Solving AP 10th Class Physical Science Model Papers Set 3 regularly is an effective strategy for time management during exams.
AP SSC Physical Science Model Paper Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 50
Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 4 sections and 17 questions.
- Internal choice is available only for Q.No.12 in section III and for all the questions in section IV.
- In 2 hours, 15 minutes is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the answer booklet only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section-I
(8 × 1 = 8 Marks)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
A gas released in an experiment turns lime water into milky white. Write the name of the gas.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide
Question 2.
Identify which type of lens it is.
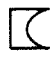
Answer:
Plano Concave Lens
Question 3.
Galena is an ore of which metal?
Answer:
Lead (Pb)
![]()
Question 4.
Write an example for Dobereiner’s triad.
Answer:
Li, Na, K
Question 5.
Which metal is better conductor from the given table?
| Material | Resistivity (at 20°C) (in Ω-m) |
| Copper | 1.68 × 10-8 |
| Iron | 1 × 10-7 |
Answer:
Copper
Question 6.
State Hund’s Rule.
Answer:
The orbitals of equal energy (degenerate) are occupied with one election each before the pairing of electrons starts.
Question 7.
What is the value of 1 cal/g-°C in J/kg-K?
Answer:
4186 J/kg-K
Question 8.
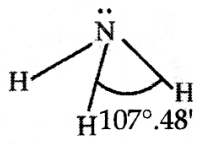
Draw the structural diagram of the Ammonia molecule as per the valence-shell electron pair repulsion
theory.
Answer:
Section-II
(3 × 2 = 6 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 9.
Write any two questions to know the differences between heat and temperature.
Answer:
- What is heat?
- What is temperature?
- Which quantity transfers from a hotter body to a colder body when they are in thermal contact?
- Which body is said to be a hotter body?
![]()
Question 10.
What is an ore? On what basis a mineral is choosen as an ore?
Answer:
Ore: A mineral from which a metal can be extracted economically and conveniently is called ‘Ore’.
To choose a mineral as an ore the following are considered:
- The percentage of the metal in that mineral.
- The metal can be profitably extracted from it or not.
- Convenience of extraction of metal.
Question 11.
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Answer:
The process of changing the speed of light when light travels from one medium to another is called refraction of light. During refraction the speed and wavelength change.
Section-III
(3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 12.
Draw any one of the following diagrams.
(A) Draw ray diagrams for the following positions for the convex lens.
(i) Object is placed beyond 2F2.
(ii) Object is placed in between F2 and optic center P.
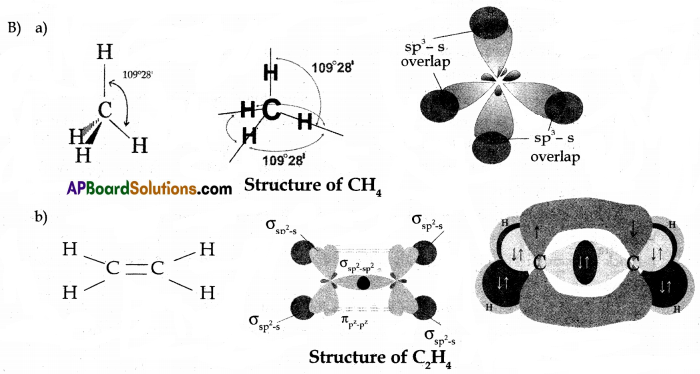
(B) Draw the structures of the following molecules.
(a) CH4
(b) C2H4
Answer:
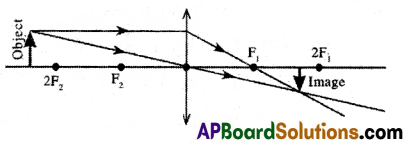
(A) (i) When the object is placed beyond 2F2:
(a) image is formed between F1 and 2F1.
(b) image is real, inverted, and diminished.
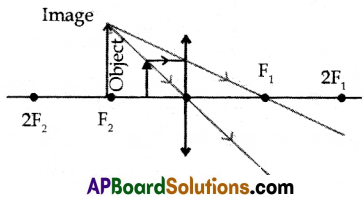
(ii) When an object is placed between F2 and optic center:
(a) image is formed on the same side of the lens.
(b) image is erect, virtual, and magnified.
(c) image is formed between F2 and 2F2.
Question 13.
| Material medium | Water | Benzene | Crown Glass | Diamond |
| Refractive Index | 1.33 | 1.50 | 1.52 | 2.42 |
(A) Between benzene and crown glass, which has more optical density?
(B) What are the units of refractive index?
(C) In which medium the speed of light will be more?
(D) If a light ray enters from the diamond to the water, how this ray will bend concerning the normal line?
Answer:
(A) Crown glass
(B) No units
(C) Speed of light is more in water (Rarer medium)
(D) Light bends away from the normal.
![]()
Question 14.
How can you appreciate the role of a small fuse in a house wiring circuit in preventing damage to various electrical appliances connected to the circuit?
Answer:
- A fuse is a thin conducting wire made of material with a low melting point.
- It is generally included in the household wiring at the mains.
- When the circuit draws more current than the rated value due to overlapping, excess heat is produced which melts the fuse wire.
- The molten fuse wire breaks the circuit preventing any current from entering, thus protecting appliances.
- In this way fuse wire is highly appreciable.
Section-IV
(3 × 8 = 24 Marks)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each question carries 8 marks.
- Each question has an internal choice.
Question 15.
(A) What is Hypermetropia? Explain the correction of the eye defect ‘Hypermetropia’.
(OR)
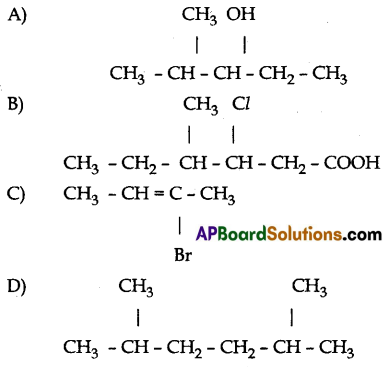
(B) Write IUPAC names for the following carbon compounds.
Answer:
(A) (i) In the case of hypermetropia, the rays coming from a nearby object after refraction from the lens, form an image beyond the retina.

(ii) Let the point of minimum distance at which the eye lens forms a clear image on the retina be known as the near point.

(iii) People with a defect of hypermetropia cannot see objects placed between near point (H) and point of least distance of distinct vision (L).
(iv) Eye lens can form a clear image on the retina when any object is placed beyond a near point.
(v) To correct hypermetropia, we need to use a lens that forms an image of an object beyond the near point when the object is placed between the near point (H) and the least distance of clear vision (L). So, we need a double convex lens.
(OR)
(B) (A) 2 – methyle pentane – 3 – ol
(B) 3 – chloro, 4 – methyle hexanoic acid
(C) 2 Bromo – Bute – 2 – ene
(D) 2, 5 Dimethyle hexane
Question 16.
(A) Define the modem periodic law. Discuss the construction of the long form of the periodic table.
(OR)
(B) What is hybridisation? Explain the formation of Boron Trifluoride (BF3) using hybridization.
Answer:
(A) Modern Periodic Law: The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic number (or) electron configuration.
(i) The modern periodic table has eighteen vertical columns known as groups and seven horizontal rows known as periods.
(ii) Elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic numbers in periods.
(iii) In groups the elements are placed having similar electronic configurations or having a similar number of electrons in their outermost shells.
(iv) Based on which subshell, the differentiating electron enters, the elements are classified as s, p, d, and f block elements.
s-block elements: The elements with valence shell electronic configuration ns1 and ns2 are called s-block elements.
p-block elements: The elements with valence shell electronic configuration ns2np1-6 are called p-block elements.
The s and p elements are together known as Representative elements.
d-block elements: The elements with valence shell electronic configuration ns2np6 (n – 1)d1 to ns2np6 (n – 1)d10 are called d-block elements. These are also called Transition elements.
f-block elements: The elements in which f-orbitals are being filled in their atoms are called f-block elements. These elements are also called ‘Inner Transition elements’.
Inert gases: The elements with complete outermost shell configuration (ns2np6) are known as Inert gases. He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Radon do not react with any other elements. So these are called Inert gases.
The first period contains 2 elements
2nd and 3rd periods contain 8 elements each.
The 4th and 5th periods contain 18 elements each.
6th period contains 32 elements.
7th period is incomplete.
The elements from Ce58 to Lu71 are called Lanthanoids. These elements are 4f block elements.
The elements from Th90 to Lr103 are called Actinoids. These elements are 5f block elements. Lanthanides and Actinides are shown separately at the bottom of the periodic table.
(OR)
(B) Hybridisation: The phenomenon of intermixing of orbitals of the same atom which have almost the same energy to form an equal number of new orbitals of equivalent energy is known as hybridization.
Formation of Boron Trifluoride (BF3):
- The central atom in BF3 is boron.
- The electronic configuration of a boron atom in its excited state is 1s2 2s1 2p2
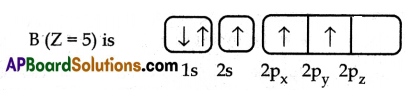
- In the excited boron atom, the ‘2s’ orbital and two ‘2p’ orbitals intermix to give three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals.
- In the formation of BF3 molecule, three sp2 hybrid orbitals of boron overlap with half-filled 2pz orbitals of three chlorine atoms in their axes to give three \(\sigma_{\mathrm{sp}^2-\mathrm{p}}\) bonds.
- BF3 molecule so formed has a trigonal planar structure.
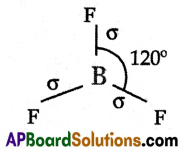
- The bond angle in BF3 is 120°.
![]()
Question 17.
(A) State Ohm’s law and explain the procedure to verify Ohm’s law.
(OR)
(B) Write an experiment to prove that the presence of air and water are essential for corrosion. Explain the procedure.
Answer:
(A) Ohm’s Law: The potential difference between the ends of a conductor in a circuit is directly proportional to the flow of current in the circuit.
V ∝ I (or) \(\frac{V}{I}\) = constant
Verification/Experiment:
(i) Set up a circuit as shown in the figure.
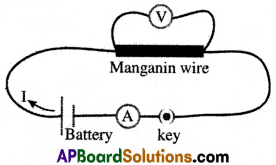
(ii) The figure consists of a nichrome wire AB of length, say 0.5 m, an ammeter, a voltmeter, and four cells of 1.5 V each.
(iii) First use only one cell as the source in the circuit.
(iv) Note the reading in the ammeter (I), for the current and reading of the voltmeter (V) for the potential difference across the nichrome wire AB in the circuit.
(v) Now tabulate the values in the table as mentioned below.
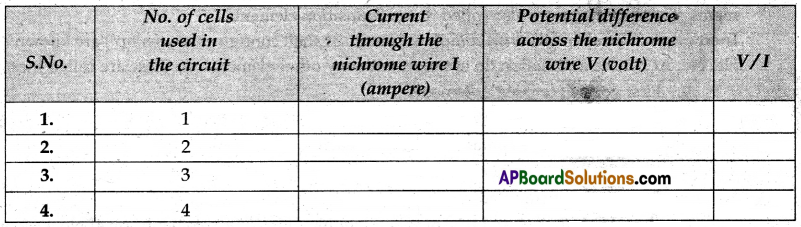
(vi) Next connect two cells in the circuit and note the respective readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the values of current through the nichrome wire and potential difference across the nichrome wire.
(vii) Repeat the above steps using three cells and then four in the circuit separately.
(viii) Calculate the ratio of V to I for each pair of potential difference V and current I.
(ix) Plot a graph between V and I, and observe the nature of the graph.
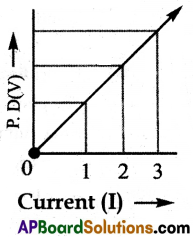
(x) From the above activity we will find that approximately the same value for \(\frac{V}{I}\) is obtained in each case.
(xi) Thus the V-I graph is a straight line that passes through the origin of the graph as shown above.
(xii) From the above graph \(\frac{V}{I}\) is a constant ratio, hence Ohm’s law is verified.
(OR)
(B) (1) Take three test tubes and place clean iron nails in each of them.
(2) Label these test tubes A, B, and C. Pour some water into test tube A and cork it.
(3) Pour boiled distilled water into test tube B, add about 1 ml of oil, and cork it. The oil will float on water and prevent the air from dissolving in the water.
(4) Put some anhydrous calcium chloride in test tube ‘C’ and cork it. Anhydrous calcium chloride will absorb the moisture, if any from the air.
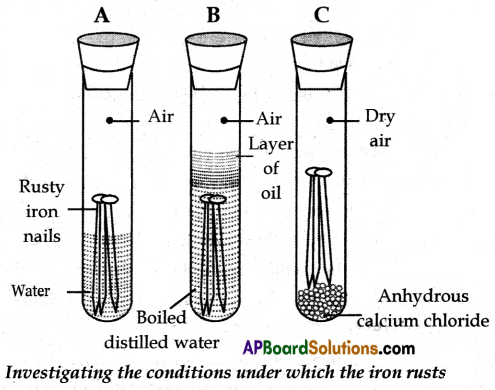
(5) Leave these test tubes for a few days and then observe them.
(6) You will observe that iron nails in test tube ‘A’ get rusted. But they do not get rusted in test tubes ‘B’ and ‘C’.
(7) In test tube ‘A’, the nails are exposed to both air and water. In test tube ‘B’ the nails are exposed to only water and the nails in test tube ‘C’ are exposed to dry air.
(8) From this activity we conclude that both air and water are necessary for corrosion (Rusting) of iron.