Access to a variety of TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2019 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity.
TS Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2019
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section – ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section – ‘B’ and any two questions in Section – ‘C’.
- In Section – A, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section -”’8′, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section – ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Section – ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all the questions.
Question 1.
What are isotonic solutions?
Answer:
Isotonic solutions: Two solutions having same osmotic pressure . ‘ at a given temperature are called Isotonic Solutions.
e.g.: Blood is isotonic with 0.9% \(\left(\frac{W}{V}\right)\) NaCl [Saline]
Question 2.
What is a galvanic cell? Give one example.
Answer:
The electro chemical cell which converts chemical energy into electrical energy by the use of spontaneous redox reaction is called Galvanic cell.
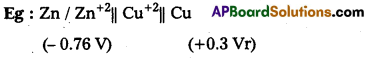
Question 3.
Give the composition of the following alloys.
i) Brass
ii) Bronze
Answer:
i) Brass – 60% Cu, 40% Zn.
ii) Bronze – Cu 75 to 90%, Sn-10-25%
![]()
Question 4.
What is Lanthanoid contraction?
Answer:
Lanthanide contraction : The slow decrease of Atomic radius (or) atomic size in lanthanides with increase of atomic number is called Lanthanide contraction.
Question 5.
What is Ziegler – Natta catalyst?
Answer:
A mixture of tri alkyl Aluminium and titanium chloride is called Zieglar Natta catalyst.
E.g. : (C2H5)3 Al + TiCl4.
Question 6.
What is vulcanization of rubber?
Answer:
The process of heating natural rubber with sulphur to improve it’s properties at 373 – 415 K in presence of Zno or Zn – sterate is called vulcanization of rubber.
Question 7.
How Grignard reagent is prepared?
Answer:
Alkyl Magnesium halide is called Grignard reagent. It is prepared by the reaction of Alkyl halides with Magnesium metal in presence of dry ether.
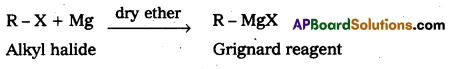
Question 8.
Write equation for carbylamine reaction.
Answer:
Carbylamine reaction: Aniline reacts with chloroform in presence of alcoholic KOH to form foul smelling phenyl Isocyanide.
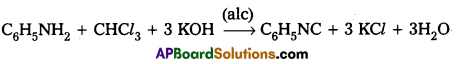
Question 9.
What are Enantiomers?
Answer:
The optical isomers which are mirror images but non-superior imposable are called Enantiomers.
![]()
Question 10.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of the ir basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2 NH, NH3.
Answer:
(C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3 > C6H5NH2
Section – B
Question 11.
Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 5g of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) in 450 ml Solution.
Weight 1000
Answer:
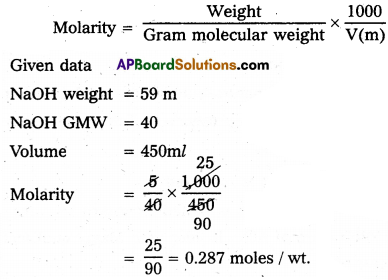
Question 12.
Derive Bragg’s equation.
Answer:
Derivation of Bragg’s equation : When X-rays are incident on the crystal or plane, they are diffracted from the lattice points (lattice points may be atoms or ions or molecules). In the crystal the lattice points are arranged in regular pattern. When the waves are diffracted from these points, the waves may be constructive or destructive interference.
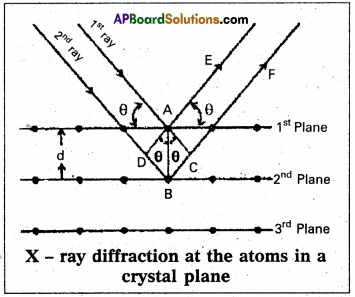
The 1st and 2nd waves reach the crystal surface. They undergo constructive interference. Then from the figure 1st and 2nd rays are parallel waves. So, they travel the same distance till the wave form AD.
The second ray travels more than the first by an extra distance (DB + BC) after crossing the grating for it to interfere with the first ray in a constructive manner. Then only they can be in the same phase with one another. If the two waves are to be in phase, the path difference between the two ways must be equal to the wavelength (λ) or integral multiple of it (n λ, where n = 1, 2, 3 )
(i.e.,) nλ = (DB + BC) [where n = order of diffraction]
DB = BC = d sin θ
θ = angle of incident beam,
(DB + BC) = 2d sin θ
d = distance between the planes
nλ. = 2d sin θ
This relation is known as Bragg’s equation.
![]()
Question 13.
Write any four differences between physisorption and chemisorption.
Answer:
Distinguishing characteristics of Physisorption and Chemisorption are given in the following table :
| Physisorption | Chemisorption |
| 1. This process is weak, due to vander Waal’s forces. | 1. This process is strong, due to chemical forces. |
| 2. The process is rever sible. | 2. The process is irreversible. |
| 3. This is a quick process. i.e., takes place quickly. | 3. This is a slow process. |
| 4. The process decreases with increase of tempe rature. | 4. The process increases with increase of temperature. |
| 5. This is a multilayered process. | 5. This is a unilayered process. |
| 6. The process depends mainly on the nature of the adsorbent. | 6. The process depends both on the nature of adsorbent and adsorbate. |
Question 14.
Explain roasting and calcination.
Answer:
Roasting :
Removal of the volatile components of a mineral by heating mineral either alone (or) mixed with some other substances to a high temperature in the presence of air is called Roasting.
- It is applied to the sulphide ores.
- SO2 gas is producted along with metal oxide.
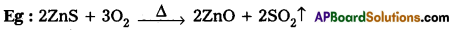
Calcination :
Removal of the volatile components of a mineral by heating in the absence of air is called calcination.
- It is applied to carbonates and bicarbonates.
- CO2 gas is produced along with metal oxide.

Question 15.
How is nitric acid manufactured by Ostwald’s process?
Answer:
Step – 1 : In step -1 Ammonia is oxidised to form Nitric oxide in presence of catalyst.
![]()
Step – 2 : Nitric oxide is oxidised to form Nitrogen dioxide.
2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2
Step – 3 : Nitrogen dioxide dissolved in water to form Nitric acid.
3 NO2 + H2O → 2 HNO3 + NO
Here to get 98% HNO3 it undergo distillation followed by dehydration with H2SO4.
Question 16.
Write the IUPAC names of the following co-ordination compounds :
a) [CO(NH3)4 (H2O) Cl]Cl2
b) [Ni(CO)4
c) K3(Fe(CN)6]
d) [Cr(NH3)4(H2O)3]Cl3
Answer:
a) [CO(NH3)4 (H2O) Cl]Cl2 – Mono aquo monochloro – Tetra amine cobalt (III) chloride
b) [Ni(CO)4 – Tetra carbonyl Nickel (O)
c) K3(Fe(CN)6] – Potassium Hexa Cyano ferrate (III)
d) [Cr(NH3)4(H2O)3]Cl3 – Tri amine Tri aquo Chromium Chloride (III)
![]()
Question 17.
What are harmones? Give one example for steroid hormones and polypeptide hormones.
Answer:
Hormones : Hormone is defined as an “organic compound synthesised by the ductless glands of the body and carried by the blood stream to another part of the body for its function”. Eg : testosterone, estrogen.
- Example for steroid hormones : Testosterone, Estrogen
- Example for poly peptide hormones : Insulin
- Example for Amino acid derivative : Thyroidal hormones thyroxine.
Question 18.
Write notes on Antiseptics and Antibiotics.
Answer:
Antiseptics :
The chemical compounds that kill (or) prevent the growth of micro organism are called antiseptics. Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces.
E.g. : Dettol, Bithional etc.
Antibiotics :
The chemical substances produced by micro organisms and inhibit the growth or destroy microorganisms are called antibiotics.
(Or)
The substance produced totally or partly by chemical synthesis which in low concentration inhibits the growth (or) destroy micro¬organism by intervening in their metabolic process are called antibiotics. E.g. : Penicillin, Chloramphenicol etc.
Section – C
Question 19.
How is chlorine prepared by Deacon’s process? Explain its reactions with Hot Cone. NaOH. H2S and Na2S2O3
Answer:
Deacon’s process : In Deacon’s process chlorine is obtained by the oxidation of hydrogen chloride gas by atmospheric oxygen in the presence of CuCZ2 (catalyst) at 723 K.
![]()
Cl2 reacts with hot Cone. NaOH to form sodium chloride and sodium chlorate
3Cl2 + 6 NaOH → 5 NaCl + NaClO3 + 3 H2O
Cl2 reacts with H2S and forms HCl and ‘S’
Cl2 + H2S → 2 HCl + S
‘S’ is precipitated by the reaction of Cl2 with Na2S2O3.
Na2S2O3 + Cl2 + H2O → Na2SO4 + 2 HCl + S
Question 20.
Give a detailed account of the Collision theory of reaction rates of bimolecular reaction.
Answer:
Collision theory of reaction rate bimolecular reactions salient features.
- The reaction molecules are assumed to be hard spheres.
- The reaction is postulated to occur when molecules collide with each other.
- The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
- For a bimolecular elementary reaction A + B products
Rate = ZAB. e-Ea/RT; ZAB = collision frequency. - All collisions do not lead to product formation.
- The collisions with sufficient kinetic energy (Threshold energy) are responsible for product formation. These are called as effective collisions.
- To account for effective collisions a factor p called to proba¬bility factor or steric factor is introduced.
Rate = P ZAB . e-Ea/RT - The proper orientation of reactant molecular lead to bond formation where as improper orientation makes them back and no product are formed.
![]()
Question 21.
With a suitable example write equations for the following:
i) Kolbe’s reaction
ii) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
iii) Williamson s ether synthesis
iv) Cannizaro reaction.
Answer:
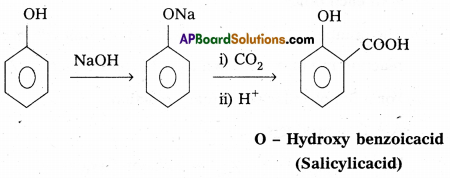
i) Kolbe’s reaction :
Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide. This undergoes electrophillic substitution with CO2 to form salicylic acid.
ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction :
Phenol reacts with chloroform in presence of NaOH to form salicylaldehyde (O – Hydroxy benzaldehyde). This reaction is known as Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
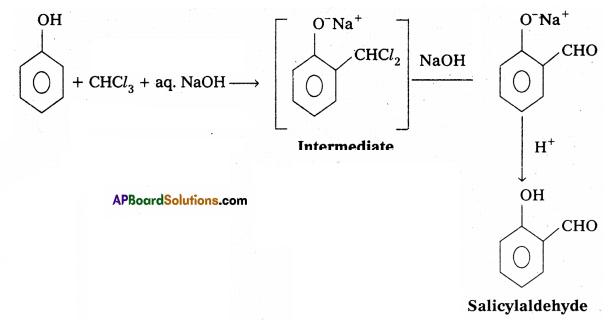
iii) Williamsons ether synthesis :
This method is used for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The reaction of an alkyl halide with sodium alkoxide to form • ethers is known as Williamson’s Synthesis.
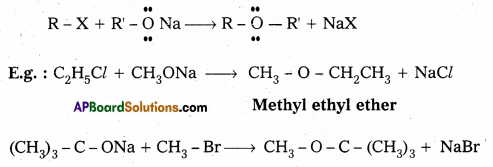
iv) Cannizaro’s reaction :
Aldehydes without a-hydrogen reacts with strong base to form an alcohol and salt of carboxylic acid.
