Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 3 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define Partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits :
- Easy formation : It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsary.
- Large resources : The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial capacity: They pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making : The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility : The partnership is flexible in nature and at any time after mutual consent, the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations.
- Sharing risks : The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation: All partners actively participate in the business as per their specilisation and knowledge.
Limitations :
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is the fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership firm suffers from uneertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional capital for the expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferability of share : No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among the partners is the main cause for the dissolution of the partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions : Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
What is a Joint Stock Company ? What are its features ?
Ans.
“A Company is an association of persons who contribute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade or business and share the profits or losses arising there from”. – L.J. Ldndley
A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of individuals for profit having a capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership”.
From the above definitions, the features of Joint Stock Com-pany is as given below.
Features :
1) Association of persons : A company is an association of persons join hands with a common motive earning profits through business.
2) Separate legal entity : The company is created by law. It has a separate legal entity apart from its members. Eventhough it is invisible and intangible having no body or soul, it can act just like any other human being. It can enter into contracts, purchase and sell goods, conduct lawful business in its own name. It can sue and can be sued in a court of law.
3) Perpetual existence : The company has a perpetual exist-ence. The shareholders may come or may go but the company will go on forever. The continuity of the company is not affected by death, lunacy or insolvency of shareholders.
4) Common seal: A company being an artificial person cannot put its signature. The law requires every company to have a seal and get its name engraved on it. The seal of the company is affixed on all important documents and contracts signature.
5) Limited liability: The liability of shareholders is limited to the value of the shares they have purchased.
6) Transferability of shares: The shareholders of the public company is free to transfer their shares. They do not need the consent of other shareholders.
7) Separation of Ownership and Management: The share-holders are the owners of the company. But they are too many. They are “widely scattered and cannot take part in the day-to-day affairs of the company. The management is entrusted to Board of Directors who are elected by the shareholders. So, the ownership is separated from management.
8) Membership : To form a Joint Stock Company minimum two members are required in the case of private company and seven members in the case of public company. The maximum membership is fifty in private companies and unlimited in public companies.
9) Formation: The Company comes into existence only when it is registered under the Indian Companies Act, 1956.
10) Submitting annual statements : A Joint Stock Company is required to file annual statements with the Registrar of companies at the end of the financial year. These statements are available for inspection in the office of the Registrar.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the merits and demerits of raising finance by issuing preference and equity shares ?
Answer:
The capital of the company is divided into number of equal parts known as shares. A company can issue different types of shares to get funds from investors to suit their requirement. Some investors prefer regular income though it may be low, others may prefer higher returns and they will be prepared to take risk. Under the companies act, 1956, a company can issue only two types of shares.
1) Preference shares
2) Equity shares.
1) Preference shares : As the name suggests, these shares have certain preferences as compared to equity shares. There is a preference for payment of dividend and also repayment of capital at the time of liquidation. When the company has distributable profits, the dividend is first paid to preference shares. In the event of liquidation, after the payment of outside liabilities, preference share capital is returned.
Merits:
- Rate of return is guaranteed to those investors who prefer safety and want to earn income certainly.
- The shares are helpful in raising long term capital of the company.
- Redeemable preference shares have the added advantage of repayment of capital whenever there is surplus in the company.
- As fixed rate of dividend is payable, this enables the company to adopt trading on equity.
- There is no need to mortgage assets for the issue of shares.
Demerits:
- Fixed rate of dividend is paid on these shares. This is a permanent burden to the company.
- These shares do not carry any voting right and cannot participate in the management of the company.
- Compared to other types of securities such as debentures, usually cost of raising capital is high.
2) Equity shares : They are also known as ordinary shares. Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company as they carry voting rights.These shareholders are paid dividend after paying to the preference shares. The rate of dividend depends upon the profits of the company. There may be higher rate of dividend or they may not get anything. Hence they take more risk as compared preference shareholders. Equity capital is returned after meeting all other claims including preference shares.
Merits:
- Equity shares do not create any obligation to pay fixed rate of dividend.
- They can be issued without creating any charge over the assets of the company.
- It is permanent source of capital and the company need not repay it except under liquidation.
- Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company.
- In case of profits, these shareholders get higher dividends and appreciation in the value of shares.
Demerits :
- If only equity shares are issued, the company cannot take the advantage of trading on equity.
- There is danger of over capitalisation in case of excess issue of these shares.
- These shareholders ban put obsticles in management.
- In case of higher profits, increase in the value of shares may lead to speculation in the market.
Section – B
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Distinction between Commerce and Industry.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Commerce and Industry.
| Basis of difference | Commerce | Industry |
| 1. Meaning | It is related to the activities which deals with taking of goods from producers to consumers. | It is related to all those activities which deal with conversion of raw material into finished product. |
| 2. Capital | It requires less capital. | Capital needs are high. |
| 3. Scope | It includes trade and aids to trade. | Primary, manufacturing, processing etc., industries are covered under industry. |
| 4. Risk | The risk involved is comparatively less. | It involves greater risk compared to any other activity. |
| 5. Utility | Commerce creates time and place utility. | Industry creates form utility. |
Question 5.
Briefly explain the rights of partners.
Answer:
The following are the rights of partners.
- Every partner has a right to take part in the management of the business.
- Every partner has a right to be consulted before taking important decisions.
- The partners have a right to inspect the books of accounts and can take true copies.
- Every partner will have an equal share in profits unless otherwise mentioned in the partnership deed.
- No new partner can be admitted without the consent of all the partners.
- Every partner has a right to receive interest at the rate of 6% p.a. on the loan advanced by him.
- Every partner has a right to be indemnified by the firm for the expenses incurred or losses suffered in the normal conduct of the business.
- A partner has a right to get the firm dissolved under appropriate circumstances.
- Partners have joint ownership of the assets of the firm.
- Every partner has a right, in an emergency to do such acts, for the purpose of protecting the firm from losses.
Question 6.
What are the features of Private Company ?
Answer:
The following are features of the Private Company :
- A private limited company can be started with only two members.
- It need not issue and file with the Registrar a prospectus or a statement lieu of prospectus before the allotment of shares and debentures.
- It can allot shares even before minimum subscription is received.
- It can commence business after obtaining Certificate of Incorporation.
- It need not conduct statutory meeting and file a copy of statutory report to the Registrar.
- The minimum number of directors is two. They need not retire by rotation. A single resolution is sufficient to appoint directors.
- List of directors and their consent to act as such or take up qualification shares need not be filed with the Registrar.
- It can grant loans to directors without the consent of central government.
- Quorum for meeting is subjected to Articles of Association.
- There are no restrictions on the remuneration of directors or managing director of companies.
- It need not show the documents to the public.
Question 7.
What are the sources of medium term finance ?
Answer:
The sources of medium term finance are
1) Public deposits
2) Loan from banks
3) Lease financing
1) Public deposits : Industries receive deposits from the public. These deposits are called public deposits. The period of public deposits used to be short i.e for three years. So, public deposits have been a very important source for working capital requirements.
2) Loans from banks : Commercial banks plays a vital role as they provide funds for different purposes and for different periods. They extend loan facility in the form of cash credits,overdrafts, term loans and purchasing/discounting bills of exchange. The borrower is required to provide some security or to create a charge on the assets of the firm before a loan is sanctioned.
3) Lease financing : A lease is a contractual obligation whereby the lessor or owner grants the lessee the right to use the asset in return for a periodic payment known as lease rent. At the end of the lease period, the asset goes back to the lessor. Lease financing is an important means for modernisation and diversification of the firm. Such financing is resorted to in acquiring assets like computers and electronic equipment.
Question 8.
List out the features of MNCs.
Answer:
Characteristics or features of Multi National Corporations:
- Global Operations : Multi National Corporations carry production and marketing operations in different countries of the world. They possess all the infrastructural facilities in all the countries of their operations.
- Giant Size : The assets and sales of MNC are quite large. The sales turnover of some MNCs extend the gross national product of several developing countries.
- Centralised Control : It has its head office in home country. It exercises control over all branches and subsidiaries.
- Dominant Position and Status : They occupy a dominant position in the market due to their giant size. They also takeover the firms to acquire huge economic power.
- Internationalised Research and Development: These are intended to capture the quality and serve according to the requirements of the host nation.
- Sophisticated Technology : MNC has advanced technology so as to provide world class products and services. It employs capital intensive technology in manufacturing, marketing and other areas of business.
- Professional Management : A MNC employs professional managers to integrate and manage world wide operations.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the benefits of E-business to organisations ?
Answer:
The following are the benefits of E-business to the organisation.
- Expansion of markets : E-business allows organisation to expand the markets from national to international markets.
- Saving in costs : The business concerns can reduce the cost of producing, processing, distributing, storing and feedback of information. It allows them to reduce stock levels which results in saving in costs.
- Competitive benefits : Reduction in the processing time allows the business to provide goods and services to the customers as per their requirements. It achieves competitive advantage.
- Collection of capital: It enables the business to reduce time between outlay of capital and receipt of cash of products and services.
Section – C
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is employment ?
Answer:
Employment involves working under a contract of employment for or under someone known as employer in return for a salary. The person engaged under employment works as per the directions of the employer.
Question 11.
Genetic industries
Answer:
Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale. Ex : Nurseries, C ttle breeding, Poultry farm, Fish hatcheries etc.
Question 12.
Define Company.
Answer:
According to Lord Justice Lindley “Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association or organisation of many persons who contribute money or moneys worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade and who share profit or loss arising therefrom”.
Section 566 Companies Act, defines a company is an artificial person created by law with prepetual succession and a common seal.
Question 13.
Statement in lieu of prospectus.
Answer:
If a public limited company could get the required capital by some private management may not issue prospectus. But in that case, it must file a statement in lieu of prospectus with the Registrar, at least three days before the allotment of shares. It must be signed by all the directors and must be drafted strictly in accordance with the particulars set out in Part -I of Schedule -III of the Act.
Question 14.
Deferred shares
Answer:
The rights of deferred shareholders with regard to payment of dividend and repayment of capital is deferred arid will get when all the other shareholders paid. The management retained in their hands by virtue of their voting rights. These shares are earlier issued to promoters or founders for services rendered to the company.
Question 15.
Industrial Development Bank of India
Answer:
Industrial Development Bank of India was established in July 1964 by a Special Act of Parliament. The IDBIs whole paid up capital is held by the central government. The main objectives are :
- To set up an apex institution to co-ordinate the activities of other financial institutions.
- To promote participation in private capital.
- To promote private ownership in industrial activities.
Question 16.
Define small enpterprises.
Answer:
In case of manufacturing enterprises, a Small Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in Plant and Machineiy is more than ₹ 25 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
In case of service enterprises, a small enterprise is an enterprise where investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs but not exceed ₹ 2 crores.
![]()
Question 17.
Define Globalisation.
Answer:
Globalisation refers to the increasing integration of markets and production that includes the mobility of resources like capital, labour, organisation and knowledge. Globalisation refers to shift towards a more integrated and independent world economy.
PART – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Question 18.
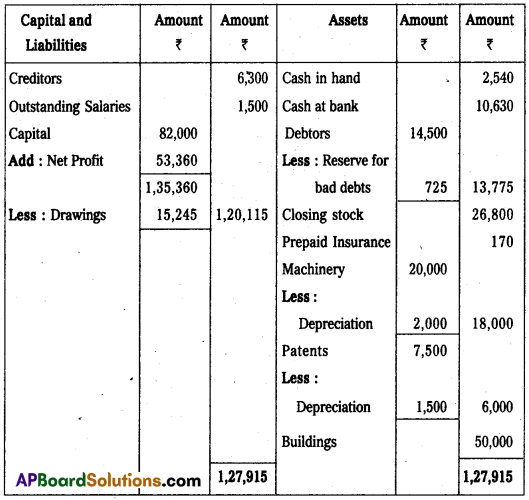
From the following Trial balance of Mr. Rajesh, prepare Trading, Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet for the year ending 31.12.2009.
Trial Balance
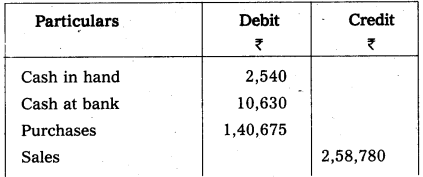
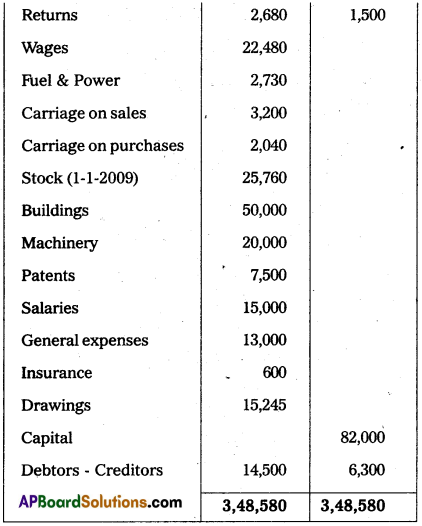
Adjustments:
- Closing stock : ₹ 26,800
- Depreciate 10% on Machinery and 20% on Patents.
- Outstanding Salaries : ₹ 1,500
- Prepaid Insurance : ₹ 170
- Provide 5% bad debts reserve on debtors.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Mr. Rajesh for the year ended 31-12-2009.
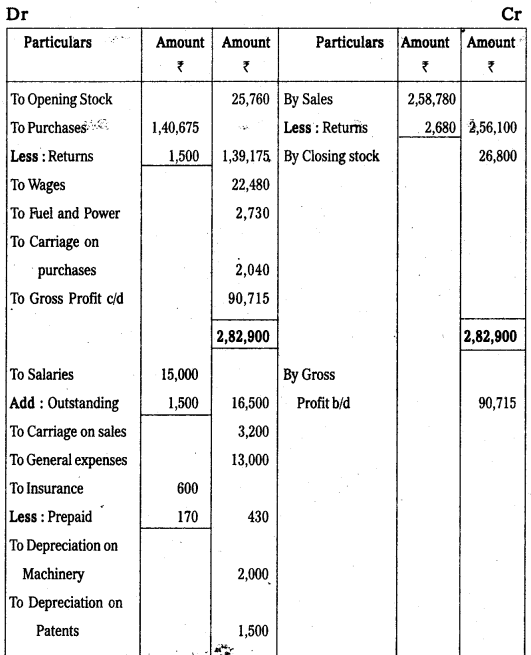
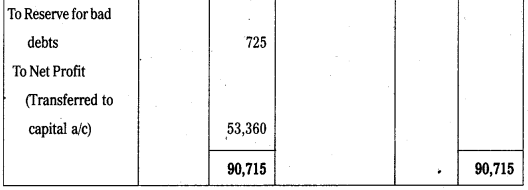
Balance Sheet of Mr.Rajesh as on 31-12-2009
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions
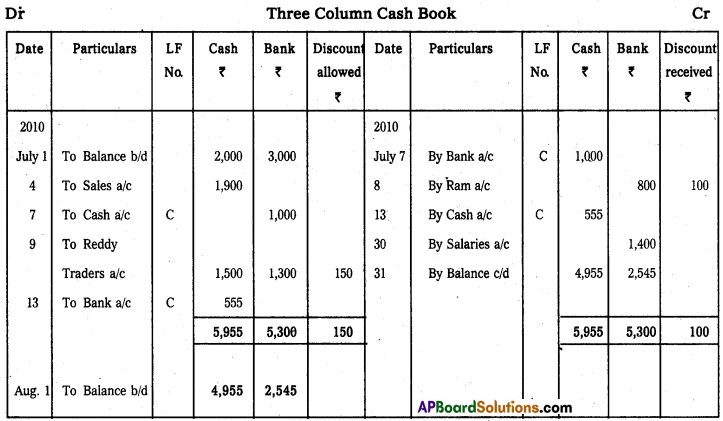
Question 19.
Prepare Triple column cash book from the following particulars.

Answer:
Question 20.
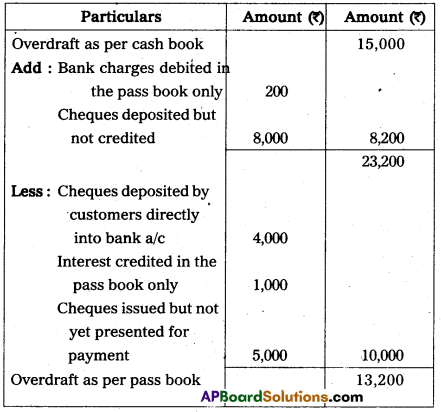
Prepare bank reconciliation statement of Mr. Murthy as on 31-03-2010.

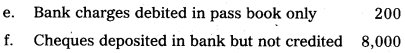
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Murthy as on 31.03.2010
Section – F
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
What are the advantages of double entry system ?
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Double entry system of book-keeping.
- The system maintains a complete record of all the business transactions, as it records both the aspects of the transaction.
- It provides a check on the arithematical accuracy of accounts with the help of trial balance.
- Errors and frauds can be deducted under this system. So, it reduces the chance of committing errors and frauds.
- It reveals the result of the operations i.e., profit or loss, by preparing profit and loss a/c.
- The financial position of the business can be ascertained through the preparation of balance sheet.
- It is a scientific system and permits the accounts to be kept in detailed form and provides sufficient information for the purpose of control.
- The results of one year can be compared with the results of previous year and reasons for the changes are known.
- It provides accounting information readily to manag-ement for making decisions.
![]()
Question 22.
From the following information prepare Ramu account.

Answer:
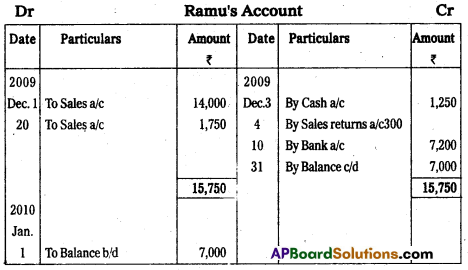
Question 23.
Prepare the subsidiary books from the following information.

Answer:
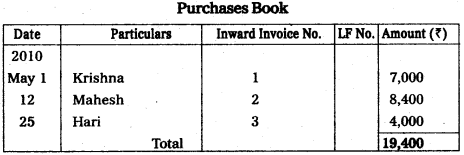
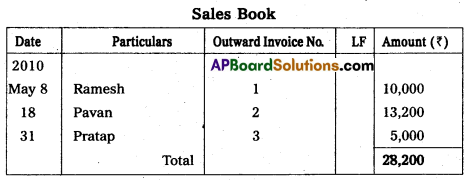
Question 24.
Explain errors not disclosed by trial balance.
Answer:
These type of errors cannot be traced out in the preparation of trial balance, because these errors cannot affect the agreement of trial balance.
- Error of principle, Ex : Repairs to Machinery debited to Machinery a/c.
- Error of omission, Ex : Sales made not recorded in the sales book.
- Error of commission, Ex : Purchase ₹ 1000 were recorded as ₹ 10,000 in the Purchases book.
- Compensating errors
- Posting wrong entry in the subsidiary book.
- Posting to correct side in wrong account.
- Recording a transaction in the books of twice.
Section – G
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Business entity concept
Answer:
Business is treated as separate from the proprietor. All the transactions are recorded in the books of business but not in the books of proprietor. The proprietor is also treated as creditor of the business when he contributes capital he is treated as a person who has invested amount in business. So, capital appears on the liabilities side in the Balance Sheet.
Question 26.
Creditors.
Answer:
A person who gives a benefit without receiving money or moneys worth immediately but claim in future, is a creditor. The creditors are shown as liability in the Balance Sheet.
Question 27.
Define Accounting.
Answer:
The American Institute-of Public Accountants defined accounting as “the art of recording, classifying and summarising in significant manner and interms of money transactions and events which are in part, atleast of financial character and interpreting results thereof.
![]()
Question 28.
Journalise the following the books of Mr. Venkat.

Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Venkat
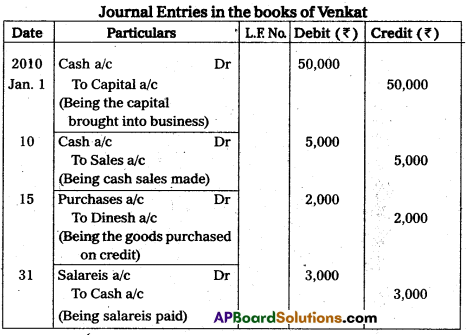
Question 29.
From the following balances, write opening entry.

Answer:
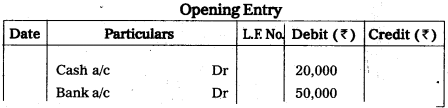
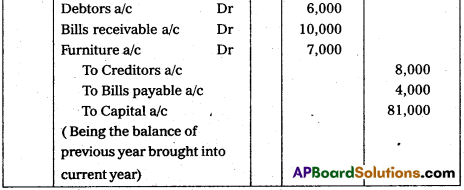
Question 30.
Prepare a trial balance as on 31.12.2009.

Answer:
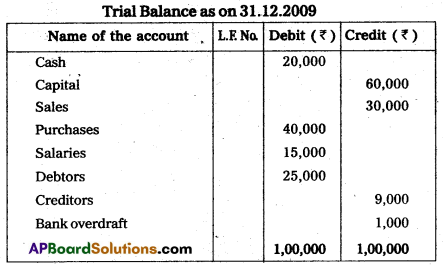
Question 31.
Error of principle
Answer:
Errors of principle occurs when errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These errors arise, when correct distinction between capital and revenue is not made. Ex : Purchase of furniture debited to purchases a/c.
Question 32.
Income received in advance
Answer:
Income relating to the next year but received in advance during the current year. These incomes are deducted from the concern incomes in the profit and loss account credit side. These incomes are shown as a liability on the Balance Sheet.