Access to a diverse set of AP 10th Class Social Model Papers Set 3 ensures a well-rounded preparation strategy.
AP 10th Class Social Model Paper Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3.15 hours
Max. Marks:100
Instructions:
- In the duration of 3 hours, 15 minutes, 15 minutes of time is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the separate booklet only.
- Question paper consists of 4 Sections and 33 Questions.
- Internal choice is available in Section IV only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section – I
12 × 1 = 12 M
Note :
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
Three movements of international economic exchanges.

Answer:
Flow of labour
Question 2.
Expand SEZ.
Answer:
Special Economic Zone
Question 3.
The place shown in the map with ‘?’ mark.
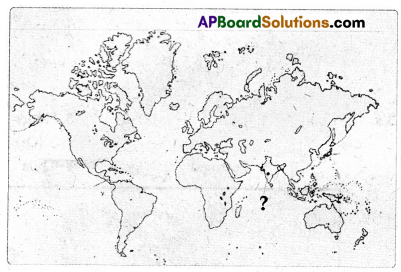
A) Cairo International Airport
B) Indira Gandhi International Airport
C) Kempegouda International Airport
D) Rajiv Gandhi International Airport
Answer:
Kempegouda International airport
Question 4.
Right to life is in our constitution under article …………………. .
Answer:
Article 21
![]()
Question 5.
Southwest monsoon first enters the state …………………… .
Answer:
Kerala
Question 6.
Which goods are taken into consideration when national income is calculated?
Answer:
Final goods.
Question 7.
Find the odd one out.
Yasar Arafat
Bin Laden
Saddam Hussain
Answer:
Bin Laden
Question 8.
Superpowers after World War – II
i. USSR
ii. …………………. .
Answer:
USA
Question 9.
Identify the unmatched pair.
i. Fidel Castroe – Latin America
ii. Salvador Allendee – Yugoslavia
iii. Nasser – Egypt
Answer:
ii (Salvador Allendee – Yugoslavia)
Question 10.
The establishment of a bipolar world by two superpowers are
A. Military supremacy
B. Economic supremacy
C. ………………………… . ?
Answer:
Ideological conflicts
Question 11.
“The nation on a move to throw away the shell of its past and ……………….. “is said by ………………….. .
Answer:
Jawahar Lal Nehru
Question 12.
“Whatever the situation in Pakistan, India would be a democratic secular state” – what is the context for the above statement?
Answer:
Partition of India as India and Pakistan.
![]()
Section – II
8 x 2 = 16 M
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 13.
Glaciers in the Himalayas are melting speedily. Write two problems by this speedily melting of glaciers.
Answer:
Problems with speedily melting of glaciers:
- Abnormal changes in climate and weather conditions.
- The levels of oceans and seas increase leading to submerging of lands surrounding them. The fertile lands become barren lands.
- The rivers like the Ganges, the Brahmaputra experience floods causing loss to crops and lands around them.
Question 14.
What is infanticide ? What is its effect on sex ratio?
Answer:
Infanticide refers to the act of killing of a newborn child. Feeling that a female child is a burden to the family, some families prefer infanticide. This adversely affects sex ratio as female population decreases.
Question 15.
Write two slogans that girls are to be educated.
Answer:
- Educating girls is educating total family.
- Girls’ education is a need to progress of a nation.
Question 16.
A part from rivers Narmada, Tapati, some more rivers like river Mahi, river Sabarmati, river Luni flow from east to west. In what sea do they merge?
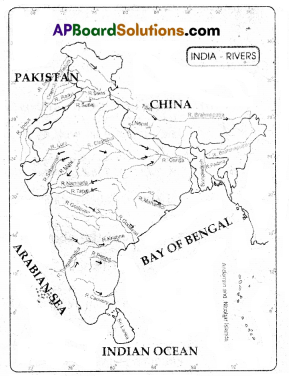
Answer:
Arabian sea.
Question 17.
What does the term Great Depression signify?
Answer:
There was worldwide economic decline triggered by a decline in demand and the fall in prices. It was called the Great Depression.
Question 18.
What was the promise asked by the Indians in 1939 to support Britain In the Second World War?
Answer:
A promise of full freedom to India.
![]()
Question 19.
What are the land reforms proposed by Jawaharlal Nehru?
Answer:
- Abolition of Zamindari system.
- Tenancy reforms.
- Land ceiling.
Question 20.
What are the two essential characteristics of a Unitary Constitution?
Answer:
- The supremacy of the central polity.
- The absence of subsidiary sovereign polities.
Section – III
8 × 4 = 32 M
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 21.
Make two pie charts (roughly) based on the information.
| Types of Farmers | Size of plots | Percentage of farmers | Percentage of cultivated area |
| Small farmers | Less than 2 hectares | 87% | 48% |
| Medium and large farmers | More than 2 hectares | 13% | 52% |
Answer:
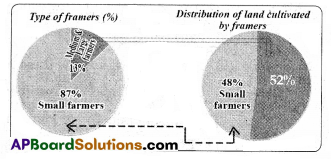
Question 22.
The Indian government came out with a new law in 2013 called the National Food Security Act to legalize people’s right to food. What do you suggest to implement this Act?
Answer:
I recommend the following suggestions to implement the National Food Security Act 2013.
- Public Distribution system should work properly.
- The government should encourage high-yielding food crops.
- The government should provide subsidies to the food products.
- To face the drought Government has to provide godown facilities.
Question 23.
Should the average temperature of the earth be treated as a natural resource for all people? Why?
Answer:
Yes, the average temperature of the earth be treated as a natural resource for all people. Taking the advantage of this renewable resource in the form of solar energy, people can reduce their dependency on non-renewable sources like coal, petroleum etc.
Question 24.
Read the text given below and write your opinion. The developments in information and communication technology have been even more remarkable and rapid. Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly to communicate from remote areas.
Answer:
- Rapid improvement in information and communication technology is one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process.
- Telecommunication using the internet in computers and mobiles facilitates to contact one another around the world very fast.
- This helped in saving paper and time.
- Social media like WhatsApp, Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram help to share information even from remote areas.
- The advanced information and communication technology helped to have access to vast information, to store it and to transmit and manipulate it.
- All these helped to have the world at our doorsteps.
- However, this is leading to abnormal plastic and fibre garbage which is causing environmental problems.
Question 25.
Right to Information Act resembles the true spirit of democracy. How do you justify?
Answer:
- Democracy according to Abraham Lincoln means government of the people, by the people and for the people.
- Through RTI, any citizen can approach any government department seeking any kind of information in written form or e-mail form at nominal prices (5/- or 10/-) in their local language.
- Therefore, this Act enables citizens informed about their government and officials making, them involved actively in the democracy.
- This ensures to prevention of corruption and makes public authorities more accountable and transparent. Eg: the 2G Spectrum case is revealed because of RTI filed by an activist.
Question 26.
What are the challenges faced by the independent Nigerian nation? In what ways is it similar or different from the challenges faced by Independent India?
Answer:
The challenges faced by the independent Nigerian nation were
- Very soon Nigeria slipped into civil war and military rule.
- Corruption and suppression of human rights.
- Military dictatorship followed.
- Reckless oil extraction created havoc in Coastal environment due to greediness of MNCs.
- Popular unrest grew steadily, various ethnic groups began demanding compensation for years of Ecological damage and control covering their lands, and oil resources.
Challenges faced by independent India where different. It became a democratic country and had challenges like refugees, poverty, and a merging of states into the Indian Union.
![]()
Question 27.
What aspects of the welfare state do you find functioning in India today?
Answer:
Welfare measures in India:
- Public Distribution System.
- Mid-Day meal scheme in government schools.
- Housing schemes. Eg: Pradhan Mantri Avas Yojana etc.
- MNREGA
- Old age pensions.
- Health schemes. Eg: Ayushman Bharat, YSR Aarogyasri etc.
Question 28.
Write the role of Dr. B.R. Amhedkar in preparing the draft Constitution of India.
Answer:
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was the chairman of the drafting committee.
- He prepared the draft Constitution and submitted it to the Constituent Assembly in 1948.
- The drafted Constitution had 395 Articles and 8 Schedules.
- He was a social revolutionary thinker and agitator against caste divisions and caste-based inequalities.
- For promotion of the depressed classes he created various provisions in the Constitution for their upliftment.
- He studied the important aspects of various Constitutions and included them in our Constitution, making it as the one of the best Constitutions in the world.
Section-IV
5 x 8 = 40 M
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 8 marks.
3) Each question has internal choice.
4) In question no.33, both A and B (India map and World map) should be answered separately.
Question 29.
A) What are the disagreements between ‘developed and developing’ countries about AGW?
(OR)
B) There have been various ways in which changes occurred in the context of water resources. Describe the positive as well as negative social changes.
Answer:
A)
- An international effort to form an agreement whereby all countries try to reduce their emission of greenhouse gases has so far not been achieved.
- The disagreements are between the developed countries and developing countries.
- Developed countries want developing countries to cut down on burning coal and other activities that add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
- Developing countries argue that developed countries developed precisely by burning fossil fuels in their development and their economic development will be seriously damaged if they don’t burn fossil fuels.
- Developing countries also argue that developed countries should do their fair share of work to find alternatives that can help the developing countries to progress.
B) Positive Social changes:
- Understanding the process of groundwater regulation by the community levels.
- Making arrangements that a portion of rainfall percolates into the soil and travel into the underground and recharge the aquifers.
- Continuous Contour trenches to be dug on the bill slopes to arrest the erosion of soil, harvest water and encourage growth of grass.
- Ban on free grazing and on felling trees.
- Recycling of used water.
Negative Social changes:
- Over-extraction from one tube well often dries up other tube wells around.
- Industries and individual landowners have no restriction on the extraction of the groundwater.
- Due to mining, dust, soil erosion, debris etc. reservoirs and tanks have lost their storage capacity.
- Urbanisation.
Question 30.
A) ‘If even the idea of what constitutes development can be varied and conflicting, then certainly there can be differences about ways of developing.’
Q. Support the above statement by taking the example of protest against Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project.
(OR)
B) As the population increased, there was more specialization – weavers, potters, metal workers and other professions emerged. The number and variety of goods produced increased and so did the trade in them. Rulers began to encourage craft persons to settle, in urban areas. Urban settlements i.e. towns where people did not work in agriculture expanded. As settlements became larger, they also became more complex because there were more functions to be performed – food production was not the only concern. Within each settlement, people specialised in certain skills. Many goods were produced for the market and sold to traders who carried them to far-off places.
Q. Explain the sequence of emergence of towns.
Answer:
A)
- The Government of India established a Nuclear Power Project near Kudankulam in Tirunelveli district of Tamilnadu.
- Kudankulam is a coastal town with fisher folks.
Developmental goal of the government:
The aim is to generate nuclear power to meet the growing energy needs of the country.
Developmental goal of the local people:
The local people want safety, security and livelihood.
Conflicting developmental goals:
Both the government and the local people have different developmental goals which are conflicting to each other: The local people with the support of scientists, environmentalists and social activists protested against the establishment of Nuclear Power Project. But on the other side government said it had taken all the safety measures for the welfare of the local people.
B)
- The way we organise ourselves and our living spaces in a place is called a settlement. It is a geographic space where we live and work. In a settlement, we have different kinds of educational, religious and commercial activities.
- Production of food and agriculture brought many changes in human lifestyles.
- As agriculture progressed, people adopted advanced techniques in agriculture.
- As settlements become larger, more complex functions are to be performed. Food production was not the only concern. People specialised in certain skills and they produced many goods.
- This lead to urbanisation to get markets for produced goods.
- In order to produce goods on large scale, advanced techniques are adopted inviting more manpower, and infrastructure facilities.
- Thus, small villages became towns.
![]()
Question 31.
A)
The Congress was torn in its mind over the question. Most Congress leaders were opposed to Hitler; Mussolini and the ideology of fascism. They were determined to resist the Fascist drive to conquer other sovereign nations. The Congress expected that the British would see their double standards in the expectation that India should support them in fighting the fascists but not giving (or at least promising) India full freedom. The British realised this but, at the same time, it was hard for them to accept that they will really have to dismantle the empire they had built.
There were different political parties in Britain. At the time of the War, Britain had an all-party government headed by Prime Minister Winston Churchill of the Conservative Party. The Conservatives were keen to retain the empire for as long as was possible. In comparison to the Conservatives, the abour party was more willing to help Indians attain freedom.
Read the above information and fill in the table:
| Fascism (Meaning) | |
| Supporter of fascism | |
| The two political parties in Britain | |
| The party that favoured India’s freedom |
(OR)
B) Substitute the suitable content in empty box.
| 1. Sun-Yat-sen | |
| 2. | Clashes in Hausa -Fulani, Yoruba, Igbo tribes in Nigeria |
| 3. | Peace settlement was signed in Pans by which war came to an end between USA and Vietnam. |
| 4. National Council of Nigeria and Cameroon |
a) 1974 January
b) San-Min-Chui, the three principles
c) Movement against Versailles Treaty in Beijing.
d) Agreement between Herbert Macauley and Azikiwe.
e) Effect of divide and rule policy.
Answer:
A)
| Fascism | A form of dictatorship |
| Supporter of fascism | Mussolini |
| The two political parties in Britain | The Labour Party and the Conservative Party |
| The party that favoured India’s freedom | The Labour Party |
B)
| 1. Sun -Yat-sen | San – Min – Chui, that three principles. |
| 2. Effect of Divide and Rule policy. | Clashes in Hausa -Fulani, Yoruba, Igbo tribes in Nigeria |
| 3. 1974 January | Peace settlement was signed in Paris by which war came to an end between USA and Vietnam. |
| 4. National Council of Nigeria and Cameroon. | Agreement between Herbert Macaulay and Azikiwe. |
Question 32.
A) Why were the railways and canals developed in Vietnam by the French?
(OR)
B) Before independence, driving away the British was the only duty or work of political parties. Nowadays what work is being done by political parties in India?
Answer:
A)
- French-built canals drained lands in Mekong Delta.
- Rice production increased. Rice became available for export. The area under rice cultivation increased from 2,74,000 hectares to 2.2 million in 1930.
- It became third largest exporter. Two-thirds of rice production was exported.
- French developed railways, linking northern and southern parts. It was linked with Siam (Modem Thailand).
5. The French did all this for their interests only. The purpose of developing railways and canals were not for developing Vietnam but to flourish through the following:
- transport of goods for trade,
- army movement,
- control entire region,
- ensure higher level of profit for French businessmen.
B)
All the political parties fought with a single aim for freedom of our country. After the independence, the aim and work of political parties changed.
1. Now, the political parties are more concentrating on populous welfare schemes like free power to agriculture, old age pensions, stipends to unemployed graduates instead of creating stabilised economy. They are for short-term political benefits but not with vision for sustainable development.
2. The present political parties are more aiming at grabbing power and stick to it at any cost. For this, they are ready to play religious, caste, colour, regional cards.
3. At the time of independence, the aim is to establish socialist economy and to develop Indian indigenous industries and handicrafts. But by passage of time, now the political parties forgot it. They are forced to open up and liberalise economy by allowing free flow of foreign capital and goods into India. This poses a big threat to indigenous Indian industries.
4. At the time of independence, the political parties had leaders that breathed to the last of their lives for the secular democratic values. Now major political parties are working with selfish motives.
Question 33.
A)
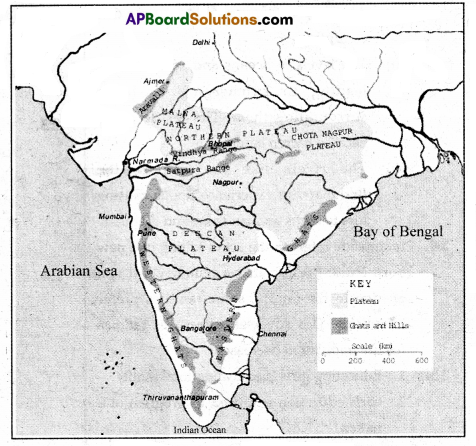
a) Answer the following looking at given map.
i) Name the ghats which are continuous and which are not continuous.
ii) What is the plateau that exists between south of Gangetic plains and north of river Narmada?
iii) Name two cities shown in the map of Deccan plateau region.
iv) In which sea do rivers Godavari and Krishna merge.
(OR)
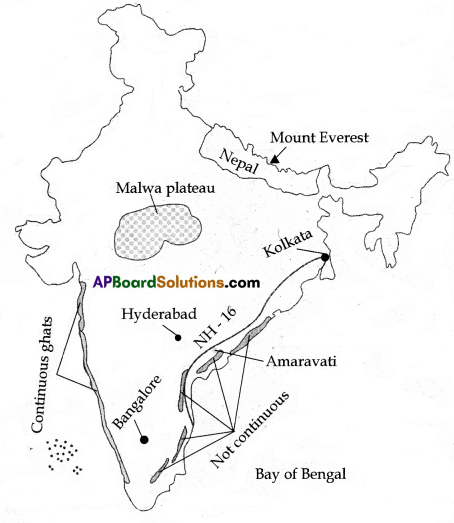
b) Locate the following underlined places in India Map.
1) NH 16
2) Kolkata
3) Mount Everest
4) Amaravati
Answer:
A)
a)
- Continuous ghats – Western ghats
Not continuous ghats – Eastern ghats - Malwa plateau.
- Hyderabad and Bangalore.
- Bay of Bengal.
(or)
b)
- NH-16
- Kolkata
- Mount Everest
- Amaravati
![]()
B)
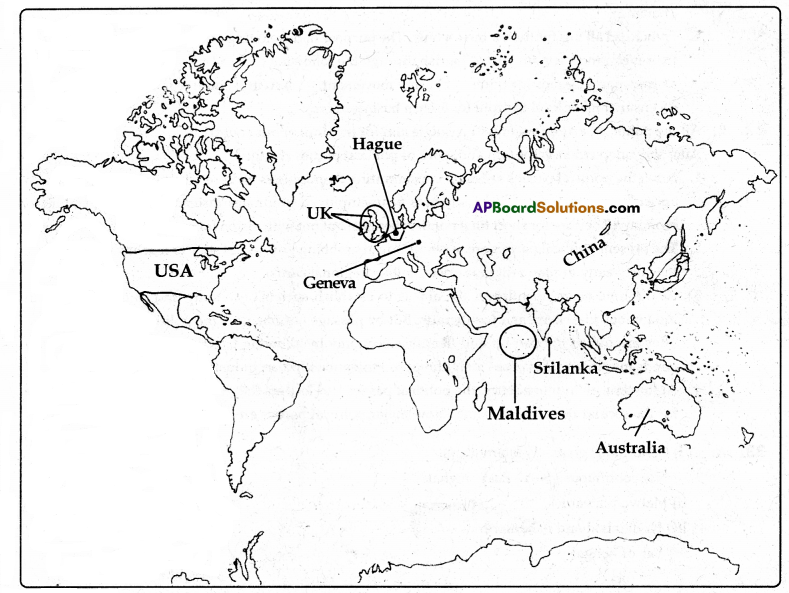
a) Locate the following underlined places in the world map.
1) Geneva
2) China
3) United Kingdom
4) USA
(OR)
b)
1) Sri Lanka
2) Hague
3) Australia
4) Maldives
Answer:
a)
- Geneva
- China
- United Kingdom
- USA
(or)
b)
- Sri Lanka
- Hague
- Australia
- Maldives