Access to a variety of TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity.
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section – ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section – ‘B’ and any two questions in Section – ‘C’.
- In Section – A, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section -”’8′, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section – ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Section – ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all the questions.
Question 1.
Give the units of rate constants for zero and first order reactions.
Answer:
| Order | Units |
| Zero | mole.lit-1 |
| First | Sec-1 |
Question 2.
What is tailing of mercury? How is it removed?
Answer:
Mercury loses it’s lustreness, meniscus and consequently sticks. to the walls of glass vessel when it reacts with ozone. This phenomenon is called tailing of mercury.
2Hg + O3 → Hg2O + O2
It is removed by shaking it with water which dissolves Hg2O.
Question 3.
PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3 Why?
Answer:
In NH3 hydrogen bonding is present. Where as in case of PH3 hydrogen bonding is not present. So PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3.
![]()
Question 4.
State Henry’s law.
Answer:
At constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas present above the surface of liquid.
(Or)
The partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution.
P = KH × x KH – Henry’s constant
P = Partial pressure
x = Mole fraction of gas
Question 5.
What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
Answer:
By adding the cryolite to the pure Alumina, the melting point of pure Alumina is lowered (which is very high 2324K) and eletrical conductivity of pure alumina is increased.
Question 6.
Arrange the following bases in decreasing order of pKb values :
C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2 NH and C6H5NH2.
Answer:
The decreasing order of pKb values of gives amines is
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2 NH
Question 7.
What are Enantiomers?
Answer:
Enantiomers: The stereo isomers related to each other as non- superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
These have identical physical properties like melting point, boiling points refractive index etc. They differ in rotation of plane polarised right.
![]()
Question 8.
What is PDI (Poly Dispersity Index)?
Answer:
Poly Dispersity Index (PDI): The ratio between weight average molecular mass (Mw) and the number average molecular mass (Mn) of a polymer is called Poly Dispersity Index (PDI).
Question 9.
Write the name of the monomers present in Buna-S and Bakelite.
Answer:
→ In Buna – S monomers are 1,3- Butadiene
(CH2 = CH – CH = CH2)
and Styrene (C6H5 – CH = CH2)
→ In Bakelite monomers are phenol (C6H5 OH) Formaldehyde (HCHO)
Question 10.
CuSO4. 5H2O is blue in colour whereas anhydrous CuSO4 in colourless. Why?
Answer:
CuSO4.5H2O is blue in colour whereas anhydrous CuSO4 is colourless because in the absence of ligand, crystal field splitting doesnot occurs.
Section – B
Question 11.
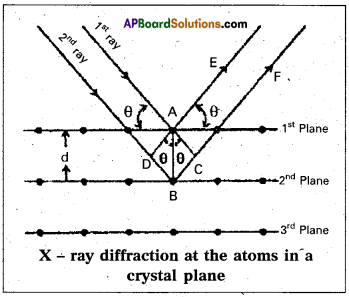
Derive Bragg’s equation.
Answer:
Derivation of Bragg’s equation : When X-rays are incident on the crystal or plane, they are diffracted from the lattice points (lattice points may be atoms or ions of molecules) . In the crystal the lattice points are arranged in regular pattern. When the waves are diffracted from these points, the waves may be constructive or destructive interference.
The 1st and 2nd waves reach the crystal surface. They undergo constructive interference. Then from the figure 1st and 2nd rays are parallel waves. So, they travel the same distance till the wave form AD. The second ray travels more than the first by an extra distance(DB + BC) after crossing the grating for it to interfere with the first ray in a constructive manner. Then only they can be in the same phase with one another. If the two waves are to be in phase, the path difference between the two ways must be equal to the wavelength (λ) or integral
multiple of it (n λ, where n = 1,2, 3 )
(i.e.,) nλ = (DB + BC)
[where n = order of diffraction]
DB = BC = d sin θ
θ = angle of incident beam,
(DB + BC) = 2d sin θ
d = distance between the planes
nλ = 2d sin θ
This relation is known as Bragg’s equation.
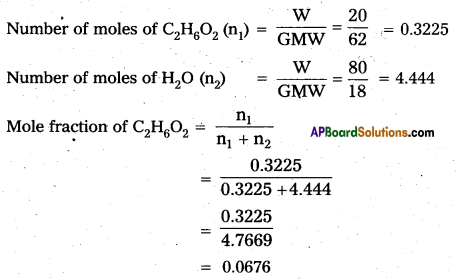
Question 12.
Calculate the molefraction of Ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in a solution containing 20% of C2H6O2 by mass.
Answer:
Given 20% of C2H6O2 solution by mass
Question 13.
What is catalysis? How is catalysis classified? Give two examples for each type of catalysis.
Answer:
Catalysis :
A substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed in the process, is called a catalyst. The action of catalyst in altering the rate of a chemical reaction is called catalysis.
Types of catalysis :
Catalysis is classified into two types as a) Homogeneous catalysis and b) Heterogeneous catalysis.
Homogeneous catalysis :
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in the same phase as that of reactants, is known as homogeneous catalysis.
Heterogeneous catalysis :
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in a phase different from that of the reactants is known as heterogeneous catalysis.
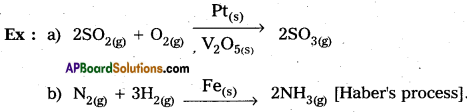
Question 14.
Write the IUPAC names of the following co-ordination compounds :
a) [PtCl2 (NH3)2]
b) [Ni(CO)4]
c) K3[Al(C2O4)3]
d) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl
Answer:
a) [PtCl2 (NH3)2] – Diamine Diamine Platinum (II)
b) [Ni(CO)4] – Tetra Carbonyl Nickel (O).
c) K3[Al(C2O4)3] – Potassium Trioxalate Aluminate (III)
d) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl – Bis Ethylene diamine dichloro Cobalt (III) Chloride.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain the purification of Sulphide ore by Froth floatation method.
Answer:
Froth floatation method :
- This method is used to concentrate sulphide ores.
- In this process a suspension of the powdered ore is made with water.
- A rotating paddle is used to agitate the suspension and air is blown into the suspension in presence of an oil.
- Froth is formed as a result of blown of air, which carries the mineral particles.
- To the above slurry froth collectors and stabilizers are added. Collectors like pine oil enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles.
- Froth stabilizers like cresol stabilize the froth.
- The mineral particles wet by oil and gangue particles wet by water.
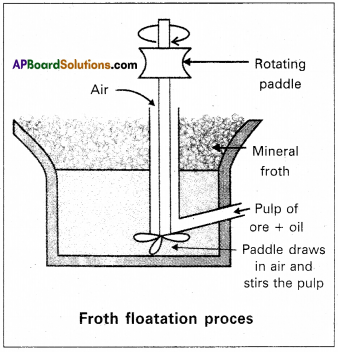
- The froth is light and is skimmed off. The ore particles are then obtained from the froth.
By using depressants in froth floatation process, it is possible to separate a mixture of two sulphide ores. Eg : In the ore containing ZnS and PbS, the depressant used is NaCN. It prevents ZnS from coming to the froth but allows PbS to come with the froth.
Question 16.
Write short notes on :
a) Carbylamine reaction
b) Racemisation
Answer:
a) Carbylamine reaction : Aniline reacts with chloroform in present of alc.KOH to form foul smelling phenyl isocyanide. This reaction is called carbylamine reaction.
C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + 3 KOH (ale) → C6H5NC + 3 KCZ + 3H2O
b) Racemisation :
Racemic mixture: Equal portions of Enantiomers combined to form an optically inactive mixture. This mixture is called racemic mixture.
1) Here rotation due to one isomer will be exactly cancelled by the rotation of due to other isomer.
2) The process of conversion of enantiomer into a racemic mixture is called as racemisation.
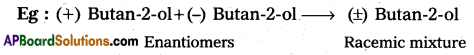
Question 17.
What are Hormones? Give one example for each:
i) Steroid hormones.
ii) Polypeptide hormones.
iii) Amino acid derivatives.
Answer:
Hormones : Hormone is defined as an “organic compound synthesised by the ductless glands of the body and carried by the blood stream to another part of the body for its function”. Eg : testosterone, estrogen.
- Example for steroid hormones : Testosterone, Estrogen
- Example for polypeptide hormones : Insulin
- Example for Amino acid derivative: Thyroidal hormones thyroxine.
![]()
Question 18.
Write short notes on :
a) Artificial sweetening agents.
b) Food preservatives.
Answer:
a) Artificial sweetening agents:
The chemical substances which are used instead of sucrose (or) sugar are called artificial sweetening agents. E.g. : Aspartame, Alitame, saccharin. These decrease the Calorific in take and at the same time several times sweeter than sucrose.
b) Food preservatives:
The chemical substances which prevent the spoilage of food due to microbial growth are called food preservatives.E.g. : Sodium benzoate, Salt of sorbic acid etc.
Section – C
Question 19.
a) How is XeF2 and XeF4 prepared? Give their structures.
Answer:
Xenon forms the binary fluorides XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 as follows. These are formed by direct combination of Xe and F2.
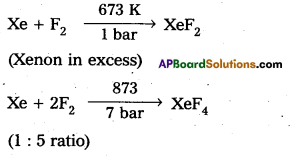
Structure of XeF2 :
1) In XeF2 central atom is ‘Xe’. ,
2) Xe’ undergoes sp3d hybridisation in it’s 1st excited state.
3) Shape of molecule is linear.
4) Xe form two σ.bonds with two fluorines.
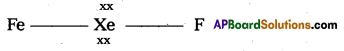
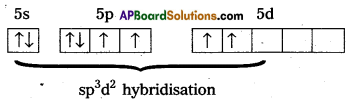
b) Structure of XeF4 :
1) Central atom in XeF4 is Xe’.
2) Xe undergoes sp3d2 hybridisation in it’s 2ndexcited, state.
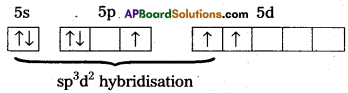
3) Shape of the molecule is square planar with bond angle 90° and bond length 1.95A.
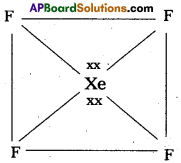
4) Xe – forms four o-bonds by the overlap of sp3d2 – 2pZ (F) orbitals.
b) How is chlorine prepared by Deacon’s method? Explain its reaction with the following:
i) Iron
ii) Na2S2O3
Answer:
Deacon’s process : In Deacon’s process chlorine is obtained by the oxidation of hydrogen chloride gas by atmospheric oxygen in the presence of CuCl2 (catalyst) at 723 K.
![]()
i) Iron : Cl2 reacts with Iron to form FeCl3
2 Fe + 3Cl2 → 2 FeCl3
ii) Na2S2O3 : ‘S’ is precipitated by the reaction of Cl2 with Na2S2O3.
Na2S2O3 + Cl2 + H2O → Na2SO4 + 2 HCl + S
Question 20.
a) Describe the salient features of the collision theory of reaction rates of bimolecular reaction.
Answer:
Collision theory of reaction rate bimolecular reactions salient features.
- The reaction molecules are assumed to be hard spheres
- The reaction is postulated to occur when molecules collide with each other.
- The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision
frequency (Z). - For a bimolecular elementary reaction A + B products
K= ZAB.e-Ea/RT;ZAB = collision frequency. - All collisions do not lead to product formation.
- The collisions with sufficient kinetic energy (Threshold energy) are responsible for product formation. These are called as effective collisions.
- To account for effective collisions a factor p called to probability factor or steric factor is introduced. K = PZAB.e-Ea/RT
- The proper orientation of reactant molecular lead to bond formation where as improper orientation makes them back and no product are formed.
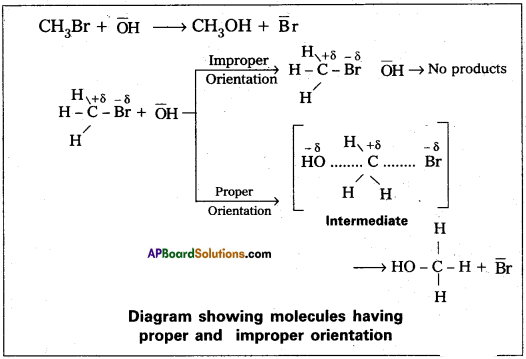
- In this theory activation energy and proper orientation of the molecules to gather determine the creteria for an effective collision and hence the rate of a chemical reaction.
b) State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions. Give its applications.
Answer:
Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions : The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolytes can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and the cation of the electrolytes.
λm0 = λA+0 + λB–0
λA+0 = Limiting molar conductivity
λA+0 = Limiting molar conductivity of cation
λB–0 = Limiting molar conductivity of anion
Applications :
1) Kohlrausch’s law is used in the calculation of the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolytes.
Eg: λCH3COOH = λCH3COONa + λHCl – λNaCl
= λCH3COO– + λNa+ + λH+ + λCl– – λNa+ – λCl–
= λCH3COO– + λH+
2) This law is used in the calculation of degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte.
3) This law is used in the calculation of solubility of sparingly soluble salts like AgCl, BaSO4
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the following reactions :
i) Williamson’s synthesis.
ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
iii) Cannizaro reaction.
iv) Aldol condensation.
Answer:
i) Williamson’s synthesis :
Alkyl halides reacts with sodium j alkoxides to form ethers. This reaction is called Williamson’s
synthesis.
R-X + R’-ONa → R-O-R’ + NaX
E.g. : Ethyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide to form. diethyl ether.
C2H5Cl + C2H5ONa → C2H2OC2H5 + NaCl
ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction :
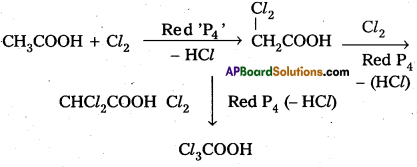
Carboxylic acids having a – hydrogen reacts with halogen and red phosphorus to form a-halo carboxylic acids. This reaction is called H.V. Z. reaction.
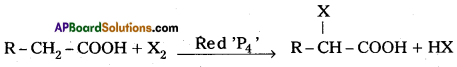
Eg : Acetic acid reacts with Cl2 and red ‘P’ to form finally trichloro acetic acid.
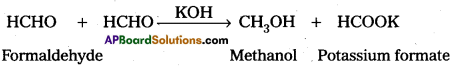
iii) Carinizaro reaction:
Aldehydes without a-hydrogen undergo reaction with strong base to form an alcohol and salt of carboxylic acid. This reaction is called Cannizaro reaction.
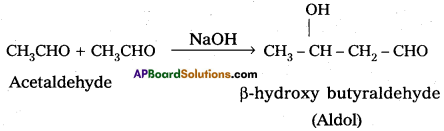
iv) Aldol condensation:
Aldehydes having a-hydrogen undergo reaction in presence of base to form the products Aldol. This resction is called aldol condensation