Solving AP 10th Class Physical Science Model Papers Set 4 regularly is an effective strategy for time management during exams.
AP SSC Physical Science Model Paper Set 4 with Solutions
Time: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 50
Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 4 sections and 17 questions.
- Internal choice is available only for Q.No.12 in section III and for all the questions in section IV.
- In 2 hours, 15 minutes is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the answer booklet only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section-I
(8 × 1 = 8 Marks)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
Find the focal length of a piano convex lens, when its radius of curvature of the surface is R and n is the refractive index of the lens.
Answer:
f = \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{\mathrm{n}-1}\)
Question 2.
The most and the least electronegative element pairs among the following is:
(a) Oxygen, Fluorine
(b) Fluorine, Oxygen
(c) Fluorine, Cesium
(d) Carbon, Fluorine
Answer:
(c) Fluorine, Cesium
Question 3.
Which of the following molecules doesn’t have sp3 hybridization?
(CH4, BF3, NH3, H2O)
Answer:
BF3
![]()
Question 4.
Match the suitable answers of Section-B, with Section-A.
| Section-A | Section-B |
| 1. Formula for refractive index | (P) V/C |
| 2. Possible values of refractive index | (Q) C/V |
| (R) > 1 | |
| (S) < 1 |
Answer:
1 – Q, 2 – R
Question 5.
From the given figure, in which thermometer (A or B) mercury level increases.
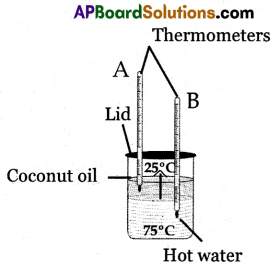
Answer:
Thermometer ‘A’
Question 6.
Take 2 ml of NaOH in a test tube, add two drops of phenolphthalein solution, and then add a few drops of dil. HCl to it. What is your observation concerning colour?
Answer:
It turns pink when NaOH is added to it, and it loses its pink colour when HCl is added.
Question 7.
Draw the shape of the V-I graph of a Non-Ohmic conductor.
Answer:
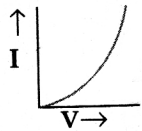
V-I graph for Non-Ohmic conductors will be non-linear.
Question 8.
Complete the following table.
| Element | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration |
| Boron | ____(1)____ | 1s2 2s2 2p1 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | ____(2)_____ |
Answer:
1. 5
2. 1s2 2s2 2p3
Section-II
(3 × 2 = 6 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 9.
Why should we connect electric appliances in parallel to household circuits? What happens if they are connected in a series?
Answer:
We should connect the electric appliances in parallel to the the household circuit because if they are connected in series, then if one of them is turned off, the rest will also shut off and the potential is distributed. For a typical household appliance, the voltage should be the same.
Question 10.
The sun appears red during sunrise and sunset. Give reason.
Answer:
The sun appears red during sunset and sunrise because at this time the sun is far from the earth and the light that reaches the earth from the sun scatters the most and all other colours of light get scattered. The least scattered light is red and it enters our eye.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention any two uses of graphite in day-to-day life.
Answer:
Uses of graphite in daily life:
- It is used as a lubricant.
- It is used as lead in pencil.
- It is used as an electrode in batteries.
- It is used in graphene sheets.
Section-III
(3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 12.
Draw any one of the following diagrams:
(A) Draw a neat diagram of the froth floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ore and why we add pine oil to the mixture in this process.
(OR)
(B) Draw the magnetic field lines formed by the bar magnet and solenoid and compare them.
Answer:
(A) Froth floatation:
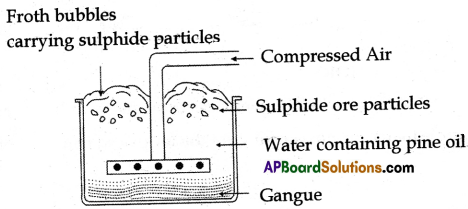
Froth floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ores
To get more foam we add pine oil to the mixture
(OR)
(B)
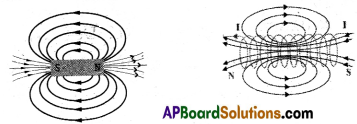
Magnetic field lines due to bar magnet Magnetic field lines due to solenoid
- The magnetic field lines set up by a solenoid resemble those of a bar magnet.
- Solenoid behaves like a bar magnet.
- Like a bar magnet having north and south poles, one end of the solenoid behaves like a north pole and the other behaves like a south pole.
- The field lines are closed loops.
Question 13.
“A boy who is suffering from eye defect has been given a prescription as – 2D.” Based on the information given, answer the following questions.
(a) Identify the eye defect he is suffering.
(b) Write the nature and focal length of the lens.
Answer:
(a) The power of the lens is -ve. So it is a concave lens. Hence the boy is suffering from Myopia.
(b) Lens is concave.
P = \(\frac{1}{f_{(m)}}\)
f(m) = \(\frac{1}{P}\)
= \(\frac{1}{-2}\)
= 0.5 m
= -50 cm
∴ Focal length of the lens = 50 cm
![]()
Question 14.
A house has 3 tube lights of 20 watts each. On average, all the tube lights are kept on for five hours. Find the energy consumed in 30 days.
Answer:
Energy consumed = Power × time
Power = 20 watts, time = 5 hours, No. of lights = 3
∴ Energy consumed by 1 light in one day = 1 × power × time × 1
= 1 × 20 × 5 × 1
= 100 watt-hours
Energy consumed by 3 lights in 30 days = 3 × 20 × 5 × 30
= 9000 watt-hours
= 9 KWH
Section-IV
(3 x 8 = 24 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 8 marks.
- Each question has an internal choice.
Question 15.
(A) Explain
(i) Why do stars appear twinkling?
(ii) Brilliance of Diamond
(OR)
(B) Explain the working of an electric motor with a neat diagram.
Answer:
(A) (i) (i) Stars appear to be twinkling due to atmospheric refraction.
(ii) Starlight reaches the surface of the earth through many layers of atmosphere.
(iii) These layers have different optical densities due to which they offer different refractive index values to the incoming light.
(iv) So, the light bends many times giving different apparent positions of the star which we see as twinkling.

(ii) (i) Total internal reflection is the main cause for the brilliance of diamonds.
(ii) The critical angle of diamonds is shallow (24.4°)
(iii) Due to repeated internal reflections diamond sparkles.
(iv) By cutting the diamond in such a way that the incident angle at each place is greater than the critical angle (C), T.I.R will take place again and again.
(v) The simple transparent crystal by cutting utilizes the principle of T.I.R and gets the same brilliance as the diamond.
(OR)
(B) Electric motor: An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Principle: It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force.
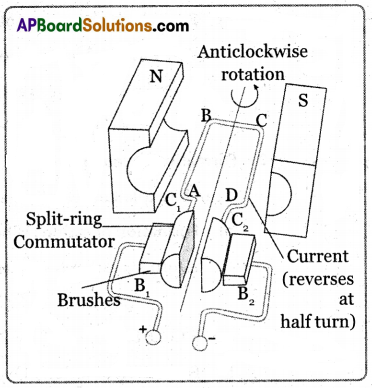
Working Procedure:
- It consists of the armature, a strong horseshoe-type magnet, split rings, and carbon brushes.
- Initially let the plane of the coil be in a horizontal position.
- The split ring touches brush B1 and split ring C2 touches brush B2 when the current flows in the direction ABCD as shown in the figure.
- According to the right-hand rule, no force acts on arm CB and DA because they are parallel to the magnetic field.
- The force acting on the arm AB pushes it downwards while the force acting on the arm CD pushes it upwards. So the armature rotates in the anti-clockwise direction.
- After half a rotation the split ring comes in contact with brush B2 and C2 in contact with brush Br So the current in the coil is reversed and flows in the direction DCBA.
- If the direction of the current in the coil is unchanged the coil gets to and fro motion.
- In an electric motor, the split rings act as a commutator that reverses the direction of the flow of current through a circuit.
- Now the coil rotates continuously in the anti-clockwise direction.
Question 16.
(A) Explain the Aufbau principle with an example.
(OR)
(B) Explain the formation of sodium chloride and calcium oxide based on the concept of electron transfer from one atom to another atom.
Answer:
(A) In the ground state the electronic configuration can be built up by placing electrons in the lowest available orbitals until the total number of electrons added is equal to the atomic number. This is called the Aufbau principle.
Two general rules help us to predict the electronic configurations.
(i) Electrons are assigned to orbitals in order of increasing value of (n + l)
Eg: for 2s orbital (n + l) = 2 + 0 = 2
for 3s orbital (n + l) = 3 + 0 = 3
Hence, 2s has lower energy than 3s orbital.
(ii) For subshells with the same value of (n + l), electrons are assigned first to the subshell with a lower ‘n’ value.
Eg: (n + l) value of 2p = 2 + 1 = 3
(n + l) value of 3s = 3 + 0 = 3
Here electrons are first assigned to the 2s orbital.
(OR)
(B) 1. Formation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl):
Sodium chloride is formed from the elements sodium and chlorine. It can be explained as follows.
(a) Formation of Cation: When a sodium atom loses one electron to get an octet electron configuration it forms a cation (Na+) and gets an electron configuration that of Neon (Ne).
Na → Na+ + e–
E.C: 2, 8, 1 2, 8
(b) Formation of anion: Chlorine has a shortage of one electron to get an octet in its valence shell. So it gains the electron that was lost by Na to form anion (Cl–) and gets the electron configuration that of Argon (Ar).
Cl + e– → Cl–
E.C: 2, 8, 7 2, 8, 8
(c) Formation of the compound NaCl from ions: Transfer of electrons between ‘Na’ and ‘Cl’ atoms, they form Na+ and Cl– ions. These oppositely charged ions get attracted towards each other due to electrostatic forces and form the compound sodium chloride (NaCl).
Na+ (g) + Cl– (g) → NaCl (s)
2. Formation of Calcium Oxide (CaO):
Calcium Oxide is formed from the elements Calcium and Oxygen. It can be explained as follows:
(a) Formation of cation: When a calcium atom loses two electrons to get an octet electronic configuration it forms a cation (Ca+2) and gets an electron configuration that of Argon (Ar).
Ca + 2e– → Ca+2
E.C: 2, 8, 8, 2 2, 8, 8
(b) Formation of anion: Oxygen has a shortage of two electrons to get an octet in its valence shell. So it gains the electron that was lost by Ca to form anion (O-2) and gets an electron configuration that of Neon (Ne).
O + 2e– → O-2
E.C: 2, 6 2, 8
(c) Formation of the compound CaO from ions: Transfer of electrons between ‘Ca’ and ‘O’ atoms, they form Ca+2 and O-2 ions. These oppositely charged ions get attracted towards each other due to electrostatic forces and form the compound calcium oxide (CaO).
Ca+2 (g) + O-2 (g) → CaO (s)
![]()
Question 17.
(A) Explain the procedure of finding the specific heat of a solid experimentally.
(OR)
(B) What is meant by “Water of crystallization” of a substance? Describe an activity to show the water of crystallization.
Answer:
(A) Aim: To find the specific heat of a given solid.
Apparatus: Calorimeter, thermometer, stirrer, water, steam heater, wooden box and lead shots.
Procedure:
(i) Measure the mass of the calorimeter along with the stirrer. Mass of calorimeter = m1
(ii) Now fill one-third of the volume of the calorimeter with water. Measure its mass and its temperature.
Mass of calorimeter with water = m2
∴ Mass of water = m2 – m1
Temperature of water in calorimeter = T1
(iii) Take a few lead shots and place them in hot water or steam heater. Heat them upto a temperature of 100° C. Let this temperature be T2.
(iv) Transfer the hot lead shots quickly into the calorimeter (with minimum loss of heat.) We will observe that the mixture settles to a certain temperature after some time.
(v) Measure this temperature T3 and mass of calorimeter along with contents (water and lead shots).
Mass of the calorimeter along with contents = m3
∴ Mass of the lead shots = m3 – m2
(vi) Since there is no loss of heat to surroundings, we can assume that the entire heat lost by the solid is transferred to the calorimeter and water to reach the final temperature.
(vii) Let the specific heats of the calorimeter, lead shots, and water be Sc, Sl, and Sw respectively. According to the method of mixtures, we know
Heat lost by the solid = Heat gain by the calorimeter + Heat gain by the water
(m3 – m2) Sl (T2 – T3) = m1 SC (T3 – T1) + (m2 – m1) SW (T3 – T1)
Sl = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{m}_1 \mathrm{~S}_{\mathrm{c}}\left(\mathrm{T}_3-\mathrm{T}_1\right)+\left(\mathrm{m}_2-\mathrm{m}_1\right) \mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{w}}\left(\mathrm{T}_3-\mathrm{T}_1\right)\right]}{\left(\mathrm{m}_3-\mathrm{m}_2\right)\left(\mathrm{T}_2-\mathrm{T}_3\right)}\)
(viii) Knowing the specific heat of the calorimeter and water, we can calculate the specific heat of the solid (lead shots).
(OR)
(B) Water of Crystallization: Water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules chemically attached to each formula unit of a salt in its crystalline form. The salts which contain water of crystallization are called hydrated salts.
Activity:
- Take a few crystals of copper sulphate in a dry test tube.
- Heat the crystals strongly by keeping the test tube over the flame of a burner for some time.
- On heating the blue-coloured copper sulphate crystals turn white and a powdery substance is formed.
- We can also see tiny droplets of water in the test tube.
- Now cool the test tube and add 2 or 3 drops of water to the white copper sulphate powder formed above.
- The blue colour of copper sulphate crystals is reformed. They become blue again.
- From the above activity, we conclude that some water molecules are fixed in the blue-coloured copper sulphate crystals.