Access to a variety of TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2020 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity.
TS Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2020
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
Define TLV.
Answer:
TLV : (Threshold Limit Value) : The permissiable level of the toxic substance (or) pollutants in the atmosphere which affects a person ^dversly when he is exposed to this for 7 – 8 hrs. in a day is called TLV.
Question 2.
Write any two gases responsible for Greenhouse effect.
Answer:
- Green plants abosrbs CO2 gas for photosynthesis and releases O2 gas.
- Due to deforestation, decomposition of lime stone and burning of fossil fuels CO2 concentration is increased in atmosphere. .
- The increase of CO2 level disturbs the O2 – CO2 balance in the atmosphere and it is responsible for green house effect (or) global warming.
Question 3.
Write chemical name and formula of Plaster of Paris.
Answer:
Plaster of paris is the hemi hydrate of CaSO4 with formula CaSO4. \(\frac{1}{2}\) H2O.
Preparation :
Plaster of paris is obtained by heating gypsum at 393 K.
![]()
- If temperature is used greater than 393 K then an hydrous CaSO4 is formed which is called dead burnt plaster’.
- Plaster of paris has an important property of setting with water.
- It forms a hard solid in 5 to 15 min. When it is mixed with suitable quantity of water.
- It is majorly used in building industry and as well as plasters.
- It is used in the bone fractures (or) sprain conditions.
- It is used in dentistry.
- It is used in manufacturing status and busts.
Question 4.
How does graphite functions as a Lubricant?
Answer:
Graphite is soft and it has layer lattice. In this structure one of the layer slided over another due to weak Vander Waal’s force of attraction. These layers are slippery. Hence, it is greasy and function as lubricant.
![]()
Question 5.
Write biological importance of Na+ and Ca+2 ions.
Answer:
Sodium ion (Na+) helps in :
i) the transmission of nerve signals.
ii) regulation of flow of water accross the cell membranes.
iii) transportation of sugars and aminoacids into the cells.
(ca+2)/calcium) :
- ca+2 is present in bones and teeth.
- ca+2 ions regulates heart beating.
- ca+2 ions are necessary for blood clotting.
- ca+2 ions are necessary for muscle centractives.
Question 6.
Calculate the weight of 0.1 moles of sodium carbonate(Na2CO3).
Answer:
Formulae :
No. of moles = \(\frac{\text { Weight }}{\text { GM Wt }}, 0.1=\frac{\text { Weight }}{106}\)
weight = 106 × 0.1 = 10.6 gms
Given
No. of moles = 0.1
G.M Wt of Na+2CO3 = 106
Question 7.
Calculate the ratio of kinetic energies of 3 gm of hydrogen and 4 gm of oxygen at a given temperature.
Answer:
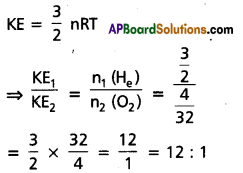
Question 8.
What is ZSM – 5? Write its use.
Answer:
- ZSM – 5 is a zeolite.
- It is used to covert alcohols directly into gasoline.
Question 9.
Write chain isomer structures of carbon compound C4 H10.
Answer:
CH4 H10

Question 10.
What is Dynamic equilibrium?
Answer:
Dynamic equilibrium : The forward and reverse reactions of a reversible reaction continue to take place with equal rates simultaneously at the equilibrium stage also. Hence the equilibrium is called Dynamic equilibrium.
Section – C
Question 11.
Explain the hybridisation involved in pcl5 molecuie.
Answer:
1) in pcl5 the electron oonftgumtfcm of phosphorus is
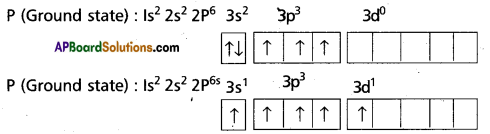
Question 12.
What is ionic bond? Explain with one example.
Answer:
The electrostatic force that binds the oppositely charged ions which are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom with low ionization potential to the other with high electron affinity is called ionic bond or electrovalent bond. It is formed when the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is more than 1.7.
Example:
Formation of sodium chloride in terms of orbital concept:
1) Na (Z = 11). The electronic configuration is = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1.
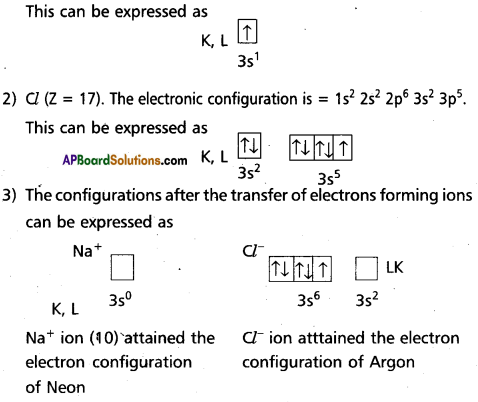
in the formation of sodium chloride the 3s electron of sodium atom is transferred to the 3p2 orbital’of chlorine atom. The Na+ ion and Cl– ion, so formed are now bound by strong coulombic electrostatic forces of attraction forming sodium chloride.
![]()
Question 13.
Define (a) boyle’s law (b) Graham’s law.
Answer:
(a) Boyle’s law:
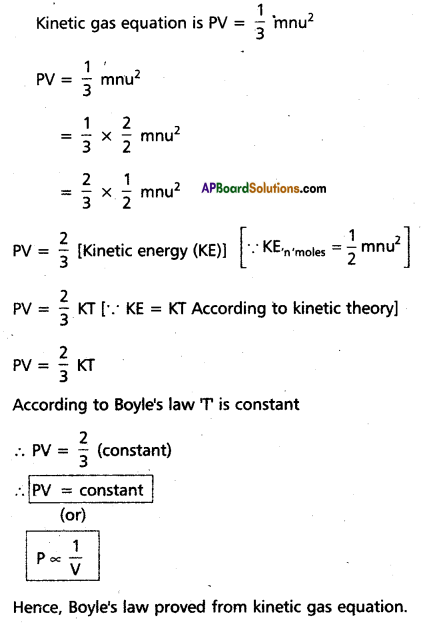
(b) Graham’s law
At constant temperature and pressure the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density, r ∝ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\)
Deduction : Kinetic gas equatio is

∴ The rate of diffusion of gases depends upon the velocity of the gas molecules.
So r ∝ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\)
This is Graham’s law
Question 14.
State and explain Hess’s law of constant that summation.
Answer:
Hess’s law states that the total amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction is always same whether the reaction is carried out in one step (or) in several steps. Illustration : This means that the heat of reaction depends only on the initial and final stages and not on the intermediate stages through which the reaction is carried out. Let us consider a reaction in which A gives D. The reaction is brought out in one step and let the heat of reaction be ∇H.
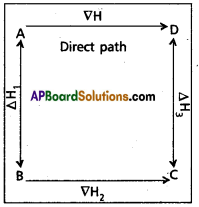
A → D; ∇H
Suppose, the same reaction is brought out in three statges as follows
A → B;∇H1
B → C;∇H2
C → D;∇H3
According to Hess law
∇H = ∇H1 + ∇H2 + ∇H3
1) Direct method : By heating carbon in excess of O2.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g); ∇H = -393.5 kj
2) Indirect method : Carbon can be converted into CO2 in the following two steps.
C(s) + \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\) O2(g) → CO2(g); ∇H = -110.5 kj
CO(g) + \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\) O2(g) → CO2(g); ∇H2 = -283.02kJ
Total ∇H = -393.52kJ (∇H1 + ∇H2)
The two ∇H values are same.
Question 15.
A carbon compound contains 10.06% carbon. 0.84% hydrogen, 89.10% chlorine. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound [At. wt. C = 12, 1, Cl = 35.5]
Answer:
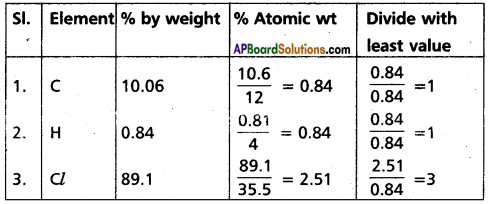
∴ Emperical formula of given compound = C1H1Cl3 = CHCl3
![]()
Question 16.
Explain electron deficient and electron rich hydrides with one example each.
Answer:
i) Electron-deficient hydrides : These are the molecular hydrides in which the available no.of valency electrons is less than the number required for jnormal covalent bond formation, (or) These are the molecular hydrides in which the available valency electrons are lessthan the required for writting the Lewis structure of he molecule.
Eg : (AlH3)n, BH6 etc.
These hydrides acts as Lewis acids i.e. electron pair acceptors. These forms dative bond with donors,
ii) Electron-rich hydrides :
- These are the molecular hydrides in which the valency electrons on the central atom are more than that are required for bond formation, (or) These are the molecular hydrides in which the available valency electrons are more than the required for writting the Lewis structure of the molecule.
- The hydrides contains lone pairs on central atoms.
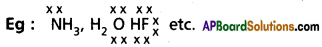
- These hydrieds have high boiling points than those of he hydrides of the subsequent members of group becfause of hydrogen bond formation.
Question 17.
Explain borax bead test with a suitable example.
Answer:
Borax bend test: This test is useful in the identification of basic radicals in qualitative analysis. On heating borax swells into a white, opaque mass of anhydrous sodium tertra borate. When it is fused, borax glass is obtained. Borax glass is sodium meta borate and B6O3. The boric anhydride, B2, O3, combined with metal oxides to form metal metaborates as coloured beads. The reactions are as follows :

Question 18.
Explain Bronsted – Lewis acid base theory.
Answer:
Bronsted acid Base : The substance which accepts a proton from the other substance is called Bronsted base,
e.g. : N3, H2O etc.
Lewis acid base : A substance which can accept an electron pair to from a co – ordinate covalent bond with donor is called Lewis acid.
e.g. : H+, BF3, SnCl2, etc.
Section – C
Question 19.
Write the postulates of Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom. Explain various lines in hydrogen spectra.
Answer:
Niels Bohr quantitatively gave the general features of hydrogen atom structure and it’s spectrum. His theory is used to evaluate several points in the atomic structure and spectra.
The postulates of Bohr atomic model for hydrogen as follows :
Postulates :
- The electron in the hydrogen atom can revolve around the nucleus in a circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits (or) stationary states. These circular orbits are cocentric (having same center) around the nucleus.
- The energy of an electron in the orbit does not change with time.
- When an electron moves frorq lower stationary state to higher stationary state absorption of energy takes place.
- When an electron moves from higher stationary state to lower stationary state emission of energy takes place.
When an electronic transition takes place between two . stationary states that differ in energy by ∆E is given by
∆E = E2 – E1 = hu
∴ The frequency of radiation absorbed (or) emitted ν = \(\frac{E_2-E_1}{h}\) E1 and E2 are energies of lower, higher energy states respectively.
∴ The angulay momentum of an electron is given by mvr = \(\frac{\mathrm{nh}}{2 \pi} \) An electron revolve only in the orbits for which it’s angular momentum is integral multiple of \(\frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
Line spectra of Hydrogen – Bohr’s Theory :
1. Incase of hydrogen atom line spectrum is observed.and this can be explained by using Bohr’s Theory.
2. According to Bohr’s postulate when an electronic transition takes place between two stationary states that differ in nergy in energy is given by
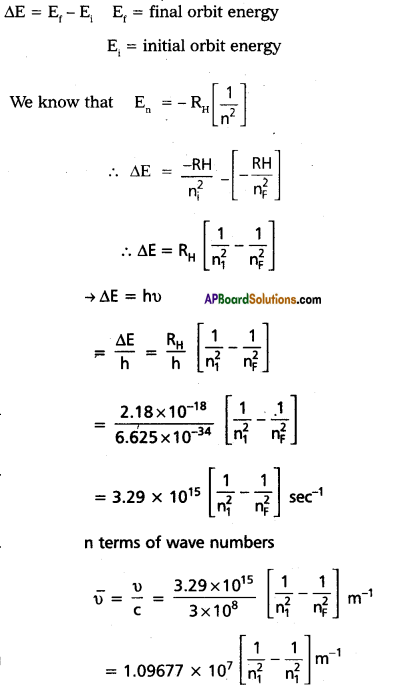
- Incase of absorption spectrum nf > ni energy is absorbed (+Ve)
- Incase of emission spectrum ni > nf energy is emitted (-Ve)
- Each spectral line in absorption (or) emission spectrum associated to the particular transition in hydrogen atom.
- Incase of large no, of hydrogen atoms large no. of transitions possible they results in large no. of spectrtal lines.
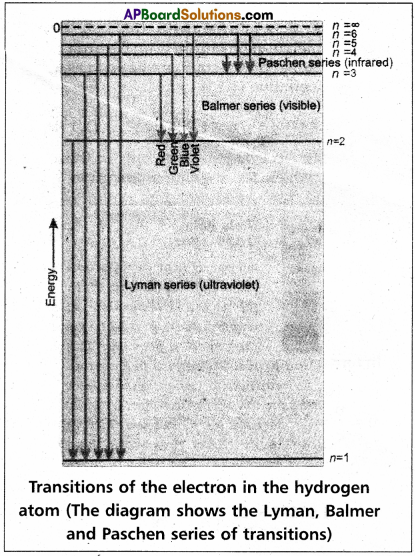
| ‘n’ value | Series | Region |
| 1. | Lyman series | UV region |
| 2. | Balmer series | visible |
| 3. | paschen series | Near I.R. |
| 4. | Brackette series | I.R. |
| 5. | pfund series | Far I.R. |
Question 20.
What is periodic property ? How the following properties vary in a group and in a period?
Answer:
Atomic radius :
Recurrence of similar properties of elements at definite regular intervals with increasing atomic number i.e., according to their electronic configurations is known as periodicity. Any property which is periodic in nature is called periodic property.
Atomic radius :
The atomic radius decreases from left to right in period. With an increase in the atomic number in a period the nuclear charge increases. As a result the effective nuclear charge over the outermost electrons increases, due to this the orbitals are pulled closer to the nucleus causing in a decrease in the atomic radius.
The atomic radius increases from top to the bottom in a group because – with an increase in the atomic number the electrons are added to new shells resulting an increae in the number of inner shells. Hence, atomic radius increases in the number of inner shells. Hence atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group.
Electron gain enthalpy:
Electron gain enthalpy increases in a period from left to right because the size of the atom decreases and the nature of the element changes from metallic to non-metallic nature when we move from left to right in a period.
Electron gain enthalpy decreases from top to bottom in a group because there is an increase in the atomic size. But, the second element has greater electron gain enthalpy than the first element.
E.g. : Chlorine has more electron affinity value (-348 kJ mol-1) than Fluorine (-333KJ moM). It is because fluorine atom is smaller in size than chlorine atom. There is repulsion between the incoming electron and electrons already present in fluorine atom i. e., due to strontger inter electronic repulsions.
Electronegativity :
Electronegativity increases fronj left to right in a period since the atomic radii decreases and nuclear attraction increases. In a group electronegativity decreases from top to botom due to an increase in atomic radii and a decrease in nuclear attraction.
![]()
Question 21.
Describe any two methods of preparation of acetylene. How does it react with water and hydrogen bromide? Write equations.
Answer:
Preparation of acetylene :
1. Dehydrohalogenation : Acetylene is obtained when dibromo ethane is heated with alcoholic KOH.
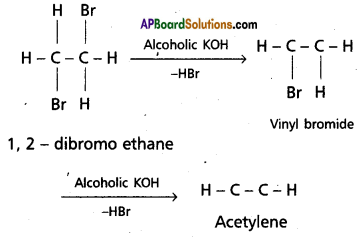
2. Acetylene is obtained by heating iodoform with silver powder.
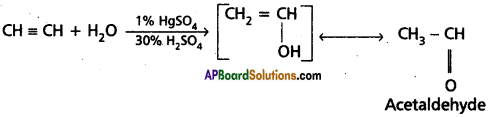
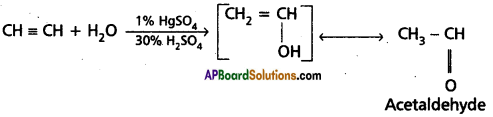
3. Addition of water : Acetylene undergoes addition reaction with water in the presence of mercuric sulphate and sulphuric acid. Vinyl alcohol formed in the reaction undergoes rear¬rangement and gives acetaldehyde.
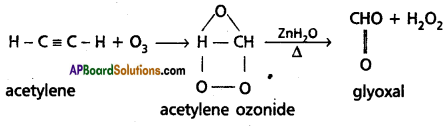
4. Reaction with ozone : Acetylene reacts with ozone to form an ozonide which on hydrolysis in presence of Zn forma glyoxal.