Access to a variety of TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Question Paper May 2019 allows students to familiarize themselves with different question patterns.
TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Question Paper May 2019
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 75
Section – A
(10 × 2 = 20)
I. Very Short Answer type questions.
- Attempt all questions.
- Each question carries two marks.
Question 1.
Find the equation of the circle whose extremities of a diameter are (-4, 3), (3, -4).
Solution:
The equation of the circle whose extremities of a diameter are (-4, 3), (3, -4) is
⇒ (x – x1) (x – x2) + (y – y1) (y – y2) = 0
⇒ (x + 4) (x – 3) + (y – 3) (y + 4) = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x + 4x – 12 + y2 + 4y – 3y – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + x + y – 24 = 0.
Question 2.
Find the Polar of (3, -1) with respect to 2x2 + 2y2 = 11.
Solution:
Let S ≡ x2 + y2 – \(\frac{11}{2}\) = 0
The polar of (3, -1) with respect to s = 0 is s1 =0
⇒ x(3) + y(-1) – \(\frac{11}{2}\) =0
⇒ 3x – y – \(\frac{11}{2}\) = 0
⇒ 6x – 2y – 11 = 0.
![]()
Question 3.
Find the equation of the radical axis of the circles x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 7 = 0, 4(x2 + y2) + 8x + 12y – 9 = 0.
Solution:
Let s ≡ x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 7 = 0
s1 ≡ x2 + y2 + 2x + 3y – \(\frac{9}{4}\) = 0
The radical axis of s = 0, s1 = 0 is s – s1 = 0
⇒ (x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 7) – (x2 + y2 + 2x + 3y – \(\frac{9}{4}\)) = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 7 – x2 – y2 – 2x – 3y + \(\frac{9}{4}\) = 0
⇒ 2x + 3y + (\(\frac{9}{4}\) – 7) = 0
⇒ 2x + 3y + \(\left(\frac{9-28}{4}\right)\) = 0
⇒ 2x + 3y – \(\frac{19}{4}\) = 0
⇒ 8x + 12y – 19 = 0
Question 4.
Find the equation of the parabola whose vertex is (3, -2) and focus is (3, 1).
Solution:
The abecissae of the vertex and focus are equal to 3.
∴ The axis of the parabola is x = 3, a line parallel to y – axis, focus is above the vertex.
∴ a = \(\sqrt{(3-3)^2+(1+2)^2}\) = 3.
Hence equation of the required parabola is
(x – 3)2 = 4(3) (y + 2)
⇒ (x – 3)2 = 12 (y + 2).
Question 5.
Find the product of lengths of the perpendiculars from any point on the hyperbola \(\frac{x^2}{16}-\frac{y^2}{9}\) = 1 to its asymptotes.
Solution:
Equation of the hyperbola is \(\frac{x^2}{16}-\frac{y^2}{9}\) = 1
Here a2 = 16 and b2 = 9.
∴ Product of the perpendiculars from any point on the hyperbola to its asymptotes = \(\frac{a^2 b^2}{a^2+\bar{b}^2}\) = \(\frac{16(9)}{16+9}\) = \(\frac{144}{25}\)
Question 6.
Evaluate \(\int \frac{x^8}{1+x^{18}}\)dx on R.
Solution:
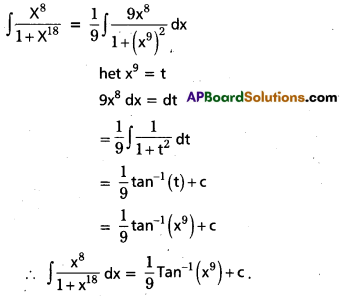
Question 7.
Evaluate \(\int e^x\left(\frac{1+x \log x}{x}\right)\)dx on (0, ∞)
Solution:
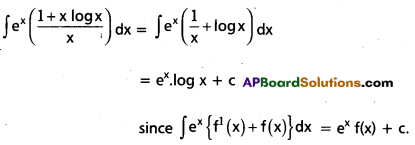
Question 8.
Evaluate \(\int_0^{\infty} \frac{d x}{x^2+a^2}\)
Solution:
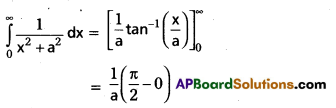
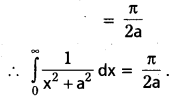
![]()
Question 9.
Find the area bounded between the curves y = x2, y = x3
Solution:
Given curve equations are y = x2, y = x3

Question 10.
Solve \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1+y^2}{1+x^2}\)
Solution:
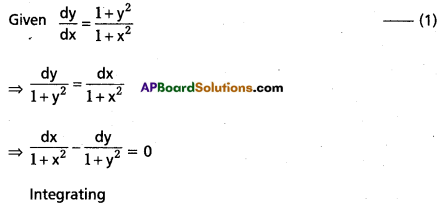
\(\int \frac{d x}{1+x^2}\) – \(\int \frac{d y}{1+y^2}\) = c
⇒ tan-1x + tan-1y = c
∴ The general solution of (1) is
tan-1x – tan-1y = c.
Section – B
II. Short Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt any five questions.
- Each question carries four marks.
Question 11.
Find the equation of the tangent at the point 30° (parametric value of θ) of the circle x2 + y2+ 4x + 6y – 39 = 0.
Solution:
Given circle equation is s ≡ x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y – 39 = 0
Here 2g = 4 ⇒ g = 2
2f = 6 ⇒ f = 3 and c = – 39
Radius r = \(\sqrt{g^2+f^2-c}\)
= \(\sqrt{4+9-(-39)}\)
= \(\sqrt{4+9+39}\)
= \(\sqrt{52}\) = 2\(\sqrt{13}\)
The equation of the tangent at 0 of the circle.
s = 0 is (x + g) cos θ + (y + f) sin θ = r

Question 12.
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the point (2, 0), (0, 2) and orthogonal to the circle 2x2 + 2y2 + 5x – 6y + 4 = 0.
Solution:
Let x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 ………… (1) be the required circle.
If (1) passes through the point (2, 0) then
4 + 0 + 4g + 0 + c = 0
⇒ 4g + c = – 4 ……… (2)
If (1) passes through the point (0, 2) then
0 + 4 + 0 + 4f + c = 0
⇒ 4f + c = – 4 ………. (3)
(2) – (3)
⇒ 4g – 4f = 0
⇒ g – f = 0
⇒ g = f ………… (4)
If (1) is orthogonal to x2 + y2 + 5/2x – 3y + 2 = 0 then
29\(\left(\frac{5}{4}\right)\) + 2f\(\left(\frac{-3}{2}\right)\) = c + 2
⇒ \(\left(\frac{5}{2}\right)\)g – 3f = c + 2
⇒ \(\left(\frac{5}{2}\right)\)g – 3g = c + 2 [∴ from (4)]
⇒ \(\frac{-1}{2}\)g = c + 2
⇒ – g = 2c + 4
⇒ g = – 2c – 4 ………. (5)
From (2)
4(-2c – 4) + c = -4
⇒ -8c – 16 + c = -4
⇒ -7c = 12
⇒ c = -12/7
From (5)
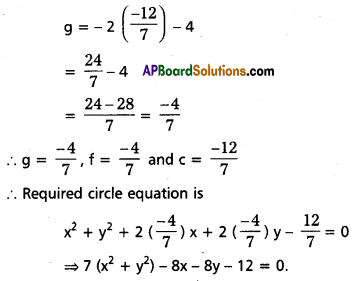
Question 13.
Find the length of the major axis, minor axis, latus rectum, eccentricity of the ellipse 9x2 + 16y2 = 144.
Solution:
Given 9x2 + 16y2 = 144
⇒ \(\frac{x^2}{16}+\frac{y^2}{9}\) = 1
Here a2 = 16 ⇒ a = 4
b2 = 9 ⇒ b = 3
Length of major axis = 2a = 2(4) = 8
Length of minor axis = 2b = 2(3) = 6
Length of latus rectum = \(\frac{2 b^2}{a}\) = \(\frac{2(9)}{4}\) = \(\frac{9}{2}\)
Eccentricity = \(\sqrt{\frac{a^2-b^2}{a^2}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{16-9}{16}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\)
![]()
Question 14.
Find the equation of the tangent to the ellipse 2x2 + y2 = 8 which are
i) parallel to x – 2y – 4 = 0
ii) perpendicular to x + y + 2 = 0.
Solution:
i) Parallel to x – 2y – 4 = 0
Slope will be : \(\frac{\sqrt{1}}{2}\)
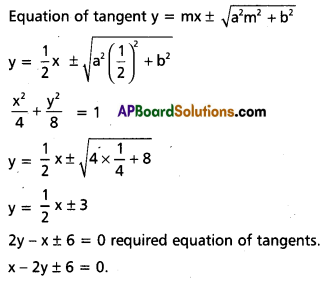
ii) Perpendicular to x + y + 2 = 0 ,
Slope of tangent be T as it is perpendicular to above line y = mx ± +Ja2m2 + b2 => y = x ± ^4 + 8
y = mx ± \(\sqrt{a^2 m^2+b^2}\)
y = x ± \(2 \sqrt{3}\)
⇒ y = x ± \(\sqrt{4+8}\)
⇒ x – y ± \(2 \sqrt{3}\) = 0
Question 15.
Tangents to the hyperbola \(\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2}\) = 1 makes angles θ1, θ2 with transverse axis of a hyperbola. Show that the point of intersection of these tangents lies on the curve 2xy = k (x2 – a2) when tanθ1 + tanθ2 = k.
Solution:
Equation of the hyperbola is \(\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2}\) = 1
Equation of the tangent to the hyperbola
Can be taken as y = mx ± \(\sqrt{a^2 m^2-b^2}\)
Let p(x1, y1) be the point of intersection of the tangents.
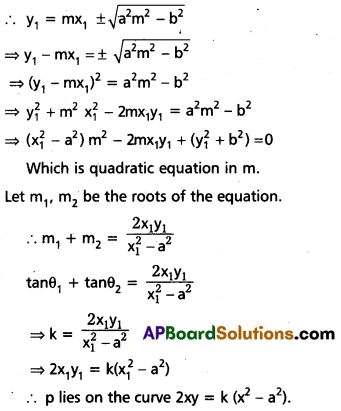
Question 16.
Find the area bounded between the curves y2 = 4x, y2 = 4(4 – x).
Solution:
Given curve equations are y2 = 4x ………. (1)
y2 = 4(4 – x) …………… (2)
From (1) & (2)
4x = 4 (4 – x)
⇒ 4x = 16 – 4x
⇒ 8x = 16
⇒ x = 2
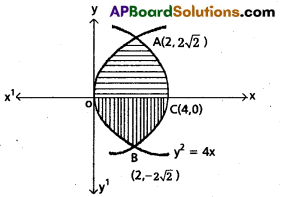
From (1) y2 = 8
⇒ y = ± 2\(\sqrt{2}\)
∴ Points of intersection are A(2, 2\(\sqrt{2}\)) and B(2, -2\(\sqrt{2}\))
From fig required area is symmetric about x – axis
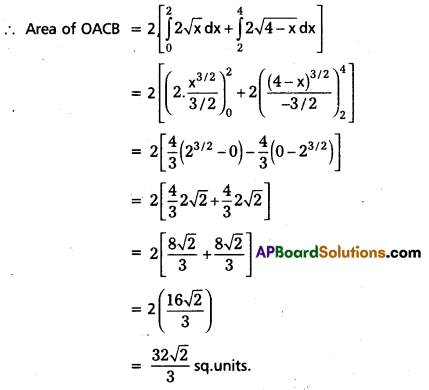
Question 17.
Solve \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) – y tan x = ex sec x.
Solution:
Given differential equation is
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) – y tanx = ex sec x ….. (1)
Here P = – tanx and Q = ex secx
I.F. = \(e^{\int P d x}\)
= \(e^{-\int \tan x d p}\)
= e-log|sec x|
= elog cosx = cos x.
∴ The general solution of (1) is
y(I.F.) = ∫Q(I.F)dx + c
⇒ y cosx = ∫exsecx cosx dx + c
⇒ y cosx = ∫exdx + c
⇒ y cosx = ex + c
Section – C
(5 × 7 = 35)
III. Long Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt any five questions.
- Each question carries seven marks.
Question 18.
Find the equation of a circle which passes through (2, -3), and (-4, 5) and having the centre on 4x + 3y + 1 = 0.
Solution:
Let x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 ………… (1)
be the required circle.
If (1) passes through (2, -3) then
4 + 9 + 4g – 6f + c = 0
4g – 6f + c = -13 ……….. (2)
If (1) passes through (-4, 5) then
16 + 25 – 8g + 10f + c = 0
⇒ 8g – 10f – c = 41 ………. (3)
center (-g, -f) lies on 4x + 3y + 1 = 0
⇒ 4(-g) + 3(-f ) +1 = 0
⇒ -4y – 3f + 1 = 0
⇒ 4g + 3f – 1 = 0 ……… (4)
(2) + (3) ⇒ 12g – 16f = 28
⇒ 3g – 4f = 7
⇒ 3g – 4f – 7 = 0 ……… (5)
Solving (4) & (5)
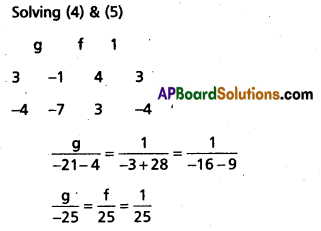
g = -1, f = 1
From(2) + 4 + 6 + c = -13
⇒ c = -23
∴ g = -1, f = 1, c = -23
Hence required circle equation is
x2 + y2 – 2x + 2y – 23 = 0.
Question 19.
Find the transverse common tangents of the circles x2 + y2 – 4x – 10 y + 28 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y + 4 = 0.
Solution:
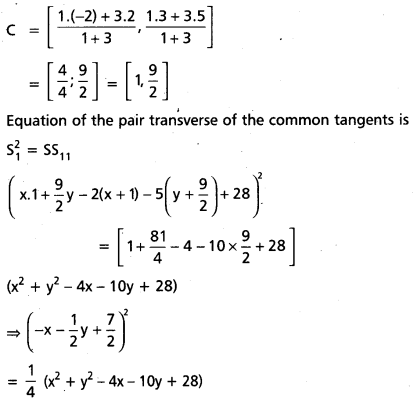
(-2x – y + 7)2 = (x2 + y2 – 4x – 10y + 28)
4x2 + y2 + 4xy – 28x – 14y + 4 = x2 + y2 – 4x – 10y + 28
3x2 + 4xy – 24x – 4y + 21 = 0
(3x + 4y – 21); (x – 1) = 0
3x + 4y – 21 = 0; x – 1 = 0.
Question 20.
Show that the equation of common tangents to the circle x2 + y2 = 2a2 and the parabola y2 = 8ax are y = ± (x + 2a).
Solution:
The equation of tangent to parabola y2 = 8ax is y = mx + 2 a/m
⇒ my = m2x + 2a
⇒ m2x – my + 2a = 0 …….. (1)
If (1) touches the circle x2 + y2 = 2a2 then
r = d
⇒ \(\sqrt{2} a\) = \(\frac{|2 a|}{\sqrt{m^4+m^2}}\)
⇒ 2a2 = \(\frac{4 a^2}{m^4+m^2}\)
⇒ 1 = \(\frac{2}{m^4+m^2}\)
⇒ m4 + m2 = 2
⇒ m4 + m2 – 2 = 0
⇒ m4 + 2m2 – m2 – 2 = 0
⇒ m2 (m2 + 2) – 1 (m2 + 2) = 0
⇒ (m2 + 2) (m2 – 1) = 0
⇒ m2 – 1 = 0
⇒ m2 = 1
⇒ m = ± 1.
∴ Required tangents are
⇒ y = 1 (x) + \(\frac{2 a}{1}\), y = – 1 (x) + \(\frac{2 a}{-1}\)
⇒ y = x + 2a, y = -x – 2a
⇒ y = x + 2a, y = – (x + 2a)
⇒ y = ± (x + 2a).
Question 21.
Evaluate \(\int \frac{2 \cos x+3 \sin x}{4 \cos x+5 \sin x}\)dx.
Solution:
Let 2 cosx + 3 sinx = A (4 cosx + 5 sinx) + B\(\frac{d}{d x}\)(4 cosx + 5 sinx)
= A(4 cosx + 5 sinx) + B (- 4 sinx + 5 cosx)
Equating the co-efficient of sinx and cosx, we get
3 = 5A – 4B ⇒ 5A – 4B – 3 = 0 …… (1)
2 = 4A + 5B ⇒ 4A + 5B – 2 = 0 ……… (2)
Solving (1) and (2)
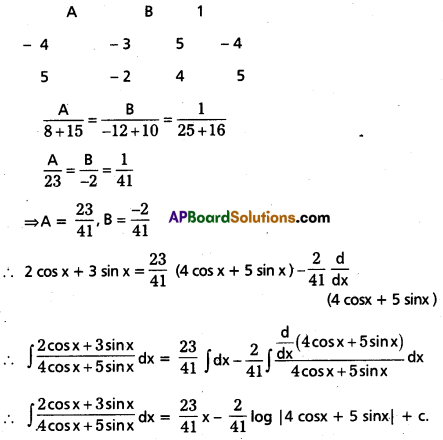
Question 22.
Obtain the reduction formula for In = ∫cosnx dx, n being a positive integer, n ≥ 2, and deduce the value of ∫cos3x dx.
Solution:
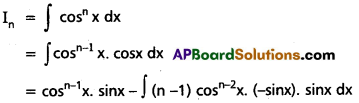
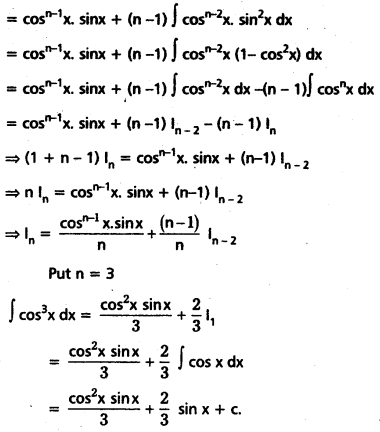
Question 23.
Evaluate \(\int_0^1 \frac{\log (1+x)}{1+x^2}\)dx.
Solution:
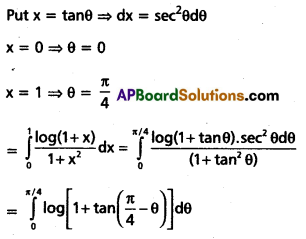
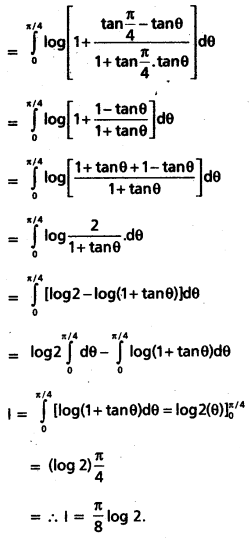
Question 24.
Solve \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{4 x+6 y+5}{3 y+2 x+4}\)
Solution:
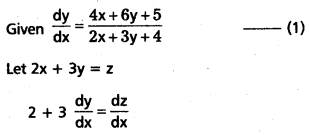

Integrating
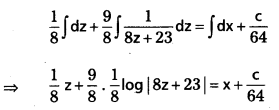
⇒ 8z + 9 log |8z + 23| = 64x + c
⇒ 8(2x + 3y) + 9 log |8(2x + 3y) + 23| = 64x + c
⇒ 24y – 48x + 9log|16x + 24y + 23| = c
⇒ y – 2x + 3/8 log |16x + 24y + 23| = k where k = c/24
∴ The general solution of (1) is
y – 2x + 3/8 log |16x + 24y + 23| = k.