Access to a variety of AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2019 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity. question patterns.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2019
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
Name the major particulate pollutants present in Tropo-sphere.
Answer:
The major particulate pollutants present in troposphere are dust, mist, fumes, smoke, smog etc.
Question 2.
Why is KO2 Paramagnetic?
Answer:
In KO2 the O2– ion have one unpaired Electron so it is para-magnetic.
![]()
Question 3.
What is closed system? Give example.
Answer:
Closed system : A system which may exchange energy but nqt matter with surroundings is called a closed system.
Ex : Consider boiling of water in a closed metallic vessel. Here, heat is transferred from the burner (surroundings) to the system. Steam remains inside the vessel. Thus, matter is not exchanged.
Question 4.
Calculate the kinetic energy (in SI units) of 4g of methane at – 73°c.
Answer:
ke’= 3/2 nRT
= 3/2 × 1/4 × 8.314 × 200
R = 623 J
n = 4/16 = 1/4
T = – 73°c = 200°k
R = 8.314 J
Question 5.
What is PAN? What effect is caused by it?
Answer:
Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate is called as PAN.
Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate is (PAN) is a powerful eye irritant.
Question 6.
Describe the important uses of Quicklime.
Answer:
Uses :
- Quick lime is used in the purification of sugar.
- Quick lime is used in the manufacture of dyestuffs.
- Quick lime is used in the manufacture of Na2CO3 from NaOH.
- It is an important material for manufacturing of ce/ment and it is the cheapest form of alkali.
Question 7.
State Le-Chatelier’s principle?
Answer:
Le Chatelier’s Principle – Statement: “If a system at equi-librium is subjected to the change of pressure, temperature (or) concentration, the system is shifted in such a way as to nullify the effect of change”.
Question 8.
Define Normality.
Answer:
Normality : The no.of gram equivalent weights of solute present in one litre of solution.
Question 9.
State Hess law.
Answer:
Hess law : The heat change in a reaction is same whether the reaction takes place in one step (or) in several steps.
Question 10.
Write the I.U.P. A. C names of the following compounds:
a) (CH3)3C CH2C(CH3)3
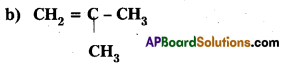
Answer:
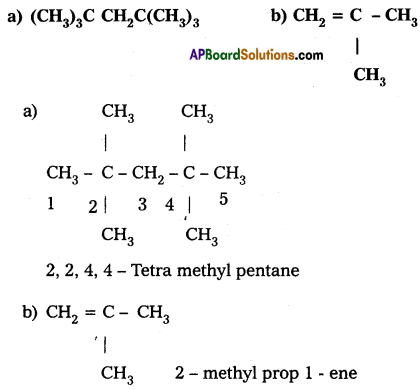
Question 11.
Define sp2 Hybridisation. Explain the structure of Ethylene (C2H4).
Answer:
sp2– hybridisation : Inter mixing of one’s orbital and two ‘p’ orbitals of an atom of identical energy to for three new hybrid or-bitals. This is called sp2 hybridisation.
Formation of double bond between the carbon atoms of C2H4
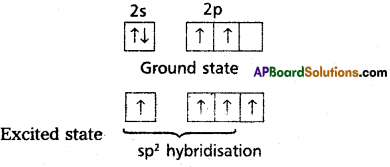
- In ethylene two carbons undergo sp2 hybridisation.
- One of sp2 hybrid orbital of carbon overlaps with sp2 hybrid orbital of another carbon atom to form C – C sigma bond.
- The two other sp2 hybrid orbitals of each carbon overlap with ‘s’ orbital of hydrogen atoms to form C – H bonds.
- The unhybridised orbital of one carbon atom overlap side wisely with the similar orbital to form weak n bond.
Question 12.
Write the postulates of Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases.
Answer:
Assumptions :
- Gases are composed of minute particles called molecules. All the molecules of a gas are identical.
- Gaseous molecules are always, at a random movement. The molecules are moving in all possible directions in straight lines with very high velocities. They keep on colliding against each other and against the walls of the vessel at very small intervals of time.
- The actual volume occupied by the molecules is negligible when compared to the total volume occupied by the gas.
- There is no appreciable attraction or repulsion between the molecules.
- There is no loss of kinetic energy when the molecules collide with each other or with the wall of vessel. This is because the molecules are spherical and perfectly elastic in nature.
- The pressure exerted by the gas is due to the bombardment of the molecules of the gas on the walls of the vessel.
- The average kinetic energy of the molecules of the gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature, Average K.E. oc T.
- The force of gravity has no effect on the speed of gas molecules.
Boyle’s law:
According to kinetic theory of gases, the pressure of a gas is due to collisions of gas molecules on the walls of the vessel. At a particular temperature the molecules make definite number of collisions with the, walls of the vessel; When the volume of the vessel is reduced the molecules have to travel lesser distance only before making collisions on the walls. As a result the number of collisions per unit increases. The pressure then increases, i.e., the pressure increases when the volume is reduced at constant temperature. This explains Boyle’s law.
Charles’ law :
According to kinetic theory of gases, the average kinetic energy of the molecules is directly propor-tional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
K.E. ∝ T
but K.E. = \(\frac{1}{2}\) m2
As temperature increases, the velocity of the molecules also increases. As a result the molecules make more number of collisions against the walls of the vessel. This results in an increase of pressure if the volume is kept constant. If the volume is allowed to increase the number of collisions de-crease due to the increased distance between the molecules and the walls of the vessel. The pressure then decreases. In other words, with rise of temperature, the volume should increase in order to keep the pressure constant.
V ∝ T at constant pressure.
This is Charles’ law.
![]()
Question 13.
How does Diborane react with the following :
(a) CO
(b) NH3
Answer:
a) Reaction with carbon monoxide :
Diborane reacts with CO at 100° C and 20 atm. pressure to form borane carbonyl.
![]()
b) Reaction with ammonia
Diborane reacts with ammonia at 120° C first forms B2H6.2NH3 (or) [BH2(2NH3)] + [BH2(NH3)2]+[BH4]– and on further heating forms borazole (or) borazine. Which is also called as “In organic ben-zene”. It has iso structural with benzene. Hence it is named as “In-organic Benzene”.
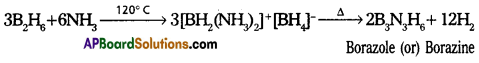
Question 14.
What is meant by Bond order? Calculate the bond orders in the following:
(a) N2
(b) O2+
Answer:
Bond order: The half of the difference between the no.of bond¬ing electrons and anti bonding electrons is known as bond order,
a) N2: Molecular orbital energy level sequence.
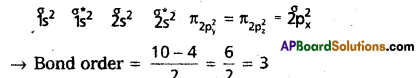
c) O3+: Molecular orbital energy level sequence is
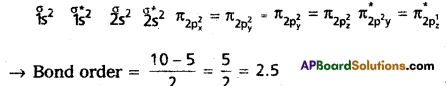
Question 15.
A carbon compound contains 12.8% Carbon, 2.1% Hydro-gen, 85.1% Bromine. The molecular weight of the com-pound is 187.9. Calculate the molecular formula.
Answer:
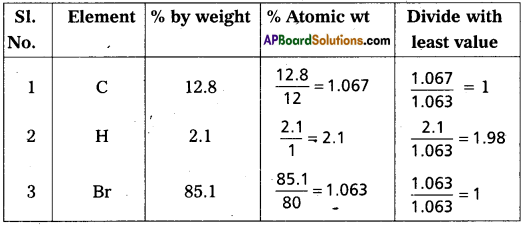
∴Emperical formula of the compound = C1 H2 Br
Molecular formula = n (Emperical formula)
n = \(\frac{\text { Molecular wt }}{\text { Emperical wt }}=\frac{187.9}{94}\)
Given molecular wt = 187.9
∴ Molecular formula = 2 (CH2Br)
Emperical wt = 94 (CH2Br)
= C2H2Br2
Question 16.
Derive the relation between Kb and Kc for the equilibrium reaction
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Answer:
Given equation (Equilibrium reaction)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Relation between Kp and Kc is
Kp = Kc(RT)∆n
∆n = np – nR
= 2 – (1 + 3) = -2
∆n = -2(-ve)
∴ Kp < Kc
![]()
Question 17.
Write any two oxidising and two reducing properties of H202 with equations.
Answer:
- H2O2 has the ability to function as an oxidising agent as well as reducing agent in both acid and alkaline solutions.
- In H22p oxidation state of oxygen is -1. It oxidised to O2. Here H2O2 is reductant.
- H2Op can be reduced to H2O (or) OH’. Here H2O2 is oxidant.
i) Oxidising action in acidic medium :
2Fe(aq)+2 + 2H(aq)+2 → 2Fe(aq)+3 + 2H2O(l)
ii) Reducing action in acidic medium :
2MnO4– + 6H+ + 5H2O2 → 2Mn+2 + 8H2O + 5O2
iii) Oxidising action in basic medium :
2Fe+2 + H2O2 → 2Fe+3 + 2OH–
iv) Reducing action in basic medium :
2MnO4– + 3H2O2 → 2MnO2 + 3O2 + 2H2O + 2OH–
Question 18.
a) SiF6-2 is known while SiCl6-2 is not. Explain,
a) SiF6-2 is known while SiCl6-2 is not. Explain,
b) Diamond has high melting point. Why?
Answer:
a) SiF6-2 is known while SiCl6-2 is not because
1. Si+4 has small size so it cannot be accomodate six large chloride
2. The interaction between lone pairs of Cl– ion and Si+4 is not very strong.
b) 1. In Diamond each carbon undergoes sp3 hybridisation and it is surrounded by four other carbon atoms with strong a – bonds tetrahedrally.
2. The C – C bond energy in diamond is very high and it has 3 – dimensional structure.
3. Due to these reasons diamond has high melting point.
4. It has melting point 4200 K.
19. What are Quantum Numbers? Explain the significance of Quantum Numbers.
Answer:
- In general a large no.of orbitals are posible in an atom.
- These orbitals are distinguished by their size, shape and orientation.
- An orbital of smaller size means there is more chance to find electron near the nucleus.
- Atomic orbitals are precisely distinguished by quantum numbers. Each orbital is designated by three major quan- turn numbers.
- Principal quantum number (n)
- Azimuthal quantum number (l)
- Magnetic quantum number (m)
1) Principal quantum number:
The principal quantum num-ber was introduced by Neils Bohr. It reveals the size of the atom (main energy levels). With increase in the value of ‘n’ the distance between the nucleus and the orbit also increases.
It is denoted by the letter ‘n’. It can have any simple integer value 1, 2, 3,…. but not zero. These are also termed as K, L, M, N etc.
The radius and energy of an orbit can be determined basing on “n” value.
The radius of nth orbit rn = \(\frac{n^2 h^2}{4 \pi^2 m^2}\)
The radius of nth orbit is En = \(\frac{-2 \pi^2 \cdot m e^4}{n^2 h^2}\)
2) Azimuthal quantum number:
It was proposed by Sommer- feld. It is also known as angular momentum quantum number or subsidiary quantum number. it indicates the shapes of orbitals. It is denoted by T. The values of T depend on the values of ‘n’, T has values ranging from ‘O’ to (n – 1) i.e., l = 0, 1, 2, …… (n – 1). The maximum number of electrons present in the subshells s, p, d, f are 2, 6, 10, 14 respec-tively
| Subshell | l – value | Shape |
| s | l = 0 | spherical symmetric |
| p | l = 1 | dumb – bell |
| d | l = 2 | double dumb – bell |
| f | l = 3 | four fold dumb – bell |
Energy levels and subshells
| Principal quantum number (n) | Azimuthal quantum number (0) | Symbol | Number of subshells |
| 1 | 0 | s | 1 (1s) |
| 2. | 1 | s | 2 (2s,2p) |
| 0 | p | ||
| 3. | 0 | s | 3 (3s,3p,sd) |
| 1 | p | ||
| 2 | d | ||
| 4. | 0 | s | 4 (4s, 4p, 4d, 4f) |
| 1 | p | ||
| 2 | d | ||
| 3 | f |
Magnetic quantum number :
It was proposed by Lande. It shows the orientation of the orbitals in space, ‘p’ – orbital has three orientations. The orbital oriented along the x-axis is called px orbital, along the y-axis is called py -orbited and along the z-axis is called pz orbital. In a similar way d – orbital has five orientations. They are dxy, dyz, dzx, dx2–y2 and dz2. It is denoted by’m’. Its values depends on azimuthal quantum number, ‘m’ can have all the integral values from -1 to +1 including zero. The total number of’m’ values are (2l + 1).
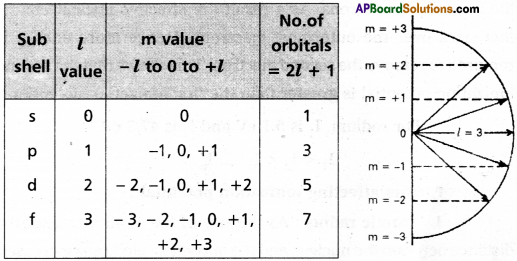
Question 20.
Define IE1, and IE2. Why IE2 > IE1 for a given atom? Discuss the factors that affect IE of an element.
Answer:
1) Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to re¬move the most loosely held electron from isolated a neutral gaseous atom to convert it into gaseous ion. It is also known as first ionization energy because it is the energy required to remove the first electron from the atom.
It is denoted as I1 and is expressed in electron volts per atom, kilo calories (of) kilo joules per mole.
M(g) + l1 → M(g) + e– I1 is first ionization potential.
2) The energy required to remove another electron from the unipositive ion is called the second ionization energy. It is denoted as I2.
M(g)+ + I2 → M(g)2+ + e–
3) The second ionization potential is greater than the first ionization potential. On removing an electron from an atom, the unipositive ion formed will have more effective nuclear charge than the number of electrons. As a result the effective nuclear charge increases over the outermost electrons. Hence more energy is required to remove the second electron. This shows that the second ionization potential is greater than the first ionization potential. For sodium, I1 is 5.1 eV and I2 is 47.3 eV I1 < I2 , I3 ……. In Factors affecting ionization potential:
1. Atomic radius :
As the size of the atom increases the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons increases. So the effective nuclear charge on the outermost electrons decreases. In such a case the energy required to remove the electrons also decreases. This shows that with an increase in atomic radius the ionization energy decreases.
2. Nuclear charge :
As the positive charge of the nucleus increases its attraction increases over the electrons. So it becomes more difficult to remove the electrons. This shows that the ionization energy increases as the nuclear charge increases.
3. Screening effect or shielding effect:
In multielectron atoms, valence electrons are attracted by the nucleus as well as repelled by electrons of inner shells. The electrons present in the inner shells screen the electrons present in the outermost orbit from the nucleus. As the number of electrons in the inner orbits increases, the screening effect increases. This reduces the effective nuclear charge over the outermost electrons. It is called screening or shielding effect. With the increase of screening effect the ionization potential decreases. Screening efficiency of the orbitals falls off in the order s > p > d > f.
(Magnitude of screening effect) ∝ \(\frac{1}{\text { (Ionization enthalpy) }}\)
TREND IN A GROUP:
The ionisation potential decreases in a group, gradually from top to bottom as the size of the elements increases down a group.
TREND IN A PERIOD:
In a period from left to right I.P. value increases as the size of the elements decreases along the period.
![]()
Question 21.
a) Describe any two methods of preparation of Benzene with corresponding equations.
b) How benzene reacts with the following :
(i) CH3Cl/Anhy. AlCl3
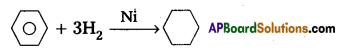
(ii) H2/Ni
Answer: Preparations of Benzene :
From Acetvle Acetyle undergo polymerisation in red hot metal tubes to form benzene
![]()
From Decarboxylation : Benzene is prepared by the decarboxylation of sodium benzoate
![]()
Reaction with halogen
Benzene reacts with halogens in presence of law is acid to for halobenzene.
C6H6 + X2 C2H5 X + HX
Reaction with Acetyl Chloride : Benzene reacts with acetyl chloride inpresence of A1C13 to for Acetophenone.
i) Benzene reacts with CH2C1 and A1CI3 to for methyl benzene (Toluene)
![]()
ii) Benzene reacts with hydrogen in presence of Ni to for Cyclohexane.