Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 1 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is a Stock Exchange? Explain its functions.
Answer:
Introduction:
Stock exchange is an organized secondary market, where the listed securities are bought and sold by the investors.
Definition:
“Stock exchange is an association, organization or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, established to assist, regulate and controlling business in buying, selling and dealing in securities”. – The Securities Contracts Act 1956
“Security exchanges are marketplaces where securities that have been listed thereon may be bought and sold either for investment or speculation”. – “Pyle”
Functions of Stock Exchange:
- Provides infrastructure for trading: In the stock exchange, instantaneously trading gets executed. It draws investment by providing a ready and continuous market for securities.
- Provides information regarding prices: It gives sensible information through reliable sources and publishers to investors about the prices of securities. The proposed investor knows the quotation and the investor knows the price of his holdings.
- Protects investor’s wealth: It protects the interests and wealth of investors through the enforcement of its rules and regulations.
- Clearing House: Without a clearing house one will find a lot of trades mismatched. It acts on behalf of both buyer and seller and helps in the trading of securities.
- Provides liquidity: The holder of securities can easily encash the securities by selling them to the buyer whenever he wants.
- Helps to raise new capital: The requirement of additional capital of an existing company can be raised by issuing the rights shares, through the stock exchange.
- Acts as a Barometer: An efficient stock exchange acts as a Barometer of business conditions in the country.
- Increases credit worthiness of company: A company that got its shares to be listed in the stock exchange enjoys a good reputation.
- Minimizes the dangers of speculation: Following the rules and regulations of the Acts, minimizes the dangers of speculative dealings and price manipulations.
- Facilitates speculation: Stock exchange facilitates speculation thereby businessmen can speculate and earn profits from fluctuations in security prices.
![]()
Question 2.
Define Banking and explain the functions of Banking.
Answer:
Bank is derived from the French word “Banco” which means a Bench. It is believed that the early bankers, the Jews of Lombardy transacted their business on benches in the marketplace.
Definition:
“Banking is defined as accepting for lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise”. – Banking Regulation Act 1949 – Section 5(1)(b)
Functions of Banks:
The core functions of a bank are
- Acceptance of money deposits from the public.
- Lending (or) making advances to the public.
- Undertaking Agency Services.
- Rendering General Utility Services.
1. Acceptance of Deposits:
Banks accept money from the public in various forms which constitute borrowings by banks. The deposits are one of the main sources of funds for the banks.
2. Lending (or) Making Advances to the Public:
Banks lending the deposit amounts. It is a profit motive. The bank will not lend the whole of the deposits it keeps a certain amount to meet contingencies and the remaining portion is lent to the business community at a higher rate of interest. The difference between the rate of interest allowed and deposits and the rate charged on the loans is called as ‘spread’, it is the main source of income for a bank. An advance is a credit facility provided by a bank to its customers. It is generated for shorter periods. Further, the purpose behind granting an advance is to meet the day-to-day requirements of a business.
3. Agency Functions or Services:
Banks perform these functions for their customers. These are
- To collect or pay bills, cheques, interest, dividends, rent, etc., on behalf of customers. For rendering these services, banks collect charges from their customers.
- To act as executor, trustee, and attorney on the customer’s will.
- To work as a correspondent, agent, or representative of their clients.
4. General Utility Services:
These services are provided to the general public. These are
- A letter of credit may be issued by the bank at the request of the importer to the exporter.
- Bank drafts and traveler’s cheques are issued to provide facilities for fund transfer from one part of the country to another part.
- Acceptance or collection of foreign bills of exchange.
- Banks arrange safe deposit lockers for the safe custody of customers’ securities, valuables, and jewelry.
- Other general public utility services.
Question 3.
Define Management and explain the Principles of Management.
Answer:
Generally, management has been defined as “getting things done through others”.
Definitions:
- Management is a multipurpose organ that manages a business and manages managers and manages workers and work. – Peter F. Drucker.
- Management is the art of knowing what you want to do and then seeing that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. – F. W. Taylor.
- “To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control.” – Henry Fayol.
It has been observed that management is used as a collective noun to refer to all those who manage within a particular organization including those who help line managers by performing a staff function. ‘Henry Fayol’ has been rightly called the “Father of administrative management” for his practical approach to management theory. He has identified 14 fundamental principles of management. Those are:
- Division of labour and specialization
- Parity of authority and responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of direction
- Subordination of individual to general interest
- Remuneration of personnel
- Centralization
- Scalar chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
- Esperit-de-corps
1. Division of Labour and Specialisation:
Division of labour leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of individual employees. Division of labour is a famous principle of economics. Fayol applied this principle to management. He recommended work of all kinds must be subdivided and allocated to several persons. Subdivision makes each task simpler and results in greater efficiency.
2. Parity of Authority and Responsibility:
According to Fayol, authority and responsibility must flow in the same direction. Responsibility is the natural outcome of authority. A proper balance between authority and responsibility helps to prevent the misuse of authority and promotes a fair fixation of responsibility.
3. Discipline:
Discipline means the observation of certain rules and regulations. People in the organization should be bound to accept certain codes of conduct. The three basic requisites of discipline are disciplined supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreement on goals, and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command:
The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only one superior. No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one person. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
5. Unity of Direction:
Unity of direction is essential for achieving unity in action, in the pursuit of common goals by a group of persons. For this Fayol advocates ‘one head and one plan’. Unity of direction (one head, one plan) is not the same as unity of command (one employee receives orders from one superior).
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest:
According to this principle, the fulfillment of individual objectives, in the long run, is contingent upon the attainment of common objectives in the short run. Thus, in case the need arises, an individual must sacrifice in favour of larger group objectives.
7. Remuneration of Personnel:
Remuneration is the price paid to the personnel for the services rendered by them. According to Fayol, the system of remunerating personnel should be fair and satisfactory to both the employees and the employer. It should be attractive to employ and retain the best personnel.
8. Centralization:
It refers to the extent to which authority is concentrated or dispersed. The appropriate degree of centralization will vary with different concerns. It is a problem of finding the measure that will give the best overall yield. Under centralization managers or executives play an important role.
9. Scalar Chain:
It refers to the line of authority from the highest to the lowest executive for communication. However, in the routine course of business, employees at the same level can communicate with each other following the principle of ‘Gangplank’.
10. Order:
Fayol has classified order into two categories.
- Material Order: Material order is described as a place for everything and everything in its place.
- Social Order: Social order demands the employment of a “right man in the right place”.
11. Equity:
Equity is a combination of kindliness and justice. It seeks to elicit loyalty and devotion from personnel. Managers should show kindness and justice in dealing with their subordinates.
12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel:
High turnover increases inefficiency. An employee needs time to adjust to the new work, and its environment and demonstrate efficiency. Therefore, stability of tenure is a desirable principle for ensuring efficiency. Unnecessary employee turnover is the cause and effect of bad management.
![]()
13. Initiative:
The initiative is the freedom to propose and execute a plan. To have freedom in this respect is the greatest satisfaction for an intelligent person. A manager, who induces his subordinates to think and act on their own, is always better and more successful than the one who does not.
14. Esperit-de-corps:
It is a French phrase which means “Union is Strength.” It means the union is strong. There should be loyalty and concern for the honor of the organization to which one belongs. This can be achieved through the adoption of the principle of unity of command.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Distinguish between Indigenous Bankers and Money Lenders.
Answer:
| Concept | Indigenous Bankers | Money Lenders |
| 1. Meaning | Indigenous bankers are part of the unorganized money market in rural areas. | Money lenders are also part of an unorganized money market spread throughout the country. |
| 2. Financing | Indigenous bankers finance trade and commerce. | Money lenders are financing for consumption rather than trade. |
| 3. Interest Rate | Indigenous bankers charge interest rates lower than money lenders. | Money lenders charge interest rates more them indigenous bankers. |
| 4. Security | Indigenous bankers require security for giving loans. | Money lenders do not insist on securities for giving loans. |
Question 5.
Explain the need for Insurance.
Answer:
Insurance protects the businessman from financial loss by transferring the risk onto the insurance company. The business of the insurance company is to assume risks. The basic principle of insurance is “Spreading of the risk of loss among the number of persons”. Insurance gives the businessman a sense of security which is a real boon to him. From per national standpoint, insurance pools the savings of the individual policyholders. In this way, insurance may be regarded as an important agency of capital information. Life is full of uncertainties. The necessity to remove such uncertainties led to the need for insurance. Insurance is the provision that a prudent man makes against untoward happenings that may occur by chance. Business is also full of risks. The occurrence of any event which is uncertain is termed a risk. Likewise, these risks can be guarded using insurance.
Question 6.
What are the characteristics of an Entrepreneur?
Answer:
Characteristics of Entrepreneurs are:
- Innovation: Entrepreneurs deal with the changes. He does not continue with the old ideas.
- Risk-taking: Any new business poses a risk for entrepreneurs. They may succeed or fail. Entrepreneur takes risks.
- Self-confidence: They have the confidence that they can change the existing position.
- Hard work: Entrepreneurs are hard workers. Few people in our society work harder than entrepreneurs.
- Goal setting: Entrepreneurs get happiness by setting and striving for goals. They may not always achieve those goals.
- Accountability: Entrepreneurs take success or failure in their stride.
- Leadership: Leadership represents an abstract quality of a man.
- Managerial drill: The entrepreneur requires the managerial skill to achieve the goals of the enterprise.
Question 7.
List out various aspects to be covered in preparing a Project Report.
Answer:
The task of project report preparation encompasses information under various heads. Necessary documents, quotations, and inquiries should be attached with the details under given heads to herm a project report. It may not be out of place to emphasize that the project report should be prepared by the entrepreneur himself. This not only would save him money but also clarify many doubts thereby making him more optimistic about the success of the project report. A project report should normally cover a brief introduction of the proposed project, the constitution and nature of the unit, the details and promoters and products, marketing and competitions, manufacturing process, machinery and plant capacity, raw materials availability, land and building, general management and technical staff involved, cost of the project means of finance, working capital requirements, cost of production and profitability, project schedule, repayment schedule, security offered, etc.
Question 8.
What are the services of wholesaler to manufacturer?
Answer:
Services of wholesaler to manufacturer:
- Enabling large-scale production.
- Sharing/transfer of risk.
- Financial assistance in the form of advance payments.
- Advice regarding the market conditions.
- Removing the place barrier.
- Facilitating continuous production.
- Discharging the distribution function and thereby allowing the manufacturer to concentrate on production.
- Reducing the burden of storing the goods in a warehouse.
![]()
Question 9.
Why Management is considered a multi-faceted concept?
Answer:
Management is considered a multi-faceted concept why because it has.
- Social responsibility.
- Science as well as art.
- Management has a distinct entity.
- Purposive activity.
- Management is pervasive.
- Management is a group activity.
1. Social Responsibility:
Management has been accepted as a profession in the area of discipline and its responsibilities have increased.
2. Science as well as Art:
Management is considered both a science and an art because it is systematized knowledge that provides laws capable of universal application and has a cause.
3. Management has a Distinct Entity:
Managers at the higher level do not work at the operative level. They get the work done by others.
4. Purposive Activity:
It is a tool that helps efficient use of human and physical resources to accomplish the predetermined goals.
5. Management is Pervasive:
Management is relevant for all types of organizations – economic political and political.
6. Management is a Group Activity:
Since management is essential to undertaking any organized activity, one may infer that management is concerned with a group activity.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Define Jobbers & Brokers.
Answer:
He is a speculator who deals with securities independently and purchases and sells the securities in his name. A broker is a link between a Jobber and the general public who deals with a large variety of securities and works for a commission.
Question 11.
Write about Tele-Banking.
Answer:
“Telebanking refers to banking on the telephone”. The customer can dial the branch’s designated telephone number which is connected to a computer, by dialing his identification number, the software provided in the machine will become interactive with the customer asking him to dial the code number of the service required by him and give the suitable answer. The customer can enquire about his balance, previous transactions, or fund transfers between the accounts.
Question 12.
Who are the Pure Entrepreneurs?
Answer:
Pure entrepreneurs undertake any activity to satisfy their ego. He is motivated to achieve or prove his excellence.
Question 13.
What is meant by Project Appraisal?
Answer:
It is the process of examining the viability of a project which is based on technical feasibility, and marketability of the products.
Question 14.
What are the benefits of General Stores?
Answer:
General Stores:
These are usually small shops and establish¬ment located in residential areas. They usually sell essential commodities.
Benefits:
- They deal in a large variety of consumer goods.
- They sell goods for cash and also on a credit basis.
- They provide home delivery service to their customers.
Question 15.
What do you mean by Street Shops?
Answer:
Street Shops:
These shops are also called “street stalls”. These are called street stalls because these types of retailers display their goods on tables or under the tent.
![]()
Question 16.
What is an Export Processing Zone?
Answer:
They are set up in underdeveloped parts of a host country, aiming to reduce poverty and unemployment and stimulate the area’s economy.
Question 17.
What is POSDCORB?
Answer:
POSDCORB
P = Planning
O = Organising
S = Staffing
D = Directing
CO = Co-ordinating
R = Reporting
B = Budgeting
Part – II (50 Marks)
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
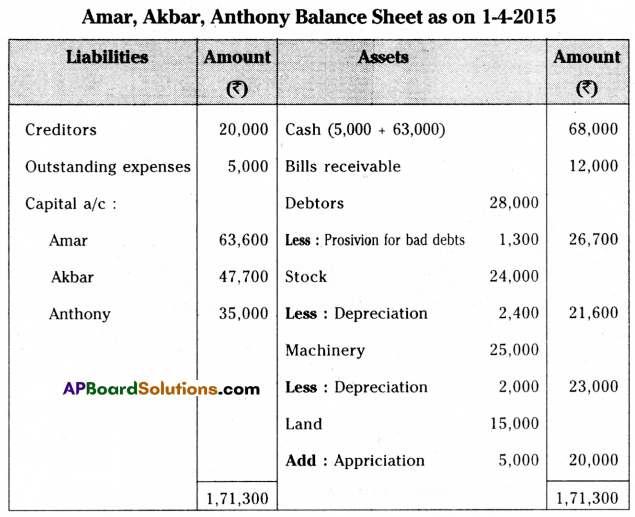
Amar and Akbar are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 3 respectively. Their balance sheet as of 31st March 2015 was as under.
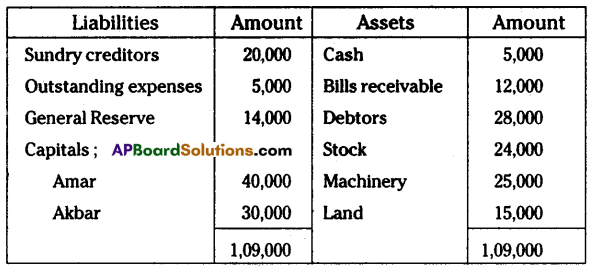
On the above date, Anthony was admitted into partnership for 1/4th share in the future profits on the following conditions:
(a) Anthony should bring ₹ 35,000 towards capital and ₹ 28,000 towards goodwill in cash
(b) Land to be valued at ₹ 20,000
(c) Machinery valued at ₹ 23,000
(d) Stock be depreciated by 10%.
(e) Provide for bad debts ₹ 1,300
Pass necessary journal entries, ledger accounts, and give balance sheet for new firm.
Answer:
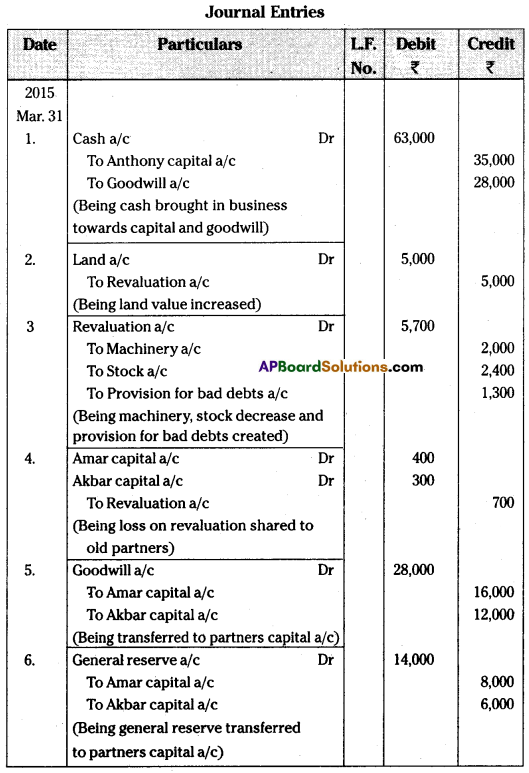
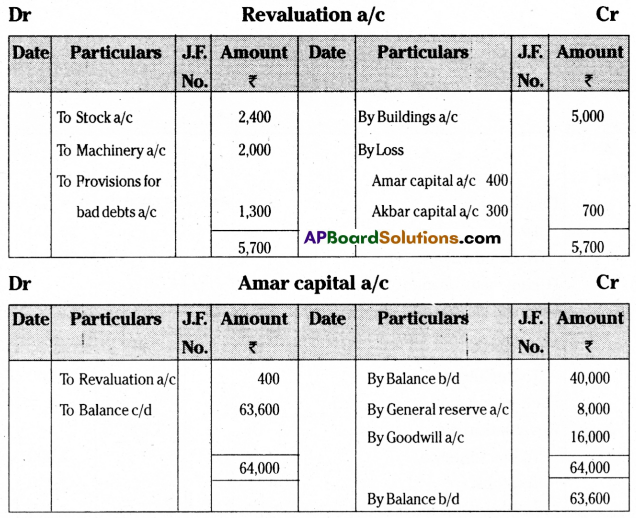
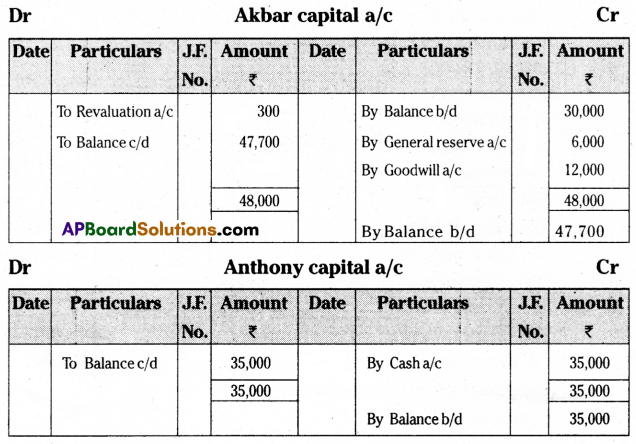
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions:
Question 19.
On 1-1-2015, Kamala of Hyderabad consigned goods valued at ₹ 30,000 to Ravi of Madras. Kamala paid cartage and other expenses ₹ 2000 on 1-4-2015. Ravi sent the account sales with the following information.
(a) 50% of the goods sold for ₹ 22,000.
(b) Ravi incurred expenses amounting to ₹ 1,200.
(c) Ravi is entitled to receive commission @ 5% on sales.
A bank draft was enclosed for the balance. Prepare the necessary ledger accounts in the books of Kamala.
Answer:
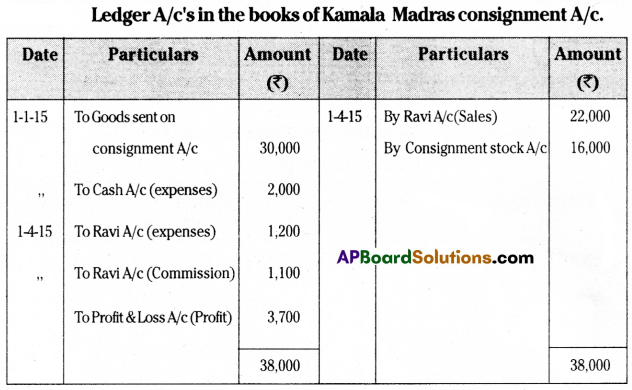
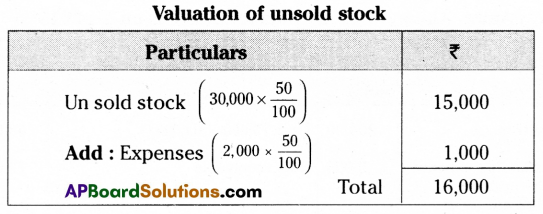
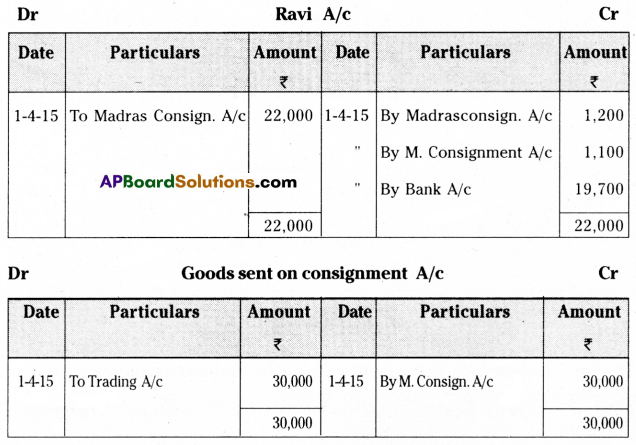
![]()
Question 20.
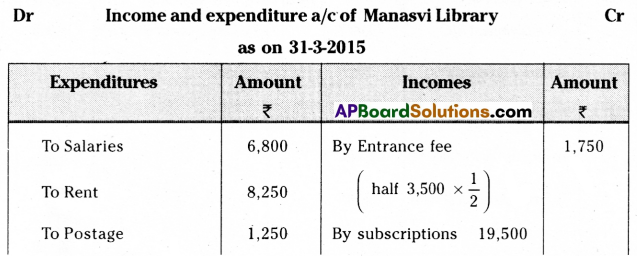
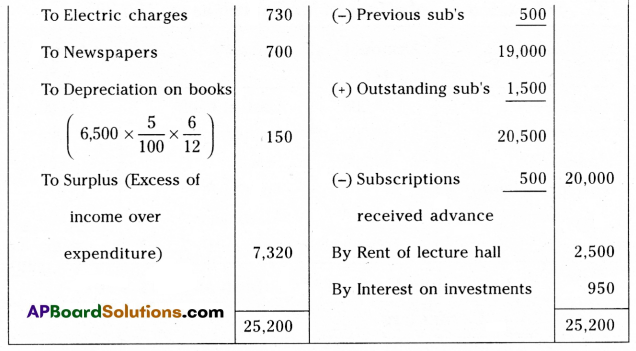
Following is the Receipts and Payments Account of “Manasvi Library” for the year ended 31st March 2015.
Receipts and Payments Account of Manasvi Library for the year ended 31-03-2015.
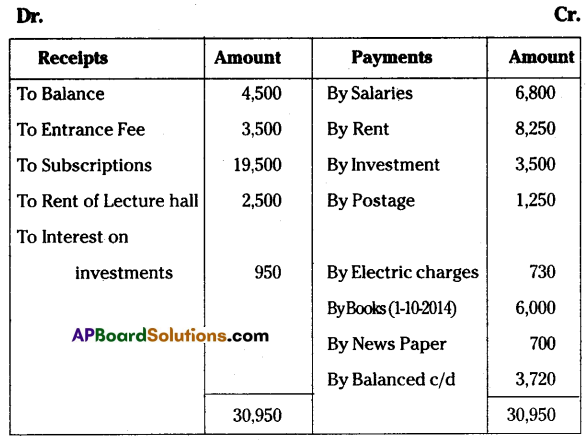
Additional Information:
1. Subscription amount includes ₹ 500 for the previous year and outstanding subscription for the current year is ₹ 1,500.
2. Subscription received in advance ₹ 500.
3. Capitalize half of the entrance fee.
4. Books are to be depreciated at 5% per annum.
You are required to prepare an income and expenditure account.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions:
Question 21.
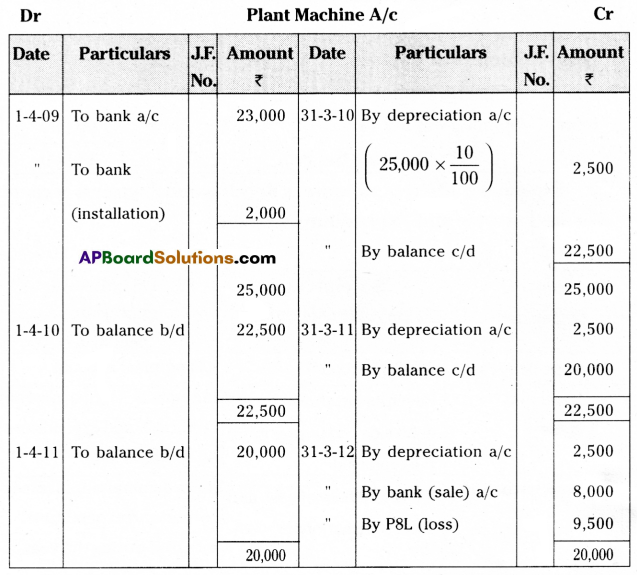
Raghava bought a Plant and Machine on 1st April 2009 for ₹ 23,000 and paid ₹ 2,000 for its installation. Depreciation is to be allowed at 10% under the straight-line method. On 31st March 2012 the Plant was sold for ₹ 8,000. Assuming that the accounts are closed at the end of the financial year. Prepare Plant & Machine a/c.
Answer:
Question 22.
Subash commenced his business on 1st April 2010 with a capital of ₹ 60,000. His position on 21st March 2011 was given below:
Furniture ₹ 18,000, Cash at bank ₹ 12,000, Bill payable ₹ 9,000, Creditors ₹ 11,000, Machinery ₹ 20,000, Stock ₹ 12,000, Debtors ₹ 23,000. During the year he withdrew ₹ 6,000 for personal use. Prepare a statement of affairs and find out a profit.
Answer:
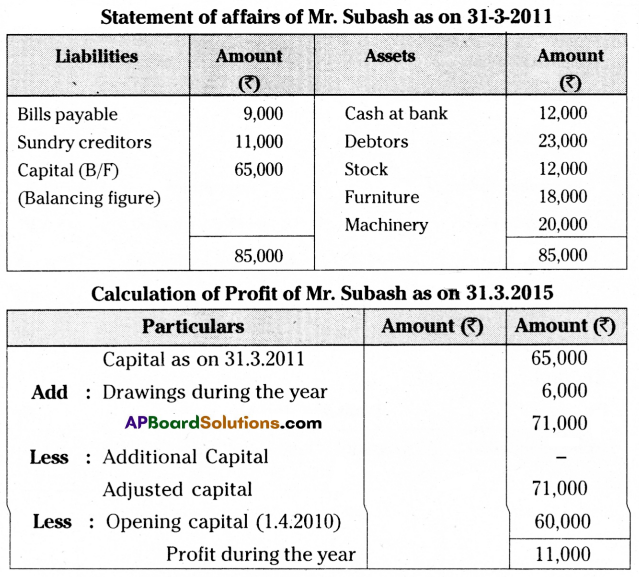
Question 23.
Explain the differences between the Receipts and Payments account and the Income and Expenditure account.
Answer:
| Basic of Difference | Receipts and Payments Account | Income and Expenditure Account |
| 1. Type of Account | It is a real account. | It is a nominal account. |
| 2. Debit and Credit Sides | Receipts are shown on the debit side and payments are on the credit side. | Income is shown on the credit side and expenditure on the debit side. |
| 3. Basic Structure | It is a summary of cash and bank transactions. | It is a summary of income earned and expenditures incurred during the year. |
| 4. Opening Balance | Opening balance which represents cash in hand or at a bank. | There is no opening balance. |
| 5. Object | It is prepared to present a summary of cash transactions for a given period. | It is prepared to ascertain the net results of all revenue transactions for a given period. |
| 6. Closing Balance | The closing balance shows cash in hand or at the bank. | The closing balance shows either a surplus or a deficit. |
| 7. Contents | Both revenue and capital items are considered. | Only revenue items are considered. |
| 8. Accrued Items | It does not include accrued items, i.e., accrued incomes and expenses. | It includes accrued incomes and expenses. |
| 9. Adjustments | No adjustments are required. | All adjustments relating to current-year income and expenditure are taken into consideration. |
Question 24.
Define Computerised Accounting. Explain its features.
Answer:
Computerized accounting is nothing but replacing the manual accounting system of maintaining the books of account with the use of relevant software packages for accounting on a computer. As its name suggests “Computerised Accounting” is an accounting done with the support of a computer. It tends to involve dedicated accounting software and digital spreadsheets to keep track of a business or client’s financial transactions.
Features of Computerised Accounting are:
1. Fast, Powerful, Simple and Integrated:
Computerized accounting is developed to automate and integrate all accounting transactions. All the accounting information, that is recorded will be at the fingertips of the user. It is very simple to operate with a greater speed.
2. Total Visibility:
The company will have greater visibility into the day-to-day business operations.
3. Improved user Free Experience:
Computerized accounting permits companies to enter data in various ways. It makes the work a pleasure. The company can adopt specific company needs with this feature.
4. Accuracy and Error-Free:
Computerized accounting provides users with definable templates with which they can get accurate and error-free data within no time as and when the button is clicked by the user.
5. Scalability:
Computerized accounting is designed to meet the current and future needs of the companies irrespective of their size and style.
6. Supremacy:
Computerized accounting is capable of storing huge volumes of transactions with greater retrieval capacity and efficiency.
7. Improved Business Performance:
Integrated and enhanced features of computerized accounting cover accounting, inventory, and reporting.
![]()
8. Rapid Decision Making:
Critical management information system reports instantly to make appropriate decisions at the right time.
9. Absolute Reliability:
Computerized accounting provides accurate critical financial information.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions:
Question 25.
What is the Reducing Balance Method?
Answer:
A method under which depreciation is calculated at a fixed percentage on the original cost of the asset in the first year and on written down value in the subsequent year.
Question 26.
What is Statement of Affairs?
Answer:
To find out capital, a statement showing various assets and liabilities of a business concern is prepared on a particular date, which is called a statement of affairs. It is similar to a balance sheet.
Question 27.
What is the Delcredere Commission?
Answer:
Remuneration or additional commision paid to the consignee for taking the responsibility of collecting the amount on credit sales made by him.
Question 28.
What is meant by Legacy?
Answer:
Legacy is the amount received by the organization as per the “will” of a person.
Question 29.
A and B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 3. They have admitted C’ into partnership by giving 1/4th share. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio.
Answer:
Old Ratio of A & B = 2 : 3 or \(\frac{2}{5}: \frac{3}{5}\)
C’s share = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Remaining share = 1 – \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) will be given to A and B in their old profit-sharing ratio.
New profit sharing ratio of A = \(\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{2}{5}=\frac{6}{20}\)
New profit sharing ratio of B = \(\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{9}{20}\)
New profit sharing ratio of C = \(\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{5}{5}=\frac{5}{20}\)
AB & C’s new profit sharing ratio = \(\frac{6}{20}: \frac{9}{20}: \frac{5}{20}\) (or) 6 : 9 : 5.
Question 30.
Write the formula for calculating the sacrificing ratio.
Answer:
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
![]()
Question 31.
What is the feature of scalability?
Answer:
Computerized accounting is designed to meet the current and future needs of the companies irrespective of their size and style.
Question 32.
What is spread spreadsheet package?
Answer:
A spreadsheet is an interactive computer application program. It helps the organization for analysis and storage of data in tabular form. It is a table of values arranged in rows and columns. Each value can have a pre-defined relationship to the other values.