Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 1 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Explain the functions of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
An entrepreneur performs all the functions necessary right from the generation of an idea and upto setting up an enterprise. The following are the functions of an entrepreneur.
- Formation of a new producing organization: The function of an entrepreneur is to rationally combine the factors of production into a new producing organization.
- Decision making: An entrepreneur as a decision maker makes various decisions regarding ascertaining the objective of the enterprise, sources of finance, product mix, pricing policies, promotion strategies, appropriate technology, or new equipment.
- Innovation: Innovation is the main function of an entrepreneur. Innovation means doing new things or doing things that are already being done in a new way. An entrepreneur puts science and technology to economic use. Innovative entrepreneurs are essential for rapid industrialization and economic development.
- Management: An entrepreneur performs managerial functions such as formulation of production plans, providing raw materials, physical facilities, and production facilities, and organizing and managing sales.
- Risk bearing: An entrepreneur undertakes the responsibility for loss that may arise due to unforeseen contingencies in the future. He guarantees interest to creditors, wages to labour, and rent to landholders.
- Supervision, control and direction: J.S.Mill mentions superintendence, control, and direction as entrepreneurial functions. Supervision involves assembling the means, turning maximum output at minimum cost, and supervising the work. The entrepreneur has to regulate and control the flow of goods, the use of finance and machinery. He also has to control and direct the activities of the employees.
- Planning: Planning is the first step in the direction of setting up an enterprise. The entrepreneur prepares a scheme for the proposed project in a formal systematic approach. The authorities, if satisfied fully with the requirements, grant legal sanction for the project.
According to Kilby, an entrepreneur performs the following major four functions.
- Exchange functions
- Administrative function
- Management and control functions
- Technological functions
Question 2.
What is international trade? Explain its importance.
Answer:
The trade that takes place between the countries is called international trade. The exchange of goods and services between the traders of two countries is international trade. International trade involves not only the exchange of goods but also currencies between nations. International trade is the process of transferring goods produced in one country to the consumers of another country. This is also called Foreign trade or External trade. Due to the globalization development of means of communication and transport, international trade has opened the way to huge imports and exports.
Importance of International Trade:
Foreign trade becomes necessary for every country because no country is capable of producing everything for the consumption of its people and the development of its economy. Hence foreign trade is necessary on the following grounds.
- Different countries of the world have different natural resources. However, some countries may not possess such mineral wealth. Therefore, one country has to depend on another country for natural resources which results in the need for foreign trade.
- Some countries are more suitably placed to produce some goods more economically due to the availability of raw materials, labour, technical know-how, etc. Then the other countries. In such cases, foreign trade is needed to import goods from those countries where they can be produced cheaply instead of producing goods at a higher cost.
- No country can produce all her needs. Production of different commodities requires different climatic conditions. For example, Cuba can produce sugar, Egypt can produce cotton, etc. Foreign trade among these countries helps all these countries to get all their requirements.
- International trade has reduced inequalities and facilitated the growth of the economy in different countries.
- International trade lowers the prices of goods and services all over the world.
- International trade promotes increased international understanding, exchange of ideas and culture, and world peace.
- In the era of globalization, no economy in the world can remain cut off from the rest of the world. Therefore, every country has to depend upon some other country or other.
![]()
Question 3.
Define banking. Explain the functions of banking.
Answer:
The word Bank is derived from the French word ’Bancus’ which means a bench. According to the Banking Regulation Act of 1949, banking is defined as “Accepting for lending or investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise”. The basic functions of banks are classified as primary functions and secondary functions.
(A) Primary Functions:
(i) Accepting Deposits: The Bank accepts various types of deposits, such as
- Fixed deposits: Fixed deposits are also called time deposits or term deposits. In this deposit, the amount cannot be withdrawn until maturity. The interest rate is also high.
- Current Deposits: Current accounts bear no interest companies, institutions, governments, and businessmen hold the current account. The greatest advantage of having a current account is that there is no restriction on withdrawals.
- Savings Deposits: These accounts aim to encourage small savings from the public. Certain restrictions are imposed on the depositors regarding the number of withdrawals and the amount to be withdrawn in a given period.
- Recurring deposits: The purpose of these accounts is to encourage regular savings, particularly by the fixed-income group. Generally, money is deposited in these accounts in monthly installments for a fixed period. It is repaid to the depositors along with interest on maturity.
(ii) Advancing of Loans: Lending is carried out purely on profit motive. Banks lend the amount which is mobilized through the deposits. The different forms of lending are:
Loans: A specified amount sanctioned by the bank is called a ‘Loan’. A loan is granted against the security of property or personal security. The loan may be repaid in a lump sum or installments. The loan may be classified into i) Demand loan ii) Term loan. A demand loan is repayable on demand. It is repayable at short notice. Medium and long-term loans are called term loans. It is granted for more than a year and repayment is done on a longer period.
Cash Credit: Cash credit is an arrangement where the bank agrees to lend money to the borrower upto a certain limit. The amount is credited to the borrower’s account. The borrower draws the money as and when he needs it. Interest will be charged only on the amount drawn. Banks may impose commitment charges on unutilized ports.
Overdraft: Banks grant overdraft to current account holders by which he is allowed to draw an amount ip excess of the balance held in their accounts. Interest is charged on the overdrawn amount.
Discounting of bills of exchange: A holder of a bill of exchange may be in urgent need of cash before the due date. He may sell or discount the bill with the bank. He will receive a lesser amount than the actual amount. On maturity, the bank gets it payment from the debtor.
(B) Secondary Functions:
These services include agency services and general utility services.
1. Agency services: Banks perform some agency services on behalf of their customers.
- Banks help their customers in transferring funds from one place to another place through cheques, drafts, etc.
- Banks collect and pay various credit instruments like cheques, bills of exchange, promissory notes, etc.
- Banks undertake to purchase and sell various securities like shares, bonds, debentures, etc., on behalf of their customers.
- Banks preserve the wills of their customers and execute them after death.
2. General utility services: These services are
- Letters of credit issued by the banks to their customers certifying their creditworthiness.
- Banks issue travellers cheques to help to travel without fear of theft or loss of money.
- Banks provide safe deposit locker facilities to the public at selected branches.
- Accepting or collecting foreign bills of exchange.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Define entrepreneurship.
Answer:
In a conference on entrepreneurship held in the United States, the term entrepreneurship was defined as “Entrepreneurship is an attempt to create value through recognition of business opportunity, the management of risk-taking appropriate to the opportunity and through the communication and management skills to mobilize human, financial and material resources necessary to bring a project to function”.
Question 5.
What is meant by SEZ?
Answer:
Special Economic Zones (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws that are more liberal than the country’s economic laws. The main aim of SEZ is to attract large foreign investments. It is intended to make SEZ as engine for economic growth. The SEZ Act was passed by the Parliament in May 2005. An SEZ is specifically described as a duty-free enclave deemed to be a foreign territory for trade operations.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of E-Banking?
Answer:
E-banking brings certain advantages.
- It reduces costs: The cost of banking transactions is considerably reduced. It increases the profitability of the banks.
- Prompt in services: There is a high degree of personalization and fast and flexible execution. Thus E-Banking prompt service and there is greater customer satisfaction.
- Anywhere and any time banking: It is a 24-hour a day and 7 days a week banking service. Bank accounts can be accessed from anywhere.
- So the customer can obtain information on his account and conduct transactions from his home or office.
- Cashless banking: Handling of cash is not necessary in E-Banking.
- Global coverage: It provides global network coverage of bank services. NRIs can monitor their bank account in Indian banks, from abroad.
- Central database: The database of each branch is centralized. Customer can deposit, withdraw, or remit money from any branch of their bank.
- Internet banking helps banks reduce the workload of their branches, such as the generation of statements, the balance of inquiry, etc.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the different components of the money market?
Answer:
The following are the basic components of the money market.
1. Call Money Market:
It is an important sub-market of the Indian money market. It is also known as money at call and money at short notice. It is also called as Interbank loan market. In this market, money is demanded for extremely short periods. The duration of such a transaction is from a few hours to 15 days. It is located in industrial and commercial locations such as Mumbai, Calcutta, Delhi etc. These transactions help stock brokers and dealers to fulfill their financial requirements. The rate at which money is made available is called a call rate. The rate is fixed by the market forces such as demand for and supply of money.
2. Acceptance Market:
A market consisting primarily of short-term instruments of credit typically used by exporters to get paid more quickly for their exported goods.
3. Bill Market:
The Bill market is meant for short-term bills. It includes commercial bills and treasury bills. It helps the government by marketing treasury bills and helps other sectors.
4. Collateral Loan Market:
It is an important section of the money market, which takes the form of loans, O.D.S., and Cash credits. These advances are covered by collaterals like government securities, gold, silver, stock merchandise, etc.
Question 8.
What do you know about BSE?
Answer:
Bombay Stock Exchange:
The first stock exchange was established as the ‘Native Share and Stock Brokers Association in Bombay in 1875, the predecessor of the present-day Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). BSE is located in Dalai Street, Mumbai, which is Asia’s first stock exchange and one of India’s leading exchange groups. Over the past 140 years, BSE has facilitated the growth of the Indian corporate sector by providing it an efficient capital-raising platform. In 1956, the BSE became the first stock exchange to be recognized by the Indian Government under the Securities Contracts Regulation Act, 1956. It is 4th largest stock exchange in Asia and the 9th largest in the world. More than 5000 companies are listed on BSE making it the World’s No. 1 exchange in terms of listed securities.
Question 9.
Explain the composition and jurisdiction of the state commission.
Answer:
The state commission settles consumer disputes at the state level. The state commission is headed by the judge of a high court and comprises other members not less than two and not more than as prescribed, one of whom shall be a woman. The state commission shall have jurisdiction to entertain consumer complaints where the value of goods and services for which the compensation claimed exceeds ₹ 20 lakhs and less than ₹ 1 crore. The state commission is empowered to call for the records and pass appropriate orders in respect of any consumer dispute within the state jurisdiction. The state commission is empowered to transfer any complaint pending before on the district forum to another district forum within the state. The state commission has circuit Benches. In case the aggrieved party is not satisfied with the order of the state commission, he can appeal to the national commission within 30 days of passing the order.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Definition of Entrepreneur.
Answer:
According to Peter F. Drucker an entrepreneur is one who “searches for change, responds to it and exploits opportunities and the innovation is the specified tool of an entrepreneur”.
Question 11.
Wholesaler.
Answer:
Wholesale trade means buying and selling the goods in relatively large quantities or in bulk and the traders who engage in the wholesale trade are called wholesalers. A wholesaler buys goods in large quantities from manufacturers and sells them in small lots to retailers or industrial users. A wholesaler is the first intermediary and serves as a link between producers and retailers.
Question 12.
ATM.
Answer:
ATM means Automatic Teller Machine. An ATM is an unmanned device located on or off the bank premises. The operation mechanism is that an ATM is inserted into the ATM, and the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to a processor which activates the account. It works 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. ATMs are being used to withdraw, deposit, and transfer funds.
Question 13.
Re-insurance.
Answer:
The insurance company undertakes the risk according to its capacity. If a company undertakes more risks than its capacity, then it tries to share the risks with some other insurance company. When an insurance company insurer completes part of the risk with another insurance company, then it is called re-insurance.
Question 14.
Recurring deposit.
Answer:
In Recurring deposits, the depositor is required to deposit a fixed amount of money every month for a specific period. After the completion of the specific period, the consumer gets back the deposited amount along with the cumulative interest accrued on the deposit.
Question 15.
Financial market.
Answer:
A financial market is a broad term describing any marketplace where buyers and sellers participate in the trade of financial assets such as equities, bonds, currencies, and derivatives.
![]()
Question 16.
Nifty.
Answer:
NIFTY stands for National Stock Exchange 50. It is an index computed from the performance of top stocks from different sectors listed in the NSE. NIFTY consists of 50 companies from 24 different sectors. The companies that form an index of NIFTY may vary from time to time based on many factors considered by the NSE.
Question 17.
Meaning of consumer.
Answer:
Under the Consumer Protection Act 1986, The word consumer has been defined separately for goods and services. For goods, a consumer buys any s goods for consideration and any user of such goods other than the person who buys it, provided such use is made with the approval of the buyer. For services, a consumer has any service or services for consideration and any beneficiary of such services provided the service is availed with the approval of the person who had hired the service for consideration.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
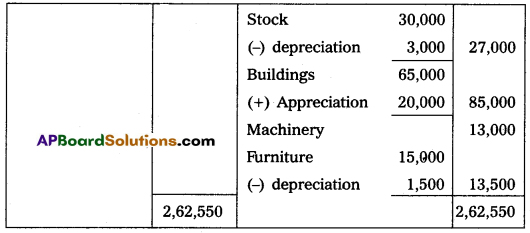
Question 18.
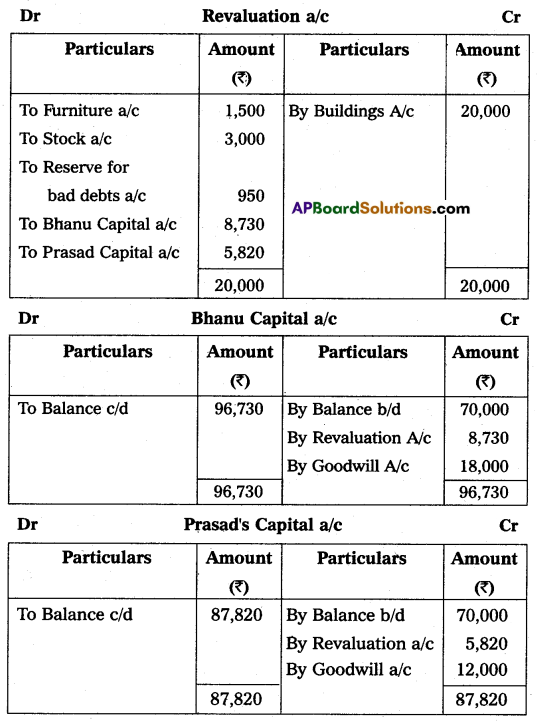
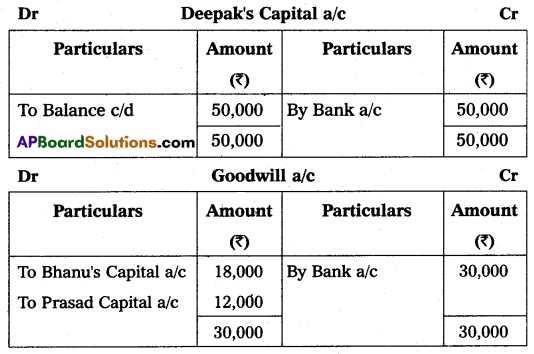
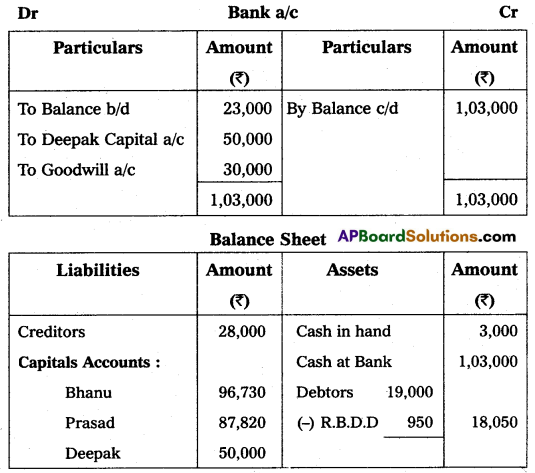
Bhanu and Prasad are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively. Their Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2015, was as under:
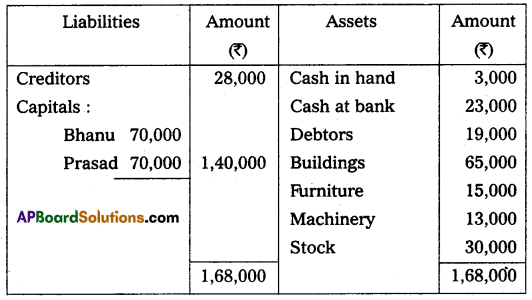
On that date, they admit Deepak into partnership for 1/3 share in future profit on the following terms:
(i) Furniture and stock are to be depreciated by 10%.
(ii) The building is appreciated by ₹ 20,000.
(iii) A 5% provision is to be created on Debtors for doubtful debts.
(iv) Deepak is to bring in ₹ 50,000 as his capital and ₹ 30,000 as goodwill.
Make necessary Ledger Account and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
Manikanta of Vijayawada Consigned goods of value of ₹ 20,000 to Ayyappa of Ahmedabad. Manikanta paid for-warding charges ₹ 1,000 and drew a bill of two months on Ayyappa for ₹ 10,000. The bill was discounted with bankers for ₹ 9,500. Ayyappa sent received the account sales of the consignment stating that the entire stock was sold for ₹ 28,000 agent commission ₹ 2,000 and a bank draft for the balance. Prepare necessary accounts.
Answer:
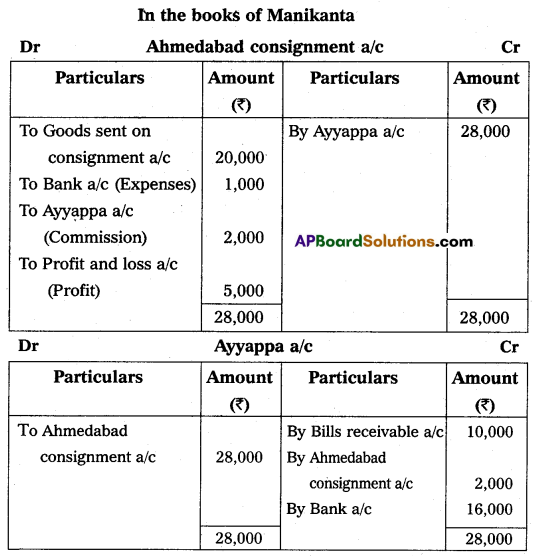
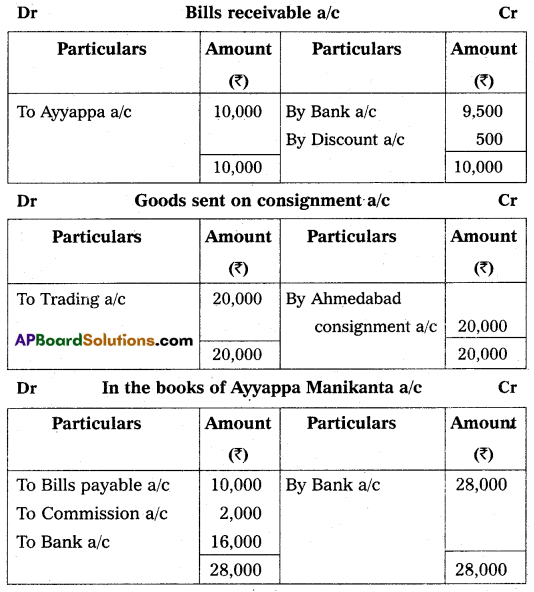
(Or)
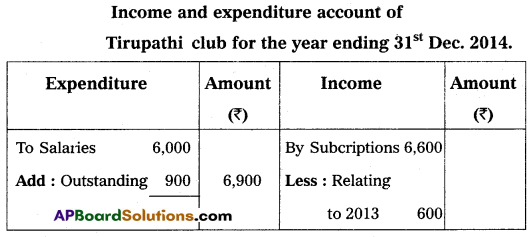
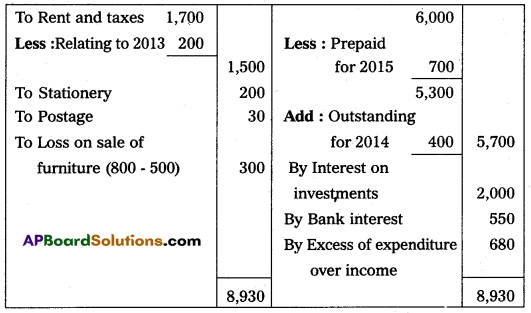
Question 20.
Prepare income and expenditure A/c of Tirupathi Club from the following receipts and payments A/c, for the year ending 31-Dec-2014.
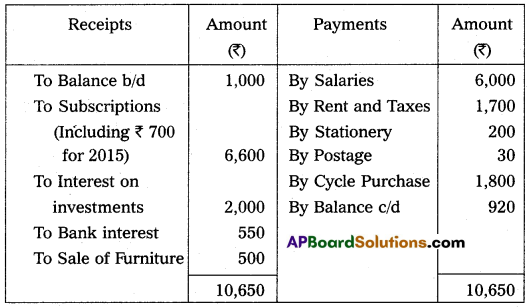
Adjustments:
(a) Rent paid included ₹ 200 for December 2013.
(b) Salaries Payable ₹ 900.
(c) Subscriptions received included ₹ 600 for the year 2013.
(d) Subscriptions Due for the year 2014, ₹ 400.
(e) Cost of furniture sold ₹ 800.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
State any five advantages of the computerized accounting system.
Answer:
Computerized accounting offers the following advantages.
- Speed: Accounting data is processed faster by using a computerized accounting system than it is achieved through manual efforts.
- Accuracy: The possibility of error is eliminated in a computerized accounting system because the primary accounting data is entered for all the subsequent usage and the process is preparing the accounting reports.
- Reliability: The computer system is well-adapted to performing repetitive operations. They are immune to tiredness, boredom, or fatigue. As a result, computers are highly reliable compared to human beings.
- Up-to-date information: The accounting records, in a computerized accounting system are updated automatically as and when accounting data is entered and stored. Therefore, the latest information about accounts gets reflected when accounting reports are produced and printed.
- Real-time user interface: Most of the automated accounting systems are interlinked through a network of computers. This facilitates the availability of information to various users at the same time on a real-time basis (That is spontaneously).
![]()
Question 22.
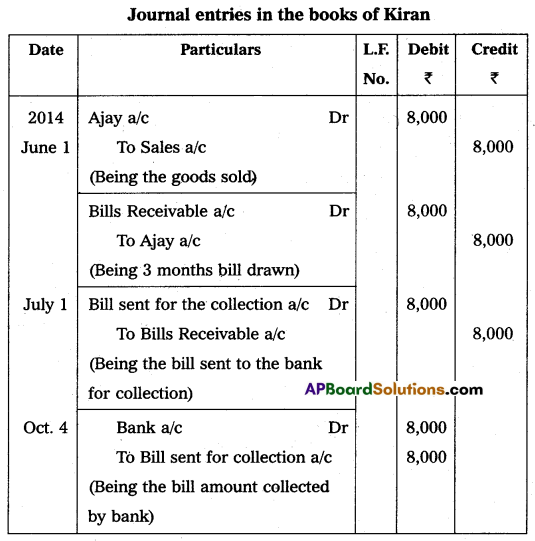
On 1st July 2014 Ajay purchased goods worth ₹ 8,000 from Kiran and accepted the bill which was drawn by Kiran payable after three months for the same amount. Kiran sent the bill to his bank for collection. The bill was honoured on the due date of maturity. Pass necessary journal entries in the books of Kiran.
Answer:
Question 23.
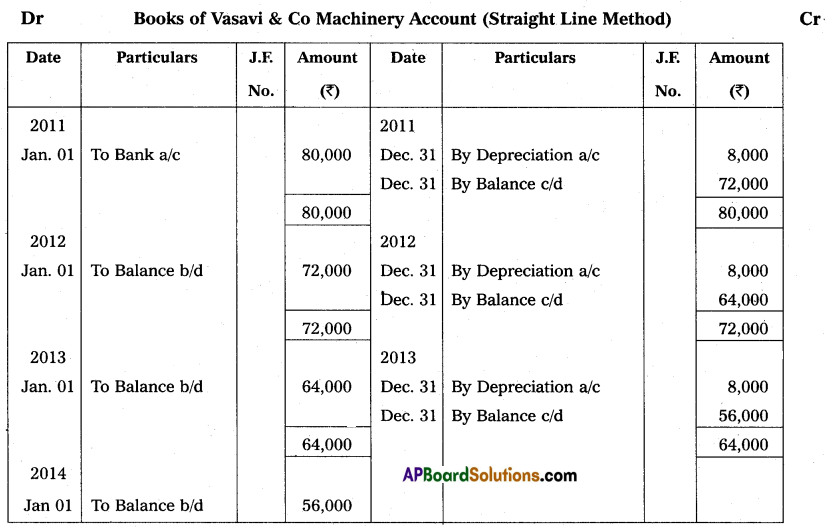
Vasavi & Co purchased machinery for ₹ 80,000 on 1st January 2011. Depreciation is provided annually at 10% of the original cost every year. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Prepare Machinery Account for the first 3 years.
Answer:
Annual Depreciation = Original Cost × \(\frac{\text { Rate of depreciation }}{100}\)
= 80,000 × \(\frac{10}{100}\)
= ₹ 8,000
Annual Depreciation = ₹ 8,000
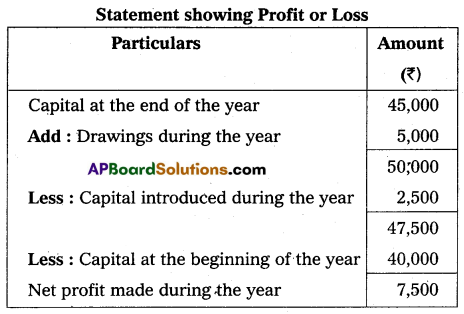
Question 24.
Find out the profit from the following data:
Capital at the beginning of the year – ₹ 40,000
Capital at the end of the year – ₹ 45,000
Drawings during the year – ₹ 5,000
Capital introduced during the year – ₹ 2,500
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is meant by discounting a bill?
Answer:
When the bill is encashed from the bank before its due date, it is known as the discounting of the bill. The bank deducts a small sum of money as a discount from the amount of the bill and disburses the balance amount to the drawer of the bill.
Question 26.
What is depreciation?
Answer:
Spicer and Pegler define depreciation as follows: ‘Depreciation is the measure of exhaustion of the effective life of an asset from any cause during a given period’. Depreciation means a decline in the value of a fixed asset due to use, passage of time, obsolescence, or any other cause.
Question 27.
What is Account sales?
Answer:
Account sales is a document sent by the consignee to the consignor showing the details of the gross sale proceeds, the various expenses incurred by him, the commission amount due, any advance payment to the consignor which is deducted from the total amount due, and the net amount payable is shown.
Question 28.
What is Entrance fees?
Answer:
Entrance fees or admission fees received from the members. When they were admitted into the concern. In the absence of specific instructions, this amount should be treated as revenue income.
Question 29.
What do you understand by the fixed capital of partners?
Answer:
Under the fixed capital method, the capital of the partners shall remain fixed unless additional capital is introduced or a part of the capital is withdrawn as per agreement among the partners. Items like a share of profit/loss, interest on capital, drawings, interest on drawings, etc., are recorded in a separate account called partner current account.
Question 30.
What is a preference share?
Answer:
A preference share is a share that carries preferential rights regarding the payment of dividends by a fixed rate and repayment of capital at the time of winding up the company.
![]()
Question 31.
What is MIS?
Answer:
The computerized accounting system facilitates the real-time production of management information reports, which will help management monitor and control. The business effectively. Debtors analysis indicates the possibilities of bad debts and also the concentration of debt and its impact on the balance sheet.
Question 32.
Define accounts from incomplete records.
Answer:
According to R.N. Carter, single entry cannot be termed as a system, as it is not based on any scientific system like a double entry system, for this purpose, single entry is nowadays known as the preparation of accounts from incomplete records.