Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 8 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 8 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is partnership deed ? Explain its contents.
Answer:
Partnership deed forms the basis of partnership. If includes all important clauses like name of the business, contribution of capital, sharing of profits, mode of management etc. “Partnership deed is a document containing all matters according to which rights, duties and liabilities of the partners in the conduct of management of the affairs of the firm are determined”. The deed must be signed by the partners. The partnership deed can be both oral or in writing. A written agreement, however, should be preferred because nobody can dispute the contents.
The partnership deed should not contain any term which is contrary to the provisions of the partnership Act. The deed has to be stamped according to Indian Stamps Act. It should be signed by all partners and every partner should have a copy of the deed. The following clauses are generally included in the partnership deed.
- The name of the firm.
- Names and addresses of partners.
- Nature of the business.
- Location of the business.
- Duration of the period, if decided.
- The amount of capital to be contributed by each partner.
- The profit sharing ratio:
- Rights, duties and liabilities of partners.
- Salaries, Commission payable to any partner.
- Amount of withdrawals allowed to each partner.
- Rate of interest to be allowed on capital as well as rate of interest to be charged on drawings.
- The method of evaluating goodwill at the time of admission, retirement or death of partner.
- Procedure for dissolution of the firm.
- Maintenance of books of accounts and audit of accounts.
- Arbitration clause for settlement of disputes among the partners.
Question 2.
What is promotion ? Discuss various steps involved in promoting a company.
Answer:
Promotion is the first stage in the formation of a company. It involves identification of business opportunities or idea, analysing its prospects, gathering the relevant information and taking steps to implement it.
Haney defines “Promotion is the process of organising and planning the finance of a business enterprise under the corporate form”.
Grenstenberg says “Promotion may be defined as the discovery of the proposition and the subsequent organisation of funds, property and managerial ability into business concern for the purpose of making profits thereon”.
Stages in the Promotion :
1) Discovery of an idea : The success of business depends on the selection of business line. A promoter thinks that there are opportunities for a particular type of business. He develops the idea with the help of technical experts in the field. If they are convinced that profitable avenues are available, then the idea is taken forward for more exhaustive analysis.
2) Detailed investigation : The promoters will investigate various factors relating to that business from the practical point of view. The promoters will estimate the total demand of the product and determines his share of demand. After determining the prospective demand for goods, he will think of arranging finance for the venture. The possible sources of finance are studied in detail. The availability of power, labour, raw materials and machinery is also considered., An expert opinion is sought of the viability of the project.
3) Assembling the requirements : After making sure that the proposition is practical and profitable, the promoter proceeds to assemble the requirements. He has to appoint directors. He has to acquire patent rights. The promoter selects the factory site, decides about Plant and Machinery and contacts suppliers of raw materials.
4) Financing the proposition: The promoter decides about the capital structure of the company. The requirements of finances are estimated first. Then the sources from which the money will come are determined. How much share capital will be issued and the nature of loans, whether debentures or borrowing from financial institutions for a longer period are finalised.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain various sources of business finance available to Indian businessman.
Answer:
A businessman can raise funds from various sources. On the basis of the period they are classified into three :
1. Long term sources of finance
2. Medium term sources of finance
3. Short term sources of finance.
1. Long term sources of finance : These sources include
i) Issue of equity and preference shares
ii) Issue of debentures
iii) Retained earnings.
i) Shares : A company is able to get large amount of capital primarily by the issue of shares. A company generally issues various types of shares, preference shares, equity shares and deferred shares. The object of issuing different kinds of shares is to appeal investors with different temperments. Preference shares carry preferrential right with regarding to payment of dividend and repayment of capital at the time of winding up the company. Equity shares do not carry such rights. Issue of shares is the most important method of raising long term finance because the raising from the shareholders remain in the company till the time of winding up.
ii) Debentures : A company may not wish to possess more share capital. Instead it may invite persons to lend their money. Money so lent must be acknowledged. The document which the lender received is called debenture. So, debenture is an acknowledgement of debt by a company. It is usually issued under common seal, secured by fixed or floating charge on the assets of the company. A company inorder to secure long term finance for initial needs and more often for developments, to suppliment its capital may issue debentures. Money raised through debentures remain in the company for long period.
iii) Retained earnings : The ploughing back of earnings is an important source of financing the business. Instead of distributing the entire profits, some portion of the profits are retained in the business as reserve. The undistributed earnings are used to finance long term needs.
2. Medium term source of finance : These sources include i) Public deposits ii) Loans from banks iii) Lease financing .
i) Public deposits : Industries received deposits from the public. These deposits are called as public deposits. The period of public deposits used to be short i.e., for three years. So public deposits have been a very important source for working capital requirements.
ii) Loans from banks : Commercial banks occupy a vital position as they provide funds for different purposes and for different periods. They extend loans in the form of cash credits, overdrafts, purchase/discounting bills and term loans. The borrower is required to provide some security or to create a charge on the assets of the firm before a loan is sanctioned.
iii) Lease financing : A lease is a contractual agreement whereby the lessor or owner of asset grants lessee the right to use the asset in return for a periodic payment known as lease rent. At the end of the lease period, the asset goes back to the lessor. Lease financing is an important means for modernisation and diversification in the firm. Such financing is resorted to in acquiring assets like computers and electronic equipment.
3. Short term sources of finance : These sources include
i) Bank credit
ii) Trade credit
iii) Instalment credit
iv) Advances
v) C.R .
i) Bank credit : Commercial banks extend short-term financial requirements in the form of loans, cash credit, overdrafts and discounting bills. Bank loans are provided for a specific short period and the borrower has to pay interest on the entire amount of the loan sanctioned. When the bank grants cash credits, the firm can withdraw any amount within the limit and has to pay interest on the actual amount withdrawn. In overdraft, the customer can overdraw his current account for a short period. Commercial bank also provide finance to firms by discounting their bills of exchange and promissory notes.
ii) Trade credit : Just as firm grants credit to customers, so it often gets credit from suppliers. It is known as trade credit. It does not make available of funds in cash but it facilitates the purchase’of goods without immediate payment.
iii) Instalment credit : Business firm gets credit from equipment suppliers. The supplier may allow the purchase of equipment with payments extended over a period of 12 months or more. Some portion of the cost price is paid on delivery and the balance is paid in a number of instalments. The supplier charges interest on unpaid balance.
iv) Customers advance : Many times, the manufacturer of goods insist on advance by customers, in case of big orders. The customers advance represent a part of the price of the product that has been ordered which will be delivered at a later date.
v) Commercial Paper: Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for shorter period, varying from 90 days to 365 days. It is issued by one firm on another firm. The amount raised by C.P is large. As the debt is totally unsecured, firms having good credit rating can issue commercial paper.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Hindrances of trade.
Answer:
In the course of exchange of goods various problems are encountered. The hindrances in the way of smooth trade may be place, person, finance, time, knowledge and risk.
- Hindrances of place : Generally all the goods are not con-sumed at the same place where they are produced. So, the goods are to be moved to the places of consumption. The activity of move-ment of goods is called transport. Transport eliminates hindrances of place.
- Hindrances of persons : At present, it is not possible for the producers to know the consumers who are in need of their goods produced by them. A chain of middlemen like wholesalers, retailers, dealers etc. Purchases goods from the producers and take them to customers. Middlemen remove hindrances of persons.
- Hindrances of finance: There is always time lag between the production and sale of goods. It takes time to collect money and hence need finance for trade. Commercial banks removes hindrances of finance.
- Hindrances of time : As the goods are produced in anticipation of demand, there is a need to store them until they are required for consumption. Warehousing eliminates the hindrances of time and provides time utility of the goods.
- Hindrances of knowledge: The consumers may not aware of the availability of various goods in the market. The absence of information is another hindrance. It can be eliminated by advertising them in T.V, newspaper etc.
- Hindrances of risk: There is risk involved in production, transportation and warehousing. Insurance companies undertake to compensate loss suffered due to such risks and insurance eliminates hindrances of risk.
Question 5.
A co-operative form of organisation is a method of self help. Discuss.
Answer:
The co-operative movement has been associated to protect the interests of weaker sections of the society. The primary objective of this movement is how to protect economically the weaker sections of the society from oppression of economically strong segment of the society. In all forms of organisations, be it a sole trade, partnership or joint stock company, the primary motive is to increase the profits. The businessman tries to promote his own interests through all means including exploitation of consumers. The co-operative form of organisation is a democratic set up run by its members for serving their own interests. It is self help through mutual help. The philosophy behind co-operation is ‘all for each and each for all’.
In the words of Dr. H.N. Kunzen co-operative is self help as well mutual help. It is a joint enterprise of those who are not financially strong and cannot stand on their own legs and therefore, come together not with a view to get profits but to overcome disability arising out of the want of adequate finance.
Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interests. It works on the principle of self help and mutual help. The primary objective is to provide support to its members. The motto of co-operative society is “Each for all and all for each”. People come forward as a group, pool their individual resources, utilise them in the best possible manner and derive some common benefits out of it.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the ways of dissolution of partnership.
Answer:
A firm may be dissolved in the following circumstance.
1) Dissolution by agreement : A partnership can be dissolved by an agreement among all the partners.
2) Dissolution by notice : If a partnership is at will, it can be dissolved by any partner giving notice to other partners.
3) Compulsory dissolution : A firm may be compulsorily dissolved when all the others except one partner are insolvent or the activities of the firm may become illegal.
4) Contingent dissolution : A firm will be dissolved on the happening of the any of the events.
a) Death of the partner
b) Expiry of the firm
c) Completion of the venture
d) Regignation by a partner
5) Dissolution through court: A partner can apply to the court for dissolution of the firm on any these grounds.
a) Insanity of partner
b) Incapacity of partner
c) Misconduct by the partner
d) Breach of agreement
e) Transfer of share to third person
f) Regular losses.
Question 7.
Differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
| Memorandum of Association | Articles of Association |
| 1. Grade or status : It is an important and first grade document. | 1. It is subsidiary one and second grade document. |
| 2. Scope : The memorandum is a sort of constitution of the company. The company works in the frame work given by memorandum. | 2. The articles contain by – laws for the day-to day working of the company. These are framed in the orbit of Memorandum of Association. |
| 3. Provisions: The memorandum cannot contain’ anything contrary to the Companies Act. | 3. The Articles of Association is subordinate to the memorandum of association and Companies Act and cannot contain anything contrary to both. |
| 4. Limitation : A company . cannot do anything beyond the scope of memorandum. An act beyond its scope is void. | 4. Anything done beyond the scope of articles will not void and can be ratified by passing special resolution. |
| 5. Relationship : It regulates relationship between the company and members or the public. | 5. It defines the relationship between company and the members and among members themselves. |
| 6. Necessity : The memorandum is a must forgetting company registered. | 6. Public companies may not have their articles, they canndopt Table A . of Schedule I. |
| 7. Alteration : Memorandum can be altered only under special circumstances and involve may formalities. | 7. Alteration of Articles is not difficult. It can be altered by passing special resolution. |
Question 8.
Explain the merits and demerits of equity sources of finance.
Answer:
Merits of equity sources of finance :
- Equity shares do not create any obligation to pay fixed rate of dividend.
- Equity shares can be issued without creating any charge over the assets of the company.
- It is permanent source of capital and the company need not repay it except under liquidation.
- Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company who have the voting rights.
- Incase of high profits, ‘equity shareholders are the real gainers by way of increased dividends and appreciation in the value of shares.
Demerits of equity sources of finance :
- If only equity shares are issued, the company cannot take the advantage of trading in equity.
- As equity capital cannot be redeemed, there is danger of over capitalisation.
- Equity shareholders can put obstacles in the management by manipulation ana organisation themselves.
- During prosperous periods higher dividends are paid leading to increase in the value of shares in the market and speculation.
- Investors who desire to invest in safe securities with fixed income have no attraction for such shares.
Question 9.
Briefly explain the registration process of MSMEs.
Answer:
The following are the registration requirements under MSMED Act, 2006.
As per the act, any person intend to establish a micro or small enterprise may do so at his discretion.
Any person intending to establish a medium enterprise, engaged in providing or rendering of services, may do so at his discretion.
Any person intending to establish a medium enterprise engaged in the manufacture or production of goods pertaining to any industry specified in the First Schedule to the industries (Development and Regulation) Act, 1951, shall file the memorandum of medium enterprise with authority specified by the State Government or the Central Government.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Trade
Answer:
All the activities engaged in the buying and selling of goods and services comes under trade. Therefore, trade includes sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services with the intention of making profit. The object of trade is to make goods available to those who need them and willing to pay for them. Trade is the final stage of business activities and involves transfer of ownership.
Question 11.
Partner by holding out’
Answer:
If a person is considered by an outsider as partner in the firm and does not deny it, he is called partner by holding out. He neither contributes capital to the firm nor participate in profits and losses. But he is liable to third parties for the debts of the firm.
Question 12.
Co-operative Housing Society
Answer:
The low and middle income groups of people are not able to construct their own house for want of money. Co-operative society arrange loans for their members from financial institutions and government agencies against security of their houses. These societies helps the members to become owners of the house over a period of time. Ex. : Housing Board Colonies.
Question 13.
Working capital
Answer:
The capital required by business enterprise to run its day- to-day operations such as purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and holding current assets like stock of raw materials, bills receivable is called working capital. The amount of working capital required varies from business to business. Generally trading concerns require more working capital as compared to manufacturing concerns.
Question 14.
Preference share
Answer:
As the name suggests, these shares have certain preferential rights with regarding to payment of dividend and repayment of capital. When the company has distributable profits the dividend is first paid to preference shares. In the event of liquidation, after the payment of outside creditors, preference share capital is returned.
Question 15.
Industrial Finance Corporation of India
Answer:
Industrial Finance Corporation of India was the first development finance institution setup in 1948 under IFCI Act inorder or pioneer long term institutional credit to large and medium industries. It is to provide financial assistance to industry by way of rupee and foreign currency loans, underwriting, subscribing the issue of shares, stocks, bonds and debentures of industries.
![]()
Question 16.
Define MNC
Answer:
According to International Labour Organisation report, Multi National Corporation refers to an enterprise whose managerial head quarters are located in one country, while it carried out operations in number of other countries as well. According to Prof. Vernon MNC is defined as ‘a cluster of operations of diverse of nationality joined together by common management strategy’.
Question 17.
E-business
Answer:
The term E-business was first used in IBM in 1997. It defined E-business as” The transformation of key business processes through the use of internet technology”. E-business is defined “as the application of information and communication technologies which support all the activities of the business with customers”.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
Given below is the Trial Balance of Mr. Ravi on 31.3.2009.
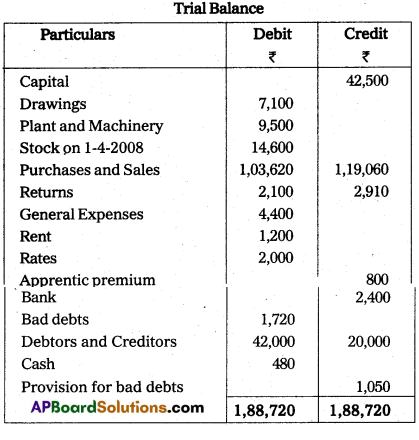
Make the following adjustments prepare his final accounts:
- Depreciate Plant and Machinery by 10%.
- Maintain the provision for bad debts at 5% on debtors.
- Rent outstanding ₹ 400.
- Rates ₹ 800 are paid in advance.
- Apprentice premium received in advance ₹ 800.
- Stock on hand on 31.12.2009 is valued at ₹ 17,000.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss Account of Mr. Ravi for the year ended 31-3-2009 .
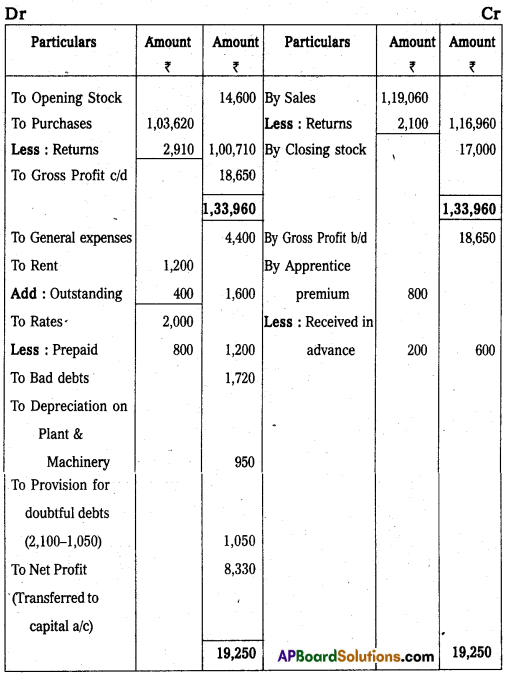
Balance Sheet of Mr. Ravi as on 31.03.2009
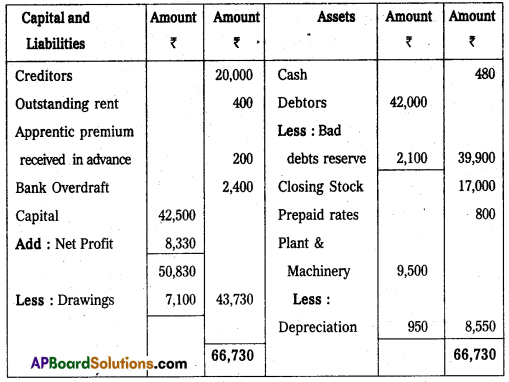
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare three column cash book from the following.

Answer:
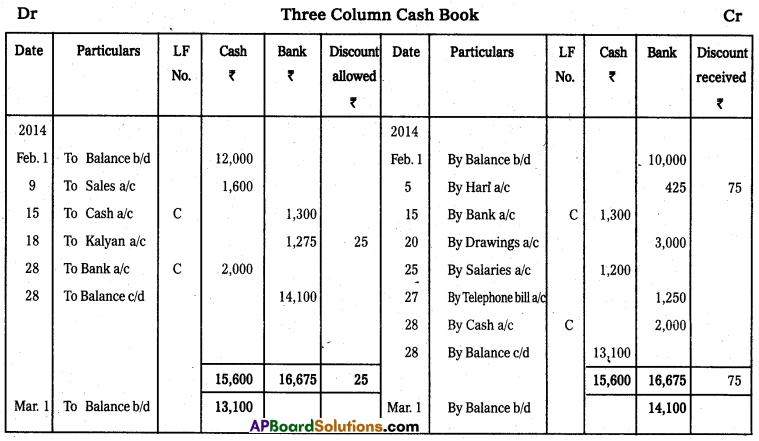
Question 20.
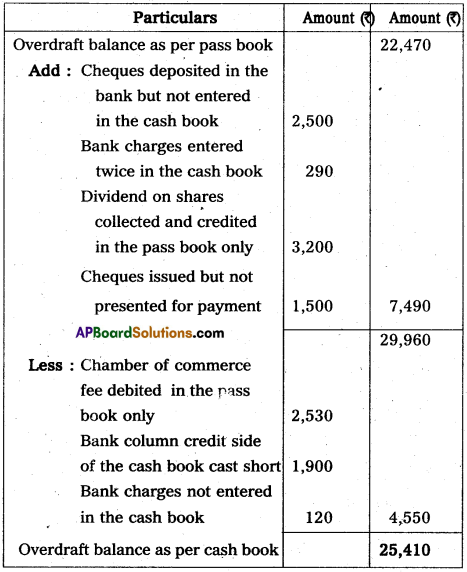
From the following particulars prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31st March 2014.
a) Overdraft balance as on 31-3-2014 as per Bank statements ₹ 22,470
b) As per standing instructions given to bank, chamber of commerce fees ₹ 2,530 was paid by bank but was not re-corded in the Cash Book.
c) On 23-3-2014, the credit side of the bank column of the Cash Book was cast ₹ 1,900 short.
d) Cheques deposited in the bank not recorded in Cash Book ₹ 2,500
e) In the Cash Book a bank charge of ₹ 290 was recorded twice while another bank charge of ₹ 120 was not recorded at all.
f) Dividend on shares ₹ 3,200 was collected by bank directly, the trader has no information.
g) Two cheques of ₹ 1,850 and ₹ 1,500 were issued but out of them only one cheque of ₹ 1,850 was presented for payment upto 31st March.
Answer:
Bank Recontilation Statement as on 31.03.2014
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
What is Journal Proper ? Explain its uses.
Answer:
All business transactions are recorded in different subsidiary books according to their nature. For example, credit purchases are recorded in purchases book, credit sales are recorded in sales book, purchases returns are recorded in purchase returns book, sales returns are recorded in sales returns book, cash transactions are recorded in cash book etc. But there are certain transactions which occassionally happen and these are not recorded in any of the subsidiary books. However, they are recorded in a special book known as ‘Journal Proper’. That is, the transactions which are not recorded in the respective subsidiary books are recorded in the journal proper.
Uses of Journal Proper : A journal proper in modem book keeping is used for recording the following transactions :
- Opening entries
- Closing entries
- Transfer entries
- Adjusting entries
- Purchase and sale of fixed assets on credit.
- Entries relating to dishonour of bills
- Rectification entries.
![]()
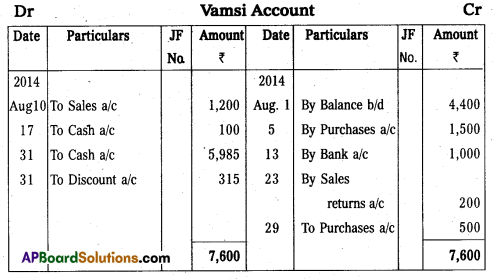
Question 22.
Prepare Vamsi’s account from the following.
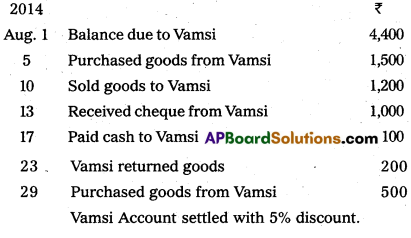
Answer:
Question 23.
Record the following in Sales book and Sales Returns book.

Answer:
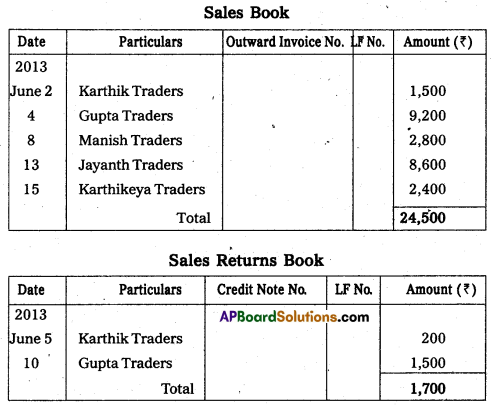
Question 24.
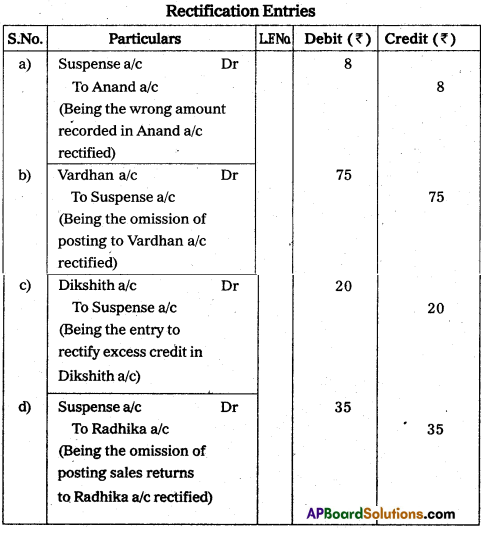
Rectify the following errors.
a) Received cash from Anand ₹ 188 has been posted to his a/cas ₹ 180
b) Goods sold to Vardhan ₹ 75 were omitted to be entered in his account.
c) Credit side of Dikshith account was overcast by ₹ 20.
d) Goods returned by Radhika ₹ 35 was not posted to her account.
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Transaction
Answer:
Transactions are those activities in Business, which involves transfer of money or goods or services between two persons or two accounts. Ex : Purchase of goods, sale of machinery, salaries paid, commission received. Transactions are of two types cash and credit transactions.
Question 26.
Accounting standards
Answer:
Accounting Standard is a principle that guides and standardises accounting practices. The generally accepted Accounting Principles are a group of accounting standards that are widely accepted as appropriate in the field of accounting. Accounting Standards are necessary so that the financial statements are meaningful across wide variety of businesses.
Question 27.
Credit note
Answer:
It is a note (document)prepared and sent to the customer to inform that his account is credited with the amount of the goods returned by him. It is a common practice to make it in red ink.
Question 28.
Imprest system
Answer:
Under this system, the petty cashier receives from the head cashier at the beginning of the month sum money called petty cash imprest. The petty cashier makes petty cash payments and enters these transactions in the petty cash book. At the end of the month, the balance in the book checked by the head cashier and advance the exact amount which is spent by the petty cashier.
Question 29.
Describe the overdraft.
Answer:
Overdraft is a credit facility given by a bank to draw the amounts repeatedly upto a certain limit sanctioned as when the need arises. This can be repaid by depositing cash or cheques and the bank charges interest on the overdraft facility availed by firm. The overdraft is also called as ‘unfavourable balance’.
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions.

Answer:
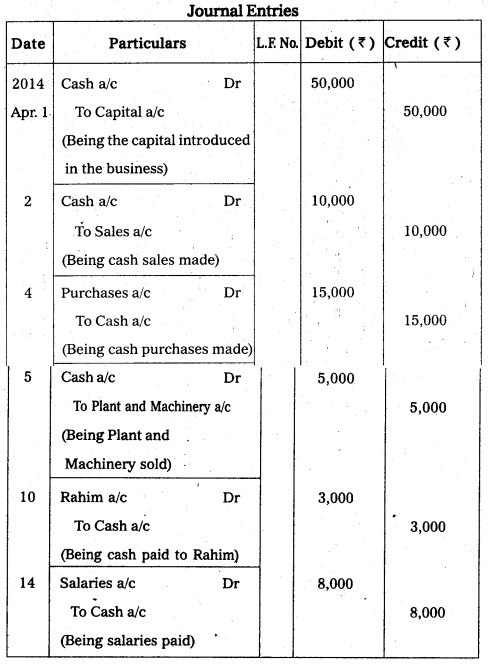
![]()
Question 31.
Pass adjustment journal entries.
i) Salaries outstanding ₹ 2,000.
ii) Create 5% reserve for bad debts on debtors ₹ 10,000.
iii) Closing stock ₹ 15,000.
Answer:
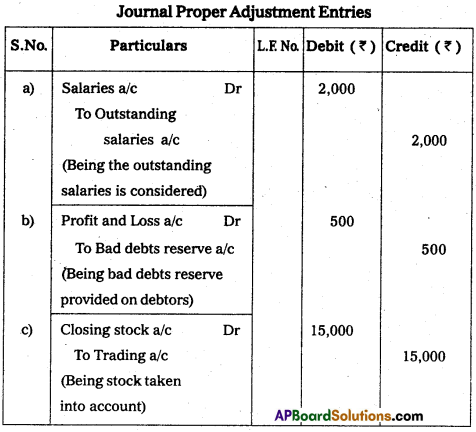
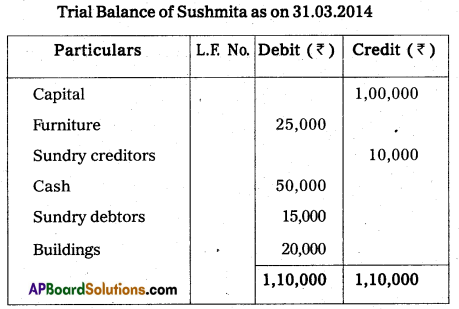
Question 32.
Prepare Trial Balance of Sushmita from the following balances as on 31.03.2014.
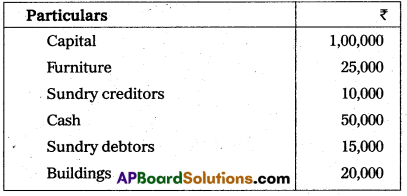
Answer: