Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is transport? What are the benefits of transport?
Answer:
Transport:
The physical distribution of goods and persons from one place to another is called “Transport”. Transport creates place utility of goods by moving them from different centers of production to places of consumption. There are several types of transport such as air, water, and land transport.
Benefits of Transport:
- Movement of goods: The important function of transport is the movement of goods. The raw materials move from their sources to the factory and the manufactured goods have to move from the factory to the consuming areas by transport.
- Transport enhances the mobility of labour and capital: Transport services encourage the movement of people from one place to another labour can migrate to the place where they can get better job opportunities.
- Creation of place utility: Transport creates place utility. It moves goods from places where they are abundant to those where they are scarce.
- Specialization and Division of Labor: Transportation facilitates the optimum utilization of national resources of a country. For example, the petroleum resources of Arab countries.
- Creation of Time Utility: With the advancement of technology, transportation time is being shortened. This creates time utility.
- Stability in prices: With the help of transport goods are transported from the place where they are abundant to the place where they are scarce. In this way, prices are equalized throughout the country.
- Contribution to national income: Transportation also contributes towards national income. For example: Railways.
- Economies of large-scale production: Transport has helped the development of large-scale industries. Transport, procure raw materials, labor, and sell the finished goods.
- Improve standard of living: Availability of a wide variety of goods, at reasonable prices improves the standard of living.
- National Defence: During the war period, all the personnel, materials, and equipment can be moved rapidly to the border areas. Transport strengthens the national defense transport system.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Capital and Money Market.
Answer:
- Capital Market: A Capital Market is an institutional arrangement through which long-term funds, both debt and equity are raised and invested.
- Money Market: The money market is a market for short-term funds that deal in monetary assets whose period of maturity is upto one year.
The distinction between Capital Market and Money Market.
| Pointer Difference | Capital Market | Money Market |
| 1. Participants | The participants in the capital market are Development Banks and Investment companies. | The main participants in the Money market are the central Bank and commercial banks. |
| 2. Instruments | The main instruments traded in the capital market are equity shares, preference shares, debentures, bonds, etc. | The main instruments in the Money market are T-bills; trade bills, commercial paper, etc. |
| 3. Period | It is a market for long-term funds for more than one year. | It is a market for short-term funds for a period not exceeding one year. |
| 4. Liquidity | Capital market securities are liquid investments but the degree of liquidity is less than the money market instruments. | Money market instruments enjoy a higher degree of liquidity. |
| 5. Investment Outlay | Investment in the capital market does not necessarily require a huge financial outlay. | In the money market, transactions entail, huge sums of money as the instruments are quite expensive. |
| 6. Safety | Capital market instruments are riskier both concerning returns and principal repayment. | Money market instruments are much safer with a minimum risk of default. |
| 7. Expected Return | Investment in capital markets gives higher returns for investors than the money markets. The returns in money market investments are low when compared with capital markets. | The returns in money market investments are low when compared with capital markets. |
| 8. Regulator | SEBI regulates the institutions and procedures. | Reserve Bank of India regulates the money market. |
Question 3.
Describe the rights and responsibilities of a consumer as per CPA 1986.
Answer:
Rights:
The government of India provided the following Six rights to all consumers under the Consumer Protection Act (CPA):
- Right to Safety: According to this right the consumers have the right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services that are hazardous (dangerous) to life and property.
- Right to Information: According to this right the consumer has the right to get information about the quality, quantity, purity standard, and piece of goods and services.
- Right to choice: According to this right every consumer has the right to choose the goods or services of his or her liking. The suppliers should not force the customer to buy a particular brand only.
- Right to consumer education: According to this right it is the right of the consumer to acquire knowledge and skills to be informed to the customer to know their rights and take actions.
- Right to seek Redressal: According to this right, the customer has the right to get compensation or seek redressal against unfair trade practices or any other exploitation.
Responsibilities:
- Be quality-conscious: To put a stop to adult creation and corrupt practices of the manufacturers and traders, every consumer must be conscious of the quality of products they buy such as 1st, Agmark, Ha/mark, etc.
- Beware of misleading advertisements: The advertisement often exaggerates the quality of products. Hence, the consumers should not rely on the advertisement and carefully check the product or ask the users before making purchases.
- Responsibility to inspect a variety of goods before making a section: The consumer should inspect a variety of goods before buying the goods and services. For this purpose, he/she should compare their quality, price, durability, after-sales service, etc.
- Collection of transaction: The consumer should insist on valid documentary evidence like a cash memo or invoice; relating to the purchase of goods or availing of any services and preserve it carefully.
- Consumers must be aware of their rights: The consumer must be aware of his rights and exercise them while buying goods and services.
- Complaint for genuine grievances: If a consumer is dissatisfied with the product/services, he can ask for redressal of grievances. In this regard, he must file a proper claim with the company first. If the company does not respond then he can approach the forums.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Explain any five characteristics of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
The following are some of the important characteristics that every successful entrepreneur must possess.
1. Innovation:
Innovation is an important characteristic of an entrepreneur in modem business. The entrepreneur makes arrangements for introducing innovations that help in increasing production on the one hand and reducing costs on the other.
2. Risk-taking:
Risk-taking is another feature of an entrepreneur. He has to pay for all the other factors of production in advance. There are chances that he may be rewarded with a handsome profit or he may suffer a heavy loss. Therefore, the risk-bearing is the final responsibility of an entrepreneur.
3. Decision Making:
An entrepreneur has to make decisions about the establishment of a business its management and the coordination of various resources. Every activity of the business requires decision-making. The entrepreneur has to make decisions every day which have an impact on the working of the enterprise.
4. Leadership:
An entrepreneur has to be a leader because he is such a person who organizes directly and controls the functions of the organization. His personality will influence the working of his subordinates who can praise and appreciate him. An entrepreneur in his role as a leader, not only guides and counsels his people but he motivates them to achieve goals quickly and efficiently.
5. Organisation of Production:
An entrepreneur procures various factors of production like land, labor, capital, raw materials, etc. For manufacturing a product or bringing out a service. He assesses the viability of different production processes and selects one which is most suitable.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain any fire opportunities for entrepreneurship in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
There are various opportunities for entrepreneurs in Andhra Pradesh are presented in brief below:
1. Information Technology:
The government of Andhra Pradesh has declared the Information Technology (IT) industry as an essential service under the “Essential Service Maintenance Act” and the industry has been exempted from power cuts. The state has numerous advantages in terms of abundant availability of highly skilled IT manpower as well as technical and social infrastructure.
2. Automobile:
A broad base of automotive component manufacturers and a large pool of highly trained, skilled, and disciplined manpower make Andhra Pradesh the desired location for automobile industries. There are more than 100 automotive component manufacturing companies in the state including the aluminum casting industry, machined components industry, delivery valves, grey iron, oils & lubricants, etc.
3. Drugs & Pharmaceuticals:
The state offers excellent opportunities for the growth of the pharmaceuticals industry in the country, due to the availability of trained and skilled manpower, good infrastructure as well as research And development facilities. The Government of Andhra Pradesh has decided the establishment of a “Pharma city” near “Visakhapatnam” with private sector participation, which provides plenty of opportunities for entrepreneurs.
4. Mines and Minerals:
Andhra Pradesh is the second largest storehouse of mineral resources in India. In includes vast deposits of coal, limestone, slabs, oil and natural gas, iron ore, gold, diamonds, etc. The state has immense potential for untapped and under-tapped minerals and provides numerous opportunities for investment and development of minerals and mining projects.
5. Agriculture and Forestry:
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people in Andhra Pradesh. Rice is a major food crop and contributes about 77 percent of the food grain production. The state. is the second largest producer of horticulture produce in India. As there are a lot of gaps. in the existing supply and demand in India and scope for foreign trade, the entrepreneurs may make use of the recently announced Industrial Policy of Andhra Pradesh and explore the possibilities of establishing agro-based units.
Question 6.
Distinguish between home trade and foreign trade.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Home trade and Foreign trade.
| Home Trade | Foreign Trade | |
| 1. Trade | Trade carries within the country. | Trade carried with other countries. |
| 2. Currency | It does not involve any exchange of currency. | It involves the exchange of currencies. |
| 3. Restrictions | It is not subjected to any restrictions. | It is subject to many restrictions. |
| 4. Risk | Transport costs and risks are less. | Transport costs and risks are higher. |
| 5. Nature | It consists of sales, transfer, or exchange of goods within the country. | It involves the import and export of goods. |
| 6. Transport of Goods | The movement of goods depends on the internal transport system. e.g.: Roads and railways. | The movement of goods takes place usually by sea wherever possible. |
| 7. Specialisation | It helps to derive benefits of specialization within the country. | It helps all trading countries to derive the benefits of specialization. |
Question 7.
Explain the advantages of SEZs.
Answer:
Advantages:
The following major benefits can be attributed to Special Economic Zones (SEZ).
- Employment generation: Special Economic Zones are considered to be highly effective tools for job creation.
- Economic development: India can be made a transformed economy if special economic zones are implemented properly because special economic zones are engines for economic development.
- Growth of labor-intensive manufacturing industry: The establishment of special economic zones may lead to faster growth of labor-intensive manufacturing and service industries in the country.
- Balanced regional development: Special economic zones are beautifully crafted initiatives for achieving balanced regional development.
- Capacity building: Special economic zones are necessary for stronger capacity building.
- Export promotion: Special economic zones induce dynamism in the export performance of a country by eliminating
- Distortions resulting from tariffs and other trade barriers.
- The corporate tax system and excessive bureaucracy.
Question 8.
What are the advantages of e-banking?
Answer:
E-banking brings certain advantages:
- It reduces costs: The cost of banking transactions is considerably reduced. It increases the profitability of the banks.
- Prompt in services: There is a high degree of personalization and fast and flexible execution. Thus E-Banking prompt service and there is greater customer satisfaction.
- Anywhere and any time banking: It is 24 24-hour in a day and 7 days in a weekly banking service. Bank accounts can be accessed from anywhere. So the customer can obtain information on his account and conduct transactions from his home or office.
- Cashless banking: Handling of cash is not necessary in E-Banking.
- Global coverage: It provides global network coverage of bank services. NRIs can monitor their bank account in Indian banks, from abroad.
- Central database: The database of each branch is centralized. Customers can deposit, withdraw, or remit money from any branch of their bank.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain any five functions of stock exchanges.
Answer:
According to the Securities Contracts Act 1956, a stock exchange is defined as “an association, organization, or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, established to assist, regulate and controlling business in buying, selling and dealing in securities”.
Functions of Stock Exchange:
1. Ready and Continuous Market:
The stock exchange provides a ready and continuous market for securities, The exchange provides a regular market for trading securities.
2. Protection to Investors:
The stock exchange protects the interest of the investors through the enforcement of rules. The rules of the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, of 1956 also govern the dealings on stock exchanges.
3. Provides the information to assess the real worth of the securities:
The value of securities is made properly on the stock exchange. This is made by taking into consideration various factors such as present and future competition in securities, and financial and general economic conditions. The stock exchange publishes the quotation of different securities on the faith of these quotations every investor knows the worth of his holdings at any time.
4. Provides Liquidity of Investment:
The stock exchange is a market for existing securities. This market is continuously available for the conversion of securities into cash and vice-versa. Persons who do not need hard cash can dispose of their securities easily.
5. Helps in Raising Capital:
There is always a demand for additional capital from the existing concerns. The demand is met through the issue of shares. Stock exchange provides a ready market for such shares.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is an entrepreneur?
Answer:
The word entrepreneur is derived from the French verb “Entrepredre” which means to “undertake”. The entrepreneur is often associated with a person who starts his own, new and small business.
According to Peter F. Drucker, an entrepreneur is one who “searches for change, responds to it and exploits opportunities, and the innovation is the specific tool of an entrepreneur”.
Question 11.
Explain any two functions of the entrepreneur.
Answer:
1. Formation of New Producing Organisation:
It is the function of an entrepreneur, to arrange land, labor, capital, raw materials, etc., required for setting up a production process. According to J.B.Say, the function of a producer/entrepreneur is to rationally combine the forces of production into a new producing organization.
2. Decision Making:
An entrepreneur as a decision maker takes various decisions regarding the following:
- Ascertaining the objective of the enterprise
- Sources of finance
- Product mix
- Pricing policies
- Promotion strategies etc.
Question 12.
Define Retailer.
Answer:
A trader who is engaged in retail trade is called a Retailer. Retailer purchases goods from wholesalers and sells them to ultimate consumers in very small quantities. The retailer is an intermediary between the wholesaler and consumers. He is the last link in the chain of distribution of goods.
Question 13.
A.T.M.
Answer:
A.T.M. means Automated Teller Machines. ATM is popularly known as Any Time Money Machine. The customer gets fast cash withdrawals, transfers, and payment of bills of cash deposits through A.T.M. ATMs located at different spots are linked to the host computer in the bank.
Question 14.
National Highway.
Answer:
National highways are meant for intertransport. These roads also connect state capitals, major cities, etc. The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has the responsibility for the development, maintenance, and operation of the national highways.
Question 15.
NIFTY.
Answer:
NIFTY is an index of the NSE, which consists of 50 companies from 24 different sectors listed on the NSE. The base year for the index is 1995-96 with the base value as 1000.
![]()
Question 16.
Treasury Bill.
Answer:
A Treasury bill is an instrument of short-term borrowing by the Government of India naturing in less than one year. They are also called “Zero Coupon Bonds” issued by the RBI on behalf of the central Government to meet its short-term requirements of funds.
Question 17.
District Forum.
Answer:
The district Forum consists of a chairman and two other members one of whom shall be a woman. A written complaint can be filed before the district forum where the value of goods & services does not exceed ₹ 20 lakh. If a consumer is not satisfied with the decision of the District Forum, he can appeal to the state commission within 30 days of the order.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
Manoj and Neeraj are partners sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively. Their balance sheet as of 31st March, 2016 was as under:
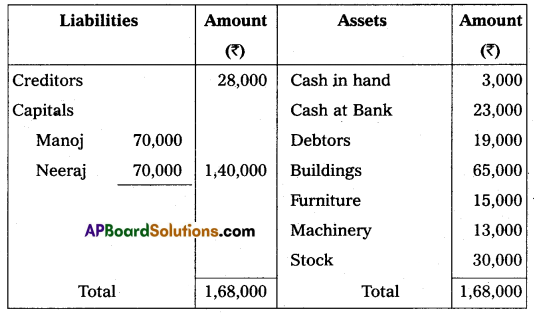
On that date, they admit Dheeraj into partnership for 1/3 share in future profit on the following terms:
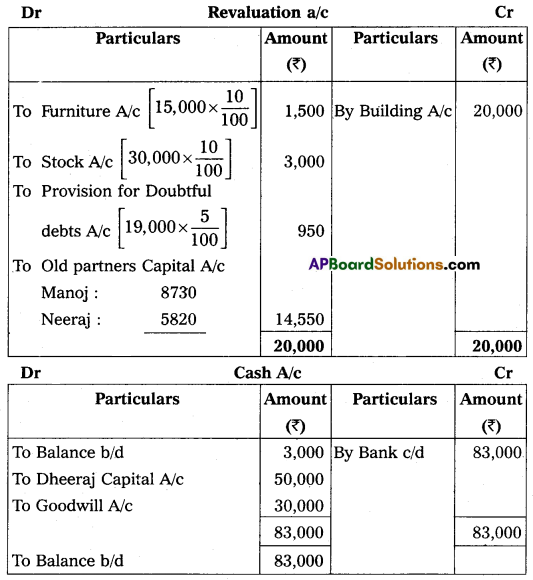
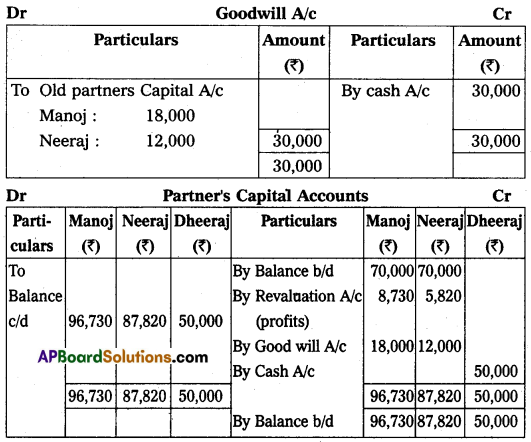
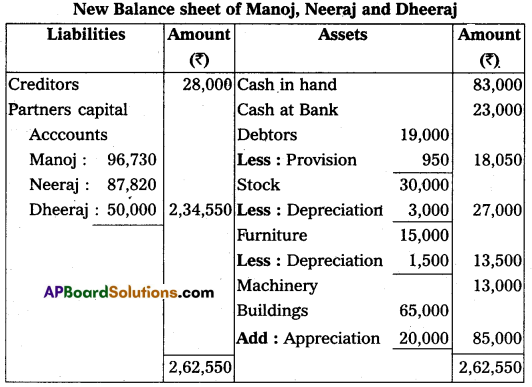
(a) Furniture and stock are to be depreciated by 10%.
(b) The building is appreciated by ₹ 20,000.
(c) A 5% provision is to be created on debtors for doubtful debts.
(d) Dheeraj is to bring in ₹ 50,000 as his capital and ₹ 30,000 as goodwill.
Make necessary Ledger Account and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
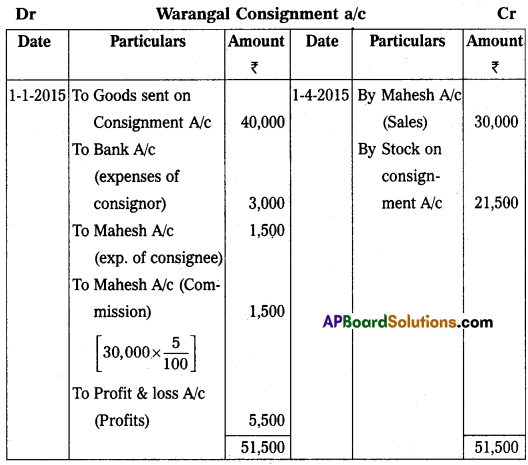
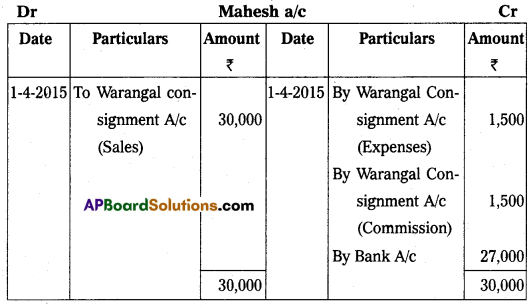
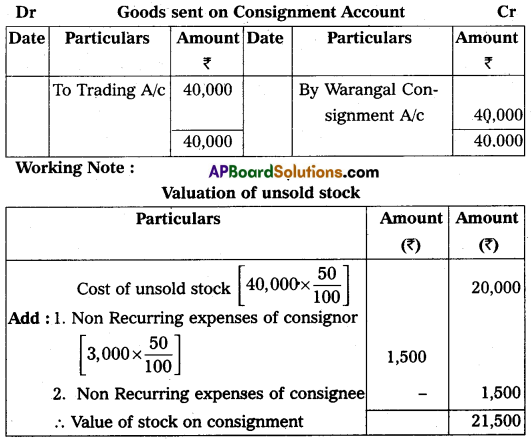
On 1st January 2015 Sudhakar of Srinagar consignment of goods value of ₹ 40,000 to Mahesh of Warangal. Sudhakar paid cartage and other expenses ₹ 3,000, on 1st April 2015, Mahesh sent account sales with the following information:
(a) 50% of the goods sold for ₹ 30,000.
(b) Mahesh incurred expenses amounting to ₹ 1,500.
(c) Mahesh is entitled to receive commission @ 5% on sales. A bank draft was enclosed for the balance due.
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts in the books of Sudhakar.
Answer:
Question 20.
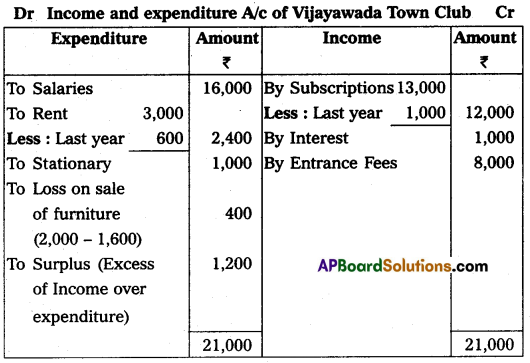
Vijayawada Town Club provided Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ending 31-12-2015. Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c:
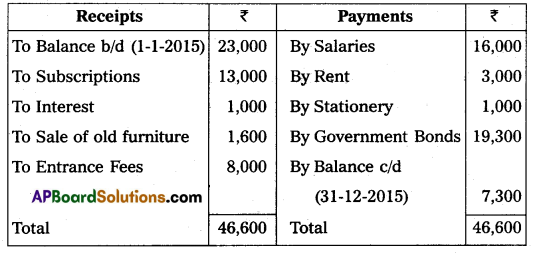
Adjustments:
(a) Subscriptions include ₹ 1,000 received for last year.
(b) Rent includes ₹ 600 paid for last year.
(c) Book value of furniture sold ₹ 2,000.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
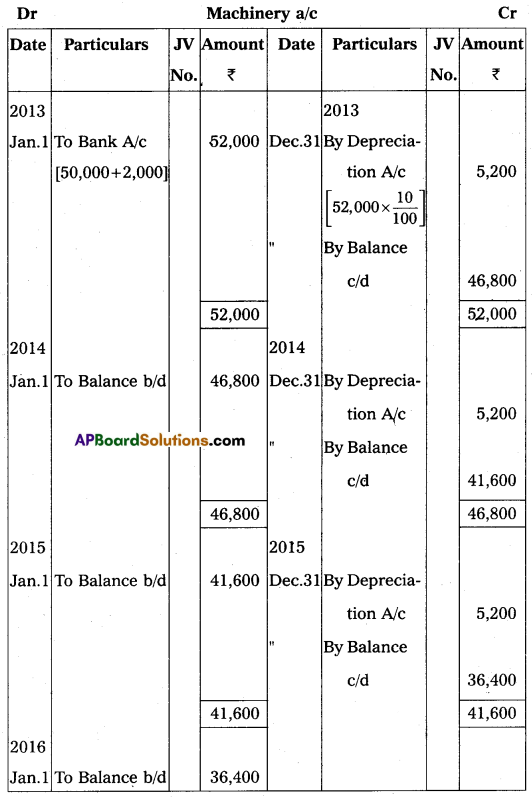
Venkatesh Traders Limited purchased machinery on 1st January 2013 for ₹ 50,000 and spent ₹ 2,000 on its installation. Depreciation is to be provided @10% p.a. under the straight-line method. Books of account are closed on 31st December every year. Show the machinery account for the first three years.
Answer:
Question 22.
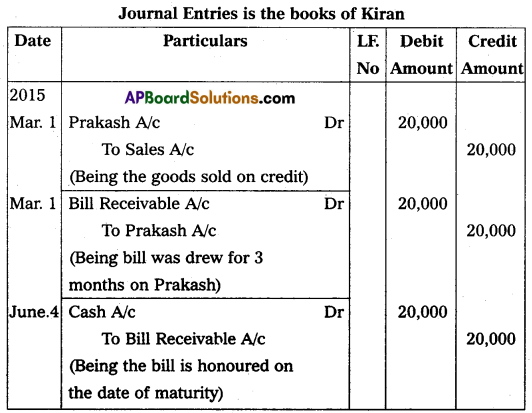
On 1st March 2015, Kiran sold goods for ₹ 20,000 to Prakash on credit and drew a bill for 3 months for the same amount. Prakash accepted the bill and returned it to Kiran. This bill is honored on the date of maturity. Pass the necessary Journal entries in the books of Kiran.
Answer:
![]()
Question 23.
Explain the types of issue of shares.
Answer:
A company can issue their shares at par value or issued at a premium or issued at a discount.
1. Shares issued at Par Value:
When a company issues its shares at their face value the shares are known as “Issued at Par”. These are also called “Issued at Face Value”.
Example: The face of the share is ₹ 100 and it is issued for ₹ 100.
2. Issued at Premium:
When a company issues its shares at the price of more than the face value, it is said to be shared “Issued at a premium”.
Example: The face value of the share is ₹ 100 and issued at ₹ 110. The excess amount ₹ 10 is called “premium” which is treated as capital income.
3. Shares Issued at Discount:
When a company issues its shares at a price less than the face value it is said to be “Shares issued at a discount”. The difference between the face value and issue price is called “Discount”.
Example: If the face value of a share is ₹ 100 and it was issued at ₹ 90. The difference of ₹ 10 is called “Discount”.
Question 24.
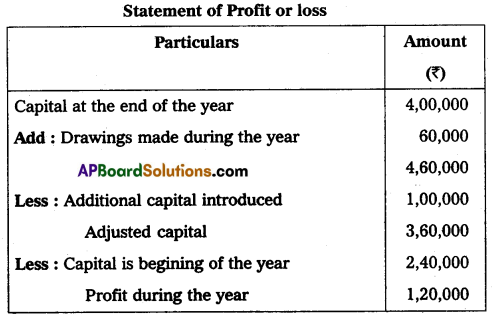
The following information is given below, prepare the statement of profit or loss:
Capital at the end of the year ₹ 4,00,000.
Capital at the beginning of the year ₹ 2,40,000.
Drawings made during the period ₹ 60,000.
Additional capital introduced ₹ 1,00,000.
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What are the parties in the bill?
Answer:
There are three parties to the bill of exchange.
- Drawer: Drawer is the person who makes or writes the bill of exchange.
- Drawee: Drawee is the person on whom the bill of exchange is drawn for acceptance.
- Payee: The payee is the person who receives the amount of the bill on its maturity.
Question 26.
Reducing balance method.
Answer:
The reducing balance method is also known as the “Diminishing Balance Method” or “Written down Value Method”. Under this method, depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage on the book value of the asset. Since the book value keeps on reducing by the annual charge of depreciation, it is known as the “Reducing Balance Method”.
Question 27.
Account Sale.
Answer:
Account sales is a document or a statement sent by the consignee to the consignor periodically. In account sales, the consignee shows the details of the gross sales proceeds, various expenses incurred by him; commission due to him, net amount payable, etc.
Question 28.
Legacy.
Answer:
Legacy is the amount that will be received by not-for-profit organizations as per the will of a deceased person. It should be treated as a capital receipt and should be shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 29.
What is the retirement of a partner?
Answer:
A partner who goes out of a firm is called a “retiring partner” or “outgoing partner”. Retirement of a partner is one of the modes of reconstituting the firm under which an old partnership deed comes to an end and the Retiring partner is entitled to receive the amount due from the firm and the firm continues its business.
Question 30.
What is equity share?
Answer:
The shares which do not enjoy any preferential right in the payment of dividends or repayment of capital are called “Equity shares”. Equity shares are also called “Ordinary shares”.
![]()
Question 31.
Computerized Accounting.
Answer:
Computerized Accounting is accounting done with the aid of a computer. It tends to involve dedicated accounting software and digital spreadsheets to keep track of a business or client’s financial transactions computerised accounting is useful to generate accounting records such as Cash books, Bank books, Journal purchases books, Sales books, ledger, Trial Balance, etc.
Question 32.
Any two advantages of Single entry system.
Answer:
- A single-entry system is a simple method of recording transactions.
- It is less expensive when compared to a double-entry system.
- It is mainly suitable for small business concerns.
- As ascertainment of profit or loss is very easy.