Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 1 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define a partnership firm and explain the features of it.
Answer:
A partnership firm is an association of two or more persons formed with the object of sharing profits arising out of business or an undertaking or a venture.
Definition : According to L.H. Haney “The relationship between persons who have agreed to carry on a business in common with a view to private gain”.
Partnership is defined by the Indian Partnership Act 1932 as “The relation between the persons who have agreed to share profits of business carried on by all or any of them acting for all”.
Features :
- Presence of business : The partnership can only be for some kind of business. The term business includes any trade, profession or occupation. If the purpose of the partnership is something other than the business, it should not be treated as partnership.
- Agreement : Partnership is the result of an agreement. It is created by mutual consent and voluntary agreement. The contract may be oral or written. But in practice written agreement is made.
- Lawful business : The partnership can only be some kind of lawful business. An agreement indulge in smuggling, black marketing etc., cannot be called as partnership.
- Sharing profits : The purpose of business should be to make profits and distribute them among partners. This is one of basic element of partnership.
- Duel role of principal and agent: The business may be carried on by all or any one acting on behalf of others. Each partner is both an agent and a principal for himself and others.
- Unlimited liability : The liability of the partners are unlimited. If the assets of the firm is not sufficient to meet the liabilities of the firm, the ‘partners has to pay from their private assets. Further, the creditors can claim their dues from anyone of the partners or from all. The partners are liable individually and jointly.
- Membership : The minimum member of number is 2 and maximum member of number is 10 in the case of banking business and 20 in any other business.
- Transfer of share : No partner can transfer his share without the consent of other partners.
- Voluntary registration : The partnership may or may not be registered. But registration of firms gets some priviliges and facilities.
- Legal entity : There is no legal entity for partnership.
- Mutual trust : The partnership deed depends upon mutual trust.
Question 2.
Explain about Memorandum of Association and the clauses of it.
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the most important document of the company. It is to be filed with the Registrar for obtaining the certificate of incorporation. It is the charter of the company. It forms the foundation on which the super structure of the company is based. It establishes the relationship between the company and the outside world. The contents of the Memorandum cannot be altered at the option of the directors or even the shareholders. It is to be altered only with the approval of central government and court approval in many cases.
The Memorandum has to be divided into paragraphs, consecutively numbered and has to be printed. It should be signed by seven members in the case of public company and by two members in the case of private company.
Clauses : Memorandum of Association contains the following clauses.
1) Name clause : In this clause, the name of the company should be stated. The company is free to adopt any name it likes. But it should not resemble the name of another registered company. It should not use any words pertaining to government or local government, such as royal, crown, state etc. The name of the company must end with the word ‘Limited’ if it is a public company or with the words ‘Private Limited,’ if it is a private company.
2) Situation clause : The place and the state in which the registered office is to be situated must be mentioned in this clause.
Registered office means a place where Common Seal, statutory books, account books etc., are kept.
3) Objects clause : This is the most important clause of the memorandum. This gives out the various objects for which the company is formed. The objects of the company must be legal and clearly defined. A company has power to carry on only those activities which are included in the objects clause. Any action beyond the express powers of the company is ultravirus i.e., beyond the scope of memorandum. Therefore, it should be carefully drafted.
4) Liability clause : This clause clearly states that the liability of the members is limited to the extent of the face value of the shares held by them.
5) Capital clause : The amount of capital required by the company is stated in this clause. This is called authorised or nominal or registered capital. The capital is divided into small units called as shares. The company must mention the number, kinds and value of each share.
6) Association and subscription clause : This clause contains the names of signatories to the memorandum of association. It should be signed by atleast 7 members in the case of public company and 2 members in the case of private company. Each subscriber has to take atleast one share in the company. The subscribers declare that they agree to incorporate the company and agree to take the shares stated against their names.
![]()
Question 3.
Define Debenture and write about various types of Debentures.
Answer:
A company may raise long term finance through public borrowings. These loans raised by the issue of debentures. A debenture is an acknowledge of a debt. A Debenture may be defined as a document under the company’s seal which provides for the payment of principal sum and interest there on at regular interval, which is usually secured by a fixed or floating charge on the company’s property or undertaking and which acknowledges a loan to the company”. A debenture holder is a creditor of the company. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures. A company may issue debentures for initial needs and for extensions and developments.
Types of debentures : The debentures issued by a company can be classified as follows :
- Simple, naked or unsecured debentures : These debentures have no charge on the assets of the company. They are not secured by any charge on any of the assets of the company.
- Mortgage or secured debentures : These debentures are secured by a charge on some or all assets of the company. There is no risk of loss either the principal or interest.
- Redeemable debentures : These debentures are to be redeemed on the expiry of a certain period. The interest on the debentures is paid periodically but the principal is returned after a fixed period say 5 years, 10 years or 15 years.
- Irredeemable debentures : Such debentures are not redeemable during the life time of the company. They are payable either on the winding up a company or reedeem such debentures when ever at deems fit.
- Registered debentures : The names of the holders are recorded in the books of the company. If such debentures are transferred, the name of the transferee is entered in the register and the name of the original holder is cancelled.
- Bearer debentures.: The debentures which are not recorded in the register of debentures are known as bearer debentures. The debentures are transferable by mere delivery.
- Convertible debentures: These debentures carry the option of getting a part or full value converted into equity shares on a fixed date.
- Non-convertible debentures : They do not enjoy any such right to get themselves converted into equity shares.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Discuss about various types of Industries.
Answer:
The industries may be classified as follows.
1) Primary industry : Primary industry is concerned with the production of goods with the help of nature. It is a nature oriented industry, which requires very little human effort.
E.g : Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry : Genetic industry is related to the re-producing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale.
E.g : Nurseries, cattle breeding, poultry etc.
3) Extractive industry : It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw form and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products.
E.g : Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry.
4) Construction industry : The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabri-cation of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, bridges, dams etc.
5) Manufacturing industry : The industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human needs. E.g : Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry.
6) Service industry : These industries are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. E.g. : Banking, transport, insurance etc.
Question 5.
Explain any five principles of a Co-operative Society.
Answer:
The Indian Co-operative Societies Act, 1932 Section 4 defines co-operatives as a “society which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principle”.
Principles :
- Voluntary membership : A co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. Everyone is at liberty to enter or leave the co-operative society as and when he likes. Any per son can become a member irrespective of his/her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
- Democracy and equality : It is organised on the basis of democracy and equality. Every member has a right to partici pate in the management. Every member has only one vote.
- State control : A co-operative society is subject to the control and supervision. In India, all co-operatives are registered under Indian co-operative societies Act or respective state co-operative laws.
- Service motto : The primary objective of co-operative society is to provide service to the members. The aim is not to earn profits. The societies earn small amount of profits to cover administration expenses.
- Knowledge of the principles of co-operation : Every person joining a co-operative society must be familiar with the fundamentals of co-operation. The important aim is to serve com-mon man. The spirit is “Each for all and all for each”.
Question 6.
Draw any five differences between a Public Company and a Private Limited company.
Answer:
Differences between private limited company and a public company.
| Nature | Private Company | Public Company |
| 1. Membership | To form a Private Company the minimum number of members is two maximum number is fifty. | Minimum number of members is seven and ‘ maximum number of members is unlimited. |
| 2. Issue of Shares | It cannot issue prospectus for inviting the public for subscription of its shares. | It can issue prospectus for inviting the public for subscription of its shares. |
| 3. Transfer of Shares | The transferability of shares is generally restricted by its articles. | The shareholders can freely transfer their shares. |
| 4. Formation | It can commerce its business as soon as it obtains certficate of incorporation from the registrar. | The business can be started only after getting certificate of commencement of business. |
| 5. Statutory meeting | It need not conduct statutory meeting and file copy of statutory report to the Registrar of companies. | A statutory meeting must be held within six months from the date of receiving the certificate of commerce meet of business and statutory report is to be submitted to the Registrar. |
Question 7.
Define Business finance and explain the significance of it.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business finance. ,
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
Significance of business finance :
- To commence a new business : Money is needed to start a new business and to procure fixed assets like land and buildings etc., working capital is required to meet the day – to – day expenses and holding current assets like cash, stock-in-trade etc.
- To expand the business : Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
- To develop and market new products : Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products.
- To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
- To take over another business : In order to overcome competition an enterprise may decide to take over another business.
- To more to new premises : Sometimes a business may be forced to shift the business in another place.
- Day-to-day running : A business needs money to meet the day – to – day requeirements.like wages, taxes etc.
Question 8.
Write a brief note on multinational corporations.
Answer:
A Multi National Corporation may be defined as a company that operates in several countries. Such a company has factories, branches or offices in more than one country. The operations of Multi National company extend beyond the country in which it is incorporated. Its head quarters are located in one country and carrying business operations in other countries. According to international labour organisation report, multinational corporation refers to an enterprise whose managerial headquarters are located in on country, while it carries out operations in other countries as well.
The Multi National Corporation also known as Transation Corporation, Global Corporation, International Corporation has been regarded as the most visible innovation of the post-war period in economic field. The economic dominance of the Multi Nationals is manifested by the fact that Multi National Corporation control between a quarter and third of all world production and the total sales of their foreign affliates are about the same as the gross national product of all the developing countries excluding the oil exporting developing countries. According to some estimates the intra-firm trade of Multi National Corporations makes up over 30 percent of the world trade.
![]()
Question 9.
Define e-business and explain its scope.
Answer:
The term E-business was first used by IBM in 1997. E-business as “The transformation of key business processes through the use of internet technologies”. E-business may be defined as the application of information and communication technologies which support all the activities of the business with customers. It also enables enterprises to link their internal and external data processing system more efficiently and flexibly and serve better to the needs and expectations of their customers. It uses web based technology to improve relationship with customers.
The scope of E-business can be studied in following areas.
- E-Business within the organisation
- Business-to-Business
- Business-to-Customer
- Customer-to-Customer
- Customer-to-Business
In second and third category there is exchange of goods and services from one business to another business and business to customer. In fourth and fifth category the transactions are facilitated by one customer to another customer and customer to business through internet.
Now-a-days one can buy products online through some sites like Flipkart, Jabong and Amazon. In the age of E-Commerce everything from gym equipment to laptops are available online. E-business is a super set of business cases. It includes E-trading, E-Engineering, E-Franchising, E-Mailing, E-operational resource management etc.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Business
Answer:
The word business literally means a state of being busy. In the words of Haney “Business may be defined as human activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. According to Wheeler “Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services to the society under the incentive of private gain”.
Question 11.
Insurance
Answer:
Business is subject to risks and uncertainities. Risks may be due to theft, fire, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Insurance companies who act as risk bearers covers risks.
Question 12.
Dayabhaga Principle
Answer:
This school of Hindu Law prevails only in the states of Assam and West Bengal. Under this the right of the property comes to a co-parcener by succession and not by birth. Share in a Joint Hindu family does not fluctuates on the basis of birth or death of a member.
Question 13.
Minor partner
Answer:
A minor is a person who has not yet attained the age of majority i.e. 18 years. According to Indian contract act, a minor cannot enter into a contract. A minor may be admitted to the benefits of existing partnership with the consent of all partners. The minor is not personally liable for the liabilities of the firm.
Question 14.
What is a Government Company.
Answer:
A company in which not less than 51% of the paid up share capital is held by the central government or state government or partly by central government and partly by state government is called Government Company.
Ex : Hindustan Machine topis, ONGC, NTPC.
Question 15.
Prospectus
Answer:
A public limited company soon after its incorporation issues a prospectus. It is a circular or notice, inviting the public to subscribe to the shares of the company. It is issued by the public company with a view to raising necessary funds from investors. It will be in the form of appeal describing the prospectus of the company.
Question 16.
Explain retained earnings.
Answer:
Retained earnings or ploughing back of profits refers to the process of reinvestment of the earning of the year after year. In this technique all the profits are not distributed to shareholders. A part of the profit is retained in the business as a reserve which are used for financing long term and short term needs of the company.
![]()
Question 17.
Medium enterprise
Answer:
In case of Manufacturing Enterprises, a medium enterprise is an enterprise where investment in Plant and Machinery is more than ₹ 5 crores, but does not exceed ₹ 10 crores.
In case of service enterprises, a medium enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2 crores but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
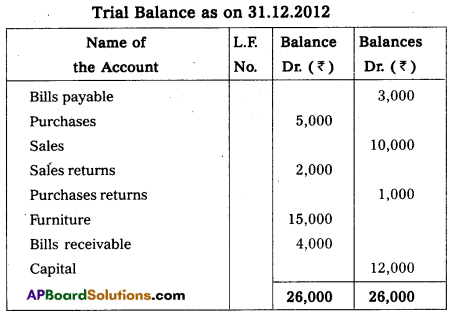
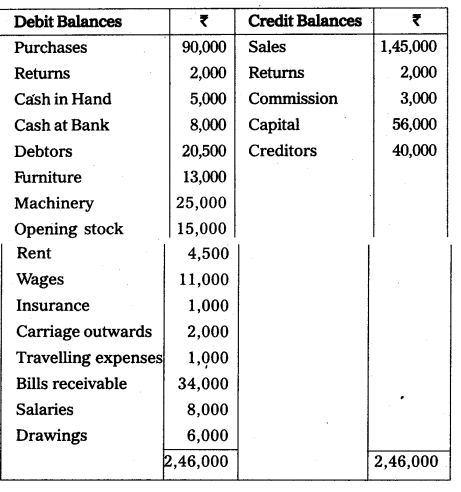
From the following Trail Balance of Maanas Prepare trading & Profit and loss a/c for the year ended 31st December 2012 and Balance Sheet as on that date.
Adjustments :
- Closing stock stock ₹ 32,000
- Write off Bad debts ₹ 500
- Provide 5/-provision for Doubtful debts
- Outstanding wages ₹ 1,000
- Provide Depreciation on Furniture 10% and on Machinery 10 %.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Maanas for the year ending 31stDecember 2012.
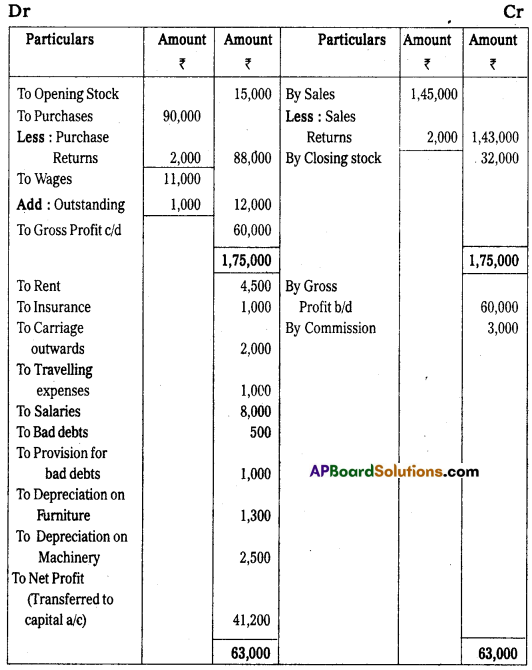
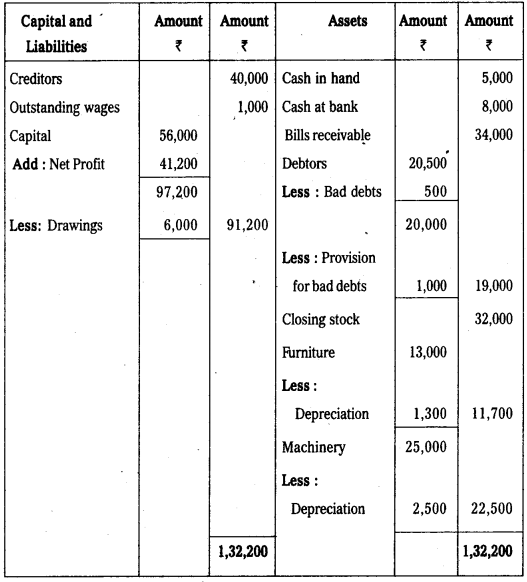
Balance Sheet of Maanas as on 31st December 2012
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare three column cash book of Renish from the following particulars.

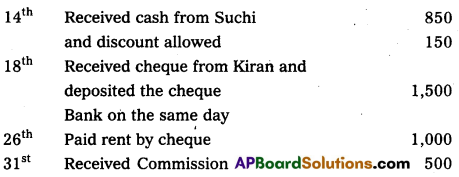
Answer:
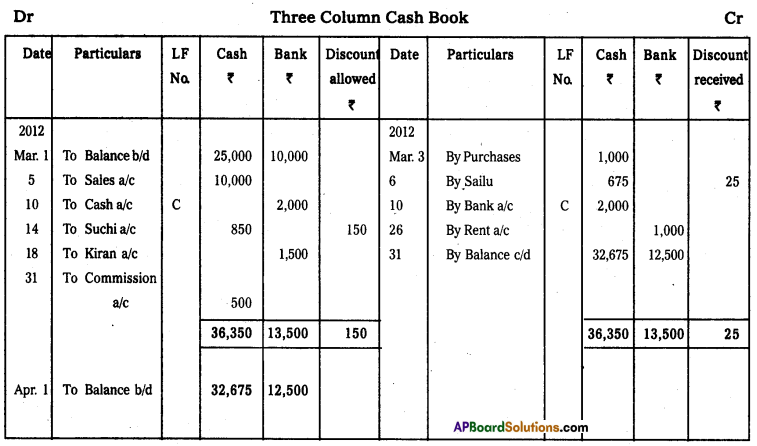
Question 20.
On 31-12-2012 Mr. Sarath Kumar’s bank balance as per pass book ₹₹ 6,000. There is disagreement between cash book and pass book balance. Prepare bank reconciliation statement by considering following transactions.

Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Sarat Kumar as on 31.12.2012
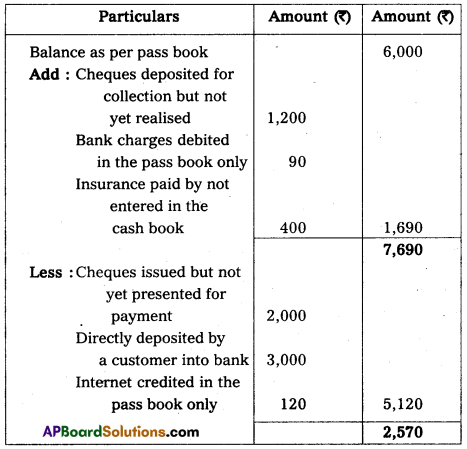
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain any five advantages of Book- Keeping.
Answer:
Advantages of book – keeping :
- Book-keeping is concerned with recording of business transactions.
- The objective is to maintain systematic records of the business.
- This is routine and clerical in nature.
- Book-keeping is done by junior staff in accounting department.
- A book-keeper is responsible for recording business transactions only.
Question 22.
Prepare X & Co., from the following transactions.
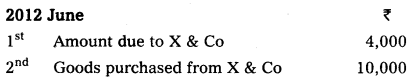

Answer:
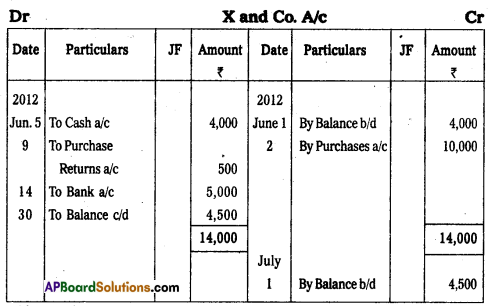
![]()
Question 23.
Enter the following transactions in the proper Subsidiary Books.

Answer:
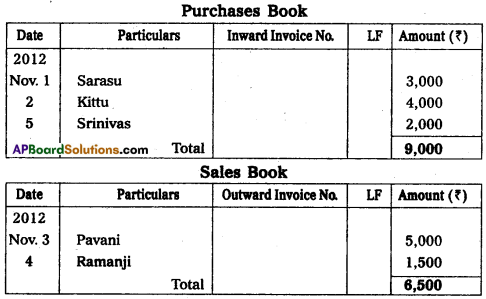
Question 24.
Explain about various types of errors.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors
1) Error of principle : Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors : When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is called clerical errors. They are again divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors : These errors arise when one error is compensated by other error or errors.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Debtors
Answer:
A person (individual or firm), who receives a benefit without giving money or money’s worth immediately, but liable to pay in future or in due course of time is a debtor. The debtors are shown as an asset in the balance sheet.
Question 26.
Suspense a/c
Answer:
Suspense account is an imaginary account, opened and used as a temporary measure to make the two side of the trial balance agree. As and when the errors which causes the disagreement in trial balance is detected, rectification entries should be passed through suspense account. Detection and rectification of all the errors will result in automatic closure of suspense account.
Question 27.
Outstanding expenses.
Answer:
Outstanding expenses are the expenses relating to the current year but unpaid during the year and are to be paid in the next year is known as outstanding expenses. Ex : Salary or rent for the month of March is due but not paid. These expenses are added to the concerned expenditure either in trading account or profit and loss account debit side. These expenses are again shown as liability in the Balance sheet.
Question 28.
Mention the rule of Debit and Credit of Real a/c.
Answer:
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. When an asset is received the asset account is debited and when the asset goes out of the business, the asset is credited.
Question 29.
Contra entry.
Answer:
Contra means the other side. If the double entry of a transaction is complete in the cash book itself such entry is called contra entry. Contra entry arises when cash and bank accounts are simultaneously involved in a transaction. It happens when either cash or cheqeus are deposited in the bank and cash is withdrawn for office use. In both the cases entries are made in cash and bank columns.
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions.

Answer:
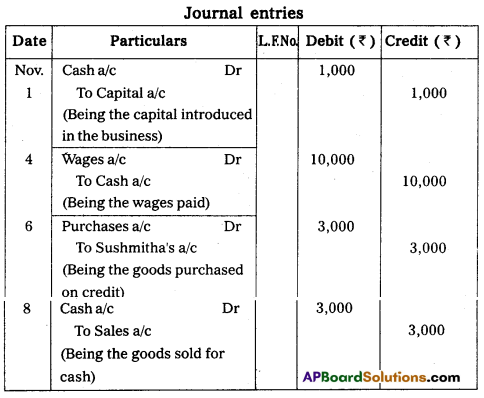
![]()
Question 31.
Write opening entries from the following.

Answer:
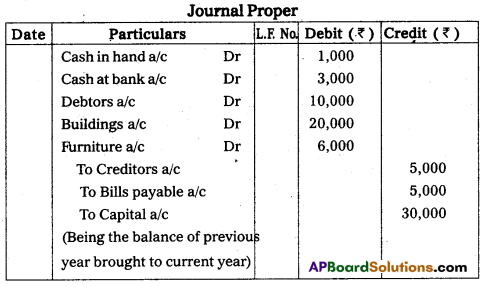
Question 32.
Prepare Trial Balance from the following particulars as on 31-12-2012.

Answer: