Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 11th Lesson Biotechnology: Principles and Processes which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 11th Lesson Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define biotechnology. [TS MAR-18]
Answer:
Biotechnology is a science which utilises the properties and uses of micro organisms or exploits cells and the cell constituents, at the industrial level, for generating useful products, essential to life and human welfare.
Question 2.
What are molecular scissors? Where are they obtained from? [AP MAR-17] [TS MAY-17]
Answer:
- Molecular scissors are the restriction enzymes which cut the DNA at specific locations.
- They are usually obtained from bacteria.
![]()
Question 3.
Name any two artificially restructured plasmids. [AP MAY-22] [TS MAR-19]
Answer:
- pBR 322 (after Boliver and Rodriguez).
- pUC 19, 101 (after University of California)
Question 4.
What is EcoRI? How does it function?
Answer:
EcoRI is a restriction enzyme obtained from a bacterium called Escherichia coli.
This enzyme specifically recognises GAA sites and cuts it between G and Answer:
Question 5.
What are cloning vectors? Given an example.
Answer:
- Vectors used for multiplying the foreign DNA sequences are called cloning vectors.
- Ex: Plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids and artificial chromosomes.
Question 6.
What is recombinant DNA?
Answer:
Recombinant DNA is a hybrid DNA formed by joining a desired gene to the original DNA molecule with the help of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question 7.
What is palindromic sequence?
Answer:
The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads the same on the two strands, when orientation of reading is same. Ex: 3′ GAATTC 5′, 5’CTTAAG 3′, MALAYALAM
Question 8.
What is the full form of PCR? How is it useful in biotechnology? [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
- Full form of PCR is Polymerase Chain Reaction.
- PCR technique is used in (i) DNA cloning (ii) gene amplification (iii) DNA finger printing
Question 9.
What is down-stream processing? [AP MAR-19] [AP, TS MAR-17] [AP,TS MAR-16]
Answer:
Separation and purification of products before they are ready for marketing is called down streaming processing.
Question 10.
How does one visualize DNA on an agar gel.
Answer:
The separated DNA fragments can be visualised only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Question 11.
How can you differentiate between exonucleases and endonucleases?
Answer:
- Exonucleases: Exonucleases cut DNA and remove nucleotides from the ends
- Endonucleases: Endonucleases make cuts at specific positions within the DNAnswer:
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write short notes on restriction enzymes. [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
In 1963 two enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of a bacteriophase in E.Coli were isolated. One of these enzymes add methyl group to DNAnswer: The other cut DNAnswer: The latter was called Restriction endonuclease. At present more than 900 REs were recognised.
Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA Palindromes are groups of letters that form the same words when read in both forward and backward directions. For example “MALAYALAM”. The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads same on the two strands when orientation of reading is kept the same. For example the following sequences read the same on the two strands in 5′ → 3′ direction. This is also true if read in the 3′ → 5′ direction.
5′ – GAATTC – 3′
3′ – CTTAAG -5′
Commonly most restriction enzymes cut the two strands of DNA double helix at different locations. Such a cleavage is generally termed as staggered cut.
- Restriction endonucleases are used in genetic engineering to form ‘recombinant’ molecules of DNA, which are composed of DNA from different genomes.
- When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same kind of’sticky ends’ and these can be joined together (end-to-end) using DNA ligases.
![]()
Question 2.
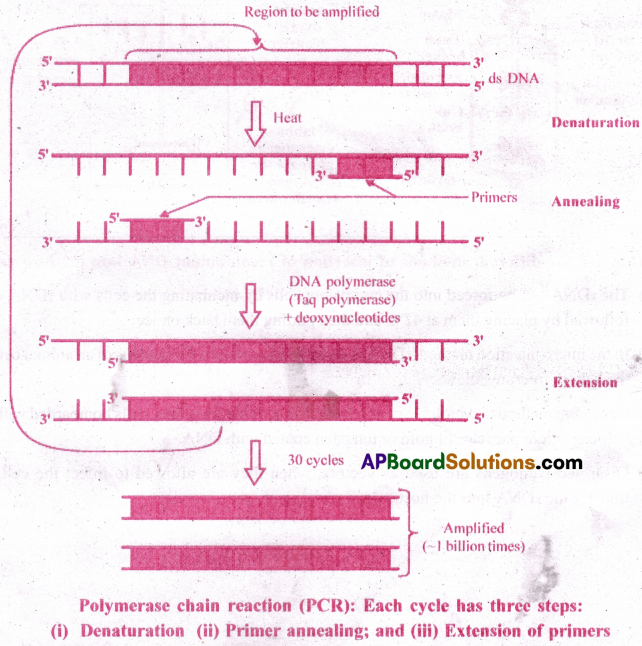
Give an account of amplification of gene of interest using PCR.
Answer:
- PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction.
- In this reaction, multiple copies of gene (DNA) of interest are synthesised in vitro using two sets of primers (small chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA) and the enzyme DNA polymerase. The enzyme extends the primers, using the nucleotides provided in the reaction and the genomic DNA as template.
If the process of replication of DNA is repeated many times, the segment of DNA can be amplified to approximately billion times i.e., 1 billion copies are made. Such repeated amplification is achieved by the use of thermostable DNA polymerase such as Taq polymerase (isolated from a bacterium, Thermus aquaticus), which remain active even during the high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNAnswer: The amplified fragment, if desired, can now be used to ligate with a vector for further cloning.
DNA finger print is the pattern of DNA fragments on the gel. Gene amplification is one technique for DNA finger printing.
Question 3.
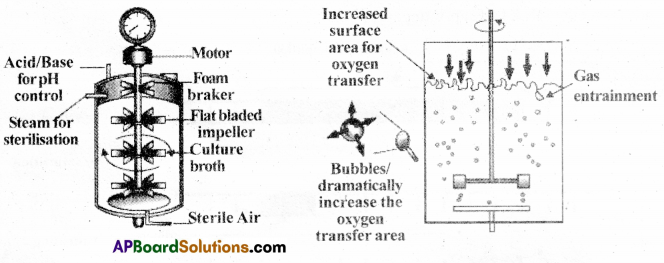
What is a bio-reactor? Describe briefly the stirring type of bio-reactor.
Answer:
- Bio-reactors are the vessel having a capacity of 100-1000 litres volume
- In these vessels raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, individual enzymes, etc., using microbial plants, animal or human cells.
- A bio-reactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions (temp, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen)
- The stirred-tank reactor is usually cylindrical to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents.
- The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability through out the bioreactor.
- The bioreactor has
a) an agitator system
b) an oxygen delivery system
c) a foam control system
d) a temperature control system
e) pH control system
f) small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.
Question 4.
What are the different methods of insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cell?
Answer:
- The rDNA can be forced into the competent cells by incubating the cells with rDNA on ice followed by placing them at 42°C arid then putting them back on ice.
- In the micro injection method, rDNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell with the help of microneedles.
- Gene gum method (or) biolistic method which is suitable for plants, cells bombarded with high velocity micro particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNAnswer:
- Disarmed pathogens are used as vectors, when they are allowed to infect the cell, they transfer the rDNA into the host.
![]()
Question 1.
Explain briefly the various processes of recombinant DNA technology. [AP, TS MAY-22] [TS MAY-17] [AP MAR-17, 16] [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
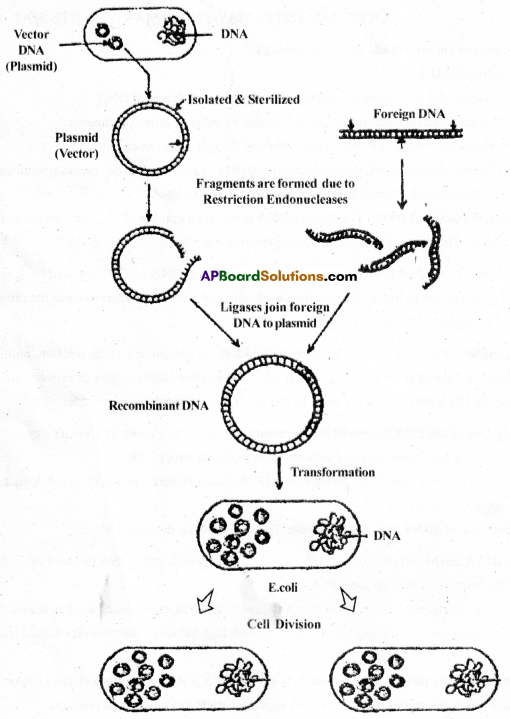
Processes of recombinant DNA technology:
1) Isolation of DNA:
- Nucleic acid is the genetic material of organisms in the form of DNAnswer:
- It is enclosed by membranes and surrounded by other cellular constituents.
- By using enzymes like lysozyme, cellulose, the cell walls can be digested.
- The membranes, RNA, proteins can be removed by using powered detergents, ribonuclease.
- By the addition of ethanol, the purified DNA is precipitated.
2) Fragmentation of DNAnswer: The purified DNA is cut into a number of fragments by restriction enzymes. This process is called resoluting enzyme digestion.
3) Isolation of desired DNA fragments: The fragments of DNA can be separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Since DNA are negatively charged, they accumulate towards the cathode and are extracted from the gel piece.
4) Amplification of the desired gene by using PCR: In polymerase chain reaction, multiple copies of desired DNA fragments are synthesized in vitro.Here two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase are used. In this process, 1 billion copies are made.
5) Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector: This requires a vector DNA and source DNAnswer:
- These are cut with the same endonuclease to obtain sticky ends.
- Both are then ligated by mixing vector DNA, gene of interest and enzyme DNA ligase to form recombinant DNAnswer:
6) insertion of rDNA into the host cell: This can be done in several ways.
- rDNA can be forced into host cells by incubating the cells with rDNA on ice. This enables the bacteria to take up the rDNAnswer:
- In micro injection method, the rDNA is directly injected irtto the nucleus of an animal cell.
- In gene gun method, cells are bombarded with high velocity microparticles of gold coated
with DNA.
7) Obtaining the foreign gene product: When alien DNA is inserted into a cloning vector, the alien DNA gets multiplied. The rDNA expresses itself to form desired products.
8) Dow nstream processing: After completion of the biosynthetic stage, the product has to be processed before it is ready for marketing as a finished product. The processes include separation and purification.
Diagrammatic representation of recombinant DNA technology
Question 2.
Give a brief account of the tools of recombinant DNA technology. [AP MAR-19] [TS MAR-17] [AP MAY-17] [AP, TS MAR-15] [AP 20]
Answer:
Tools of recombinant DNA technology:
- Restriction enzymes
- Polymerase enzymes
- Ligases
- Vectors
- Host organism
![]()
1) Restriction enzymes: Restriction enzymes belong to a larger class of enzymes called nucleases. These are two kinds
- Exonucleases: Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA
- Endonucleases: Endonucleases make cuts at specific positions within the DNAnswer:
Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic sequence in the DNAnswer:
The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs, that reads the same on the two strands Ex: EcoRl recognises 51 GAATTC 3′ sites on the DNA and cuts in between G and A
5′ G A A T T C 3′
3′ C T T A A G 5′
2) Polymerase enzymes:
- In polymerase chain reaction multiple copies of gene of interest are synthesized by using primers and DNA polymerase.
- In this process, the replication of DNA is repeated many times and 1 billion copies can be produced.
- Such amplification is achieved by Taq polymerase which remain active at high temperatures.
- The amplified fragment, if desired, can now be used to ligate with a vector for further cloning.
3) Ligages: The enzyme DNA ligage, joins the ends of plasmid DNA with that of desired gene by covalent bonding . It regenerates a circular hybrid called rDNAnswer:
4) Vectors: The DNA used as a carrier, for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA, into a suitable host called vector.
- Vectors used for multiplying the foreign DNA sequences are called cloning vectors.
- Commonly used cloning vectors are plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids.
Properties of cloning vectors:
- They must have low molecular weight
- They must have unique cleavage site for the activity of restriction sites.
- They must be able to replicate inside the host cell after its introduction.
- They require a ‘selectable marker’ which helps in identifying and eliminating non transformants.
5) Host organisms: Competent host for transformation with rDNA is required.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No. Restriction endonucleases are not present in eukaryotes. In eukaryotes the DNA is highly methylated due to the enzyme methylase. Methylation protects the DNA from the activity of restriction enzymes.
Question 2.
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Answer:
Stirred tank bioreactors are used for the large scale production of the biotechnological products.
Where as shake flasks are used for small scale production only.
The advantages of stirred tank reactor are:
- It has a curved base to facilitate proper mixing of the contents
- Alternately air can be bubbled through the reactor
- It has an agitator system, oxygen delivery system, foam control system, temp.control system.
- Small volumes of sample can be withdrawn periodically.
Question 3.
Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Answer:
There are two stages in Meiosis. They are Meiosis I and Meiosis II. In Meiosis I there is a sub stage called Pachytene stage of prophase I. During this stage crossing over occurs i.e., exchange of segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes take place. This results in the formation of recombinant DNAnswer:
Question 4.
Describe briefly (he following:
(a) Origin of replication (b) Bioreactors (c) Downstream processing
Answer:
a) Origin of replication: Origin of replication is a DNA sequence in the genome from where replication starts. It is not possible for the alien piece of DNA to replicate unless it becomes a part of chromosome which has a specific sequence known as ‘origin of replication’. This alien piece of DNA can replicate and multiply it self in the host organism. This process is also called cloning.
![]()
b) Bioreactors: These are the large vessels of 100-1000 Ltrs volume in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, individual enzymes etc., using microbial plant, animal or human cells. A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins and oxygen.
c) Down stream processing: After the completion of biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected to a series of processes before it is ready for marketing. The processes include separation and purification. These processes are collectively known as down streaming. The product has to be formulated with suitable preservatives. Such formulation has to undergo through clinical trials. Down stream processing vary from product to product.
Question 5.
Explain briefly (a) PCR (b) Restriction enzymes and DNA (c) Chitinase
Answer:
a) PCR: PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. In this reaction, multiple copies of gene (or DNA) of interest are synthesized in vitro using two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase.
b) Restriction enzymes and DNAnswer: Restriction enzymes are also called as molecular scissors. They belong to a class of enzymes called nucleases. They cut the DNA molecule at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence of six base pairs known as recognition sequence.
DNAnswer: DNA is the deoxyribo nucleic acid. It is a double stranded helical model, seen as a component of chromosome. It has the ability to replicate.
c) Chitinase: During the process of recombinant DNA technology, isolation of the genetic material (DNA) is to be done in pure state. If the DNA of a fungal cell has to be isolated, the fungal cell wall contain chitin. So the cell wall is digested by treating the cell with the enzyme chitinase. The chitinase is a class of enzymes used to degrade the cell wall. Thus the enzyme breaks the cell wall and releases the genetic material.
Question 6.
Discuss with your teacher and find out how to distinguish between (a) Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA (b) RNA and DNA (c) Exonuclease and Endonuclease
Answer:
a) Differences between Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA:
| Plasmid DNA | Chromosomal DNA |
| 1. Plasmid DNA is the extra chromosomal DNA present in the bacterium cell. | 2. It carries a few genes. |
| 1. Chromosomal DNA is the entire DNA of an organism present inside the chromosomes. | 2. It carries a several genes. |
b) Differences between RNA and DNA:
| RNA | DNA |
| 1. Consists of one stranded of nucleotides 2. Ribose sugar is present 3. Pyrimidines are cytosine and uracil 4. RNA is made up of few nucleotides (752000) 5. RNA does not replicate 6. RNA is not a genetic material. |
1.Consists of two strands of nucleotides. 2. Deoxyribose sugar is present 3. Pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine., 4. DNA is made up of several nucleotides (more than 4 millions) 5. DNA replicates 6. DNA is the genetic material. |
c) Differences between Exonuclease and Endonuclease:
| Exonuclease | Endonuclease |
| Exonucleases remove nucleotides from ends of DNA | Endonucleases cuts at specific positions within the DNA |
Question 7.
What does ‘H’ ‘in”d’ and ‘III’ refer to in the enzyme Hind III?
Answer:
‘Hind III’ is the name of a restriction endonuclease.
- While naming these enzymes,the first letter comes from the genus of the bacterium Haemophilus(H)
- The next two letters comes from the name of the species influenzae (in )
- The next letter comes from the strain of the bacterium (d)
- The Roman numbers following these four letters indicate the order in which the enzymes were isolated from that strain of the bacterium.
![]()
Question 8.
Restriction enzymes should not have more than one site of action in the cloning site of a vector. Comment.
Answer:
Cloning sites are required to link alien piece of DNA with vector.
- For this, vector requires single recognition site for restriction enzymes.
- Presence of more than one recognition sites with in the vector will generate several fragments leading to complication to gene cloning.
Question 9.
What does ‘competent’ refer to in ‘competent cells’ used in transformation experiments?
Answer:
Since DNA is hydrophilic molecule, if cannot pass through cell membranes. In order to force bacteria to take up the plasmid, the bacterial cell must first be made ‘competent’ to take up DNAnswer: This is done by treating them with a specific concentration of divalent cation, such as calcium, which increases the efficiency with which DNAnswer: enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
Question 10.
What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA)?.
Answer:
At the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA), the bacterial cell has to be treated with proteases to remove proteins.
Question 11.
While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Answer:
If the denaturation step is missed during PCR, Annealing, Extension and Amplification of DNA cannot be done.
Question 12.
What modification is done on the Ti plasmid of Agrobactcrium tumefaciens to convert it into a cloning vector?
Answer:
In rDNA technology, we came to know that bacteria and viruses transfer genes into eukaryotic cells and force them to do what they (bacteria and virus) want. For eg: Agrobacterium tumificans is a pathogen of several dicot crop plants. It is able to deliver a piece of DNA known as T-DNA’ to transfer from normal plant cells into tumor cells. The tumor inducing Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium has been modified into a cloning vector, such that it is no longer pathogenic to plants but it still able to use the mechanism to deliver genes of our interest into a variety of plants.
Question 13.
What is meant by gene cloning?
Answer:
In rDNA technology, the selected fragments of DNA are inserted into a suitable vector to produce large number of copies of genes. This is called gene cloning.
Question 14.
Decide the ratio between ester bonds and hydrogen bonds that are broken in each palindromic sequence of a DNA when treated with EcoRI during the formation of sticky ends.
Answer:
Equal ratio 2:7
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
‘Molecular scissors’ are
1) Genes
2) restriction enzymes
3) Chromosomes
4) Antibiotics
Answer:
2) restriction enzymes
Question 2.
…………. is used to transfer the alien piece of DNA into the host organism
1) Plasmid
2) Chromosome
3) Messenger RNA
4) r-DNA
Answer:
1) Plasmid
Question 3.
……….. can cut the polynucleotide strands of DNA double helix at specific points
1) Polymerases
2) Ligases
3) Endonucleases
4) Exonucleases
Answer:
3) Endonucleases
![]()
Question 4.
Palindromic nucleotide sequence in DNA
1) is the target site for the action of restriciton enzyme
2) acts as plasmid
3) acts as vector
4) is the site of origin of replication
Answer:
1) is the target site for the action of restriciton enzyme
Question 5.
Polymerase chain reaction is used for one of the following
1) Isolation of the gene of interest
2) Amplification of gene of interest.
3) Cut the DNA with restriction enzyme
4) Precipitation of DNA
Answer:
2) Amplification of gene of interest.
Question 6.
In naming of restriction enzymes, the first letter indicates
1) Genus
2) Species.
3) Name of the strain
4) The order in which the enzyme was isolated
Answer:
1) Genus
Question 7.
One of the following represents the chimaeric DNA
1) Primer
2) Plasmid DNA
3) Cut gene of interest
4) rDNA
Answer:
4) rDNA
Question 8.
……….. is a technique for DNA finger printing
1) Isolation of desired gene
2) Restriction enzyme digestion.
3) Gene amplification
4) Extraction of DNA from agarose gel
Answer:
3) Gene amplification
Question 9.
The process by which a piece of DNA is introduced into the host bacterium is known as
1) Transformation
2) Transcription
3) Translation
4) Transduction
Answer:
1) Transformation
Question 10.
The stained fragments of DNA on the gel can be seen as one of the following
1) A collection of fine threads
2) A collection of fine crystals.
3) Bright violet colour bands
4) Bright orange colour bands
Answer:
4) Bright orange colour bands
Question 11.
The first step in recombinant DNA technology is
1) Insertion of the isolated gene into a vector
2) Secection of transformed host cell.
3) Isolation of a desired gene
4) Ligation of the desired gene with a vector
Answer:
3) Isolation of a desired gene
Question 12.
The main enzyme which involves in replication of DNA in E. coli is
1) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
2) Ligase.
3) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
4) Restriction endonucleases
Answer:
1) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
![]()
Question 13.
Identify the chief enzyme that is involved in PCR technique
1) Restriction enzymes
2) DNA ligase.
3) Hydrolases
4) Taq polymerase
Answer:
4) Taq polymerase
Question 14.
Suitable vector for transgenics is
1) pBR322
2) Coliphage-lambda.
3) Tiplasmid
4) Cos-sites
Answer:
3) Tiplasmid
Question 15.
PUC 101 is a
1) Cosmid
2) Virus.
3) Plasmid
4) Mutagen
Answer:
3) Plasmid
Question 16.
Construction of first recombinant DNA was done by using plasmid of
1) Salmonella typhimurium
2) E.coli
3) Bacillus thuringeiensis
4) Yeast
Answer:
1) Salmonella typhimurium
Question 17.
Which of the following is (are) the example of chemical scissors
1) Eco-RI
2) Hind-III
3) Bam-I
4) all the above
Answer:
4) all the above
Question 18.
A piece of nucleic acid used to find out a gene, by forming hybrid with it, is called
1) C-DNA
2) DNA probe
3) T-DNA
4) Plasmid DNA
Answer:
2) DNA probe
Question 19.
In the year 1963 the two enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in E.Coil were isolated . One of these added methylgroups to host DNA, while the other cut DNAnswer: The later was called
1) restriction endonuclease
2) restriction exonuclease
3) Type III restriction enzyme
4) plasmid
Answer:
1) restriction endonuclease
Question 20.
Type of sticky end produced by the action of the F.CORI is
1) GAATTC
2) CTTAA
3) AATTC
4) TTAA
Answer:
4) TTAA
Question 21.
Which of the gene transfer method is useful more in animal cells?
1) Electroporation
2) Gene gun method
3) Micro injection
4) Calcium desired DNA fragments
Answer:
3) Micro injection
![]()
Question 22.
‘rop’ in plasmids codes for
1) Replication site
2) Cloning site
3) Selectable market
4) Proteins involved in replication
Answer:
4) Proteins involved in replication
Question 23.
In probe the nucleic acid which is tagged with a radioactive molecule could be
1) a single stranded RNA
2) a single stranded DNA
3) a double stranded DNA
4) both 1 & 2
Answer:
4) both 1 & 2
Question 24.
Which one of the following is not required in PCR?
1) Oligonucleotide primer
2) DNA template
3) Taq polymerase
4) Helicase enzyme
Answer:
4) Helicase enzyme
Question 25.
Now a days, most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is
1) ethidium bromide
2) Agarose
3) Sulphite bromide
4) Sulphate bromide
Answer:
2) Agarose
Question 26.
Which of the following could be restriction enzyme recognition site for E.Co-RI ?
1) ATGCAT
2) ATCATC
3) AAAGGA
4) ATCCTA
Answer:
3) AAAGGA
Question 27.
How many copies of DNA sample ar<? produced in PCR technique after 6-cycles
1) 4
2) 32
3) 64
4) 16
Answer:
3) 64
Question 28.
If alien DNA is introduced using sal I in PBR322 then the transformant will grow on
1) Ampicillin
2) Tetracyclin
3) Both
4) None
Answer:
1) Ampicillin
Question 29.
Which vector is used to deliver gene in animal cell
1) Retroviruses
2) Disarmed retroviruses
3) Tiplasmid
4) E.coli
Answer:
2) Disarmed retroviruses
Question 30.
Ratio between triple and double H-bond nucleotide base pairs in a palindrome recognised by Eco.RI
1) 3:2
2) 2:1
3) 1:2
4) 3:4
Answer:
4) 3:4
![]()
Question 31.
The Ti plasmid is often used for making transgenic plants. This plasmid is found in
1) Azotobacter
2) Rhizobium
3) Agrobacterium
4) Yeast plasmid
Answer:
3) Agrobacterium
Question 32.
Pick out the incorrect pair
1) T-DNA – Retroviruses
2) Pst-1 – Restriction endonuclease
3) 5′ GAATTC 3′ -Recognition sequence of E.coli
4) Plasmid – Ringlet of DNA
Answer:
1) T-DNA – Retroviruses
Question 33.
Thermostable DNA polymerase widely used in gene amplification by PCR is isolated from
1) Thermobactor
2) Beggiota
3) Thiobacillus
4) Thermus aquaticus
Answer:
4) Thermus aquaticus
Question 34.
Gene amplification by using primers can be done by
1) Micro-injection
2) ELISA
3) Gene gun
4) Polymerase Chain Reaction
Answer:
4) Polymerase Chain Reaction
Question 35.
An antibiotic resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of
1) Competent cells
2) Transformed cells
3) Recombinant cells
4) None of these
Answer:
2) Transformed cells
Question 36.
In ……….. method, gene specific probes are used.
1) Colony hydration
2) Colony isolation
3) Colony hybridization
4) Colony identification
Answer:
3) Colony hybridization
Question 37.
When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same kind of sticky ends and these can be joined together (end to end ) using
1) E.coil
2) DNAligase
3) DNA polymerases
4) restriction enzymes
Answer:
2) DNAligase
Question 38.
Assume that the occurrence of nitrogen bases in adjacent positions in a DNA strand is random. Identify the minimum number of nucleotides in a DNA strand where GAATTC can occur once on the basis of probability •
1) 512
2) 256
3) 4096
4) 1024
Answer:
3) 4096
![]()
Question 39.
The most important feature in a plasmid is
1) Origin of replication (ori)
2) A selectable marker
3) Sites for restriction endonucleases
4) All of these
Answer:
1) Origin of replication (ori)
Question 40.
In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
1) To keep the cultures free of infection
2) As selectable markers
3) To select healthy vectors
4) As sequences from where replication starts
Answer:
2) As selectable markers
Question 41.
The function of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is
1) Translation
2) Transduction
3) DNA amplification
4) None of these
Answer:
3) DNA amplification
Question 42.
Molecular scissors while inspecting the length of DNA it cleaves, the following type of bonds in DNA
1) Hydrogen bonds only
2) Phosphodiester bonds only
3) Phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds
4) Hydrogen bonds and peptide bonds
Answer:
3) Phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds
Question 43.
Agarose gel is
1) Natural polymer extracted from fungi
2) Natural polymer extracted from sea weeds
3) Artificial polymer derived from red algae
4) Synthetic polymer of fungi
Answer:
2) Natural polymer extracted from sea weeds
Question 44.
During polymerase chain reaction which primers are used for initiating the process
1) DNA primers
2) RNA primer
3) DNA and RNA primer
4) None of these
Answer:
1) DNA primers
![]()
Question 45.
Ori sequence in plasmid refers to sequence
1) that supports high copy number of the linked DNA
2) from which replication will start in plasmid
3) for restriction site
4) Both (1) and (2)
Answer:
4) Both (1) and (2)