Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2015 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2015
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits:
- Easy formation: It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources : The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial Capacity: They pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making: The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility: The partnership is flexible in nature and at any time after mutual consent, the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations.
- Sharing risks: The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation : All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations:
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is the fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership firm suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferability of share : No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for the dissolution of the partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions: Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
Distinguish between a private company and a public company.
Answer:
The following are the differences and a Public Company between Private Company and a Public Company.
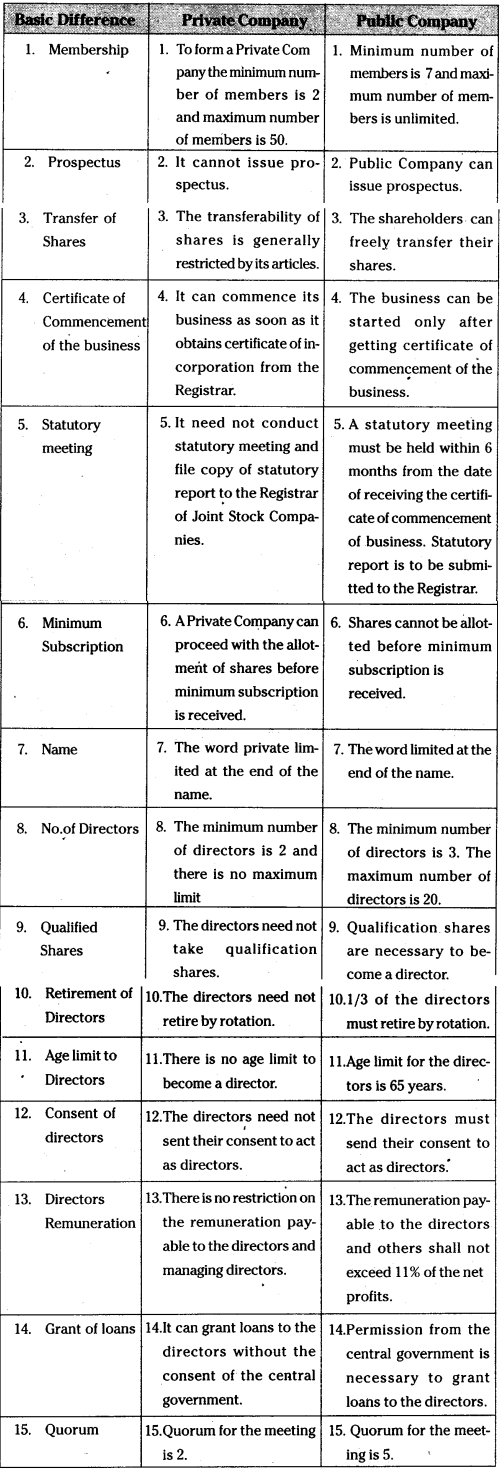
![]()
Question 3.
What is business finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organization.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business finance.
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
Need and significance of business finance :
- To commence a new business : Money is needed to start a new business and to procure fixed assets like land and buildings etc., working capital is required to meet the day-to-day expenses and holding current assets like cash, stock-in-trade etc.
- To expand the business: Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
- To develop and market new products: Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products.
- To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
- To take over another business : In order to overcome competition an enterprise may decide to take over another business.
- To more to new premises : Sometimes a business may be forced to shift the business in another place.
- Day-to-day running : A business needs money to meet the day-to-day requirements like wages, taxes etc.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each:
Question 4.
Define industry. Explain the classification of industries.
Answer:
Industry: Industry is concerned with making or manufacturing goods. It is the part of production which is involved in changing form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product.
Ex : Weaving yarn into cloth.
Classification of Industires:
1) Primary industry : Primary industry is concerned with pro-duction of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort. E.g : Farming, Fishing, Horti-culture etc.
2) Genetic industry : Genetic industry is related to the repro-ducing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale. E.g : Nurseries, cattle breeding, poultry etc.
3) Extractive industry : It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw form and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. E.g: Mining, coal, mineral, iron. ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry : The industry is engaged in-the cre-ation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabrication of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
5) Manufacturing industry i This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human uses. E.g : Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry, Iron and steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry: These industries are engaged in the provi-sion of essential services to the community. Hg : Banking, transport, insurance etc.
Question 5.
Define cooperative society. Explain any five features of cooperative society.
Answer:
The Indian Co-operative Societies Act, 1932 Section 4 defines co-operatives as a “society which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principle”.
Features of Co-operative Society:
- Voluntary membership: A co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. Everyone is at liberty to enter or leave the co-operative society as and when he likes. Any person can become a member irrespective of his/her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
- Democracy and equality : It is organised on the basis of democracy and equality. Every member has a right to participate in the management. Every member has only one vote.
- State control: A co-operative society is subject to the control and supervision. In India, all co-operatives are registered under Indian co-operative societies Act or respective state co-operative laws.
- Service motto: The primary objective of co-operative society is to provide service to the members. The aim is not to earn profits. The societies earn small amount of profits to cover administration expenses.
- Knowledge of the principles of co-operation Every person joining a co-operative society must be familiar with the fundamentals of co-operation. The important aim is to serve common man. The spirit is “Each for all and all for each”.
Question 6.
Discuss the differences between memorandum of association and cuticles of association.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.

Question 7.
Explain the classification of sources of finance.
Answer:
Sources of finance can be classified on the basis of period, ownership and generation.
On the basis of period: On the basis of period, sources of funds x are divided into long term, medium term and short term finance. Long term sources fulfill the financial requirements for a period exceeding five years and include sources such as shares, debentures and long term borrowings. Medium term finance is required for a period of more them one year and these includes borrowings from commercial banks, public deposits, lease financing. Short term funds are required for a period of less than one year and the sources are trade credit, bank crfedit, instalment credit, advances, bank overdraft, cash credit and commercial paper.
On the basis of ownership : On the basis of ownership, the sources can be classified into owners funds and borrowed funds. Owners funds are those which are provided by the owners which include issue of shares and retained earnings. Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through loans or borrowings which include loans from commercial banks, financial institutions, issue of debentures and public deposits.
On the basis of generation: Sources of finance can be generated from internal source or external source. Interned sources of funds are generated within the business such retained earnings, collection of receivables, depreciation fund, disposing surplus stock etc. External sources lie outside the business and include shares, debentures, public deposits, borrowings from banks and financial institutions etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Differentiate between the shares and debentures.
Answer:
The following are the differences between shares and Debentures.
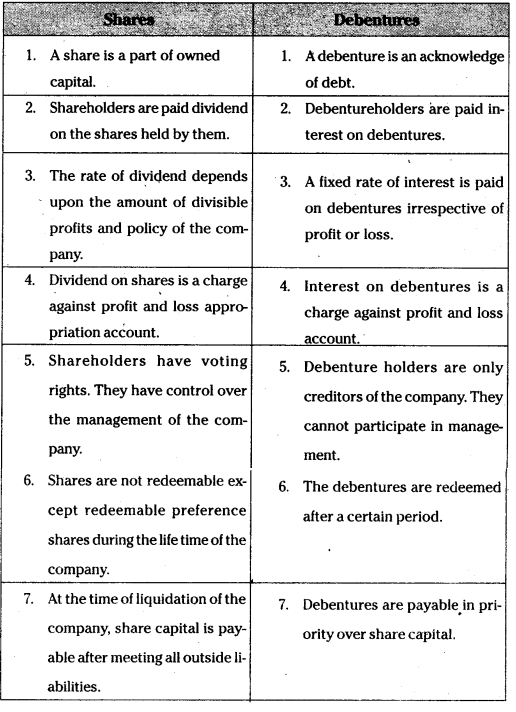
Question 9.
What is e-business ? Explain the benefits of e-business to customers.
Answer:
The term E-business was first used IBM in 1997. It is defined E-Business as” The transformation of key business processes through the use of internet technologies”. E-Business is defined as the application of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), which support all the activities of Business with customers. It also enables enterprises to link their internal and External data processing systems more efficiently and flexibly and serve better to the needs and expectations of their customers. E-business uses web based technology to improve relationship with customers.
Benefits of E-business of Customers :
- Purchasing made easy : E-Business enables consumers to shop or to do any other transaction 24 hours a day, round the year from any location.
- Wide choice : Customers will have more choices as more alternative products and services are available.
- Saving in prices : E-Business provides customers with less expensive products and services which allows them to shop in many places and conduct quick comparisons. E-business facilitates competition, which results in substantial discounts.
- Exchange of information : E-Business allows customers to interact with each other and exchange their opinions and experiences on the products purchased by them.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each :
Question 10.
What is profession ?
Answer:
Profession is an occupation involving the provision of personal service of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc.. The specfied service is provided for a professional fees charged from the clients. For example; a doctor helps his patients through his expert knowledge of science of medicine and charges a fee for the service.
Question 11.
Explain an entrepot trade.
Answer:
When the goods are imported from one country and the same is exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade.
E.g.: India importing wheat from U.S.A. and exporting the same to Sri Lanka.
Question 12.
Who is a Kartha ?
Answer:
The Senior most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs to joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager. The liability of Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of other members of two family. He is not accountable to anyone.
Question 13.
Who is called active partner ?
Answer:
An active partner is one who fakes active part in the day-to-day working of the business. He may act in various capacities as manager, advisor or organisor. He is also known as working partner or managing partner.
Question 14.
What is meant by working capital ?
Answer:
The capital required by business entreprise to run its day-to-day operations such as purchase of raw material, payment of wages and holding current assets like of raw materials, bills receivable is called working capital. The amount of working capital required varies from business to business. Generally trading concerns require more working capital as compared to manufacturing concerns.
Question 15.
What is trade credit ?
Answer:
Trade credit is the credit extended by one trader to another for the purchase of goods and services. Trade credit facilitates the purchase of supplies without immediate payment such credit appears in the record of the buyer of the goods as ‘Sunday Creditors’ or ‘account payable’. The credit is commonly used business concerns as a source of short term financing.
Question 16.
Define microenterprises.
Answer:
In case of manufacturing enterprises, a micro enterprise is an enterprise where the investment is plant and machinery does not exceed ₹ 25 lakhs. In case of service enterprises, a Microenterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
Question 17.
Define MNC.
Answer:
According to International Labour Organisation’s report, Multi National Corporation refers to an enterprise whose managerial head quarters are located in one country, while it carried out operations in number of other countries as well”.
According to Prof. Vernon MNC is defined as “a cluster of operations of diverse of nationality joined together by common management strategy”.
Part – II (Marks 50)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question :
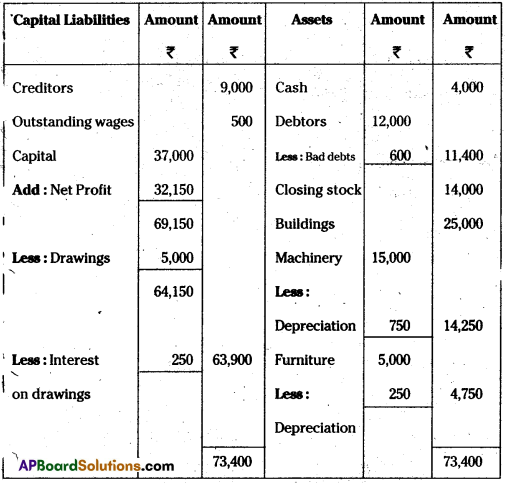
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance of Rama Traders, prepare the final accounts for the year ended 31.03.2012.
Trial Balance
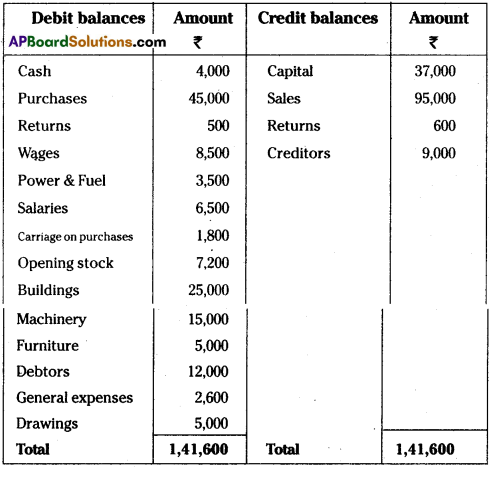
Adjustments:
i) Closing stock value Rs. 14,000
ii) Depreciation on Furniture Rs. 250 on Machinery Rs. 750
iii) Outstanding wages Rs. 500
iv) Bad debts Rs. 600
v) Interest on drawings 5%
Answer:
Trading and profit and Loss Account of Rama Traders for the year ended 31-03-2012.
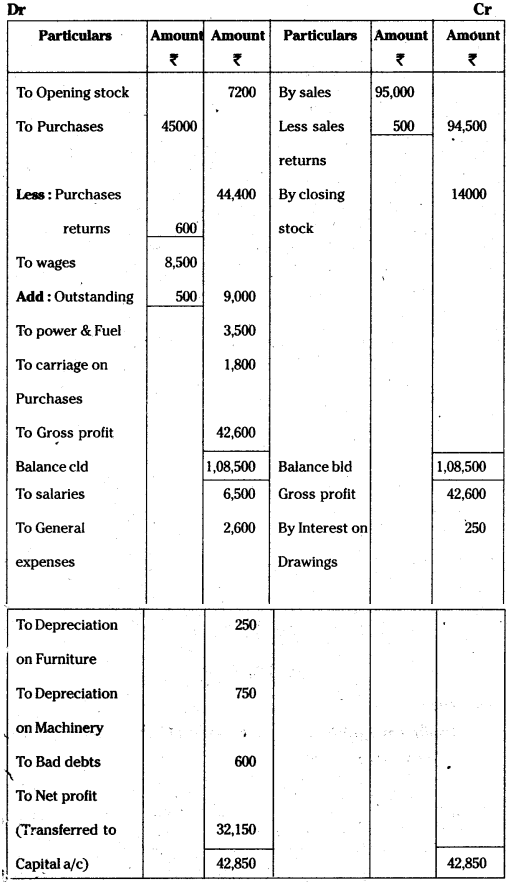
Balance sheet of Rama Traders as on 31-3-2012.
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions :
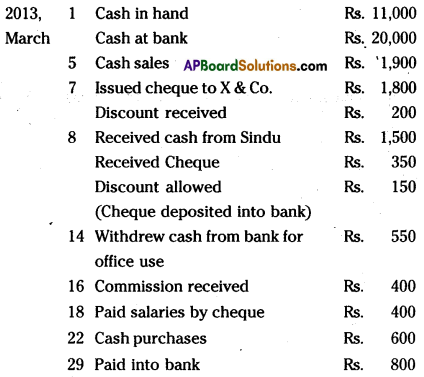
Question 19.
Prepare a three column cashbook from the following particulars:
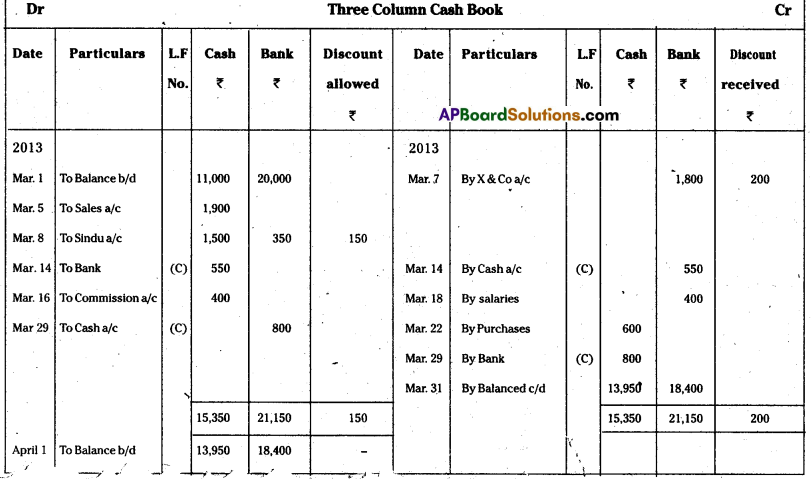
Answer:
Question 20.
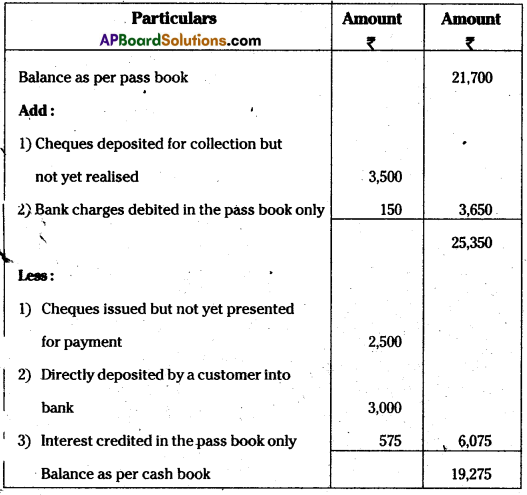
Sainath passbook showed a balance of Rs. 21,700 as on 30.09.2013. On comparing the cashbook the following discrepancies were noted.

Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement showing balance as per cashbook.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation statement of Sainath as on 30.09.2013.
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions :
Question 21.
What are the accounting concepts ? Explain any five accounting concepts in detail.
Answer:
Accounting Concepts : The term concept means an idea or thought. Basic accounting concepts are the fundamental ideas „ or basic assumptions underlying the theory and practice of financial accounting. These concepts are termed as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Concepts are as follows.
1. Business Entity Concept Business is treated separate from e proprietor. All the transactions are recorded in the books of business and not in the books of the proprietor. The proprietor is also treated as a creditor for the business. When he contributes capital he is treated as a person who has invested his amount in the business.
2) Going Concern Concept : This concept relates with the long life of the business. The assumption is that business will continue to exist for unlimited period unless it is dissolved due to some reason or the other.
3) Cost Concept: According to this concept, an asset is recorded at cost i.e. the price which is paid at the time of acquiring it. In balance sheet, these assets appear not at cost price but depreciation is deducted
and they at the amount which is cost less depreciation.
4) Accounting Period Concept: Every business man wants to kow the result of his investment and efforts after a certain period. Usually one year period is regarded as ideal for this purpose. It may be 6 months or 2 years also. This period is called accounting period.
5) Duel Aspect Concept : Under this concept, every transaction has got two fold aspect
A) Receiving the benefit and
B) Giving of that benefit.
For instance, when a firm acquires an asset (receiving the benefit) it must pay cash (giving of that benefit). Therefore, two accounts are to be passed in the books of accounts.
![]()
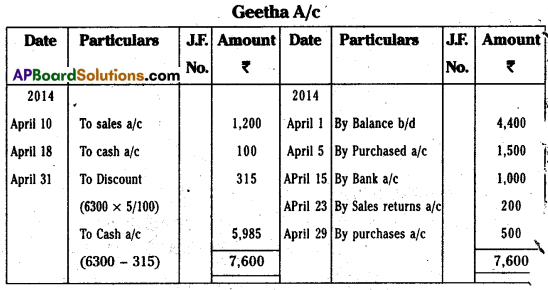
Question 22.
Prepare Geetha’s account from the following particulars :

Geetha’s account settled with 5% discount.
Answer:
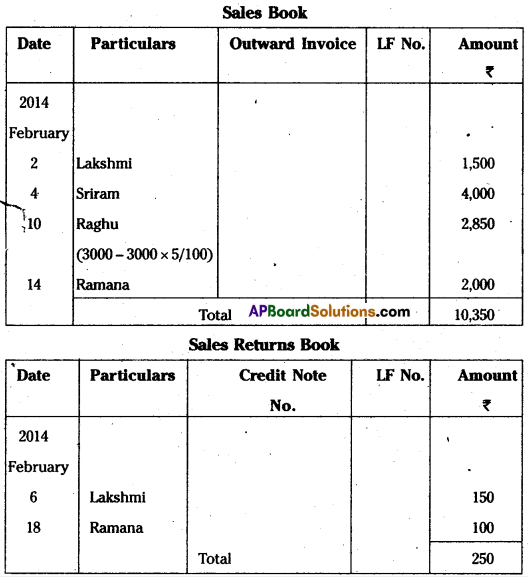
Question 23.
Enter the following transactions in the proper subsidiary books.

Answer:
Question 24.
What are the various types of errors ? Explain.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors.
1) Error of principle: Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors: When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is caused clerical errors, “‘’hey are given divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of Omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of Commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error compensated by other error or errors.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions :
Question 25.
What is bookkeeping ?
Answer:
Book-keping is the art of recording business transactions in v regular and systematic manner. According to carter “Book-keeping is the science and art of correctly recording books of accounts all those business transactions that result in transfer of money or money’s worth.
Question 26.
What is double-entry system ?
Answer:
According to J.R.Batliboi “Every business transaction has a two sold effect and than it affects two accounts in opposite direction and if a complete record were to be made of each such transaction, it would be necessary to debit one account and credit another account. This recording of two fold effect of every transaction has given rise to the term Double entry system of book-keeping is that “for every debit there must be corresponding value of credit”.
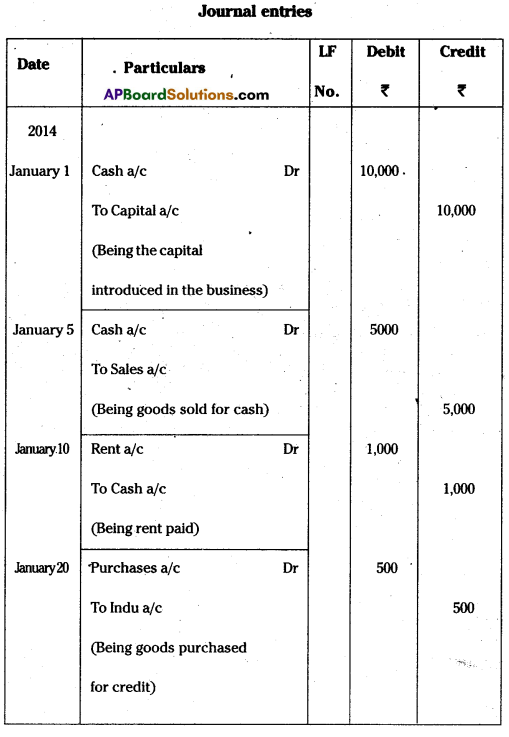
Question 27.
Journalize the following transactions.

Answer:
Question 28.
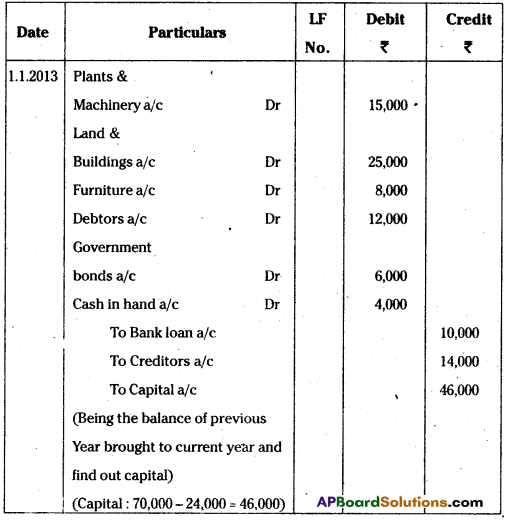
Write the opening entry as on 1.1.2013 from the following :

Answer:
Operating entry (Journal Proper)
Question 29.
What is meant by contraentry?
Answer:
Contra means the other side. If the double entry of a transaction is complete in the Cash book itself such entry is called contra entry. Contra entry arises when cash and bank accounts are simultaneously involved in a transaction. It happens when either cash or cheques are deposited in the bank and cash is withdrawn for office use. In both cases entries are made in cash and bank columns.
![]()
Question 30.
Describe the overdraft.
Answer:
Overdraft is a credit facility given by a bank to draw the amounts repeatedly upto a certain limit sanctioned as when the need arises. This can be repaid by depositing cash or cheques and the bank charges interest on the overdraft facility availed by firm. The overdraft is also called as ‘unfavourable balance’.
Question 31.
Prepare a Trial Balance from the following particulars :
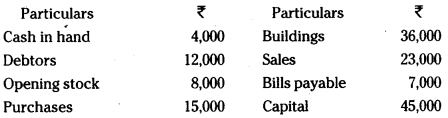
Answer:
Trial Balance
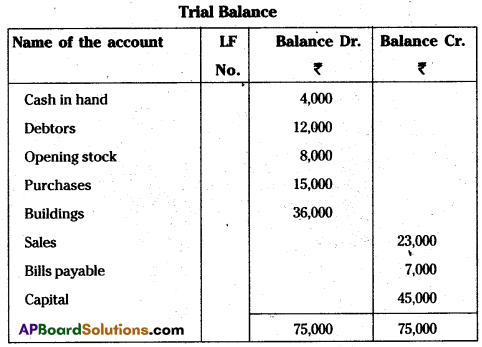
Question 32.
Define revenue expenditure with two examples.
Answer:
Revenue expenditure consists of expenditure of the benefit of which is not carried over to the several accounting periods. It is expenditure incurred in one accounting period the full benefit of which is consumed in the same period. Such expenditure is necessary for the maintenance of earning capacity including the up keep of the fixed assets.
Eg:
- Office & administration expenses,
- Selling expenses.