Access to a diverse set of AP 10th Class Social Model Papers and AP 10th Class Social Question Paper June 2023 ensures a well-rounded preparation strategy.
AP 10th Class Social Question Paper June 2023 with Solutions
Time: 3.15 hours
Max. Marks: 100
Instructions:
- In the duration of 3 hours, 15 minutes, 15 minutes of time is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the separate booklet only.
- Question paper consists of 4 Sections and 33 Questions.
- Internal choice is available in Section IV only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section -1
12 × 1 = 12 M
Note:
1. Answer all the questions.
2. Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
Which Himalayan range is famous for hill stations?
Answer:
Himachal ranges or Lesser Himalayas.
Question 2.
Define Gross Domestic Product.
Answer:
Total value of goods and services produced in the country in a year.
Question 3.
What is meant by literacy rate?
Answer:
Literacy rate is the number of people per hundred, aged 7 years and above who can read and write with understanding of any language.
Question 4.
Give two examples for Multinational Companies.
Answer:
Reliance, Wipro, Coco-Cola, Nike, Honda, Nokia.
![]()
Question 5.
Name two mega cities in India.
Answer:
Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata
Question 6.
Fill up the blank with right answer.
Hitler: Germany:: Stalin: …………………. .
Answer:
Russia
Question 7.
Expand NATO.
Answer:
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Question 8.
The popular slogan “Garibi Hatao” was given by whom?
Answer:
Smt. Indira Gandhi
Question 9.
“It is the right of the most powerful race to conquer the world”. Who said these words?
Answer:
Hitler
Question 10.
The World War – I ended with which Treaty?
Answer:
The Treaty of Versailles.
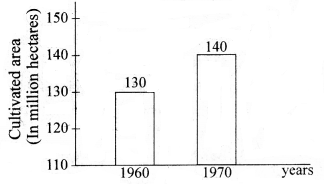
Question 11.
Plot the following information on a Bar Graph.
| Year | Cultivated Area (In million hec.) |
| 1960 | 130 |
| 1970 | 140 |
Answer:
Question 12.
Arrange the following rivers from North to South.
Ganga, Godavari, Narmada, Kaveri
Answer:
Ganga, Narmada, Godavari, Kaveri.
Section – II
8 × 2 = 16 M
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 13.
What is the Environmental sink function?
Answer:
An environment’s ability to absorb and render harmless waste and pollution is known as the Environmental sink function.
Question 14.
Suggest two measures to control the population.
Answer:
- Creating awareness among the people on problems of overpopulation.
- Incentives to the people who adopt small family system.
Question 15.
Name the two Island groups of India.
Answer:
- Andaman and Nicobar.
- Lakshadweep.
Question 16.
Name the present President and the Vice President of India.
Answer:
- President, Smt. Droupadi Murmu
- Vice President, Sri Jagdeep Dbankar
![]()
Question 17.
Write two slogans on the importance of Education.
Answer:
- Education is the way to real freedom.
- Education improves knowledge and skill.
Question 18.
“Coalition Government causes Policy Paralysis” – Comment.
Answer:
- Parties in coalition government insist the government to take decisions for their own benefit.
- So it is always difficult for ruling parties to move on decisions with the fear of withdrawal of support by parties.
Question 19.
Read the above map and answer the following questions.
(i) People of which tribe dominates the Northern Nigeria?
(ii) Which country colonised Nigeria?
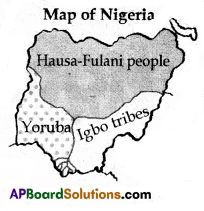
Answer:
i. Housa – Fulani people.
ii. The British
Question 20.
Based on the below Pie chart, write your observations.
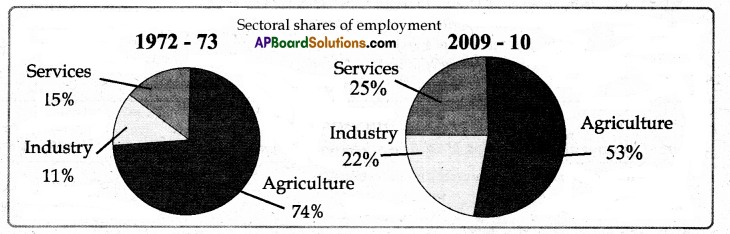
Answer:
- The Pie charts show the sectoral shares of employment in CUP during 1972-73 and 2009-2010.
- Share of Agriculture sector declined from 74% to 53% and Industrial, service sector shares increased from 11% to 22% and 15% to 25% respectively.
Section – III
8 × 4 = 32
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 21.
Why did Eric Hobshawrn call the 20th Century “the age of extremes”?
Answer:
- The world saw the. shoots of democratic aspirations grow amidst the rise of fascist domination.
- Literacy levels, average life expectancy grew immensely.
- New art forms like movies emerged.
- Scientific knowledge rose to new heights.
- Women got right to vote.
- This period experienced the great depression causing huge unemployment.
- Enormous human loss due to the world wars.
Question 22.
Explain the conditions during the emergency period.
Answer:
- General elections were postponed.
- The Fundamental Rights of the citizens were suspended.
- Press and media was censored.
- Opponent political party leaders were imprisoned.
- There were instances of arbitrary detention and torture.
![]()
Question 23.
“The impact of Globalisation is not uniform”. How?
Answer:
- The impact of globalisation in India is not uniform.
- It has benefited well-off consumers.
- It has also benefited the producers with skill, education and huge wealth.
- Certain services enabled with technology have expanded.
- Some new jobs are created.
- Some large Indian companies have grown as MNCs.
- On the other hand, most of the small producers and workers suffered due to globalisation.
- They lost their employment and rights.
Question 24.
Make a list of challenges due to Global warming.
Answer:
- The Himalayan Glaciers and ice in polir regions melt laster.
- Sea levels may raise.
- Coastal areas would be drowned.
- Millions of people would have to be shifted.
- Changes in the living conditions of flora and fauna may occur.
- Seasonal varitioncycIe may get disturbed causing huge loss in agriculture.
Question 25.
Write the benefits of RTI Act.
Answer:
- Right to Information Act enables citizens to get the required information from government.
- This makes the government accountable to individual citizens also.
- This improves transparency.
- RTI Act enriches democracy.
Question 26.
Describe the greatness of schooling revolution in Himachal Pradesh.
Answer:
- The Government and the people of Himachal Pradesh were very keen on Education.
- Government opened many schools and spent sufficient amount on infrastructure.
- They saw that the education was largely free.
- Provided good share for education in budget.
- Most of the students enjoy their schooling experience.
- Himachal parents give equal importance to girls’ education also.
Question 27.
Observe the below timeline and answer the following questions.
Timeline
| Proclamation of the Weimar Republic. | November 9, 1918 |
| Hitler becomes Chancellor of Germany. | January 30, 1933 |
| Germany invades Poland, the beginning of the Second World War. | September 1, 1939 |
| Germany invades the USSR. | June 22, 1941 |
| Mass murder of the Jews begins. | June 23, 1941 |
| The United States joined Second World War. | December 8, 1941 |
| Soviet troops liberate Auschwitz | January 27, 1945 |
| Allied victory in Europe | May 8, 1945 |
(i) Expand USSR.
(ii) What was the immediate cause for World War II?
(iii) Who became the Chancellor of Germany in 1933?
(iv) When did USA join in World War II?
Soviet troops liberate Auschwitz.
Answer:
i. Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
ii. Hitler’s invasion of Poland on 1st September 1939.
iii. Hitler
iv. On December 8, 1941.
Question 28.
Read the below map and answer the following questions.
(i) In which hemisphere is India located with reference to latitudes?
(ii) Name the smallest continent.
(iii) In which continent is India located?
(iv) Name the biggest ocean.

Answer:
i. Northern Hemisphere
ii. Australia
iii. Asia
iv. The Pacific Ocean
SECTION – IV
5 x 8 =40 M
Note:
1) Answer all the questions.
2) Each question carries 8 marks.
3) Each question has internal choice.
4) In question no.33, both A and B (India map and World map) should be answered separately.
![]()
Question 29.
(A) Explain the uses of Himalayas.
(OR)
(B) Explain the integration of Princely States in India.
Answer:
A)
- The Himalayas protect India in many ways.
- They act as barriers to the cold winds from central Asia.
- They are the reason for summer rains in India.
- They are the reason for monsoon type of climate in India.
- They are the origin of many perennial rivers such as Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
- The alluvial soil brought down by these rivers makes the plains very fertile.
- They have a great forest wealth.
- These thick forests provide us valuable timber and medicinal herbs etc.
(OR)
B)
- There were around 550 Princely states by the time of independence.
- They were asked to decide if they wanted to join India, Pakistan or remain independent.
- Sardar Patel was given charge of integration of them in Indian Union.
- He completed the task successfully.
- He warned the princely states that if they did not join Indian Union, the army would have to be sent.
- By 15th August 1947, all states except three had agreed to join the Indian Union. .
- Those three were Kashmir, Hyderabad, and Junagadh.
- Unification of these three states was also completed in the next two years.
Question 30.
(A) How does PDS ensure better food security for people?
(OR)
(B) What measures were taken to bring socio-economic change during the initial years after independence?
Answer:
A)
- Public Distribution System ensured food security to people.
- Ration shops are important means for people to assure food security.
- All the poor people get food grains at low prices through these shops.
- Even among the poor, the very poor have different entitlements.
- For example, the Antyodaya cardholders get 35 kgs of food grains per month per family.
- For school children, as part of Midday meal programme, government provides free cooked meal.
- Anganwadis provide nutritious food to kids, preschool children, and pregnant women.
- National Food Security Act -2013 ensures Food Security in India.
(OR)
B) Measures taken to bring in Socio-economic change during the initial years after independence are …
- Planning Commission was set up within a month of inauguration of the new Constitution.
- Five Year Plans were implemented to achieve progress in various sectors.
- Nehru adopted a strategy to achieve social, economic transformation of rural sector.
- As a part of land reforms, Acts on abolition of Zamindari System, tenancy reforms, and land ceilings were implemented.
- Agriculture cooperative societies were supposed to bring unity among members and provide valuable inputs like seeds, manure, fertilizers, etc.
- Local self-governments were ensured for effective implementation of government initiatives.
Question 31.
(A) Read the following paragraph and comment.
The current laws about groundwater in many states are both outdated and inappropriate. They were developed at a time when groundwater was a marginal source of water. Today shallow and deep tube wells have the potential to draw a lot of water. What should be judicious way of using this water?
(OR)
(B) Read the following paragraph and comment.
The makers of Indian Constitution confronted the fact that Indian society was ridden with inequality injustice and deprivation and was victim of colonial policies which had to facilitate social change and also development. Jawaharlal Nehru said, ‘the Constituent Assembly represents the nation on a move throwing away the shell of its past political and possibly social structure and fashioning for itself a new garment in its own making’s”
Answer:
A)
- According to the current laws, landowners have the rights over the ground water too.
- There are no restrictions on how much of water can be extracted.
- Heavy extraction of water affects other areas also.
- The water stock that would be available for future generations also will be decreased.
- Today ground water is the major source of water for the people.
- So the present groundwater laws should be changed.
- Landowners should not be allowed to extract as much water as they wish.
- There should be some restrictions on this.
- We cannot create any boundaries for groundwater because it is a flowing resource as air.
- So the groundwater should be treated as a common pool resource.
(OR)
B)The following measures were taken to facilitate social change.
- Abolition of untouchability.
- Reservations in education and public sector jobs for SC, ST, and other backward sections.
- Reservations in legislatures.
- Special protections for minorities’ rights.
Question 32.
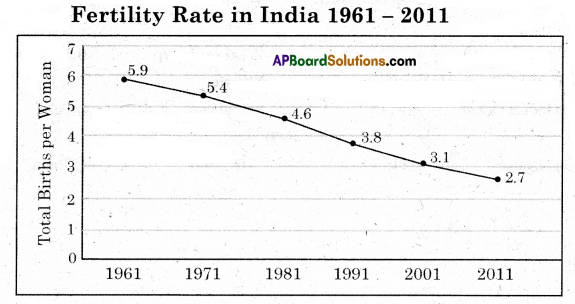
(A) Read the information of the given graph. Plot it in a table and write your observations on it.
(B) Read the timeline and answer the following questions.
| End of emergency and formation of Janata Party Governments under Morarji Desai and Charan Singh | 1977 |
| Formation of Congress Government led by Indira Gandhi | 1980 |
| Formation of TDP | 1982 |
| Operation Blue Star and the Assassination of Indira Gandhi | 1984 |
| Rajiv Gandhi Accords with HS Longowal on Punjab and AASU on Assam | 1985 |
| According with Mizo National Front | 1986 |
| Agreement with Sri Lanka | 1987 |
| Election and formation of Janata Dal Government with V.P Singh and Chandrasekhar | 1989 |
| Decision to implement Mandal Commission Recommendation | 1989 |
| Ram Janmabhoomi Rath Yatra | 1990 |
| Assassination of Rajiv Gandhi and Government led by Congress party with P.V. Narasimha Rao as P.M. | 1991 |
| Economic Liberalisation | 1990 |
| Demolition of Babri Masjid | 1992 |
| National Front Government with Deve Gowda and l.K. Gujral as PMs | 1996 |
| NDA Government led by AB. Vajpayee | 1998 |
(i) Expand NDA.
(ii) Who were the Prime Ministers in National Front Government?
(iii) In which State and in which year was the ‘Operation Blue Star’ executed?
(iv) Mention any two incidents associated with Rajiv Gandhi.
Answer:
A)
- This graphs hows the data of fertility rate in India during 1961-2011.
- In the year 1961, the fertility rate was 5.9. i.e, on an average a woman was likely to bear five or six children.
- It started decreasing from 1971.
| Years | Fertility rate |
| 1971 | 5.4 |
| 1981 | 4.6 |
| 1991 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 3.1 |
| 2011 | 2.7 |
4. The decreasing trend in fertility rate shows the fall in birth rate.
(OR)
B)
- National Democratic Alliance.
- Deve Gowda and I.K. Gujral.
- In Punjab in 1984.
- Agreement with I-IS. LongoWal in Punja b.
- Agreement with AASU in Assam.
![]()
Question 33.
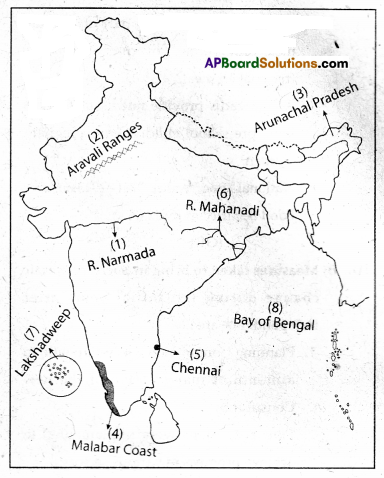
A) Locate the following in the given outline map of India.
a) 1) River Narmada
2) Aravali ranges
3) Arunachal Pradesh
4) Malabar Coast
(OR)
b)
5) Chennai
6) Mahanadi
7) Lakshadweep
8) Bay of Bengal
Answer:
A)
a)
1. River Narmada
2. Aravali ranges
3. Arunachal Pradesh
4. Malabar Coast
(OR)
b)
5. Chennai
6. vIahanadi
7. Lakshadweep
8. Bay of Bengal
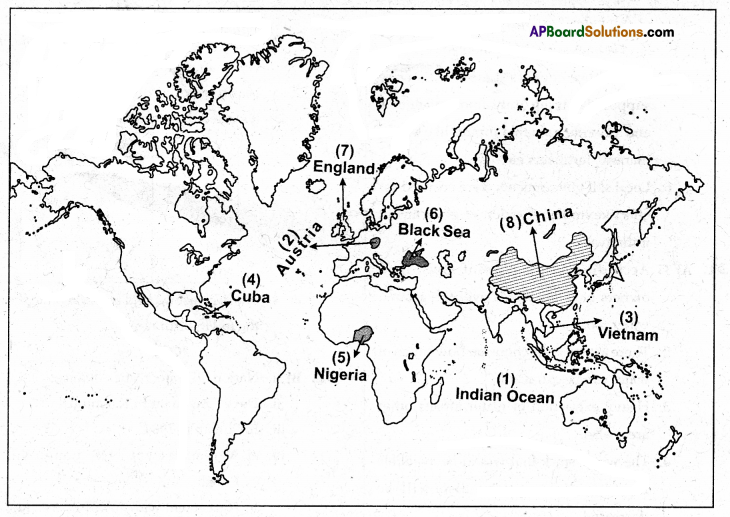
B) Locate the following in the given outline map of World.
a)
1) Indian Ocean
2) Austria
3) Vietnam
4) Cuba
(OR)
b)
5) Nigeria
6) Black Sea
7) England
8) China.
Answer:
a)
1. Indian Ocean
2. Austria
3. Vietnam
4. Cuba
(OR)
b)
5. Nigeria
6. Black Sea
7. England
8. China