are the functions of an entrepreneur.
Decision Making:
An entrepreneur as a decision maker takes various decisions regarding the following:
- Ascertaining the objective of the enterprise
- Sources of finance
- Product mix
- Pricing policies
- Promotion strategies
- Appropriate technology or new equipment etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the limitations of International Trade?
Answer:
The exchange of goods and services between the nations is called international trade. It has certain limitations and problems. The following are the limitations of international trade.
- Economic interdependence is gained from international trade. In case of war or any other political deadlock, it creates a crisis.
- Industrialization of developing countries may be adversely affected by unrestricted imports.
- Foreign trade leads to unhealthy competition among the countries, creating rivalry between them.
- The concept of the comparative cost principle which leads to rigid specialization in a few countries may create many difficulties.
- International trade may lead to lopsided or partial development at the cost of neglect of certain sectors of the economy.
Question 6.
Explain the benefits of Insurance.
Answer:
The following are the benefits of Insurance:
- Provides Certainly: Insurance helps the insured to convert his uncertainties into certainities by entering into a contract of insurance. The payment of premiums by the insured enables to reduction of the risk.
- Distribution of Losses: Insurance helps to distribute losses of any uncertain events among a large number of insurers. It enables to transfer of the risks and spreads the financial loss of insured members over the whole insurer.
- Provides Security: It provides security to the insured against the risk of uncertain events. The insurance company guarantees the insured to compensate or indemnify the loss on the occurrence of an event in consideration of payment of premium.
- Generates Capital: Insurance reduces financial risks and losses by providing facilities for capital investment in various organizations.
- Increases Efficiency: Insurance reduces the risk and increases business efficiency. It provides security for the business community which in turn paves the way for the growth and diversification of industry.
- Earns Foreign Exchange: Insurance provides security to international traders, shippers, and banking institutions, thus paving the way for the expansion of foreign trade. The increased foreign trade activities lead to securing foreign exchange which makes the country to become economically strong.
- Social Security: Insurance acts as an instrument to fight against the evils of poverty, unemployment, disease, old age, sickness, disability, accidents, fire, and similar other calamities of nature.
- Promotes Thrift: Insurance encourages people to go for savings. It alters people in their spending habits and makes them save a certain sum of money regularly.
Question 7.
State the Advantages of Railway Transportation.
Answer:
Advantages of Railway Transport:
- Railway transport facilitates long-distance travel and transport of bulky and heavy goods.
- It is a quick and more regular form of transport because it helps in the transportation of goods with speed and certainty.
- It helps in the industrialization process of a country by easy transportation of coal and raw materials at cheaper rates.
- It helps in the quick movement of goods from one place to another in times of emergencies like famines and scarcity.
- It encourages the mobility of labor and thereby provides a great scope for employment.
- Railway is the safest form of transport. The chances of breakdown and accidents on Railways are less as compared to other modes of transport.
- The carrying capacity of the railway is extremely large. Moreover, its capacity is elastic which can be easily increased by adding more wagons.
Question 8.
What do you know about NSE?
Answer:
National Stock Exchange (NSE):
The most important development in the Indian Stock market was the establishment of the National Stock Exchange (NSE). It is the latest and most modern technology-driven exchange. It was incorporated on 27th November 1992 and was recognized as a stock exchange in April 1993. It started operations in 1994, trading on the wholesale debt market segment. It launched the capital market segment in Nov. 1994 as a trading platform for equities and the futures and options segment in June 2000 for various derivative instruments. NSE has been able to take the stock market to the doorstep of investors. It has provided a nationwide screen-based automated trading system with a high degree of transparency and equal access to investors irrespective of geographical location.
Question 9.
What is meant by consumer protection?
Answer:
Consumer protection means safeguarding the interests and rights of consumers. In other words, it refers to the measures adopted for the protection of consumers from the redressal of their grievances. The most common business malpractices are the sale of adulterated, spurious, substandard, and duplicate goods, false and underweighting, hoarding and black marketing, charging more than MRP Price, etc.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Explain any one characteristic of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
The following are some of the important characteristics that every successful entrepreneur must possess.
1. Innovation:
Innovation is an important characteristic of an entrepreneur in modern business. The entrepreneur makes arrangements for introducing innovations that help in increasing production on the one hand and reducing costs on the other.
2. Risk-taking:
Risk-taking is another feature of an entrepreneur. He has to pay for all the other factors of production in advance. There are chances that he may be rewarded with a handsome profit or he may suffer a heavy loss. Therefore, the risk-bearing is the final responsibility of an entrepreneur.
![]()
Question 11.
What is import trade?
Answer:
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in goods and services into the port of the country. When purchases are made from another country, goods are said to be imported from that country to the buyer’s country. For example, China has the most modern technology for producing electronic products cheaply and India is importing these products.
Question 12.
Home trade.
Answer:
Buying and selling of goods takes place between the individuals of the same country. The buyer and seller live in the same country. It is also called Home trade or internal trade based on the scale of operations, internal trade can be classified into two types. They are (i) Wholesale trade and (ii) Retail trade.
Question 13.
Mobile banking.
Answer:
This type of service is provided free of cost to all the customers. Under this, the customer can access his bank account on the mobile screen for services such as checking the balance, ordering a demand draft, stopping payment, or viewing the last five transactions. To avail of this facility the customer is required to have a mobile phone with a WAN facility.
Question 14.
Endowment policy.
Answer:
This policy is taken up for a specific period. The policy will mature at the expiry of a specific period or attainment of a particular age or on the death of the insured whichever is earlier.
Question 15.
Two advantages of warehouse.
Answer:
Advantages of warehouses:
- It serves the businessmen who have very limited space.
- Some warehouses indirectly offer financial assistance.
Question 16.
Classification of the financial market.
Answer:
Financial markets are classified based on the maturity of financial instruments traded in them, into the money market and capital market. The financial instruments with a maturity of less than one year are traded in the money market and those with longer maturity are traded in the capital market.
![]()
Question 17.
National Commission.
Answer:
National Commission operates at the National level. It settles the consumer disputes in the country. The National Commission has a President, who should be a serving or retained Supreme Court Judge the commission also comprises other members of not less than four. The president and all the members of the commission are appointed by the central government. The National Commission shall have jurisdiction to entertain consumer complaints where the value of goods and services and compensation exceeds ₹ 1 crore.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
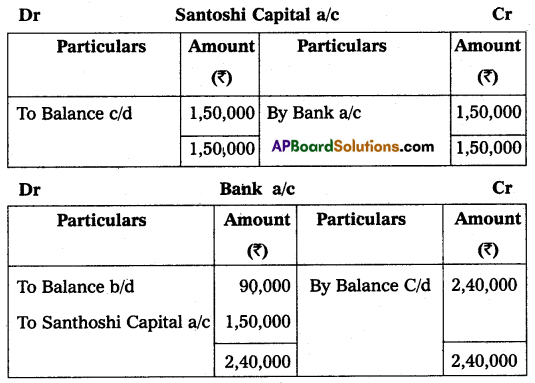
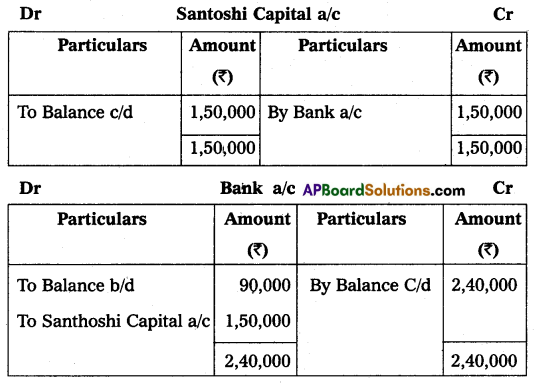
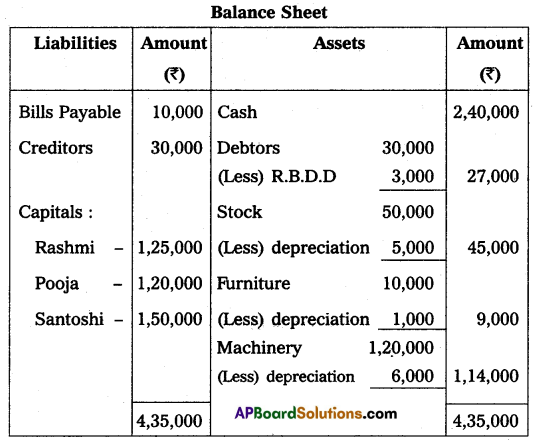
Rashmi and Pooja are partners in a firm. They share profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 1. They admit Santoshi into a partnership firm on the condition that she will bring ₹ 1,50,000 for capital and she will be given 1/3 share in future profits. At the time of admission, the Balance Sheet of Rashmi and Pooja was as under.
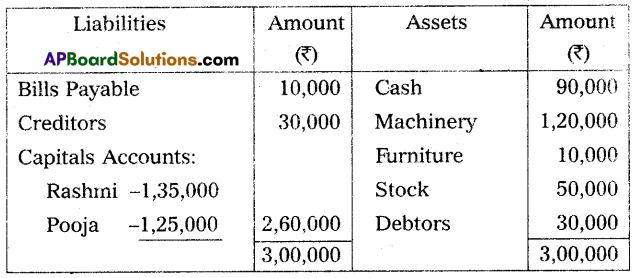
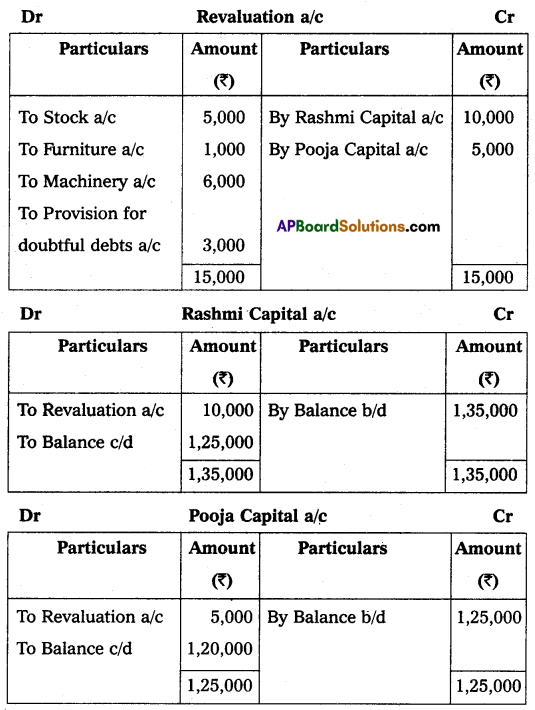
It was decided to:
(a) Revaluate stock at ₹ 45,000.
(b) Depreciate furniture by 10% and machinery by 5%.
(c) Make provision of ₹ 3,000 on sundry debtors for doubtful debts.
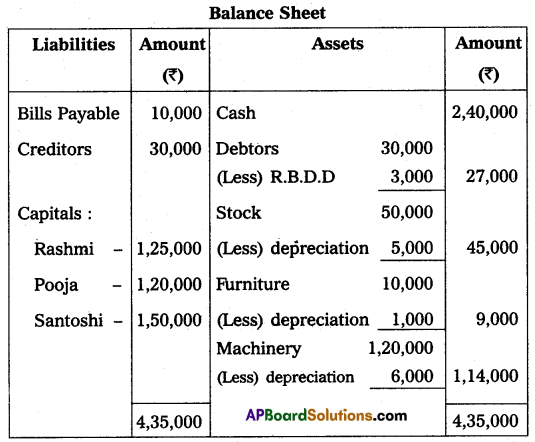
Prepare Revaluation Accounts, Partners Capital Accounts, and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
Krishna of Mumbai and Gopal of Chennai are in the consignment business. Gopal sent goods to Krishna ₹ 10,000. Gopal paid freight ₹ 500, Insurance ₹ 1,500 Krishna met sales expenses ₹ 900, Krishna sold the entire stock for ₹ 20,000 and he is entitled to a commission of 5% on sales. Write the necessary entries in the books of Gopal and Krishna.
Answer:
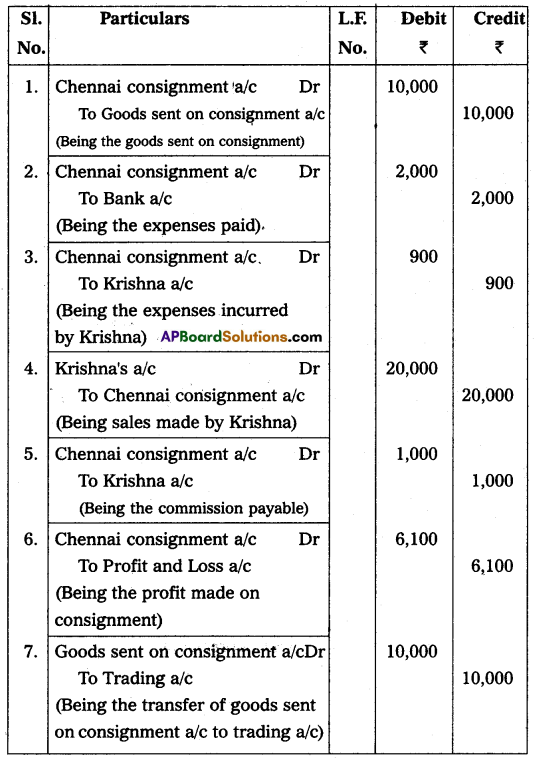
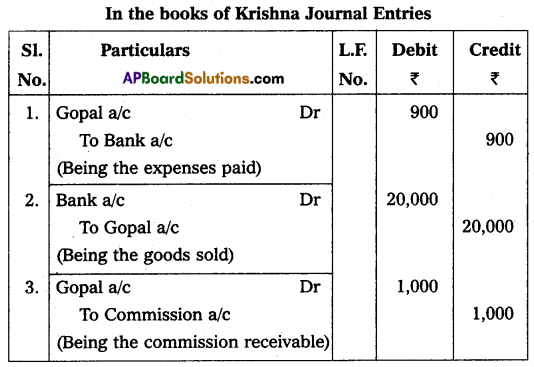
(or)
Question 20.
From the following receipts and payments accounts of other information of Kadapa City Club, Prepare income and expenditure A/c as of 31-Dec-2014 and balance sheet as of that date.
Adjustments:
(a) Subscription received included ₹ 1,200 for the year 2013, and ₹ 2,400 for the year 2015.
(b) Subscriptions due for the year 2014 – ₹ 1,800.
(c) Printing Charges payable for 2014 – ₹ 240.
(d) Salaries payable for the year 2014 – ₹ 3,600.
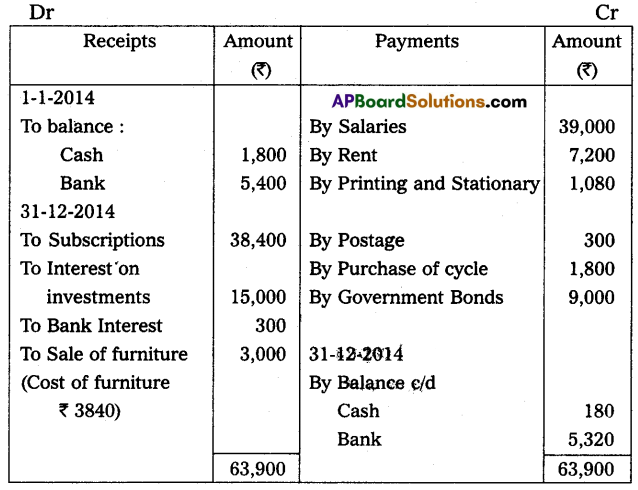
Answer:
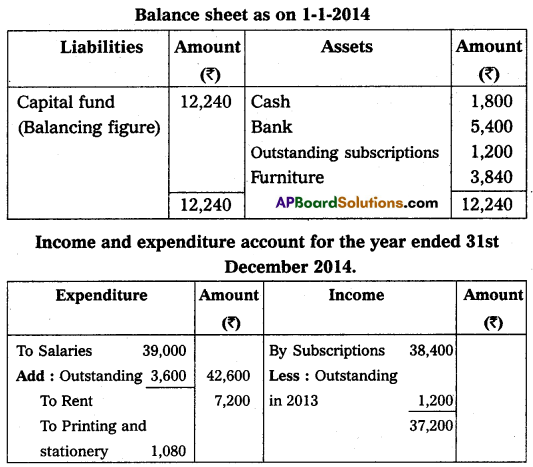
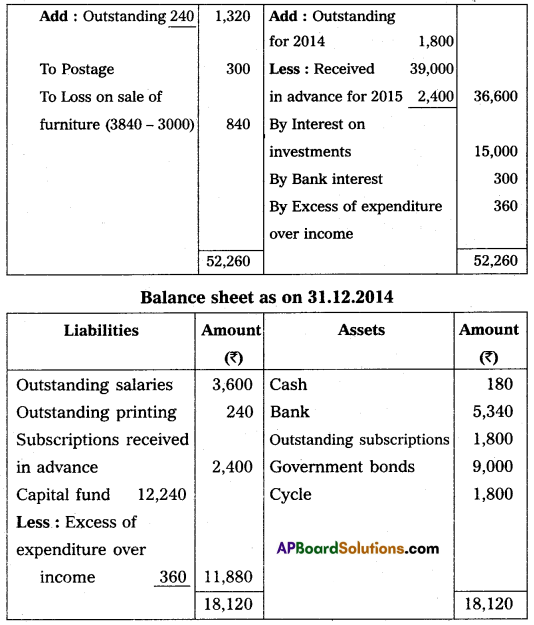
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
What are the uses of incomplete records?
Answer:
Uses of accounts from incomplete records:
- Single entry is a simple method of recording transactions.
- It is less expensive when compared to a double-entry system of bookkeeping.
- It is mainly suitable for small business concerns with a limited number of transactions.
- It is very easy to follow, a person without any adequate knowledge of the principles of accounting can understand it.
- Ascertainment of profit or loss is very easy.
Question 22.
On 25th March 2014 Vinod draw a bill for 3 months on Prakash for ₹ 3000. Prakash accepted the bill and handed over the bill to Vinod. The bill is honored on the date, of maturity. Show the journal entries in the books of Vinod and Prakash.
Answer:
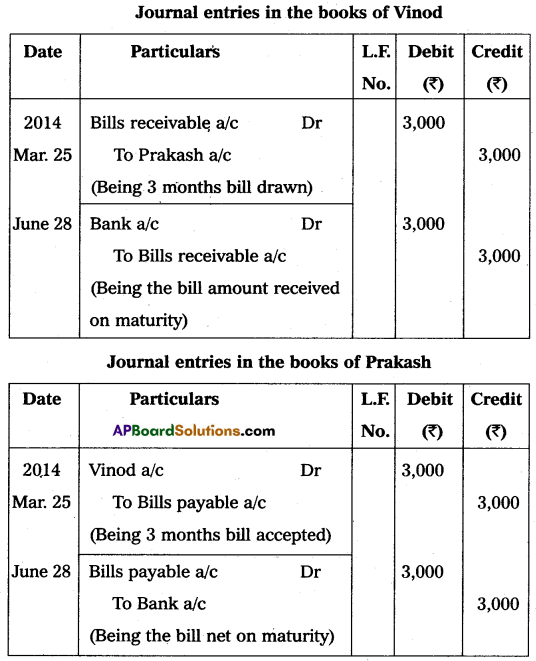
![]()
Question 23.
On 1st July 2010, Pradeep & Co purchased machinery for ₹ 50,000. Depreciation is written off at the rate of 10% p.a. under the Reducing Balance Method. Show the Machinery Account for 3 years assuming that the books are closed on 31st December every year.
Answer:
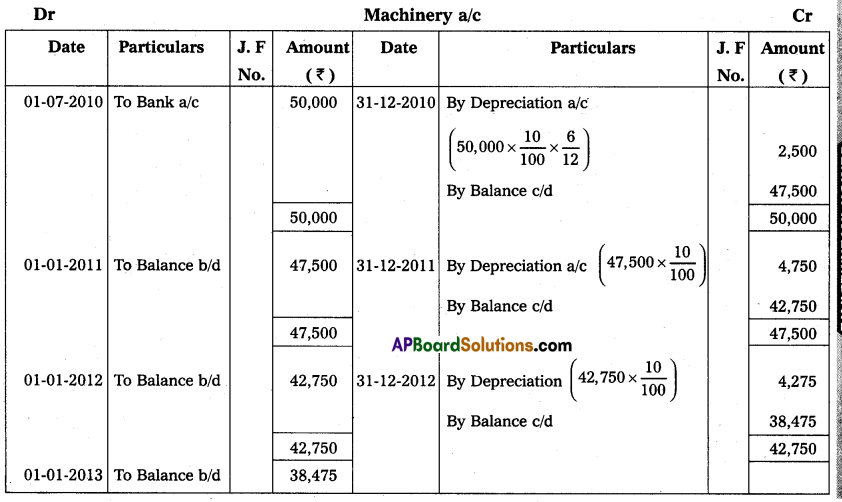
Question 24.
Bhavani Ltd. issued 20,000 shares of ₹ 20 each to the public for subscription as follows, payable ₹ 5 on application, ₹ 10 on the allotment, and the remaining balance on the first and final call. Give the Journal entries in the books of the company.
Answer:
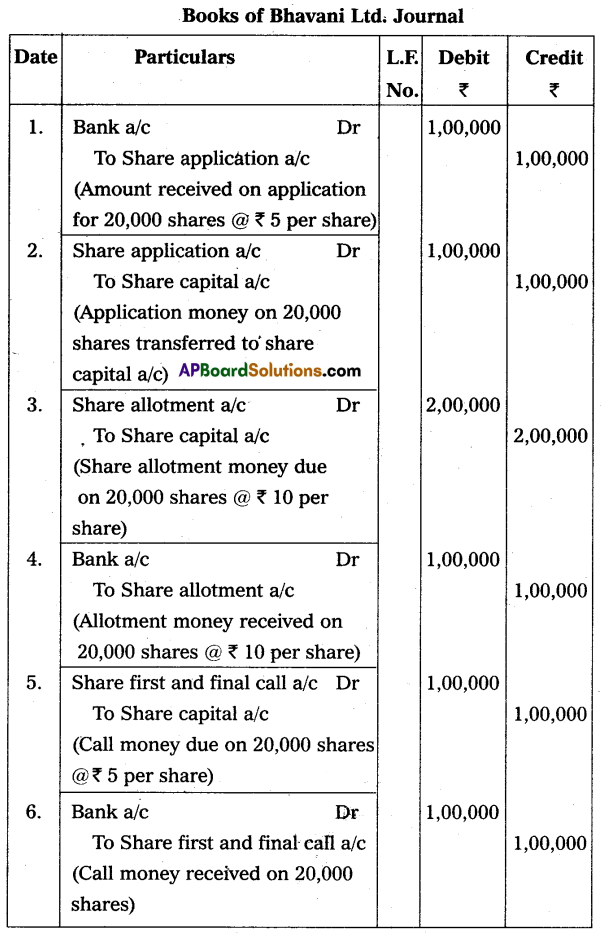
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What are the days of Grace?
Answer:
For making the payment of the bill, the drawee is allowed three extra days after the normal due date. Such three days are known as ‘Days of Grace’. If the due date is a public holiday, the previous day is the due date. If the due date is a sudden holiday, the next day is the due date.
Question 26.
What is the straight-line method?
Answer:
The straight-line method is the simple and widely used method of providing depreciation. Under this method, depreciation is calculated at a fixed percentage on the original cost of the asset every year.
Question 27.
What is a proforma invoice?
Answer:
Along with the goods, a statement is usually forwarded by the consignor to the consignee, giving a description of the goods consigned, the weight, quantity, price, and other relevant details. The statement is known as a proforma invoice. It resembles a sales invoice in appearance, but its purpose is quite different. It is intended as an evidence record of the consignment and the minimum price at which the consignee is expected to sell the goods sent to him.
Question 28.
What is the capital fund?
Answer:
Excess of assets over liabilities is called capital or (General) fund and it is made up of surplus of income over expenditure and certain items which are capitalized like life membership fees, donations, legacies, entrance fees, etc.
Question 29.
Explain the profit and loss appropriation account.
Answer:
Profit and Loss Appropriation Account is merely an extension of the Profit and Loss Account. It shows how the profits are appropriated or distributed among the partners. All adjustments in respect of partners are made through this account. It starts with the profit/loss as per P&L a/c is transferred to this account.
Question 30.
What is authorised capital?
Answer:
Authorized capital is the amount of share capital that a company is authorized to issue to the public by the memorandum of association. It is also called Nominal or Registered capital.
![]()
Question 31.
Tailored accounting Software.
Answer:
Accounting software is generally tailored in large business organizations with multi-users and geographically scattered locations. This software requires Specialised training for the users. The tailored software is designed to meet the specific requirements of the users and forms an important part of the organizational MIS.
Question 32.
Write any three limitations of incomplete records.
Answer:
The following are the limitations of accounts from incomplete records.
- It is not a scientific method of accounting because it does not record the two-fold aspect of each transaction.
- No trial balance can be prepared as it does not record the duel aspect of each transaction, so, the arithmetical accuracy of the books cannot be checked.
- In the absence of nominal accounts, trading and profit and loss accounts cannot be prepared.