Telangana SCERT TS 8th Class Physics Study Material Pdf 11th Lesson Stars and the Solar System Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Physics 11th Lesson Questions and Answers – Stars and the Solar System
Reflections on concepts
Question 1.
Why does pole star seems to be stationary?
Answer:
Stars actually do not move. They only appear to move from east to west, as the earth from where we see them, rotates west to east. The pole star is situated in the direction of the earth’s axis and that is why it does not appear to move even though all stars appear that they are moving.

Question 2.
Among all 8 planets what is the special thing about earth?
Answer:
- Earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life exists.
- Some special environmental conditions like the right temperature range, the presence of water, suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone round the earth (which protects us from the harmful Ultra – Violet rays from sun) have made life on earth, to continue.
Question 3.
How do people come to an understanding that earth is spherical?
Answer:
Nicholas Copernicus suggested that the Sun is at the centre of the universe and all other celestial objects are revolving around the Sun. Then how do day and nights occur. It was assumed that earth rotates on its axis. This model could explain the occurence of day and night. In this way people came to an understanding that earth rotates on its axis.
Question 4.
How do people come to an understanding that earth rotates on its own axis?
Answer:
- The shape of the earth is spherical. It is get clarified in 1969 when man landed on the moon and observed the earth’s shape from the moon.
- In every eclipse people, found that the shape of the earth is round, even though there is a chance of getting linear elliptical shadows by a circular orbit.
- Sailors, who started their journey in ocean, reached the same place after traveling large distance in one direction only.
- Observations about the movement of stars and different stars visible from different places on the earth also helped to think about the shape of the earth.
- Such observations made by people on the earth cone to an understanding that earth is spherical.
Question 5.
How many planets are there in our solar system? What are they?
Answer:
There are 8 planets in our solar system. They are:
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
(Note: Pluto is not considered a planet, for some reasons)
Application of concepts
Question 1.
What factors to be taken into consideration to view the pole star at your place?
Answer:
If there is a star located where the axis of rotation of the earth meets the sky, which is nothing but a stationary star. The pole star is situated in the direction of the earth’s axis and that is why it does not appear to move even though all stars appear that they are moving because of the rotation of the earth.
Question 2.
How can you find north-south direction at your place?
Answer:
- In our place, I stand facing the rising sun and stretch my hands side-wise. The left-hand side indicates the north and the right-hand side, the south.
- The shortest shadow cast by a vertical object on the ground always falls in the north-south direction.
Question 3.
Is it possible to see the pole star for the people who live in the southern hemisphere of the earth? Why?
Answer:
- The polestar is situated in the north direction along the axis of rotation of the earth. it is in the northern horizon.
- This star appears stationary since it is located in equatorial plane at a very large distance. For these reasons, people living in the southern hemisphere of the earth cannot see the polestar.

Question 4.
Draw the different phases of moon. Arrange them in a order from pournami to Amavasya.
Answer:

Question 5.
What are the planets you have seen in the sky? When do you observe those planets’?
Answer:
Mercury (Budhudu) and Venus (Sukrudu) are visible to the naked eye.
- Mercury: It can be observed just before sunrise or just after sunset, near horizon.
- Venus: It appears in the eastern sky before sunrise. Sometimes it appears in the western sky just after sunset. So it is also called, ‘morning’ or evening star’.
- Planets Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune can be seen only with the help of a telescope.
Question 6.
What is the use of artificial satellites in our daily life?
Answer:
- India built and launched several artificial satellites. Some of them are, Aryabhatta, INSAT, IRS, Kalpana -1, Edusat, etc.
- Artificial satellites have practical applications. They are used for
- forecasting weather.
- transmitting television arid radio signals.
- telecommunication.
- remote sensing (collecting information from distance in aviation and military use.)
- finding underground minerals wealth.
- finding the extent of vegetation, deserts, barren lands, etc., on the earth.
Question 7.
How do day and night occur?
Answer:
The earth rotates upon its tilted axis once in 24 hours, while the sun remains constant. So due to such rotation of the earth, days and nights occur.
Question 8.
What are the questions that engage your mind when you look at night sky?
Answer:
The night sky presents a beautiful pattern of thousands of stars against a dark semicircular dome. Following are some of the questions that tease my mind, while look at such a beautiful night sky.
- Apart from these stars and the moon, are there any other celestial objects?
- What is present in the stars? Why do they shine like the sun?
- Are the stars stationary or moving?
- Is the number of visible stars on a moonlit night the same, as that we see on a dark night?
- Why does the moon appear some nights only?
- Why the moon is waning and waxing in shape?
- Is the sky limited, or unlimited?
- Why not these celestial bodies fall on the earth, because of its gravitational pull?
- Do the same stars appear in summer as well as in winter nights?
Higher Order Thinking Questions
Question 1.
Even though we do not have clock, we can know the time by observing some shadows in day time. Think and discuss with your friends how can we know the time at night.
Answer:
Our ancestors used to know the approximate time at night, by observing the position of stars as well as the position of the moon.
Question 2.
We launched many artificial satellites around our earth for different purposes. What do you think about the impact of artificial satellites and their radiation on biodiversity?
Answer:
- The earth receives a large energy daily from the sun and maintains a steady state, by giving off most of this energy, at the same rate.
- Thus the earth maintains a surface temperature of about 17°C.
- But due to the human activities, our earth is getting warmed up. Many factors contribute for the global warming’. One of them is the ‘radiation pollution’, partly contributed by the ‘artificial satellites.
- Radiations are also emitted b’ the ‘signal towers erected for communication purposes and TV.
- Due to the radiations emitted by the satellites and the signal towers, much havoc is caused. Some of them are
- Increase of global temperature: This has a very disastrous effect on the life on this earth.
- Many birds die due to these radiations. Some species of birds, like the sparrow, are on the verge of extinction.
- Many unwanted mutations take place in plants and animals, due to radiation. Such mutations are mostly harmful.
Question 3.
How do you appreciate the construction of knowledge about the Universe by our ancestors?
Answer:
Our ancestors observed many things related to our earth, the solar system and the universe. They observed the things without having any instrument like a telescope.
A few of them are: :
- Some of them can tell the time of the day simply by looking the shadows of the objects.
- They used to estimate precisely the periods of phases of moon, lunar – eclipses, solar – eclipses, and a lot more.
- They expected the shape of the earth as round by
- observing the shadows of the earth and lunar – eclipse.
- observing distant ships approaching the port.
- observing the movement of stars and different stars visible from different places of the earth.
Question 4.
Among eight planets of our solar system, earth Is the only planet supporting life. Explain how we should protect our earth and its environment.
Answer:
The earth is the only planet with life on it. The temperature on earth varies from 1°C to 55°C on an average, making it most suitable for life to exist, It is enveloped by a layer of gases called the atmosphere’ and also a blanket of ozone’.
But due to human activities’ and their unbound greediness, our earth and the environment is getting polluted. The different types of pollution are
- Air pollution.
- Water pollution,
- Earth pollution,
- Noise pollution,
- Radiation pollution
Measures suggested to control pollution:
To control pollution and make our earth inhabitable, following steps are suggested for the ‘Action plan’.
- Shift from coal-fired thermal stations and industries to more efficient gas-fired ones.
- Harness more and more solar energy (like the Gujarat state), wind energy and tidal energy (renewable sources of energy)
- Reduce live stock (animals), which generate methane (CH, a greenhouse gas).
- Impose heavy penalties on two and four-wheeler motor vehicles, exceeding emission levels.
- Replace ‘freons in air-conditioner units, refrigerators and aerosol by other eco-friendly (not harmful to the environment) substances.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
When the moon completely covers the sun as seen from the earth is known as ……….. .[ ]
a) Partial solar eclipse
b) Total solar eclipse
c) Annular eclipse
d) Hybrid eclipse
Answer:
b) Total solar eclipse
Question 2.
The planet which is near to earth is [ ]
a) Mercury
b) Venus
c) Jupiter
d) Saturn
Answer:
a) Mercury
Question 3.
The brightest planet among all the planets [ ]
a) Mercury
b) Venus
c) Jupiter
d) Saturn
Answer:
b) Venus
Question 4.
Moon is [ ]
a) the natural satellite to earth
b) an artificial satellite to earth
c) a comet
d) an asteroid
Answer:
a) the natural satellite to earth
Question 5.
The first Indian artificial satellite [ ]
a) IN SAT
b) Kalpana -1
c) Aiyabhatta
d) EDUSAT
Answer:
c) Aiyabhatta
Suggested Experiments
Question 1.
Conduct an experiment to find out the local noon time of your village/Town.
Answer:
- Take a stick which is a little over a meter long and fix it vertically in the ground.
- Ensure that exactly one meter of the stick remains above surface of ground.
- Make your first observation at 9 AM
- Make a mark with nail or peg at the point where the tip of the shadow falls on ground. Measure the length of the shadow.
- Make similar observations for every half an hour throughout the day till four in the evening.
- Use a clock to fix the time for making observations.
- Enter the measurement of the length of the shadow and the time of measurement in a table making two columns, one for time and another for length of shadow.
- The shortest shadow cast by a vertical object on the ground always falls in the North South directions. You can use this fact to locate directions. The time when the shortest shadow occurs in called the local noon time at that place.

Question 2.
Conduct an experiment to make a sundial.
Answer:
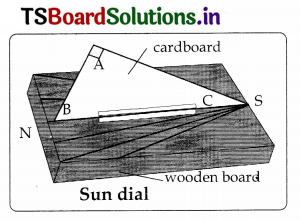
Aim: To make a sun dial.
Requirements: A piece of cardboard, piece of wood, and a paper.
Method of Preparation: ‘
- A right-angled triangle ABC is cut from a sheet of cardboard.
- In this triangle, angle A is 90°. Angle C is kept 16°, which is the latitude of the Krishna district.
- The cardboard triangle is fixed vertically in the middle of a rectangular wooden board.
- To make the triangle stand erect, strips of paper arc glued along both the edges of BC and the wooden board.
- The wooden board with the triangle is placed on a level ground in an open space. which gets sunlight throughout the day.
- The wooden hoard is so placed such that the base BC of the triangle lies in the north-south direction, with B pointing to the north.
- At 9 in the morning (9 A.M.) a line is drawn along the shadow of side AC on the wooden board.
- The time 9 AM. marked along the side of the line.
- Lines of the shadow of side AC are drawn at intervals of one- hour. through the day till sunset. The time is marked for each line drawn.
- Now the sundial is ready.
Suggested Project Works
Question 1.
Collect the information what the Chandrayaan-I brought the information from the Moon through newspapers, magazines.
Answer:
In a historic event, the Indian space program achieved a unique feat on November 14, 2008
with the placing of Indian tricolor on the Moon’s surface. The Indian flag was painted on the sides of Moon Impact Probe (MIP), one of the 11 payloads of Chandrayaan I spacecraft that successfully hit the lunar surface at 20:31 hrs on November 14, 2008.
This is the first Indian-built object to reach the surface of the Moon. The point of MIP’s
impact was near the Moons South Polar Region. Weighing 34 kg at the time of its Launch on board Chandrayaan I, MIP carried a video imaging system, a radar altimeter, and a mass spectrometer. The video imaging system took the pictures of the Moon’s surface as MIP approached the lunar surface.
The radar altimeter measured the rate of descent of the probe and the mass spectrometer made detailed studs’ of the currently thin lunar atmosphere. SLV-C11 used for launching Chandravaan I is the updated version in its ‘standard configuration. Weighing 316 tons at lift-off, the vehicle used larger strap-on motors (PSOM-XL) to achieve required higher payload capability. PSOM-XL uses 12 tons of solid propellants instead of 9 tons used in the earlier configuration of PSLV.

Chandrayaan I further expands our knowledge about Earth’s only natural satellite-the Moon. With well-defined objectives, Chandravaan 1 mission intends to put an unmanned spacecraft into an orbit around the Moon and to perform remote sensing of our nearest celestial neighbor for about two years using eleven scientific instruments unit in India and five other countries.
The primary ‘‘objectives of Chandravaan I are:
- To upgrade the technological base in the country.
- To place an unmanned spacecraft in an orbit around the Moon.
- To conduct mineralogical and chemical mapping of the lunar surface.
Question 2.
Collect information about cosmic dust (wastage) from newspapers, internet and make a poster on your school panel board about the consequences of cosmic dust.
Answer:
- Cosmic dust is a substance found throughout the universe. It is the basic medium from which everything in the universe is made.
- It consists of small grains of material crystalline in structure and aggregates of such grains.
- The composition of this dust changes radically. It depends on the circumstances in which the dust is formed.
- Clouds of cosmic dust can obscure stars, planets and others in space, so that these could not be observed clearly in the sky.
- The cosmic dust is an extremely abundant substance. It plays a very important role in many of the processes occurring in the universe, like the formation of stars and planets.
- There are number of different types of cosmic dust. For example, the ‘Saturn rings’ are the ‘circumplanetary dust’.
- In the solar systems, cosmic dust is scattered across the asteroid belts. It is the ‘interplanetary dust’.
- There is interstellar dust between the stars and as well, intergalactic dust between the galaxies.
- The effects on the sun (e.g., solar flares, solar winds, magnetic storms) and the earth’s climate are not simply due to the cosmic rays alone. They are also caused due to cosmic dust transported by the cosmic rays into the solar system.
- Studies of cosmic dust can reveal interesting information about how galaxies, individual stars and planets form and ultimately destroy themselves.
- The cosmic dust appears sometimes quite beautiful, as swirling images of nebulae have revealed.

Question 3.
What is the duration of a day and night today? Collect the information about duration of day and night for the past 7 days from the newspapers, analyze it, and say whether summer or winter is going to come.
Answer:
Date 1st July 2016
Sunrise 5: 49; Sunset 18: 51
Duration of day: 18: 51 -5 : 49 = 13 hrs 02 mts
Duration of night: 10 hrs: 58 mts. 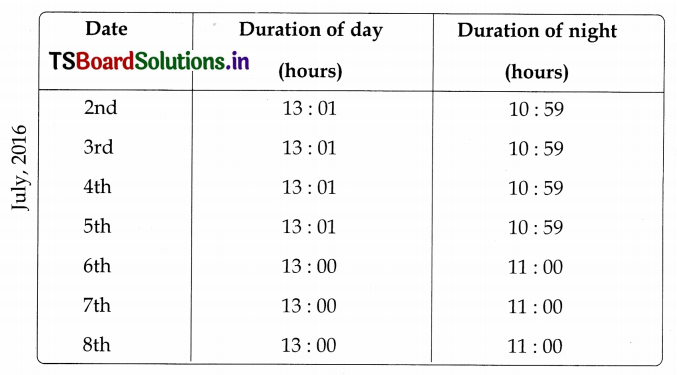 :
:
It is clear from the table, that the duration of the day is gradually decreasing and the duration of the night is gradually increasing. It indicates the passing of summer season, giving way to winter season. (information collected from ‘Panchangam by Sankaramanchivaru). In summer, the days are long and in winter, the nights are long.
Question 4.
Collect the information about chandrayan-2 and write a report.
Answer:
Chandrayaan-2 is an Indian mission to send an orbiter, lander, and rover to the Moon. The lander crashed in the Moon’s southern hemisphere in 2019. The orbiter is mapping the Moon’s topography, investigating the surface’s mineralogy and elements, studying the lunar exosphere, and looking for signatures of water ice.
(Chandrayaan-1, 2008; Chandrayaan-2, 2019) and Mars (Mars Orbiter Mission, 2013). ISRO plans to put astronauts into orbit in 2021.
the important points of Chandrayaan-2:
Image result
The primary objectives of the Chandrayaan-2 lander were to demonstrate the ability to soft-land and operate a robotic rover on the lunar surface. The scientific goals of the orbiter are: to study lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, the lunar exosphere, and signatures of hydroxyl and water ice.
TS 8th Class Physics 11th Lesson Stars and the Solar System Intext Questions
Question 1.
What are the celestial objects that we can see in the sky?
Answer:
We can see Stars, Sun, Moon, Polestar, Great bear Constellation, Cassiopeia Constellation, some planets, Comets and Asteroids in the sky.
Question 2.
Are the stars moving?
Answer:
The stars in the sky appear to be moving. But the polestar appears as not moving. Remaining stars in the sky appear to be revolving around the pole star.
Question 3.
Do you see the same stars at night and early in the morning?
Answer:
No, we did not see the same stars at night and early in the morning. Some stars are not visible to us in the morning. As the sun shine increases we are unable to see the stars except the sun.
Question 4.
Do you see the same stars during summer and winter nights?
Answer:
We did not see the same stars during summer and winter nights. Some stars do not visible during winter nights because of snow and humidity in atmosphere.
Question 5.
What is the shape of the moon ? Why does it change ? Why doesnt the sun change its shape daily like the moon?
Answer:
The shape of the moon is round. The moon revolves around the earth. So the shape of the moon appear to be change. Hut our earth revolves around the sun. So the shape of the sun does not change.
Question 6.
Where exactly is the sun situated in the sky at noon?
Answer:
The sun situated exactly on our head at noon in the sky,
Question 7.
Why does the shadow of a tree change from morning to evening?
Answer:
Because of the rotation of the earth, the direction of the sun rays on earth changes. So the shadow of a tree also changes from morning to evening.
Think and discuss
Question 1.
Look at the nails or pegs you have fixed on the ground to keep track of the shadow of the stick throughout the day. From their positions, can you tell how the position of the sun changes in the sky from sunrise to sunset? (Text. P. No. 149)
Answer:
Yes, I can tell the position of the sun in the sky by observing the position of the shadow. If the shadow moves from west to east, that indicates that position of the sun moves from east to west.
a. If the shadow does not fall of the same spot, what could be the possible reason?
Answer:
The possible reasons are
- The position of sunrise may be changed
- Because of the clouds.
b. During a period of two weeks you had made an observation that the length of the shadow at a particular time is changing day by day. Did it become longer or shorter?
Answer:
I observe that the length of the shadow decreasing day by day.
c. By observing the length/direction of shadows, can you guess the arrival of summer or winter?
Answer:
If length of the shadow decreased, it indicates the arrival of summer. Increasing in the length of the shadow, it indicates the arrival of winter.
Question 2.
Why does the sun appear to travel towards north or south?
Answer:
The earth rotates around itself and also revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit. During this revolutions half of the year it comes close to the sun and remaining halt it moves away from the sun. Because of this revolutions, the sun appears to travel towards north or south.
Question 3.
Scientists are planning to build settlements on moon and are trying to make arrangements to live there. You know that there ¡s no air on moon. How will it be possible to live on the moon then? (Text. P. No. 156)
Answer:
It is not possible to live without air. So we have to make arrangements to have air. There are two possibilities
- Creating artificial atmosphere with the equipment taken from the earth. At present, oxygen cylinders are taken in space shuttles. The same may be adopted on the moon creating small capsules.
- The Chandrayan -1 sent photos proving that there is ice on the moon. The ice may he converted into water. Oxygen may be separated from water to provide breathing air.
TS 8th Class Physics 11th Lesson Stars and the Solar System Activities
Activity – 1 :
Observing the changes in the length of shadow (Text. P. No. 148)
Question 1.
Observing the changes in the length of shadow.
Answer:
- Pick a spot in the open ground where you can be sure you will have sunlight throughout the day.
- Take a stick which is a little over a meter long and fix it vertically in the ground.
- Ensure that exactly one meter of the stick remains above the surface of ground
- You could even build a fence around your stick as shown in figure to keep people away from it.
- Make your first observation at nine in the morning. Make a mark with a nail or peg at the point where the tip of the shadow falls on ground. Measure the length of the shadow.
- Then, make similar observations for every half an hour throughout the day till four in the evening.
- Use a clock to fix the time for making your observations. Enter the measurements of the length of the shadow and the time of measurement in a table making two columns, one for time and another for length of shadow.
Questions based on the above Activity-1
a. When did you observe the longest shadow in your activity?
Answer:
In morning and in the evening of observed the longest shadow.
b. How does the length of the shadow change with time, draw the diagrams of the stick and its shadow for different times at 9 am, 11 am, 12 noon and 4 pm.
Answer:

The length of the shadow decreases from morning to noon and increases from noon to evening.
c. If you continue your activity from sunrise to sunset, at what times do you think the shadow would be the longest?
Answer:
At the time of sunrise or sunset the shadow would be the longest.
d. Where is the sun situated in the sky at noon? Where does the shadow of stick fall at that time? Think about your own shadow will be at that time?
Answer:
The sun is situated exactly vertical to our head at noon. The shadow of the stick fall on the same stick My own shadow also on meat that noon time.
e. Do you think that your shadow will be the same on all the days at noon?
Answer:
Yes, the shadows will be same on all the days at noon ? Because local noon time of a place is constant. So shadows also same.
f. In which direction does the shortest shadow of the stick fall in your activity?
Answer:
The shortest shadow of the stick fall in the north-south direction.
Activity -2: Understanding the North-South movement of the Sun (Text. P. No. 150)
Question 1.
Conduct an activity to understand the North-South movement of the sun?
Answer:
- Fix a spot near your home from where you can observe the sunrise.
- You may have to go to the terrace of a RCC building or go to an open field for the purpose.
- Choose a tree, electric pole or some other stationar object as a reference point.
- Over the next 10 to 15 days., note the spot at which the sun rises daily, keeping in mind your reference point.

- Make a daily sketch of the rising sun as well as your reference point in your notebook during this period.
- When the sun looks like travelling towards south of the sky, it is called the dakshinayanam.
- When it looks like traveling towards north of the sky it is called the uttarayanam.
Questions based on the above Activity -2
a. Was the sun travelling towards south or north during the time you made your observations?
Answer:
I observe the movement of the sun in the month of March. I observed that the sun travelling towards north.
b. Do you think that is the reason for the change in the length of the shadow of the stick day by day In the Activity-1?
Answer:
Yes, because of the sun travelling towards the north is the reason for the change in the length of the shadow of the stick. The length of the shadow of the stick decreased day by day that indicates summer is coming.
c. Assuming that you did not have any calendar and knowledge of months and seasons, can you use movement of the sun to predict the arrival of winter or summer?
Answer:
Yes, if the sun looks like travelling towards south of the sky, it is called the dakshinayanam and then it is winter season for us.
If the sun looks like travelling towards north of the sky it is called the uttarayanam, and then it is summer season for us.
Activity – 3: Make your own sun-dial (Text. P. No. 151)
Question 1.
How do you make your own sundial?
Answer:
Aim: To make a sun dial.
Requirements: A piece of cardboard, piece of wood, and a paper.
Method of Preparation: ‘
- A right-angled triangle ABC is cut from a sheet of cardboard.
- In this triangle, angle A is 90°. Angle C is kept 16°, which is the latitude of the Krishna district.
- The cardboard triangle is fixed vertically in the middle of a rectangular wooden board.
- To make the triangle stand erect, strips of paper arc glued along both the edges of BC and the wooden board.
- The wooden board with the triangle is placed on a level ground in an open space. which gets sunlight throughout the day.
- The wooden hoard is so placed such that the base BC of the triangle lies in the north-south direction, with B pointing to the north.
- At 9 in the morning (9 A.M.) a line is drawn along the shadow of side AC on the wooden board.
- The time 9 AM. marked along the side of the line.
- Lines of the shadow of side AC are drawn at intervals of one- hour. through the day till sunset. The time is marked for each line drawn.
- Now the sundial is ready.

Questions based on the above ActIvity – 3
a. Have you ever observed the movement of moon in the sky?
Answer:
Yes, I have observed the movement of moon in the sky.
b. Does the moon appear at same point at a particular time every day?
Answer:
No, the moon does not appear at some point at a particular time everyday.
c. Is the shape of the moon same on every day?
Answer:
No, the shape and position of moon appears to be change on every day.
Activity – 4: Observing phases of the moon : (Text. P. No. 152)
Question 4.
Describe an activity for observing phases of the moon.
Answer:
Activity:
- Note the date of the day alter new moon day (Amavasya). when the moon first appears in the sky.
- Note the time at night on that date, when the moon sets.
- In the same way ever day locate the moon in the sky at the time of sunset.
- Record the dato and time of the moon set and draw the picture of the moon as you see on that day in your note book, (see figure)
- Continue making observations for as many nights as possible.
- Observe the moon few days before full moon da (Pournami) to a lewdays, after full moon das’.
- Locate the position of moon in the sky at the time of sunset before Pournami. Note the time and position of moon in the sky at that time.
- Draw pictures of the shape of the moon on each of these days.
- From these shapes, dates and times, we can know information about the phases of moon and the moon.

Questions based on the above Activity -4
a. Can you calculate the number of hours between two moon rises or two moon settings?
Answer:
It takes 24 hours time in between two successive moon risings or two successive moon settings.
b. How many hours lapse between one sunrise to the next or one sunset to the next?
Answer:
The time lap between successive sunrises or successive sunsets is 24 hours.
c. Is the time period same for sun and moon every day?
Answer:
Yes, the time period is same for sun and moon every day for completing a cycle in the sky.
d. Does the moon appear at the sanie point every day during the time of sunset?
Answer:
No, the moon does not appear of the same point every day during the time of sunset.
e. What is the shape of the moon? Is it the same every day?
Answer:
The shape of the moon changes night after night. These changes in its appearance are called the phases of the moon.
f. Why the shape of the moon changes every night?
Answer:
The time period taken 1w the sun to complete one cycle in the sky is about 24 hours (I day). But moon takes about 50 minutes more than a day to complete the cycle. It results for the phases of the moon.
Activity- 5: A Moon-shaped lemon (Text. P. No. 153)
Question 5.
Observing the shape formed by Sunlight on a moon.
Answer:
- Perform this activity on a day, one week after the new moon day, when the moon is visible in the sky during the daytime.
- Take a yellow lemon or a white-washed clay ball. Pivot it firmly on a long needle.
- Stand in the sunshine and hold it up towards the moon.
- Observe the shape formed by the sunlight on the surface of the lemon. It can be observed that the shape formed on the lemon is similar to the shape of the moon.
Questions based on the above Activity- 5
a. Is there some similarities between the shape formed and the shape of the moon?
Answer:
Yes, the shape formed on th lemon by falling of sunlight is as the shape of the moon in the sky.
Activity – 6:
Why does the shape of the moon change? (Text. P. No. 154)
Question 6.
Why does the shape of the moon change? Explain with an activity.
Answer:
- Wrap a ball tightly with a white handkerchief or with a piece of white cloth. Assume this is the moon.
- Hold this ball in front ut your eves in bright sunshine and turn around yourself slowly.
- Observe how the shape of the illuminated part of the ball changes.
- The sunravs falling on the moon illuminate half its surface in all the positions.
- However, we cannot see the entire illuminated surface from the earth in all the positions.
- In sorne cases we see the entire illuminated surface while in others we see only part of it.
- In one particular positiún, we cannot see the illuminated surface at all.
- The shape of the moon we see is the shape of the illuminated portion visible to us.
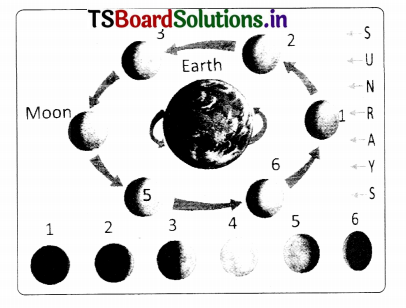
- The day of the new moon is called day 0 or day 28 (position 1). In this position. the illuminated surface is not visible from earth, so the moon cannot be seen from earth.
- Four days later, when the moon is in position 2. a small part of its illuminated surface is visible from earth. On day-7, the moon is in position 3,so more of its illuminated part is visible from earth.
- After fourteen days (at position 5) the entire illuminated surface of the moon is visible from earth. This is the day of the full moon.
- Subsequently, the moon appears smaller with each day as it passes through positions 6 (day-18), 7(day-21) and 8(day- 25). After 28 days, the moon is once again in position 1.
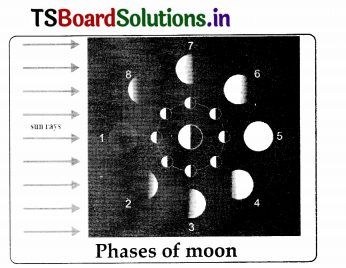
Questions based on the above Activity – 6
a. How are the sun and moon situated relative to earth on a new moon day and on a full moon day?
Answer:
- On a new moon day. the sun and moon are on the same side of the earth. Then we do not see the moon, since its dark face is towards the earth.
- On a full moon day, the sun and moon are on opposite sides of the earth. Then we can see the bright face, which is towards the earth. Revolution of the moon around the earth and phases of moon.
b. How is the surface of the moon?
Answer:
1. Moon is covered with dark dust. It is a barren land.
2. There are many craters of different sizes.
3. It has a large number of steep and high mountains.
4. Moon has no atmosphere like that on the earth.
c. Will we be able to hear any sound If we were on the moon, why?
Answer:
No. sound requires a medium to traveL Since there is no air on the moon, sound cannot travel in that space.
d. Can life exist on moon? Why?
Answer:
For life to exist, water and air are needed. These are not present on the moon. So life cannot exist on the moon.
Activity- 7: Observing the movement of constellations (Stars) (Text P. No. 159)
Question 7.
Explain an activity to observe the movement of constellations (stars).
Answer:
Yes. The stars appear to move from east to vest. This is because the earth rotates from west to east. A star which rises in the east in the evening, sets in the west in the early morning.
Activity to show that the stars revolve around the polestar. The polestar does not appear to move, since it is situated in the direction of the earth’s axis of rotation.
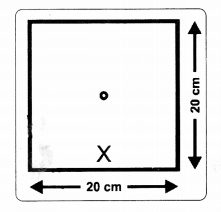
- Take a 20 cm x 20 cm square sheet of paper and make a 1 cm diameter hole in its centre.
- Mark a cross (X) on one side of the sheet of paper as shown in figure.
- Hold the seet in front of your eves with the ‘x’ mark at the bottom. ,
- Look at the polestar through the hole of the paper.
- Holding the paper steadily, write G for Great Bear and ‘C’ for Cassiopeia on the paper in the directions in which you see each of the constellations.
- Simultaneously mark the time of observation in both the cases.
- Choose a nearby tree as a reference point and draw its picture on the sheet, clearly indicating its location.
- Repeat your observations at one-hour intervals. Note G and C in the directions of these stars noting the time also.
- Repeat this activity at least four times.
- From this activity, you can know that the stars do not remain the constant positions. They revolve around the pole star.
Questions based on the above Activity – 7
a. Do the positions of the stars change with time?
Answer:
Yes. There is change ih the positions of stars with time.
b. Does the position of the pole star also change with time?
Answer:
No. There is no change in the position of pole star.
c. Does the shape of the great bear and Cassiopeia change with time or does the position of the entire constellations in the sky change?
Answer:
Yes, The shape of the great bear and Cassiopeia changes with time. The position of the entire constellation also changes.
d. What kind of path do these constellations trace in the sky?
Answer:
If seems the constellations move in a circular orbit.
Activity -8:
Why does the oo4e star appear fenced at one point? (Text. P. No. 160)
Question 8.
Describe an activity to show that the star, situated in the direction of the earths axis does not appear to move.
Answer:
Activity:
- Take an umbrella and open it.
- Make about 10-15 stars out of white paper .
- Paste one star at the position of the central rod.
- Paste other stars at different places on the cloth. near the end of each spoke. .
- Now rotate the umbrella, holding its central rod in your hand.
- The star pasted at the position of the centrai rod does not appear to move. The remaining stars move, It shows thai the star loafed in the dirtion of the earth’s axis does not appear to move, though the other stars appear moving, due to the rotation of the earth.