Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define Sole proprietorship and discuss its merits and demerits.
Answer:
In this organisation only one individual is at the helm of all affairs of business. He makes all the investments. He bears all risks and takes all profits. He manages and control the business himself. The business is run with the help of his family members or paid employees. His liability is unlimited. The sole trader is the sole organiser, manager, controller and master of the business.
Kimball and Kimball defines “Sole Proprietorship is a form of business where the individual proprietor is the supreme judge all matters pertaining to his business”.
Merits:
- Easy to form: It is very easy and simple to form a sole trading business. The capital required is small. There are no legal formalities for starting the business.
- Prompt decisions and quick action : The sole trader is the sole dictator of his business. There is no need to consult any body while taking decisions. So, decisions can be taken quickly.
- Incentive to work hard: The sole trader takes all the profits. There is a direct connection between the effort and reward. So, it is an incentive for him to work hard. He manages the business to the best of his ability.
- Flexibility in operation : Changes in the business are necessary. The sole trading concern is dynamic in its nature. The nature of the business can be easily changed according to changing market conditions.
- Business secrecy : Since the whole business in handled by the proprietor, his business secrets are known to him only. He need not publish annual accounts and there is no need to disclose the information to outsiders. So, he can maintain business secrets.
- Contact with customers : It is easy to maintain personal contact with the customers. He can easily known their tastes, likes and dislikes and adjust his operations accordingly. This results in increase of sales.
Demerits :
- Limited resources : The resources of sole trader are limited. He has only two sources of securing capital, personal sayings and borrowing on personal security. Hence he can raise very limited amount of capital.
- Instability: It has no separate legal status. The business and the owner are inseparable from one another. The business comes to an end on the insolvency, insanity or death of a sole trader.
- Unlimited liability: The liability of the sole trader is unlimited. The creditors can recover the loan amounts not only from the business assets but also from his private property.
- Not suitable for large scale operations : The resources are limited. Therefore, it is suitable only for small business and not large scale operations.
- Limited managerial skill: The managerial ability is limited. A person may not be an expert in all matters. Sometimes, wrong decisions may be taken.
Question 2.
What is Memorandum of Association ? Explain its clauses.
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the most important document of the company. It is to be filed with the Registrar for obtaining the certificate of incorporation. It is the charter of the company. It forms the foundation on which the super structure of the company is based. It establishes the relationship between the company and the outside world. The contents of the Memorandum cannot be altered at the option of directors or even the shareholders. It is to be altered only with the central governments approval and court approval in many cases.
The Memorandum has to be divided into paragraphs, con-secutively numbered and has to be printed. It should be signed by seven members in the case of public company and by two mem-bers in the case of Private company.
Memorandum of Association contains the following clauses.
1) Name clause : In this clause, the name of the company should be stated. The company is free to adopt any name it likes. But it should not resemble the name of another registered com-pany. It should not any words pertaining to Government or local government, such as royal, crown, state etc. The name of the company must end with the word ‘Limited’ if it is a public company or with the words ‘Private Limited’ if it is a private company.
2) Situation clause : The place and the state in which the registered office is to be situated must be mentioned in this clause.
3) Objects clause : This is the most important Clause of the Memorandum. This gives out the various objects for which the company is formed. The objects of the company must be legal and be very clearly defined. A company has power to carry on only those types of business which are included in the objects clause. Any action beyond the express powers of the company is ultravirus
i. e., beyond the scope of the memorandum. Therefore, it should be carefully drafted.
4) Liability clause : This clause clearly states that the liabil-ity of members is limited to the extent of the face value of the shares purchased by them.
5) Capital clause : The amount of capital required by the company is stated in this clause. This is called authorised or nominal or registered capital. This capital is divided into small units called as shares. The company must mention the number and kinds of shares and the value of each share.
6) Association and subscription clause: This clause contains the names of the persons who signed in the memorandum. The memorandum must be signed by atleast seven persons in case of public company and atleast two persons in the case of private company. Each subscriber must take atleast one share in the company. The subscribers declare that they agree to incorporate the company and agree to take the shares stated against their name. The signatures of the subscribers are attested by atleast one witness each. The addresses and occupations of subscribers and the witnesses are also given.
![]()
Question 3.
Examine the advantages and disadvantages of raising funds by issuing equity shares.
Answer:
Equity shares also known as ordinary shares represent the owner ship of a company. Equity shareholders donot get a fixed dividend but are paid on the basis of earning by the company. They enjoy the rewards as well as bear the risk. Their liability is limited to the extent of capital contributed by them in the company. They have a right to participate in the management of a company.
Equity shares are the most important source of raising long term capital by a company. The capital raised by issue of such shares is known as “Ownership Capital” or “Owner’s funds”.
Advantages / Merits.
The important Advantages of raising funds through issuing equity shares are gives below :
- Equity shares do not create any obligation to pay a fixed rate of dividend.
- Equity shares can be issued without creating any charge over the assets of the company.
- It is a permanent source of capital and the company need not repay it except under liquidation.
- Equity share holders are the real owners of the company who have the voting rights.
- In case of profits, equity share holders are the real gainers by way of increased dividends and appreciation in the value of shares.
Dis advantages/limitations :
The major Disadvantages of raising funds through issue of Equity shares are given below :
- Investors who want steady income may not prefer equity shares because they get fluctuating returns.
- The cost of equity shares is generally more as compared to the cost of raising funds through other sources.
- Issue of additional equity shares dilutes the voting power, and earnings of existing equity share holders.
- More legal formalities and procedural delays are involved while raising funds through issue of Equity shares.
Section – B
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What is foreign trade ? Explain the types of foreign trade.
Answer:
Buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries is called as foreign trade. Foreign Trade is also known as “External trade” or’ “International Trade”.
Foreign trade is classified into 3 types. They are
1) Export Trade
2) Import Trade
3) Entrepot Trade.
1) Export Trade : When a country sold goods to foreign countries is called as export trade.
For example : India exports tea to the United Kingdom.
2) Import Trade : When a country purchased goods from other foreign countries is called as Import trade.
For example : India buys petrol from Iran.
3) Entrepot Trade : When a country purchased goods from are country for the purpose of selling them to another country is . called ‘Entrepot trade. It is also known as “Re-export trade”.
For example : India imports oil from Iraq and export the same to Nepal.
Question 5.
Define partnership and state its important features.
Answer:
Definition :
According to Indian partnership Act 1932 section 4, partnership defines as “The relationship between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any one acting for all”
Features:
- Formation: The partnership form of business organisation is governed by provisions of Indian Partnership Act 1932. It comes into existence through a legal agreement where in the terms and conditions governing the relationship among the partners.
- Unlimited liability: The partners of a firm have unlimited liability. They are jointly and individually liable for payment of debts. Personal assets may be used for repaying debts in cases the business assets are insufficient.
- Existence of lawful business : The business, of which the partners have agreed to share the profits, must’be lawful. Any agreement which includes smuggling, black marketing etc. cannot be called partnership business in the eyes of law.
- Principal agent relationship: Every partner is the principal as well as agent of the firm. When a partner deals with other parties, then he acts as an agent of other partners, and at the same time the other partners become the principal.
- Voluntary registration : The registration of a partnership firm is not compulsory. But an unregistered firm suffers from some limitations which make it virtually compulsory to be registered.
Question 6.
What are the various factors that determine the selection of sources of finance ?
Answer:
The following factors should be considered for selecting the sources of finance.
1. Cost factor : While deciding the sources of funds that is utilised by the business concern, the cost of procuring the funds and the cost of utilising are to be considered.
2. Sound financial position: In the choice of sources of funds, the business should be financially sound so that it can repay the principle amount together with interest.
3. Form of business organisation : The form of business organisation influences the choice of source for raising money.
Ex : A partnership firm cannot raise money by issue of equity shares.
4. Purpose and period of time : While selecting the sources of finance, purpose and period of time is to be taken into account.
A short term need can be met by borrowing funds through trade credit, commercial paper etc., with low rates of interest. For long term finance, sources like issue of shares and debentures are more appropriate.
5. Risk factor: Business should evaluate each of the sources of finance in terms of risk involved. Ex: If equity shares are issued, they are to be repaid only at the time of winding up and dividends are not paid if the profits are not available. There is little risk involved. On the other hand, a loan is to be repaid as per schedule and the interest is to be paid whether the firm earn profits or not.
Question 7.
What are the sources of short term finance ?
Answer:
The short term loans and credits are raised by a firm for meeting its working capital requirements. It is raised for accounting period i.e. one year.
The major sources of short term finance are given below :
- Bank credit: Commercial banks extend the short – term financial assistance to business firms by means of bank credit ie. in the form of loans, cash credit, overdraft etc.
- Trade credit: Trade credit is the credit extended by one trader to another for the purchase of goods and services. It facilitates the purchase of supplies without immediate payment. It is used by every organisation.
- Installment credit: This is another method by which the – assets are purchases immediately but the payment is made in pre determined installments.
- Advances : Some business Organisations get advances from their customers and agents against orders.
- Commercial papers : Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued for raise funds for a short period varying from 90 days to 364 days. It is issued by one firm to another firm or to insurance company or to banks etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Define MNC and Explain its features.
Answer:
According to International Labour Organisation report, Multi National Corporation refers to an enterprise whose managerial head quarters are located in one country, while it carried out operations in number of other countries as well. According to Prof. Vernon MNC is defined as ‘a cluster of operations of diverse of nationality joined together by common management strategy’.
Features of MNCs:
- Giant size ; The assets aind sale of MNCs are very large. These companies operate on large scale as they trade in more than one country. Sometimes their sales turnover exceeds the Gross National product (GNP) of developing countries.
- International Operation : A MNC operates and sells their products in different countries. It operates through a network of branches and subsidiaries in host countries.
- Professional Management : A Multinational corporation employees professional experts, specialized people. MNCs try to keep their employees updated by training from time to time to handle the advance in technology effectively.
- Oligo polistic powers : Oligopoly means power in the hands of few companies only. Due to their gaint size, the MNCs occupy dominating position in the market.
- Centralized control : MNC’s will have managerial head-quarters in the home country. All the subsidiary and branches work under the supervision, guidance and control of the head office.
- Sophisticated Technology : Multinational companies make use of latest, advanced and innovative technology to produce quality goods.
Question 9.
What are the benefits of e-business to customers ?
Answer:
The following are the benefits of E-Business to consumers.
- Purchasing made easy : E-Business enables consumers to shop or to do any other transactions 24 hours a day, round the year from any location.
- Wide choice: Customers will have more choices as more alternative products and services are available.
- Saving in prices: E-Business provides customers with less expensive products and services which allows them to shop in many places and conduct quick comparisons. E-business facilitates competition, which results in substantial discounts.
- Exchange of information: E-Business allows customers to interact with other customers and exchange their opinions and experiences on products purchased by them.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Profession.
Answer:
Profession means an occupation which involves the rendering of professional services. It requires specialized education, skills and knowledge etc. They charge some fees for services rendered by them for example doctor helps his patients by his expert knowledge of science of Medicine and charges a fee for the service.
Question 11.
What is Commerce ?
Answer:
Commerce is the part of business which is concerned with the exchange of goods and services and includes all those activities which directly or indirectly facilitate that exchange. Commerce involves the process of bringing goods from the place of production to the place of consumption.
Question 12.
Karta.
Answer:
The senior most male member of the family known as “Karta”. The karta has the authority to manage the business. His liability is unlimited. His personal property can also be utilised to meet the business liability.
Question 13.
Active Partner.
Answer:
The partners who actively participate in the day to day business operations are known as “Active Partners”. They are also called as ‘Working Partners” or ” Managing Partners”.
Question 14.
What is a Government Company ?
Answer:
A company in which not less than 51% of the paid up share capital is held by the central government or state government or partly by central government and partly by state government is called Government Company.
For exampe : ONGC, NTPC.
Question 15.
Minimum Subscription.
Answer:
The minimum amount of capital to be collected by the company before the allotment of its shares is known as “Minimum subscription”. A public company can not commerce business unless the minimum subscription is received. It is fixed by the amount required for the purchase of property, payment of preliminary expenses and the working capital requirement.
Question 16.
Working Capital.
Answer:
The capital required by business enterprise to run its day to day operations such as payment of salaries, wages, taxes, rent etc. and holding current assets like stock of raw materials, bills receivable is called as Working Capital”. The amount of working capital need is varies from one business to another depend on nature, size, production policy of business.
Question 17.
Define Manufacturing enterprise.
Answer:
Manufacturing enterprises are those business enterprises which are engaged in the manufacture or production of goods and services. The manufacturing enterprises are defined in terms of investment made in plant and machinery.
| Enterprise | Investment in plant and Machinery |
| Micro manufacturing exterprise | Does not exceed ₹ 25 lakhs. |
| Small manufacturing exterprise | Morethan ₹ 25 lakhs but does not exceeds ₹ 5 crores. |
| Medium manufacturing exterprise | More than ₹ 5 crores but does not exceed ₹ 10 crores. |
Part – II
Section – D
(50 Marks)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Karuriasai, prepare Trading and Profit & Loss AJc and Balance Sheet for the year ended on 31-03-2017 :
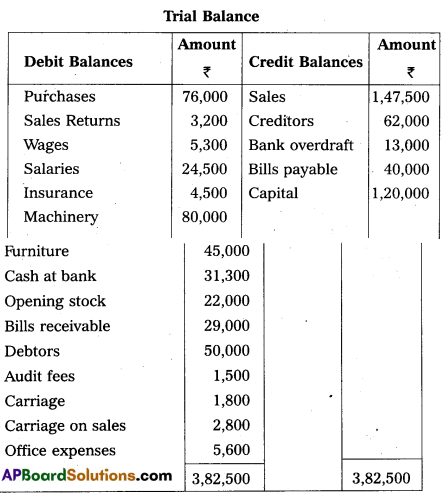
Adjustments:
1. Closing stock ₹ 34,500.
2. Outstanding salaries ₹ 5,500.
3. Depreciation on machinery 5%.
4. Prepaid Insurance ₹ 1,500.
5. Provide Reserve for Bad debts 5%.
Answer:
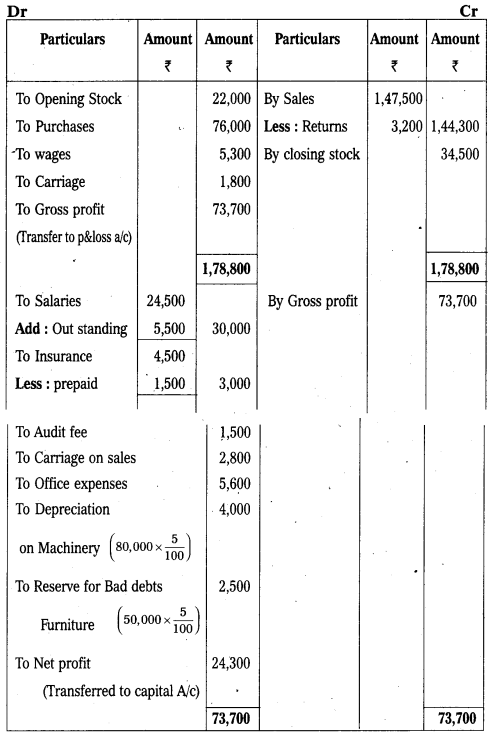
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Mr. Karuna Sai for the year ending 31-3-2017.
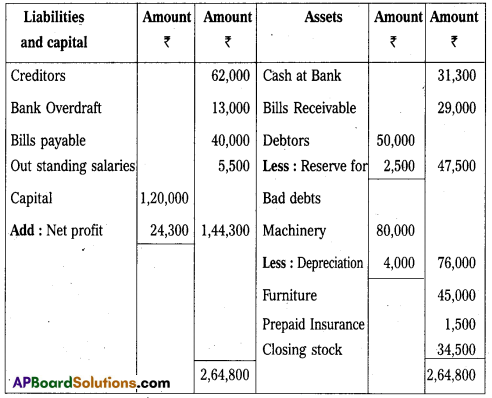
Balance Sheet of Mr. KarunaSai as on 31.03.2017.
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer ANY ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare three column Cash Book from the following particulars.

Answer:
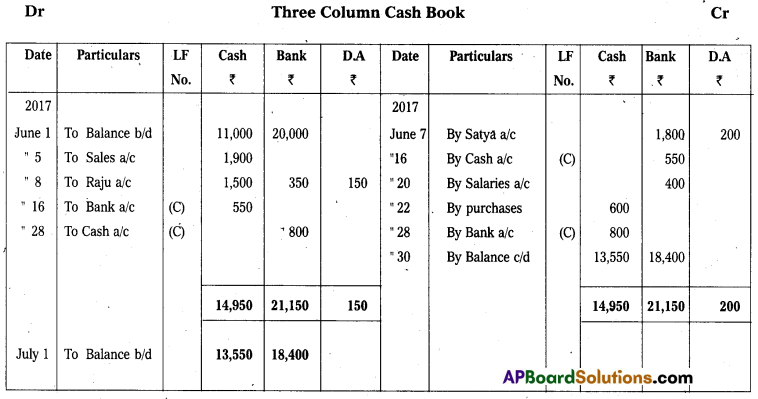
Question 20.
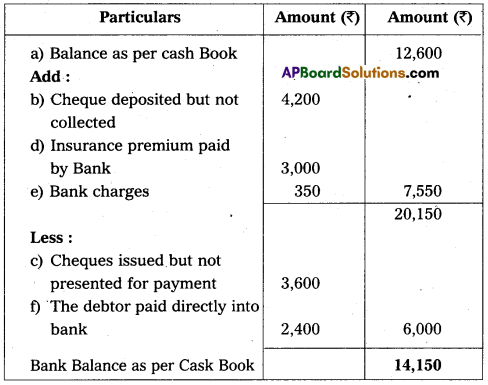
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement of M/s PKJ Ltd. as on 31-12-2016 :
a) Balance as per pass book ₹ 12,600.
b) Cheques deposited in bank but not collected ₹ 4,200.
c) Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 3,BOO.
d) Bank paid insurance premium ₹ 3,000.
e) Bank charges ₹ 350.
f) The debtor paid directly into bank account ₹ 2,400.
Answer:
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer ANY TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain the advantages of double entry system.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Double entry system of book-keeping.
- The system maintains a complete record of all the business transactions, as it records both the aspects of the transaction.
- It provides a check on the arithematical accuracy of accounts with the help of trial balance.
- Errors and frauds can be deducted under this system. So, it reduces the chance of committing errors and frauds.
- It reveals the result of the operations i.e., profit or loss, by preparing profit and loss a/c.
- The financial position of the business can be ascertained through the preparation of balance sheet.
- It is a scientific system and permits the accounts to be kept in detailed form and provides sufficient information for the purpose of control.
- The results of one year can be compared with the results of previous year and reasons for the changes are known.
- It provides accounting information readily to management for making decisions.
Question 22.
From the following information, prepare Srinivas Account as on 31-3-2016 :

Answer:
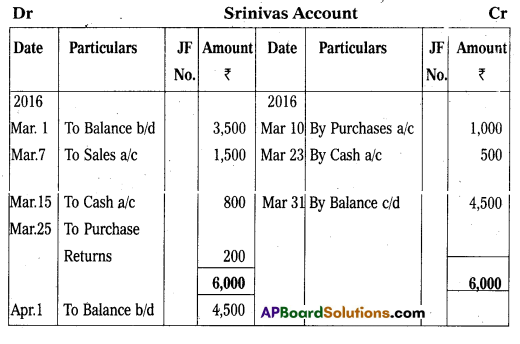
![]()
Question 23.
From the following particulars, prepare sales and sales return journal:

Answer:
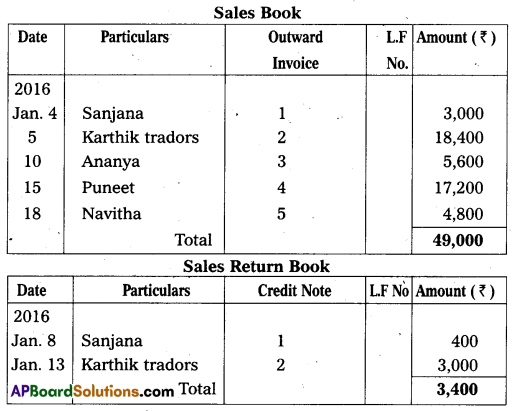
Question 24.
What are the errors disclosed by Trial Balance ?
Answer:
The errors which affect the agreement of Trial Balance are called Errors disclosed by the Trial Balance.
The following are the errors disclosed by Trial Balance:
- Posting of Transaction to wrong side of an account: Posting of transaction to wrong side of account affect the agreement of Trial Balance.
Eg: Discount allowed posted to credit side of discount account. - Posting of wrong amount to an account : Posting of wrong amount affect the agreement of Trial Balance.
Eg: Sales of ₹ 5000 posted as ₹ 500 to sales account. - Errors in totaling: Errors in totaling it may be over cast or undercast affects the agreement of trial Balance. Eg: Sales Returns Book Overcast by ₹ 100.
- Errors of carrying forward : If a mistake in carrying forward a total of one page to the next page. This error affect the agreement of Trial Balance. Eg: purchase Book total is carried forward as ₹ 1;500 instead of 150.
- Posting of only one aspect of Journal Entry into ledger: Some times accountant may post only one aspect of entry to the ledger account, it affect the Agreement of Trial Balance. Eg: Sale of goods to Ràmesh 200 Posted to sales book only.
- Recording one aspect twice: An accountant may be record one aspect twice it affect the Agreement of Trial Balance. Eg: Paid salaries ₹ 600 debited twice in salaries account.
Section – G (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer ANY FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is Book-keeping ?
Answer:
Book keeping is the branch of knowledge that reveals how to keep a record of business transactions. It covers all activities i.e Identifying, measuring, recording and classifying all business transactions.
Question 26.
Explain business entity concept of Accounting.
Answer:
As per this concept, Business organisation are treated as a separate entity which can be distinguished from the “owners” or stakeholders who provide capital to it. This concept helps in keeping private affairs of the owners and stakeholders separate from the business affairs.
Question 27.
Credit Note.
Answer:
Credit Note is a document which is prepared and sent to customer when he returned goods. It inform that his account is credited with the amount of the goods returned by him.
Question 28.
Explain error of omission.
Answer:
These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in books of accounts are called as “Error of omission”! It may be complete omission or partly omission. The complete omission does not effect Trial Balance. Example : Salaries paid pot recorded in the books of account.
![]()
Question 29.
Capital Expenditure.
Answer:
The expenditure which is incurred for acquiring fixed assets or for increase the earning capacity of assets is called as capital Expenditure. Benifits of capital expenditure are extended over a number of years. Example purchase of fixed assets like furniture, Machinery and Building are treated as capital expenditure.
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions :

Answer:
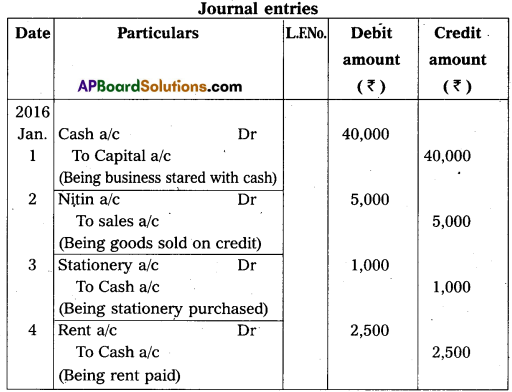
Question 31.
Write the Opening Journal Entry as on 1-1-2017 :
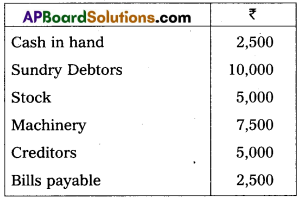
Answer:
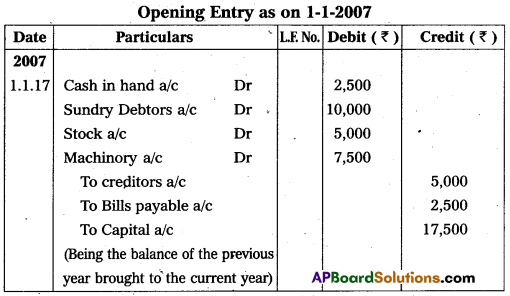
Question 32.
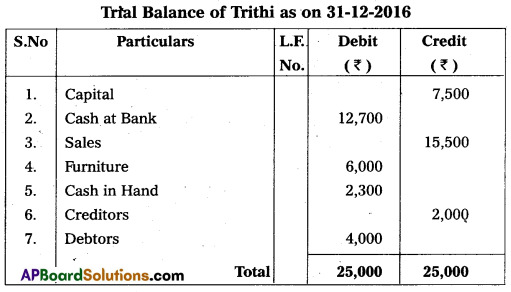
Prepare Trial Balance of Trithi as on 31-12-2016 :
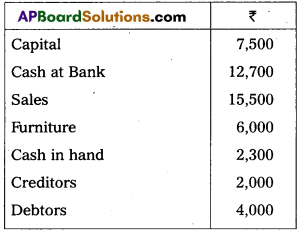
Answer:
Trial Balance of Trithi as on 31-12-2016