Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Question Paper March 2017 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Question Paper March 2017
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 75
Note: This question paper consists of three sections A, B, and C.
Section – A
(10 × 2 = 20 Marks)
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions.
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries two marks.
Question 1.
Write the complex number (1 + 2i)3 in the form of a + ib.
Solution:
(1 + 2i)3 = 1 + 3 .12 . 2i + 3 . 1 . (2i)2 + (2i)3
= 1 + 6i + 12i2 + 8i3
= 1 + 6i + 12(-1) + 8(-i)
= 1 + 6i – 12 – 8i
= -11 – 2i
= a + ib where a = -11, b = -2
Question 2.
Express the complex number 1 + i√3 in modulus amplitude form.
Solution:
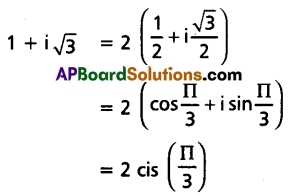
Question 3.
If 1, ω, ω2 are the cube roots of unity, then prove that (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – ω10) (2 – ω11) = 49.
Solution:
Since 1, ω, ω2 are the cube roots of unity.
∴ 1 + ω + ω2 = 0 and ω3 = 1
L.H.S. = (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – ω10) (2 – ω11)
= (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – ω9 . ω) (2 – ω9 . ω2)
= (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – 1 . ω) (2 – 1 . ω2) [∵ (ω9) = (ω3)3 = 1]
= (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – ω) (2 – ω2)
= (2 – ω)2 (2 – ω2)2
= [(2 – ω) (2 – ω2)]2
= [4 – 2ω2 – 2ω + ω3]2
= [4 – 2 (ω2 + ω) + 1]2
= [4 – 2(-1) + 1]2
= (4 + 2 + 1 )2
= 72
= 49
= R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S
∴ (2 – ω) (2 – ω2) (2 – ω10) (2 – ω11) = 49
![]()
Question 4.
If x2 – 6x + 5 = 0 and x2 – 12x + p = 0 have a common root, then find p.
Solution:
Let a be the common root of the equations x2 – 6x + 5 = 0 and x2 – 12x + p = 0
Then α2 – 6α + 5 = 0 and α2 – 12α + p = 0
⇒ (α – 1) (α – 5) = 0
⇒ α = 1, 5
If α = 1 then 1 – 12 + p = 0
⇒ p = 11
If α = 5 then 25 – 60 + p = 0
⇒ p = 35
∴ p = 11 (or) 35
Question 5.
Form the polynomial equation of the lowest degree with roots as 0, 0, 2, 2, -2, -2.
Solution:
The polynomial equation of the lowest degree with roots as 0, 0, 2, 2, -2, -2 is (x – 0) (x – 0) (x – 2) (x – 2) (x + 2) (x + 2) = 0
⇒ x2 (x – 2)2 (x + 2)2 = 0
⇒ x2 [(x – 2)(x + 2)]2 = 0
⇒ x2 (x2 – 4)2 = 0
⇒ x2 (x4 – 8x2 + 16) = 0
⇒ x6 – 8x4 + 16x2 = 0
Question 6.
If nP7 = 42 . (nP5), then find n.
Solution:
nP7 = 42 . nP5
⇒ n(n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3) (n – 4) (n – 5) (n – 6) = 42 . n(n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3) (n – 4)
⇒ (n – 5) (n – 6) = 42
⇒ (n – 5) (n – 6) = 7 × 6
⇒ n – 5 = 7 or n – 6 = 6
⇒ n = 12
Question 7.
Find the value of 10C5 + 2 . (10C4) + 10C3.
Solution:
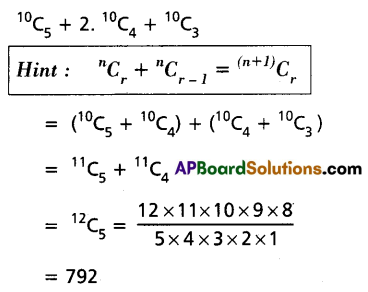
Question 8.
Find the set E of the values of x for which the binomial expansion \((2+5 x)^{-1 / 2}\) is valid.
Solution:
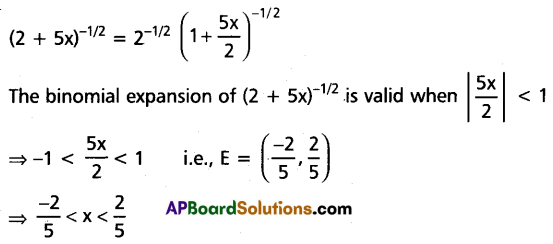
Question 9.
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the following data:
3, 6, 10, 4, 9, 10
Solution:
The arithmetic mean of the given data
\(\bar{x}=\frac{3+6+10+4+9+10}{6}\)
= \(\frac{42}{6}\)
= 7
The absolute values of the deviations are |3 – 7|, |6 – 7|, |10 – 7|, |4 – 7|, |9 – 7|, |10 – 7| = 4, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3
∴ The mean deviation from the mean = \(\frac{\sum_{i=1}^6\left|x_i-\bar{x}\right|}{6}\)
= \(\frac{4+1+3+3+2+3}{6}\)
= \(\frac{16}{6}\)
= 2.666
![]()
Question 10.
The mean and variance of a binomial distribution are 4 and 3 respectively. Fix the distribution and find P (X ≥ 1).
Solution:
Given distribution is Binomial distribution with mean = np = 4
variance = npq = 3
∴ \(\frac{n p q}{n \mathrm{p}}=\frac{3}{4}\)
⇒ q = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
so that p = 1 – q
= 1 – \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
∴ np = 4
⇒ n(\(\frac{1}{4}\)) = 4
⇒ n = 16
P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – P(X = 0)
= 1 – \({ }^{16} \mathrm{C}_0\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)^0\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{16-0}\)
= 1 – \(\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{16}\)
∴ P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – \(\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{16}\)
Section – B
(5 × 4 = 20 Marks)
II. Short Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt any five questions.
- Each question carries four marks.
Question 11.
If x + iy = \(\frac{3}{2+{Cos} \theta+i {Sin} \theta}\), then show that x2 + y2 = 4x – 3.
Solution:
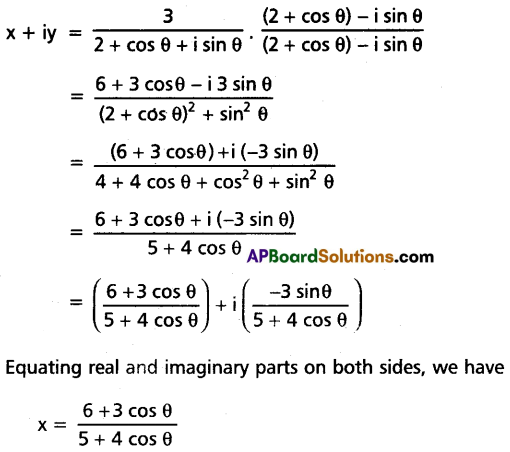
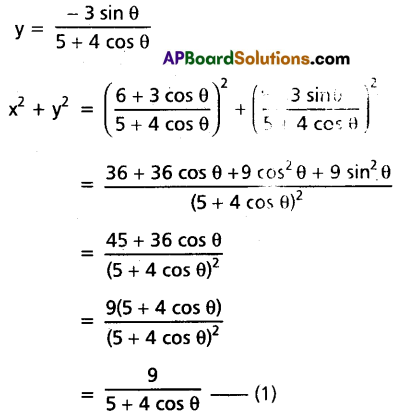
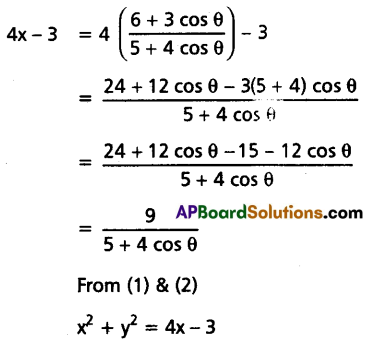
Question 12.
If x1, x2 are the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 and c ≠ 0, find the value of (ax1 + b)-2 + (ax2 + b)-2 in terms of a, b, c.
Solution:
x1, x2 are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
x1 + x2 = \(\frac{-b}{a}\), x1x2 = \(\frac{c}{a}\)

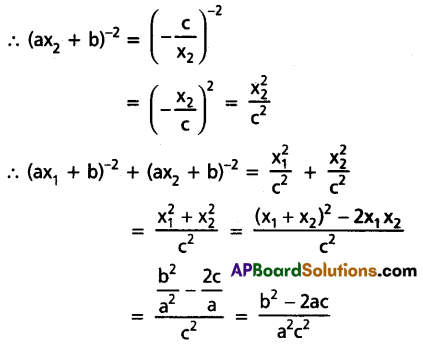
Question 13.
If the letters of the word EAMCET are permuted in all possible ways and if the words thus formed are arranged in the dictionary order, then find the rank of the word EAMCET.
Solution:
The dictionary order of the letters of the word EAMCET is A C E E M T
In the dictionary order first gives the words which begin with the letter A.
If we fill the first place with A, the remaining 5 letters can be arranged in \(\frac{5 !}{2 !}\) ways (since there are 2E’s) on proceeding like this, we get
A – – – – – = \(\frac{5 !}{2 !}\) words
C – – – – – = \(\frac{5 !}{2 !}\) words
E A C – – – = 3! words
E A E – – – = 3! words
E A M C E T = 1 word
Hence the rank of the word EAMCET is = 2 × \(\frac{5 !}{2 !}\) + 2 × 3! + 1
= 120 + 12 + 1
= 133
![]()
Question 14.
Prove that, \(\frac{{ }^{4 n} C_{2 n}}{{ }^{2 n} C_n}=\frac{1 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \ldots \ldots(4 n-1)}{[1 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \ldots(2 n-1)]^2}\).
Solution:
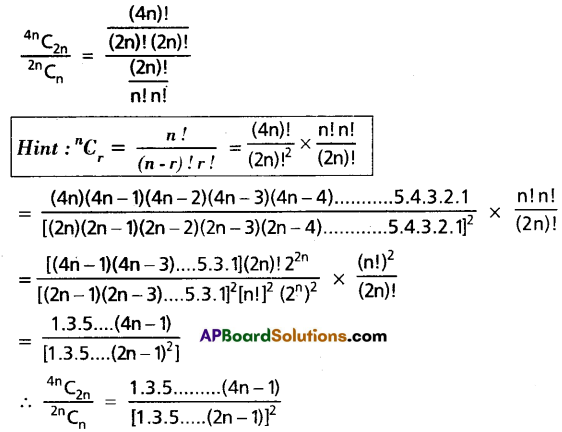
Question 15.
Resolve the fraction \(\frac{2 x^2+2 x+1}{x^3+x^2}\) into partial fraction.
Solution:
Let \(\frac{2 x^2+2 x+1}{x^2+(x+1)}=\frac{A}{x}+\frac{A}{x^2}+\frac{C}{x+1}\)
⇒ \(\frac{2 x^2+2 x+1}{x^2(x+1)}=\frac{A x(x+1)+B(x+1)+C x^2}{x^2(x+1)}\)
⇒ 2x2 + 2x +1 = Ax(x + 1) + B(x + 1) + Cx2
Put x = 0
0 + 0 + 1 = 0 + B(0 + 1) + 0
⇒ B = 1
Put x = -1
2(-1)2 + 2(-1) + 1 = 0 + 0 + C(-1)2
⇒ 2 – 2 + 1 = C
⇒ C = 1
Now equating the co-efficient of x2 terms on both sides, we have
2 = A + C
⇒ 2 = A + 1
⇒ A = 1
∴ \(\frac{2 x^2+2 x+1}{x^3+x^2}=\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x^2}+\frac{1}{x+1}\)
Question 16.
A and B are events with P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.4 and P(A ∩ B) = 0.3. Find the probability that
(i) A does not occur
(ii) neither A nor B occurs
Solution:
We have AC = the event “A does not occur”
(A ∪ B)C = neither A nor B occurs.
∴ P(AC) = 1 – P(A)
= 1 – 0.5
= 0.5
Since P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.5 + 0.4 – 0.3
= 0.6
P[(A ∪ B)C] = 1 – P(A ∪ B)
= 1 – 0.6
= 0.4
Question 17.
Find the probability of drawing an Ace or a Spade from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards.
Solution:
Hint: A pack of cards means of pack containing 52 cards, 26 of them are red and 26 of them are black coloured. These 52 cards are divided into 4 sets: Hearts, Spades, Diamonds and Clubs. Each set contains 13 card names, A, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,8, 9, 10, K, Q, J.
Let E1 be the event of drawing a spade and E2 be the event of drawing an ace.
E1 and E2 are not mutually exclusive.
n(A) = 13, n(B) = 4, n(A ∩ B) = 1
∴ P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= \(\frac{13}{52}+\frac{4}{52}-\frac{1}{52}\)
= \(\frac{16}{52}\)
= \(\frac{4}{13}\)
Section – C
(5 × 7 = 35 Marks)
III. Long Answer Type Questions.
- Attempt any five questions.
- Each question carries seven marks.
Question 18.
If n is an integer then show that (1 + Cos θ + i Sin θ)n + (1 + Cos θ – i Sin θ)n = \(2^{n+1} {Cos}^n\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right)\) \({Cos}\left(\frac{n \theta}{2}\right)\).
Solution:
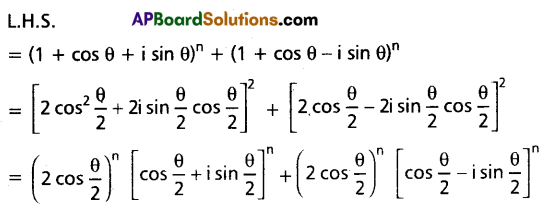
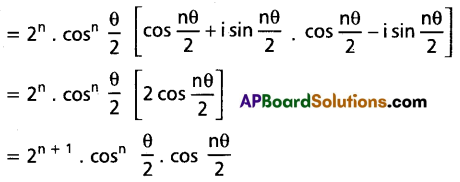
Question 19.
Show that x5 – 5x3 + 5x2 – 1 = 0, has three equal roots, and find that root.
Solution:
Let f(x) = x5 – 5x3 + 5x2 – 1
f'(x) = 5x4 – 15x2 + 10x = 5x(x3 – 3x + 2)
f'(1) = 5(1) (1 – 3 + 2) = 0
f(1) = 1 – 5 + 5 – 1 = 0
x – 1 is a factor of f'(x) and f(x)
∴ 1 is a repeated root of f(x).

x3 + 2x2 – 2x – 1 = 0
∴ 1 is a root of the above equation (∵ the sum of the coefficients is zero)
∴ 1 is the required root.
![]()
Question 20.
If n is a positive integer, then prove that
Solution:
Write S = \(C_0+\frac{C_1}{2}+\frac{C_2}{3}+\ldots+\frac{C_n}{n+1}\) then
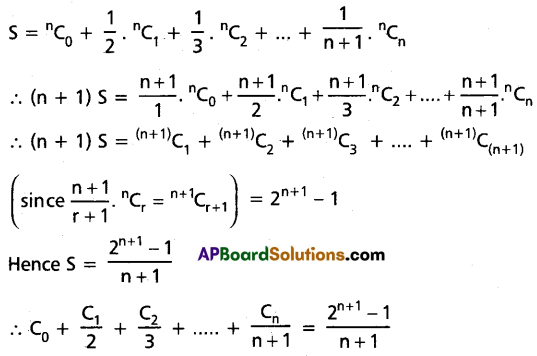
Question 21.
Find the sum of the series \(\frac{3.5}{5 \cdot 10}+\frac{3 \cdot 5 \cdot 7}{5 \cdot 10 \cdot 15}+\frac{3 \cdot 5 \cdot 7 \cdot 9}{5 \cdot 10: 15 \cdot 20}\) + …….∞.
Solution:
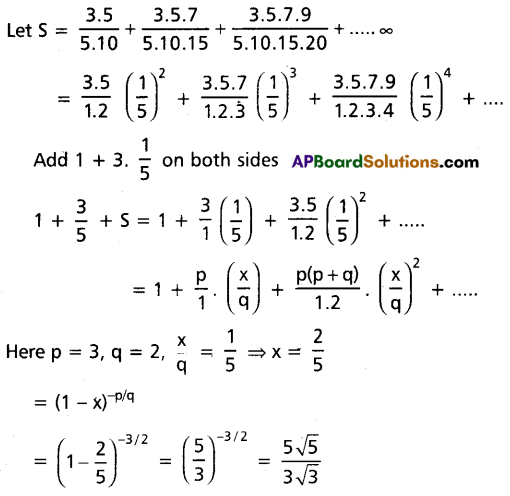
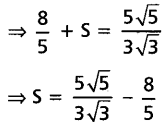
Question 22.
Calculate the variance and standard deviation of the following continuous frequency distribution:
| Class Interval | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 | 70-80 | 80-90 | 90-100 |
| Frequency | 3 | 7 | 12 | 15 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
Solution:
Let assumed mean A = 65 then yi = \(\frac{x_i-65}{10}\)
Construct the table
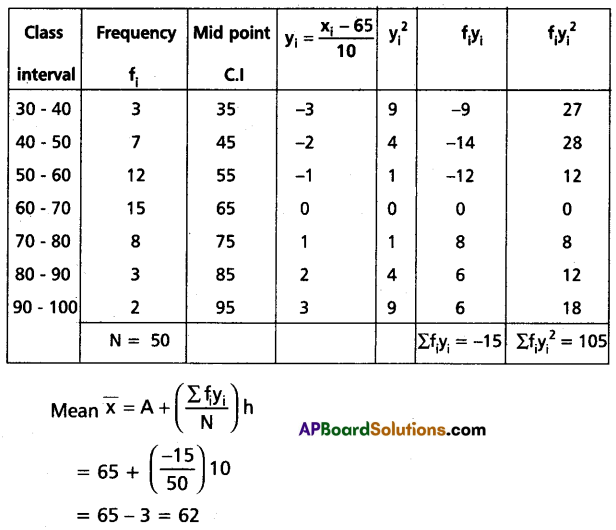
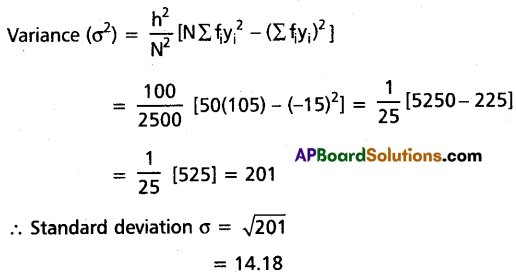
Question 23.
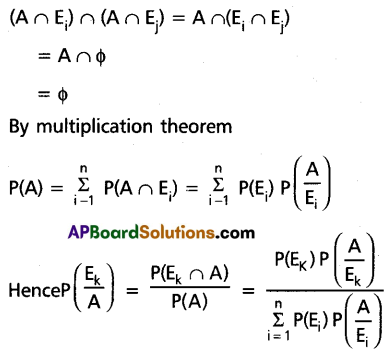
State and Prove Baye’s theorem.
Solution:
Statement: Let E1, E2, ………, En are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events or a random experiment with P(Ei) ≠ 0 for i = 1, 2, 3, ………., n. Then for any event A or the random experiment with P(A) ≠ 0.
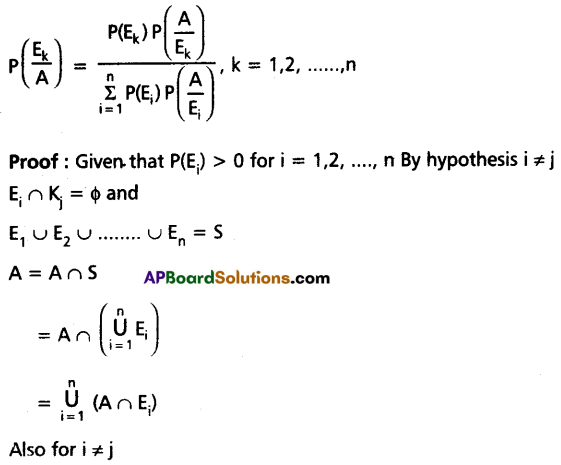
![]()
Question 24.
| X = x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.1 | K | 0.2 | 2K | 0.3 | K |
is the probability distribution of a random variable X. Find the value of K and the variance of X.
Solution:
The Sum of the Probabilities = 1
⇒ 0.1 + k + 0.2 + 2k + 0.3 + k = 1
⇒ 4k + 0.6 = 1
⇒ 4k = 1 – 0.6 = 0.4
⇒ k = 0.1
Mean = (-2) (0.1) + (-1) k + 0 (0.2) + 1 (2k) + 2(0.3) + 3k
= -0.2 – k + 0 + 2k + 0.6 + 3k
= 4k + 0.4
= 4(0.1) + 0.4
= 0.4 + 0.4
= 0.8
∴ µ = 0.8
Variance (σ2) = \(\sum_{i=1}^n x_i^2 P\left(x=x_i\right)-\mu^2\)
Variance = 4(0.1) + 1(k) + 0(0.2) + 1(2k) + 4(0.3) + 9k – µ2
= 0.4 + k + 0 + 2k + 4(0.3) + 9k – (0.8)2
= 12k + 0.4 + 1.2 – (0.8)2
= 12(0.1) + 1.6 – 0.64
= 1.2 + 1.6 – 0.64
= 2.8 – 0.64
= 2.16
∴ σ2 = 2.16