Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 9 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 9 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Distinguish between a Private Company and a Public Company.
Answer:
The following are the differences and a Public Company between Private Company and a Public Company.
| Private Company | Public Company |
| 1. To form a Private company the minimum number of members is 2 and maximum number of members is 50. | 1. Minimum number of members is 7 and maximum number of members is unlimited. |
| 2. It cannot issue prospectus. | 2. Public company can issue prospectus. |
| 3. The transferability of shares is generally restricted by its articles. | 3. The shareholders can freely transfer their shares. |
| 4. It can commence its business as soon as it obtains certificate of incorporation from the registrar. | 4. The business can be started only after getting certificate of commencement of the business. |
| 5. If need not conduct statutory meeting and file copy of statutory report to the registrar of Joint Stock Companies. | 5. A statutory meeting must be held within 6 months from the date of receiving certificate of commencement of business. Statutory report is to be submitted to the registrar. |
| 6. A private company can proceed with the allotment of shares before minimum subscription is received. | 6. Shares cannot be allotted before minimum subscription is received. |
| 7. The word private limited at the end of the name. | 7. The word limited at the end of the name. |
| 8. The minimum number of directors is 2 and there is no maximum limit. | 8. The minimum number of directors is 3. The maximum number of directors is 20. |
| 9. The directors need not take qualification shares. | 9. Qualification shares are necessary to become a director. |
| 10. The directors need not retire by rotation. | 10. 1/3 of the directors must retire by rotation. |
| 11. There is no age limit to become a director. | 11. Age limit for the directors is 65 years. |
| 12. The directors need not sent their consent to act as directors. | 12. The directors must send their consent to act as directors. |
| 13. There is no restriction on the remuneration payable to the directors and managing directors. | 13. The remuneration payable to the directors and others shall not exceed 11% of the net profits. |
| 14. It can grant loans to the directors without the consent of the central government. | 14. Permission from the central government is necessary to grant loans to the directors. |
| 15. Quorum for the meeting is 2. | 15. Quorum for the meeting is 5. |
Question 2.
Define Multi National Corporation and explain the advantages of Multi National Corporation.
Answer:
A Multi National Corporation may be defined as a company that operates in several countries. The operations of multinational corporations extend beyond the country in which it is incorporated. Simply stated it is located in one country and carries on business in other countries.
Advantages of MN Cs to host countries :
1. Provides Capital: MNCs bring in much needed capital for the development of industries. These corporations make direct foreign investment and speed up the process of economic development.
2. Transfer of Technology : Developing countries are technically backward. They lack resources to carry on research and development. MNCs serve as a vehicle for the transfer of advanced technology to these countries.
3. Generate Employment : It creates large-scale emplo-yment opportunities in host Countries. They offer excellent pay scales and career opportunities to managerial, technical and clerical staff.
4. Foreign Exchange : MNCs help the host countries to increase their exports. They reduce their dependence on imports. MNCs enable the host countries to improve their balance of payments position.
5. Managerial Revolution : MNCs helps to professionalise management in host countries. They employ modem management techniques and trained managers. They build up “Knowledge Base”.
6. Break Monopolies : MNCs encourage healthy competition and break domestic monopolies.
7. Growth of Domestic firms : MNCs contributes to the development of domestic firms. They encourage domestic suppliers, anciliary units, bankers and other institutions to expand their activites.
8. Innovation : MNCs bring out innovation in their production and distribution activities.
9. Improvement of Relations : MNCs encourage international brotherhood through international business.
Advantages of MNCs to host countries :
1. Availability of Resources : The country can obtain raw materials, labour and land at comparatively low cost.
2. Develop Exports : They can export components and finished products for assembling or distribution in foreign markets. Thereby market is widened.
3. Generate Income : They can earn huge income from dividends, licencing fees, royalty and management contracts.
4. Provides Employment: They can increase job and career opportunities at home and abroad in connection with overseas operations.
5. Make use of Expertise : They can acquire technical and managerial expertise of foreign countries.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the benefits of E-business.
Answer:
Benefits of E-Business can be classified into
1. Benefits to consumer
2. Benefits to organisation
3. Benefits to society
1. Benefits to consumer :
- Purchasing made easy : E-Business enables the consu-mers to shop or to do any other transaction 24 hours a day, round the year from any location.
- Wide choice : Customers will have more choice as more alternative products and services are available.
- Saving in prices : E-Business provides customers with less expensive products and services which allows them to shop in many places and conduct quick comparisons. E-Business facilitates competition, which results in substantial discounts.
- Exchange of information: E-Business allows customers to interact with other customers and exchange their opinions and experiences on products purchased by them.
2. Benefits to Organisation :
- Expansion of markets : E – Business allows organisation to expand the markets from national to international markets.
- Saving in costs : The business concerns can reduce the cost of producing, processing, distributing storing and feedback of information. It allows them to reduce stock level results in saving in cost.
- Competitive benefits : Reduction in the processing time allows the business to provide goods and services to the customers as per their needs. It achieves competitive advantage.
- Collection of capital: It enables the business to reduce the time between the outlay of capital and the receipt of cash of products and services.
3. Benefits to the society :
- Availability of products: E-Business enables the people in developing countries and particulary to the people living in rural areas to enjoy products and services which otherwise not available to them.
- Public welfare : E-Business allows some of the goods and services to be sold at lower prices. It will benefit the poor people.
- Environmental benefits : E-Business enables people to do shopping at home and less travelling for shopping. It results less traffic on the roads and reduces air pollution.
Section – B
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
State the Business Objectives.
Answer:
Business objectives are classified as economic, social, human and national objectives.
1. Economic objectives:
- Earning profits
- Creation of customers
- Technological improvement
2. Social objectives:
- Availability and supply of quality goods
- Fair remuneration to employees
- Creation of employment opportunities
- Co-operation with government
- Social welfare
3. Human objectives:
- Labour management co-operation
- Welfare of workers
- Development of human resources
- Labour participation in management
4. National objectives:
- Producing goods according to national priorities
- Optimum utilisation of natural resources
- Development of small scale industries
- Self-reliance.
Question 5.
State the types of foreign trade.
Answer:
When trade takes place between two countries it is called foreign trade or external trade or international trade. Two countries are involved in foreign trade. External trade generally requires permission from the respective countries. The hindrances of place, time, risk and exchange are overcome with the help of various agencies. Foreign trade may be classified into export trade, import trade and entrepot trade.
- Export trade : This trade refers to sale of goods to foreign countries. Ex : India exports tea to U.K.
- Import trade: The purchase of goods from other countries is known as import trade. Ex : India buys petrol from Iran.
- Entrepot trade : When goods are imported (purchased) from one country with a view to exporting (selling) them to other country, it is called entrepot trade or re-export trade.
Question 6.
Explain the limitations of sole trader.
Answer:
The following are the limitations of sole trading business.
- Limited resources : The resources of sole trader is limited. He has only two sources of securing capital, personal savings and borrowing On personal security. Hence, he can raise very limited amount of capital.
- Instability: It has no separate legal status. The business and the owner are inseparable from one another. The business comes to an end on the death, insolvency, insanity of the owner.
- Unlimited liability : The liability of the sole trader is unlimited. The creditors can recover the loan amounts not only from the business but also from the private property,
- Not suitable for large scale operations: The resources are limited. Therefore, it is suitable only for small business and not large scale operations.
- Limited managerial skill : The managerial ability is limited. A person may not be an expert in all matters. Sometimes wrong decisions may be taken.
- Restricted growth : The limitations of capital and managerial ability will restrict the growth development and expansion of the business.
- Dependence on the paid employees : When the business expands, the sole trader has to depend on paid employees. They may not work hard and show interest. Hence the efficiency suffers.
Question 7.
Briefly explain any three types of co-operative societies.
Answer:
According to the needs of people the following of co-operative societies are started in India.
1) Consumers Co-operative Society: These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaver sections from the clutches of hungry businessmen. These societies make bulk purchases directly from the producers and sells these goods to the members on retail basis. The commission and profits of the middlemen are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2) Producers Co-operative Society: Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production and they also – face marketing problems. The production of goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society.
The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profits in the general pool. Ex.: APco, Co-Optex, Emmiganur weavers co-operative society.
3) Marketing Co-operative Society : These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middlemen. The goods are sold when the market is favourable. These societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, warehousing, insurance, finance etc.
Question 8.
Explain the differences between Partnership and Joint Hindu Undivided Family.
Answer:
Differences between Partnership and Joint Hindu Family Firms.
| Partnership Firm | Joint Hindu Family Firm |
| 1) Act applied : It is governed by Indian Partnership Act, 1932. | 1) It is governed by two schools of Hindu Law i) Mitakshara ii) Dayabhaga |
| 2) Creation: It is created by mutual agreement, between the partners. | 2) It is result of the operation of Hindu Law. No agreement is needed. |
| 3) Liability : The liability of every partner is unlimited, joint and several. | 3) The liability of Karta is unlimited and other coparceners liability is limited. |
| 4) Maximum Number: The maximum number of members is 10 in the banking business and 20 in other cases. | 4) There is no limit to the maximum number of members. |
| 5) Admission of new partner: A new partner can be admitted with the mutual consent of other partner. | 5) An outsider cannot be admitted as co-parcener. |
| 6) Dissolution : It can be dissolved on the death or retirement of a partner. | 6) Only partition can bring this to an end. |
| 7) Registration: Registration is optional. | 7) Registration is not necessary. |
| 8) Minor : A minor can become a partner in the firm. | 8) In this business, even a child, as soon as he is born becomes the member. |
Question 9.
Briefly describe specialised financial institutions.
Answer:
Specialised financial institutions are the institutions which have been setup to serve the increasing financial needs of commerce and trade in the areas of venture capital, credit rating and leasing etc.
1. IFCI Venture Capital Rinds Ltd. : Formerly known as Risk Capital and Technology Finance Corporation Ltd. is a subsidiary of IFCI. It was promoted with the objective of broadening entrepreneurial base in the country by facilitating funding to ventures involving innovative product /process/ technology.
2. ICICI Venture Funds Ltd : Formerly known as Technonology Development and Information Company of India Ltd. was established in 1988 as a joint venture with the Unit Trust of India. Subsequently, it became a fully owned subsidiary of ICICI. It is a Technology Venture Finance Company set upto sanction project finance for new technology ventures. The industrial units assisted by it are in the fields of computer, chemicals/polymers, drugs, diagnostics and vaccines, biotechnology, environmental engineering etc.
3. Tourism Finance Corporation of India Ltd. : TFCI is a specialised financial institution setup by Government of India for promotion and growth of tourist industry in the country. Apart from conventional tourism projects, it provides financial assistance for non-conventional tourism projects like amusement parks, ropeways, car rental services, ferries for inland water transport ” etc.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Warehousing
Answer:
Goods are purchased in anticipation of demand. There is time gap between production and consumption. Hence, it became necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. Agricultural products like wheat and rice are seasonal in nature but they are consumed throughout the year. Umbrellas and woollen clothes are produced throughout the year but they are demanded in a particular season. So these goods are to be stored till they are demand. Warehousing creates time utility.
Question 11.
Extractive industries
Answer:
These industries are engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industry comes in raw form and they are utilised by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. Ex : Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil, rubber etc.
Question 12.
Active partner
Answer:
An active partner is one who takes active part in the day-to-day working of the business. He may act in various capacities as manager, advisor or organisor. He is also known as working partner or managing partner.
Question 13.
Co-operative farming society
Answer:
These societies are basically agricultural co-operatives. These are formed by small land owners. They pool their resources to achieve the benefits of large scale farming and maximising agricultural product. They solve the problems of finance, irrigation seeds, fertilizers etc.
Question 14.
Partnership firm
Answer:
Partnership is an association of two or more persons who pool their financial resources and managerial resources and agree to carry on business and share the profits and losses. The persons who form the partnership are individually known as partners and collectively a firm or partnership firm.
![]()
Question 15.
Private company
Answer:
A Private Company is one which by its Articles of Association
- Limits the number of members to 50
- Restricts the right of transfer of shares and
- Prohibits any invitation to public to subscribe for its shares and debentures.
Question 16.
Business finance.
Answer:
Business finance viewed as the activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting. The financial needs and overall objectives of the enterprise. So, business finance is the process of acquiring and utilising funds by the business. A business concern needs money to get started, to operate and to expand.
Question 17.
Bank Loan
Answer:
A loan is a direct advance made in lumpsum against some security. A specified amount is sanctioned by the bank to the customer. The loan amount is paid in cash or credited to customers account. The customer has to pay interest on the amount from the date of sanctioning the loan.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
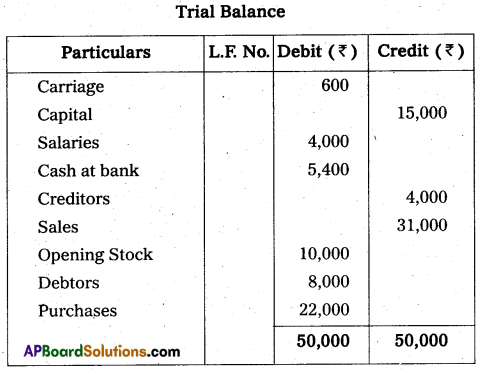
From the following Trial Balance and additional information, you are required to prepare final accounts for the year ending 31-03-2013.
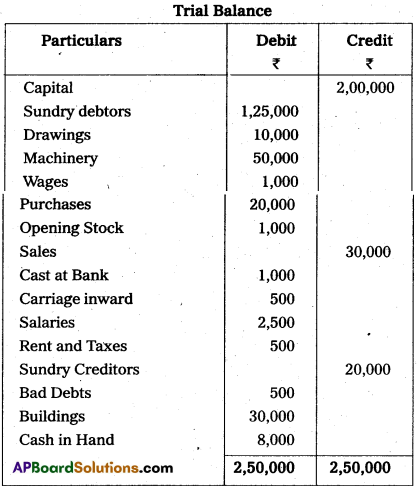
Additional Information :
- Closing Stock : ₹ 1,500
- Outstanding Rent and Taxes : ₹ 500
- Charge depreciation on Buildings @ 5% and Machinery @ 10%
- Wages prepaid : ₹ 500
- Further bad debts to the extent of ₹ 200
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31-03-2013
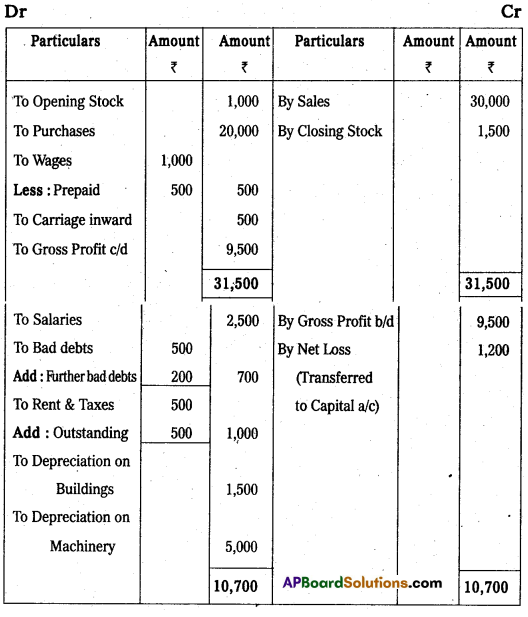
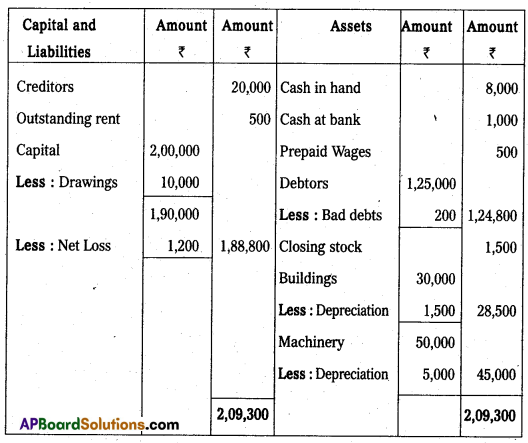
Balance Sheet as on 31-03-2013
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare Analytical cash book from the following particulars.

Answer:
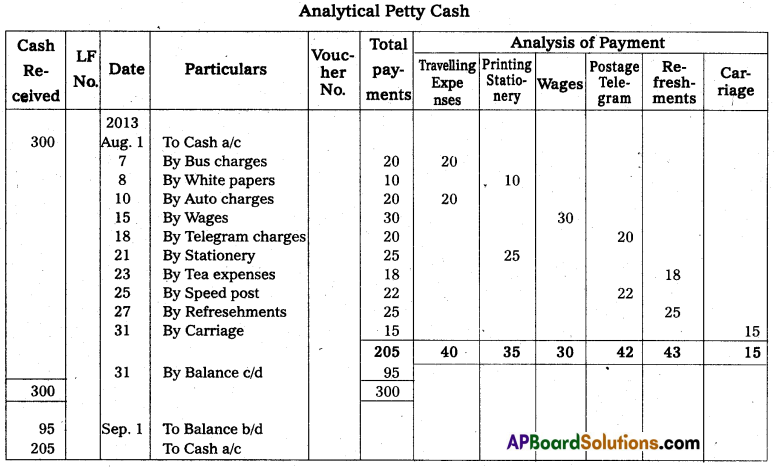
Question 20.
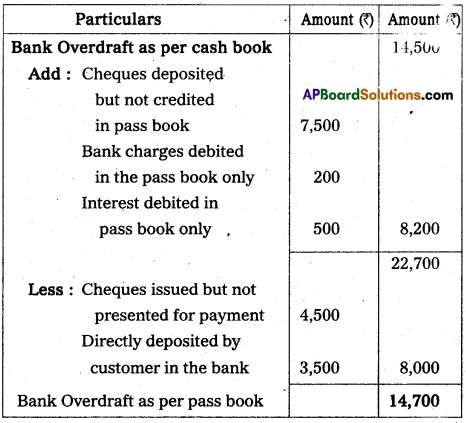
Prepare Bank Reconciliation statement of P.R.G Rao and Sons as on 31-03-2014.
a) Bank overdraft as cash book ₹ 14,500.
b) Cheques issued but not yet presented for payment ₹ 4,500.
c) Directly deposited by a customer in our bank account ₹ 3,500
d) Cheques deposited into bank but not credited ₹ 7,500
e) Bank charges debited in the pass book only ₹ 200
f) Interest debited in the pass book only ₹ 500
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of PRG Rao as on 31.03.2014
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain capital and revenue expenditure with suitable examples.
Answer:
Business expenditure of a concern can be broadly classified into
1) Capital expenditure
2) Revenue expenditure
3) Deferred revenue expenditure.
1) Capital expenditure : Capital expenditure is the expenditure which is normally incurred for acquiring fixed assets which increases the earning capacity of the business. Benefits capital expenditure are extended over number of years. Examples of capital expenditure are purchase of fixed assets like plant, building, installation of machinery and their improvement. These are shown as assets in Balance Sheet.
2) Revenue expenditure : Revenue expenditure is the expenditure which is incurred in normal course of business activities. The benefit of revenue expenditure is limited to only one accounting year. Ex : Payment of salaries, rent, carriage, advertisement etc. These are debited to profit and loss’account.
3) Deferred Revenue Expenditure: Any amount of revenue expenditure nature spent in huge sums and its benefit spread over more than one year is called deferred revenue expenditure. It includes the expenses like preliminary expenses, discount on issue of shares and debentures, heavy amount spent on advertisement, shifting of business premises etc.
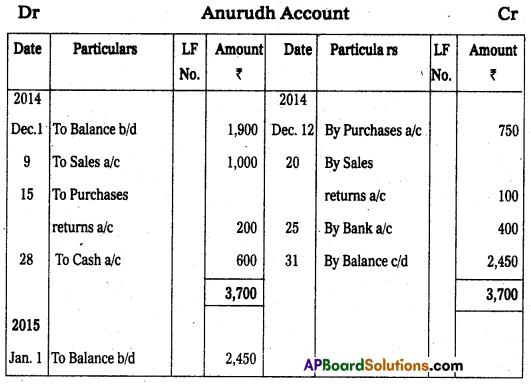
Question 22.
Prepare Anurud’s Account from the following.

Answer:
![]()
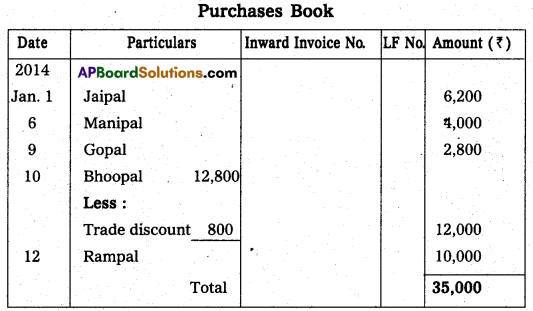
Question 23.
Prepare Purchases Book.

Answer:
Question 24.
What is suspense account ? Why it is opened ? Explain.
Answer:
When the trial balance does not agree, an effort is made to locate the errors and rectify them. But if the errors cannot be located easily and quickly and at the same time, if the final accounts are to be prepared urgently, the difference in the trial balance is made good by writing it smaller side of the trial balance under the name suspense account and such temporary suspense account is closed later when the errors are located and rectified.
The suspense account is an imaginary account opened temporarily for the purpose of just tallying trial balance. Ex: If the debit side of the trial balance exceeds credit side, then the difference is put on the credit side and suspense account shows credit balance.
If the credit side of the trial balance exceeds debit side, then the difference is put on the debit side and the suspense account shows debit balance. The difference in trial balance are due to one side errors. The errors which involve both the accounts permits the trial balance to agree and therefore they do not give rise to suspense account. The balance of the suspense account is shown on the balance sheet either on liabilities or assets side, depending upon whether the suspense account has a credit or debit balance.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Drawings
Answer:
It is the amount of cash or value of the goods withdrawn by the proprietor from the business for his personal use. The amount – of drawings is deducted from the capital.
Question 26.
Trade discount
Answer:
The rebate offered by the supplier on the catalogue price is known as trade discount. If trade discount is given, it should be deducted from the purchase price and only net amount of purchases is to be recorded in the books.
Question 27.
Nominal accounts
Answer:
Nominal accounts relate to expenses, incomes or gains or losses. Ex : Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Interest a/c. The rule in Nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains”.
Question 28.
What is posting ?
Answer:
The process of transferring the entries recorded in the journal or subsidiary books to the respective accounts in the ledger is Called posting. So, posting means the process of grouping all the transactions relating to a particular account at one place.
Question 29.
Adjustment entries
Answer:
There are certain incomes and expenses are not recorded even at the date of closing the accounts. If they are not taken into account correct profit or loss cannot be as certained. So, necessary adjustment entries with regarding to those expenses and incomes are recorded in journal proper.
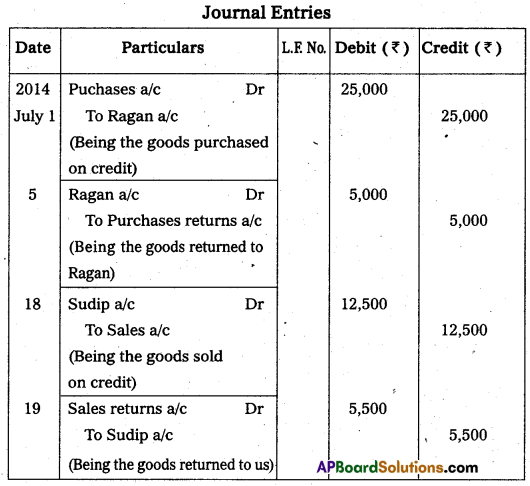
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions.

Answer:
Question 31.
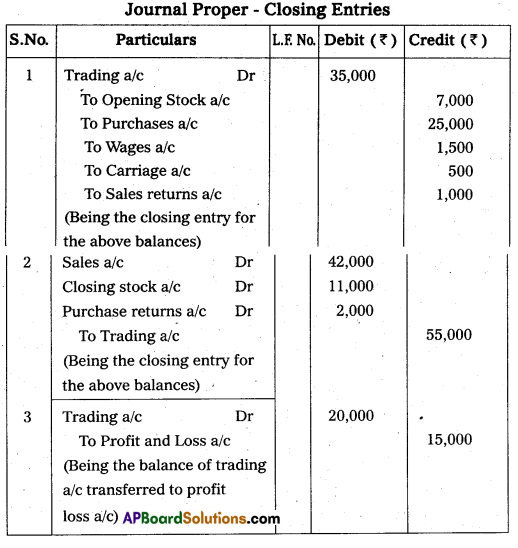
Write the closing entry from the following particulars.
Opening stock ₹ 7000
Purchases ₹ 25,000
Sales ₹ 42,000
Purchase returns ₹ 2,000
Sales returns ₹ 1,000
Wages ₹ 1,500
Carriage ₹ 500
Closing Stock ₹ 11,000
Answer:
![]()
Question 32.
Prepare Trial Balance from the following balances.
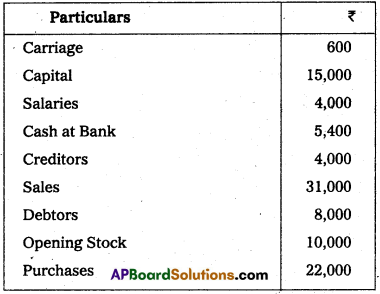
Answer: