TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 8 Biology Solutions 8th Lesson Production of Food from Plants Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Biology 5th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Production of Food from Plants
Question 1.
State reasons why wheat is cultivated in Kharif Rabi?
Answer:
- If we cultivate wheat crop in Kharif season or in the month of July it takes 8-10 weeks for growing. After that flowering will take place.
- Wheat plants flowering takes place only in long night durations.
- We get hot climate from February onwards.
- It is suitable for maturing the grains.
- Therefore wheat is cultivated in the Rabi season only.
Question 2.
Ramaiah’s field is flattened. Somalah’s field has many up and downs. Who will get more crop?
Answer:
Ramaiah will get more production from his field. The yielding capacity increases, by levelling the soil. Water, salts and other nutrients will be evenly distributed though out the field due to levelling.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the advantages of ploughing?
Answer:
- Ploughing the soil is essential as it has many advantages.
- After ploughing I soil becomes porous and soft.
- Water easily enters the soil to retain more water which will be taken up by the plants.
- As ploughing loosens the soil, air enters the soil and this will be used by the roots for their respiration.
- In ploughed soils, there will be uniform temperature.
- Harmful insects will be killed during ploughing.
Question 4.
Treating with fungicides before sowing the seed is necessary. Why?
Answer:
- Before sowing, farmer should make sure that the seeds are treated with fungicides to prevent them from infection so that the crop yield will be maximum.
- During storage, fungi or bacteria grow if the seeds are exposed to moisture.
- If such infected seed is used for raising a crop, the quality and yield from the crop will be poor causing economic loss to the farmers.
- Moreover, infected seeds, if carried, for sowing from one field to another, spread the diseases to new places.
- Therefore, healthy, uninfected seed should be used for sowing.
Question 5.
Why do farmers dry the paddy crop after cutting them from fields?
Answer:
Before preserving in storages farmers dry the paddy crop after cutting from fields. If moisture is there in the grains it helps to develop moulds (fungi). Such grains neither germinate nor suitable to eat. To overcome this problem farmers dry the grains in sun light.
Question 6.
Give some examples of plants that grow after replanting?
Answer:
Paddy, tomato, sugarcane, brinjal, coconut etc.
![]()
Question 7.
Rahim removed weeds in his crop field, but David did not. Guess who gets more yield. Why?
Answer:
Rahim gets more yielding than David, because Rahim followed the method called weeding. He knew that weeds compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, light and space. Sometimes weeds carry diseases. Rahim also got information about weeds that they give shelter for insects, pests and micro-organisms. Weeds are capable of germinating and growing faster than crop plants. Due to the above reasons Rahim was aware of weeding to get more yield. But David didn’t concentrate on weeding and he did not get much crop.
Question 8.
What is natural manure? How to prepare it and give two examples?
Answer:
Natural manure
This is also called bio fertilizers. These fertilizers are formed by decomposing plant and animal wastes. In rural areas farmers keep these plant and animal wastes outside the village in open space. Some bacteria like Azatobacter, Nitrobacter decompose and it becomes manure which contain nutrients. Wherever the manure is added to the soil, there it provides nutrients to the plants. Eg: Compost.
Question 9.
Why do farmers plough their field during summer?
Answer:
Farmers plough the field during summer for the following reasons
- For loosening the soil.
- The soil is well aerated.
- Harmful microorganisms are killed by sun’s heat.
- Soil friendly microorganisms and earthworms can grow well.
- Nutrients are mixed up and down while ploughing the soil.
![]()
Question 10.
Rajendar cultivated cotton crop in his field. He did not get sufficient yield. Can you guess the reasons?
Answer:
The following reasons tell us insufficient yield of cotton from Rajendar’s field.
- Naturally cotton grows in Khanf season (June – October), Rajendar might have cultivated the cotton crop in Rabi season.
- Insufficient supply of water to the cotton field, might affect yielding.
- Rajendar might not have followed proper methods like ploughing, levelling the field etc.
Question 11.
Place a fist full of Bengal gram (or any other seeds) seeds in a bowl of water. Do you find some seeds float while others sink?
a. Why do some seeds float and others sink?
Answer:
The floated seeds and their cotyledons are not fully developed. The seed coat is wrinkled. Necessary nutrients to the seeds are lacking. Therefore wrinkled and undeveloped seeds were floating on water.
b. Which seeds do you think will germinate and why?
Answer:
The seeds sank into the water germinate well. Because their cotyledons and germination containing material is sufficient.
c. Which seeds do you think will not germinate and why?
Answer:
The floated seeds do not germinate1 because the nutrients for germination are not present.
d. Which seeds do you think farmers should use for sowing in the field?
Answer:
The seeds sink in water germinate well. So the farmers should use sunken seeds.
Question 12.
I am a plant. I grow in crop fields. Farmers pluck me. I do not know the reason. Can you tell who am I?
Answer:
Unwanted plants that grow in the fields that compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, light and space are called weeds. These weeds compete with prime crops for nutrients water and light. Because of presence of these plants the prime plants could not grow properly. So farmers pluck them from the field.
![]()
Question 13.
Go to your nearest fertilizer shop and collect the information about chemical fertilizers and fill the table. Copy the following table in your note book.
Answer:
| Name of the fertiliser | % of Nutrients | Name of the crops used | ||
| N | P | K | ||
| Godavari | 14 | 35 | 14 | Cotton, groundnut, chillies. |
| Nagarjuna NPK | 19 | 19 | 19 | Tomato, potato. |
| Vijaya complex (urea) | 17 | 17 | 17 | For all crops. |
| Gromor | 14 | 35 | 14 | Paddy, groundnut, grapes, tobacco. |
| Gromor | 28 | 28 | 0 | Paddy, wheat, banana. |
| Godavari | 10 | 26 | 26 | Paddy, banana, wheat. |
Question 14.
Prepare a flow chart from ploughing to yielding in paddy.
Answer:
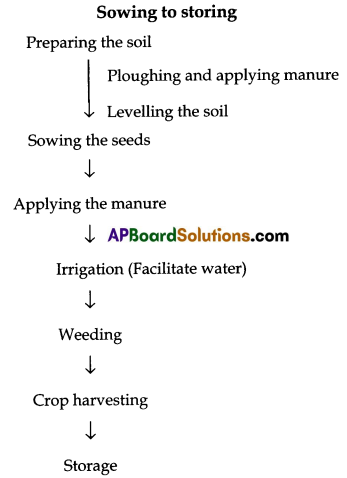
Question 15.
How do you appreciate the irrigation system used in the drought prone areas?
Answer:
- Farmers follow some innovative methods of irrigarion in the drought prone areas. Sprinkler is used for conserving water in agriculture in the areas where water is scarcely available. It provides uniform watering all over the field. It is beneficial in such a way that every drop of water reaches to every plant in a field.
- Drip irrigation is another method. It is more useful where the availability of water is poor. Water reaches the plant drop by drop.
![]()
Question 16.
Narendra sprayed over-dose of pesticides in his cotton crop. Ramesh says it is a hazard to bio diversity and crop yield. Can you support Ramesh? How?
Answer:
I support Ramesh, Ramesh had a lot of information about harmful effects of over dose of pesticides. He gave instructions to Narendra in the following way.
- When pesticides are sprayed they reach into the soil and water and are absorbed by the plants.
- Pesticides get into the bodies of plants and animals through the soil and water.
- When these plants and animals are eaten by other animals the pesticides get into their bodies.
- When animals or plants received more dosage of pesticides, those pesticides pass down the food chain and accumulate in the bodies of higher animals including man.
- These accumulated pesticides cause sickness and may lead to the death of organisms. Finally the entire bio-diversity will be disturbed.
- Useful micro-organisms in the soil of crop fieLd may get poison to their bodies and die. As a result soil fertility decreases and finally crop yielding also decreases. That is why Ramesh advised Narendra that the over dose of pesticides is a hazard to bio-diversity and crop yielding.
Question 17.
Venkatesh observed the irrigation method for paddy field. He wanted to follow the same practice for his Maize crop. What suggestions do you give him?
Answer:
The following suggestions I would like to give Venkatesh on irrigation methods to his maize crop.
- We should know how much of water is needed to maize crop at regular intervals.
- We have to see whether the maize completely depends on regular supply of water or not.
- Venkatesh will be suggested to follow modem methods of irrigation like sprinklers and drip irrigation. Hence he can save more ground water and it is beneficial that every drop of water reaches to every plant in a field.
- He has to know that rice crop needs rather more water than maize. Sometimes if maize receives excessive water it may damage the internal metabolic activities of the plants. Therefore Venkatesh will be instructed about irrigation techniques for maize crop.
Question 18.
Soak the paddy seeds in water for one day. Sow them in the soil contained watch glass. Find the germinated seed, its coleoptile etc with magnifier, label the parts.
Answer:
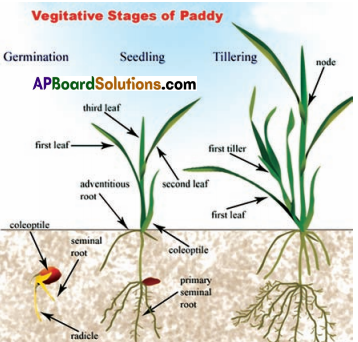
Question 19.
What is the relationship between night duration and crop yielding?
Answer:
Crop production is based on the flowering plant and duration of night. The effect of night duration in flowering plants differs from plant to plant. In some plants when night duration is 12½ hours, the flowering will be more. For example flowering of wheat plants takes place only in long night durations. Plants like maize, cotton flowering will be more when the night duration is more than 12½ hours.
![]()
Question 20.
Suppose the farmers in your village planned to grow the same kind of crop in entire surrounding lands. Write the disadvantages of this same crop cultivation.
Answer:
The following disadvantages we see due to same crop cultivation.
- There will be heavy need for water if they are highly irrigated crops like rice or sugarcane. It leads to scarcity of water.
- If any one of the plants or crop fields is attacked with disease it spreads all over the area rapidly.
- As a result yield of crop decreases. Farmers lose heavily. They may lose the capacity of growing next crop.
- Same crop harvesting facilitates spread of weeds rapidly from one crop field to another.
TS 8th Class Biology 8th Lesson Production of Food from Plants Intext Questions
Question 1.
List out the crops that are grown in our country.
Answer:
Rice, wheat, jowar (sorghum), bajra (millet), pulses, sugarcane, jute, cocount, cotton, tea etc. are the crops grown in our country.
Question 2.
Write the main reasons invented by scientists for flowering of plants.
Answer:
Crop production is based on flowering of plant. After conducting so many experiments scientists invented the following reasons for flowering of plant.
- The flower will come out from the plant after certain growth. In some plants flowering takes place after growing certain height, branches, nodes and after producing 7-9 leaves.
- Flowering of plants also depends upon the duration of night. The effect of night duration in flowering plants differs from plant to plant. In some plants when the night duration is 12½ hours the flowering will be more.
- In some plants night duration is not at all the reason for flowering. They can give flowers any time during the year. Eg: Soyabean
Question 3.
Explain with example on effect of night duration for flowering differs from plant to plant.
Answer:
Flowering of plants also depends upon the duration of night. The effect of night duration in flowering plants differs from plant to plant. In some plants when the night duration is 12½ hours the flowering will be more.
Eg: Flowering of wheat plants takes place only in long night durations. Plants like maize, cotton flowering will be more when the night duration is more than 12½ hours.
![]()
Question 4.
Paddy (rice) is also called a ‘global grain’. Explain.
(or)
Write about growing paddy is common in so many countries.
Answer:
- Rice is the prime, most essential and important staple food crop. It is also called ‘global grain’.
- Rice was cultivated in the late Mesolithic period (9000-8000 B.C) and in the Harappan civilization (2300 B.C).
- It is grown as a Kharif or a Rabi crop from Rajasthan to Arunachal Pradesh and from Kerala to Jammu and Kashmir.
- Although a crop of the warm tropical wet lands, it also grows in the cooler temperature regions of China, Japan and Australia.
- Of all countries in the world, India has the largest area of land under rice cultivation.
Question 5.
You might have seen the agricultural practice of paddy in your area. Write those observations in brief.
Answer:
- The paddy growing field is divided into so many plots (Kayyalu or Madulu).
- Levelling the land and providing water for the crop is easy within these plots (Kayyalu).
- For yielding more quantitative and qualitative crops, farmers sketch a plan before sowing the seeds.
- While planning they take nature of the soil, humidity, rainfall and temperature into consideration, because they vary from time to time and place to place.
- They cultivate the crops accordingly. In general, farmers start agricultural works before monsoon reaches (May and June months).
- At that time farmers celebrate festivals like Eruvaka.
Question 6.
What is the relationship between rice growing festivals and culture in our area ? Give your interesting idea.
Answer:
Rice growing is a seasonal task and associated with many festivals. The sowing and transplanting is associated with Akshaya Trithiya and harvesting associated with Sankranti and Onam. Indian cultures are often described in stories and songs. Agricultural tasks are carried out to the tune and rhythm of certain songs.
Question 7.
Explain in brief about series of activities involved in the cultivation of paddy ?
(or)
What are the practices of paddy cultivation. Write in detail.
Answer:
The following practices are used for growing paddy in the field.
1. Preparing the soil: Ploughing and saddling the soil is to be done to germinate the seeds properly and for uniform supply of water is called soil preparation for crop.
- Ploughing: Nursery is first harrowed and ploughed. The nursery might be first covered with manure and then flooded. Now-a-days different types of ploughs are widely used.
- Levelling the soil: Levellers are used to remove the ups and downs in the field. By levelling the soil water nutrients can be reached.
2. Crop harvesting : Collecting grains from the crop by cutting the matured plant is called harvesting. This is the most important task in agriculture. Harvesting is done either manually or by using machines.
3. Storage : Farmers store the food and wait for the reasonable market price. Storage of produce is an important task. There are different storage practices in our state. Eg: Cold storage, bins, godowns.
![]()
Question 8.
How farmers prepare the soil before sowing ?
(or)
Write about the first and foremost agricultural practice in the field.
Answer:
1. Agriculture practices are done either through man power or through tools.
2. To germinate the seeds properly and uniform water supply, soil should be prepared well. For this farmers follow the given methods.
- Ploughing and applying manure : The nursery is first harrowed and ploughed. The nursery might be first covered with manure and then flooded. The ‘V’ shaped ridges are formed while ploughing to every part of the land.
- Sowing the seed: Selection and sowing the seed is an important step in agriculture. Farmers select wrinkle free, round shaped and more weighing seeds for sowing. Farmers follow different methods for sowing seeds.
Eg: Sowing by dispersal, sowing with hands and sowing with seed drill etc.
3. Applying manure and pesticides: Manures and fertilizers are applied at an appropriate time to the field. Correct use of manure at an appropriate time boosts up the growth and productivity of the plant. To control the pests in the crop field pesticides must be dusted or sprayed on the crop.
4. Facilitate water (Irrigation): Water is an important factor required for plant growth. Irrigation refers to providing water to the plants and removal of excess stagnant water from the plants.
5. Weeding: Weeds compete with crop plants for water, space and nutrients. There are many methods to control the weeds in fields. They are manual, mechanical and chemical methods.
6. Levelling the soil: The fields have a lot of ups and downs after ploughing. So leveller is used for levelling, so that water and nutrients can be reached to every part of the land. It also helps in sowing seeds and planting.
Question 9.
Visit a farmer. Ask him about sowing the seeds in the ploughed soil. Note down the information in your project book. Narrate it in the class room.
Answer:
The farmer explained about sowing of seeds in the following way.
- Sowing of seed in the field is an important task.
- Every farmer should be aware of selecting seeds.
- Selection of seeds is another important step in agriculture.
- Usually farmers prefer more desirable, disease resistant and high yielding seeds.
- It is important to observe that all the seeds are ready to germinate properly.
- Before sowing, seeds must be treated with chemicals that kill the bacteria or fungi.
- Every farmer should remember that healthy, uninfected seed should be used for sowing.
- Because infected seeds, if carried, for sowing from one field to another, spread the diseases to new places.
- Seed sowing is done either by hand or by transplantation method.
Question 5.
You might have seen the agricultural practice of paddy in your area. Write those observations in brief.
Answer:
- The paddy growing field is divided into so many plots (Kayyalu or Madulu).
- Levelling the land and providing water for the crop is easy within these plots (Kayyalu).
- For yielding more quantitative and qualitative crops, farmers sketch a plan before sowing the seeds.
- While planning they take nature of the soil, humidity, rainfall and temperature into consideration, because they vary from time to time and place to place.
- They cultivate the crops accordingly. In general, farmers start agricultural works before monsoon reaches (May and June months).
- At that time farmers celebrate festivals like Eruvaka.
Question 6.
What is the relationship between rice growing festivals and culture in our area? Give your interesting idea.
Answer:
Rice growing is a seasonal task and associated with many festivals. The sowing and transplanting is associated with Akshaya Trithiya and harvesting associated with Sankranti and Onam. Indian cultures are often described in stories and songs. Agricultural tasks are carried out to the tune and rhythm of certain songs.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain in brief about series of activities involved in the cultivation of paddy?
(or)
What are the practices of paddy cultivation. Write in detail.
Answer:
The following practices are used for growing paddy in the field.
1. Preparing the soil: Ploughing and saddling the soil is to be done to germinate the seeds properly and for uniform supply of water is called soil preparation for crop.
- Ploughing: Nursery is first harrowed and ploughed. The nursery might be first covered with manure and then flooded. Now-a-days different types of ploughs are widely used.
- Levelling the soil: Levellers are used to remove the ups and downs in the field. By levelling the soil water nutrients can be reached.
2. Crop harvesting: Collecting grains from the crop by cuffing the matured plant is called harvesting. This is the most important task in agriculture. Harvesting is done either manually or by using machines.
3. Storage: Farmers store the food and wait for the reasonable market price. Storage of produce is an important task. There are different storage practices in our state. Eg: Cold storage, bins, godowns.
Question 8.
How farmers prepare the soil before sowing ?
(or)
Write about the first and foremost agricultural practice in the field.
Answer:
1. Agriculture practices are done either through man power or through tools.
2. To germinate the seeds properly and uniform water supply, soil should be prepared well. For this farmers follow the given methods.
- Ploughing and applying manure : The nursery is first harrowed and ploughed. The nursery might be first covered with manure and then flooded. The V’ shaped ridges are formed while ploughing to every part of the land.
- Sowing the seed: Selection and sowing the seed is an important step in agriculture. Farmers select wrinkle free, round shaped and more weighing seeds for sowing. Farmers follow different methods for sowing seeds.
Eg: Sowing by dispersal, sowing with hands and sowing with seed drill etc.
3. Applying manure and pesticides: Manures and fertilizers are applied at an appropriate time to the field. Correct use of manure at an appropriate time boosts up the growth and productivity of the plant. To control the pests in the crop field pesticides must be dusted or sprayed on the crop.
4. Facilitate water (Irrigation): Water is an important factor required for plant growth. Irrigation refers to providing water to the plants and removal of excess stagnant water from the plants.
![]()
5. Weeding: Weeds compete with crop plants for water, space and nutrients. There are many methods to control the weeds in fields. They are manual, mechanical and chemical methods.
6. Levelling the soil : The fields have a lot of ups and downs after ploughing. So leveller is used for levelling, so that water and nutrients can be reached to every part of the land. It also helps in sowing seeds and planting.
Question 9.
Visit a farmer. Ask him about sowing the seeds In the ploughed soil. Note down the information In your project book. Narrate it in the classroom.
Answer:
The farmer explained about sowing of seeds in the following way.
- Sowing of seed in the field is an important task.
- Every farmer should be aware of selecting seeds.
- Selection of seeds is another important step in agriculture.
- Usually farmers prefer more desirable, disease resistant and high yielding seeds,
- It is important to observe that all the seeds are ready to germinate properly.
- Before sowing, seeds must be treated with chemicals that kill the bacteria or fungi.
- Every farmer should remember that healthy, uninfected seed should be used for sowing.
- Because infected seeds, if carried, for sowing from one field to another, spread the diseases to new places.
- Seed sowing is done either by hand or by transplantation method.
Question 10.
Arrange the following circles in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
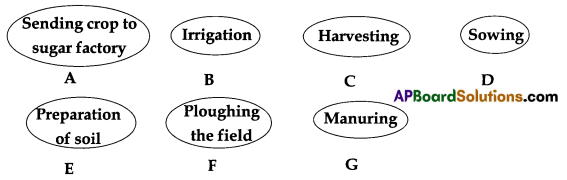
Answer:
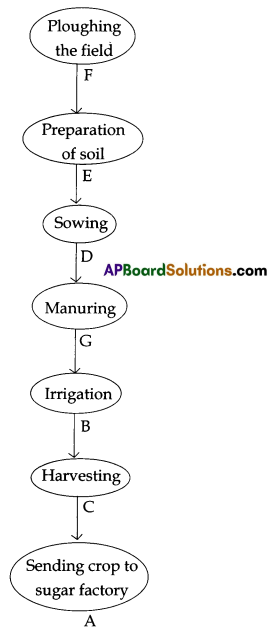
Question 11.
What are weeds? What are the disadvantages of weeds in the crop field?
Answer:
Def: Unwanted plants that grow in the fields arid compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, light and space are called weeds. Disadvantages of weeds in the crop field:
- Weeds reduce the crop yield. Sometimes they act as carriers for various diseases.
- They give shelter for insects, pests and micro-organisms. They come in the way of agricultural operations.
- Weeds are capable of germinating and growing faster than crop plants.
- They flower and form seeds much earlier than the crop plants.
- They even pollute the surroundings with their pollen grains and seeds.
![]()
Question 12.
How can we control weeds?
Answer:
We can adopt the following ways to remove weeds and control their growth.
- Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil.
- The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
- The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time.
- Weeds are also controlled by using chemicals called weedicides like 2-4- D (2-4 – Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid)
- Weedicides are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds. They do not damage the crops.
![]()
Question 13.
What do you understand by the term “Irrigation” ? How much water should be given to crops?
Answer:
Irrigation: Giving proper amount of water to agricultural crops is called irrigation.
- Fields are irrigated by water from canals, water ways or from wells.
- Bunds and furrows are important methods of irrigation.
- Neither too much nor too little water can give us good yield.
- Excess of water destroys crops and thus, it should be drained off by providing suitable outlet.
- Bunds and furrows are important for the plants which are to be submerged in water. Eg: Rice.
Question 14.
Write about different methods of harvesting rice?
Answer:
Harvesting is the most important task in agriculture. Collecting grains from the crop by culling the matured plant.
Harvesting of paddy: In paddy crop harvesting could be done either manually or by using machines. After cutting, the grain is sent out to dry in the field for 2 to 3 days.
Some methods of harvesting paddy:
- Threshing: Beating dry plants stocks on a hard surface to remove the grain is called threshing. It is also helped by having bullocks trample the grain.
- Winnowing: The grains are poured out of a basket or tray held up the wind blows the chaff, dust and lighter seeds aside while the heavy grains collect below.
- Modern methods: At present machines are widely used for harvesting the crop. These machines are called harvesters.
- Harvesting on roads: In some villages farmers used to harvest crops on the roads instead of using bullocks or harvestors. It is a dangerous practice. Sometimes accidents may occur.
![]()
Question 15.
Write the differences between chemical fertilizers and Natural fertilizers.
Answer:
| Chemical fertilizers | Natural fertilizers |
| 1. These are made up of inorganic salts. | 1. These are made by the decomposition of plants and animal (organic) wastes. |
| 2. These are prepared in factories | 2. These are prepared in open places. |
| 3. No humus can be found. | 3. Deposits of humus layer is found in the soil. |
| 4. More amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potash deposits in the soil. | 4. Less amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potash deposits in the soil. |
Question 16.
Have you come to know about seed crisis? How are farmers aware of this seed crisis?
Answer:
Generally farmers purchase seeds in the nearby market. The grains that are available in the packets play vital role. Sometimes the rate of germination of the seeds is not upto the mark, which was labelled on the packet. Sometimes they never germinate too, Some international companies sell genetically modified seeds. Every year farmers are imposed to purchase seeds from companies only. Because the seeds produced by the plants may again be sterile.
Question 17.
Define Broadcasting. Write about different types of sowing seeds.
Answer:
Def : The method of dispersing seeds by sprinkling is called broadcasting.
Types of sowing seeds:
i) Seed drill : Seed drill is an instrument used to sow seeds in soil. A funnel like device on the top of the seed harrow. Based on the roots and distance between plants, farmers select 3 – 6 piped seed drills. After that farmers cover the seeds with soil.
ii) Seeding by dispersal : In a well prepared field, the seeds are thrown at random. But some areas may have few or no seedlings while some areas of the field may have too many seedlings. Distribution of seeds and manure are carried out at the same time by modern implements.
![]()
Question 18.
Now – a – days farmers are implementing modern techniques in planting seedlings in the crop field. They use modern device to sow the seeds and seedlings. Write about one of such a devices.
(or)
Write about modern seed drill. Write its uses.
Answer:
Now a days farmers use the sophisticated seed drill with the help of tractor. This seed drill is attached to a tractor and helps to sow seeds in 5 or 6 rows. It also covers the sowed seed with soil immediately with the help of a blade attached to it. Use: It is time saving and easiest way of sowing the seeds.
Question 19.
The paddy variety ‘SRI’ paddy requires specific gap betwen the plants. Ask your elders about ‘SRI’ paddy plantation.
(or)
Collect the valuable information from daily news paper or Internet.
Answer:
- At present farmers in some states are advised to implement System for Rice Intensification (SRI) method to adopt seedling distance while planting.
- Planning the planting space is important for good yield.
- Normally sufficient number of seedlings are planted in the main field at a rough spacing of 20 x 10 cm.
- Under SRI about 16 single seedlings are planted at spacing of 25 x 25 cm.
Initial stage: A rope is used for marking the seedling space in the initial stage. But this is not proved popular. In addition to rope method bamboo sticks and iron rods are used for better measurements and accurate plantations.
Advantages of SRI:
- Requisition of labourers for SRI method are definite for 1 hectare land.
- Seedlings are planted at proper distances.
- Consumption of water by plants in the SRI method plantation field is very less.
- Farmers can expect high yield of crop harvesting.
Question 20.
Write the observation of disease symptoms you did on the plants in your school campus or at some crop fields.
Answer:
- Diseases are caused by different types of insects and micro organisms like aphids, white flies, mosquitoes, fungi, bacteria, viruses etc.
- Small holes and tears in leaves are evidence of damage caused by insects, often caterpillars.
- A crumpled or twisted leaf might show that Aphids have been sucking it juice.
- A fungal infection is usually seen as white, black, yellow, brown spots or a fluffy or powdery coating on leaves.
- Some discolourations also could be caused by bacteria or viral infections.
- Root infections like boring worms, insects or fungus are not seen above the ground. But they lead to wilting of plants.
![]()
Question 21.
Some of the associations might be useful or harmful for the plants with other organisms. Explain briefly. (Appreciation)
Answer:
Every plant has characteristic insects and other living things depending on it. Some of these associations might be useful or harmful for the plants.
Uses of association:
- Insects help in pollination of flowering plants.
- Wasps and lady bugs eat more harmful insects.
- In the wild they might actually serve to keep in check the plant population.
Harmful effects:
- Large number of pests cause immense harm.
- It is easy for pests to spread from one plant to the another, multiply further into large number and thus destroy crop.
- This is highly possible in plantations with the same kind of plants.
- Some insects like Aphids and the white fly besides sucking plant sap also carry viral infections.
Question 22.
Insects are the most common agricultural pests. Give your answer with an example. Add the information about seasonal pest diseases.
Answer:
- Insects are the most common agricultural pests.
- They multiply when food is plentiful.
- At other times they stay dormant or their numbers small.
- A crumpled or twisted leaf might show that aphids have been sucking its juice.
- Root infections like boring worms, insects or fungus are not seen above the ground. But they lead to wilting of plants.
Question 23.
Over usage of pesticides in the crop field is harmful and destroy and disturb the ecosystem. Can you accept this truth ? If so explain with your knowledge. Give examples.
Answer:
- Over usage of pesticides in the crop field is very harmful. They destroy and disturb the ecosystem.
- Pesticides get into the bodies of microscopic plants and animals in the soil and water.
- When these plants and animals are eaten by fish the pesticides get into their bodies.
- A bird that eats these fish might get a concentrated lethal dose.
- DDT also accumulates in the egg shells weakening them and making the shells break before hatching.
- In such a way the pesticides are eaten, passed down the food chain and accumulate in the bodies of higher animals including human beings causing sickness and sometimes death.
Question 24.
How are natural manures prepared in villages ?
(or)
How can you prepare natural manure.
Answer:
Natural manure is also called as bio-fertilizer. This is formed due to decomposing of plant and animal wastes.
Plant and animal wastes are kept outside the village in open space. Some bacteria like Azatobacter, Nitrobacter decompose and it becomes manure which contain nutrients.
![]()
Question 25.
Look at the picture given below and write the constituents in it?
Answer:
Nitrogen (20%) Phosphorus (5%) Potash (10%)

Question 26.
What would happen if over dosage of manure is added to soil ?
Answer:
Sometimes in order to get more yielding of crops farmers use more amounts of fertilizers. In turn this leads to soil and water pollutions. After sometime soil becomes either acidic or alkaline. As a result soil may lose its fertility. Thus it brings only grief to the farmers.
Question 27.
Write about methods of irrigation in agriculture.
Answer:
Def: The process of watering crop plants in the field is known as irrigation. There are three methods of irrigation which are commonly practised in our country.
i) Furrow Irrigation : In this method the water is allowed to enter the field through channels or furrows made between two rows of crop.
ii) Basin Irrigation: In this method of irrigation the field is just filled with water. Farmers dig small canals from tank or big canals or wells to fields to supply water.
iii) Ancient methods of Irrigation: In the ancient practices of agriculture, farmers used to cultivate lands by using motor, yatam, chain pump etc., Cattle or human labour is used in these methods.
![]()
iv) Modem methods of Irrigation:
- Sprinkler: These are used in the areas where water is scarcely available. It provides uniform watering all over the field.
- Drip irrigation: It is implemented in the areas where availability of water is poor. As the water reaches the plants drop by drop this is called Drip irrigation.
Question 28.
How is weeding done ?
Answer:
- Weeding is done in different methods by the farmers. Most of the weeds are uprooted at the time of ploughing. Those who still remains are manually uprooted.
- It is better to root out the weeds before flowering. Sometimes weeds are removed with the help of weed harrow.
- Dante or Guntaka is generally used by the farmers to remove weeds from the fields.
- When the crop is fully grown the above methods may not be useful for uprooting weeds.
- So, farmers use weedicides like 2-4-Dichiorophenoxy acitic acid to control the weeds. But this weedicide do not work on monocots.
Question 29.
How do you feel about farmers when they remember and love nature with their first crop ? Who are the friends of farmer?
Answer:
Sparrows are friends of farmers.
Before harvesting, paddy farmers particularly young children in the family collect unriped grain (PaJa Kankulu).
They make a bundle and hang it at the roof of the verandah.
This is for farme is family friend ‘Sparrow’.
The little bird sparrow makes a nest in the roof and eats those grains.
And say thanks to the family by its chirping.
That is the way the farmers love nature.
Question 30.
Is there any need of conveying message to the future generation about the importance of agriculture as a beneficial profession? How do you suggest on the issue to meet the demand of food production?
Answer:
- To meet the needs of food requirements of growing population there should be increase in cultivated land.
- But now-a-days some parts of the agricultural land in rural areas becoming uncultivated land.
- Because non availability of seeds, power, water supply and with marketing problems, farmers think that agriculture is a non profitable task.
- In fact agriculture is the flesh and blood of our country. So upcoming generation should develop more passion towards agriculture which would be the only beneficial profession in future.
Question 31.
How are cold storages useful for us?
Answer:
In cold storages vegetables, fruits, tamarind, chillies and other products that are usually damaged and decoloured within a short time are stored. As the temperature is very low here, the vegetables and fruits can be kept for a long time in the cold storage units.
![]()
Question 32.
Draw neat labelled diagram showing sprouting paddy seed.
Answer:

Question 33.
What are crops?
Answer:
The plants which are grown in large number to get useful products are known as ‘crops’.
Question 34.
What are long term crops? Give examples.
Answer:
Crops which take 180 days and above for harvesting are called ‘Long term crops’. Eg: Jowar, red gram.
Question 35.
Define short term crops? Give examples.
Answer:
Crops which take 100 days for harvesting are called “Short term crops”. Eg: Green gram, black gram.
Question 36.
Define the following. Give examples, a) Kharif b) Rabi
Answer:
a) Kharif : The crops grown in the rainy season are termed as Kharif. Eg: Rice.
b) Rabi : The crops that grown only in winter season are generally called Rabi. Eg : Vegetables, fruits and cereals etc.
Question 37.
Why farmers cultivate different crops in Rabi and Kharif seasons ?
Answer:
Crop production is based on flowering of plant. All the cultivated plants do not show flowering throughout the year. Some crop plants have flowering in definite seasons. Thus flowering of crop plants make the farmers to cultivate two different seasons. By keeping this in mind farmers cultivate some crops in Rabi and some crops in Kharif season.
Question 38.
Why is wheat cultivated in the Rabi season only ?
Answer:
We get hot climate from February onwards. It is suitable for maturing the grains. That is the reason wheat is cultivated in the Rabi season only.
Question 39.
What are the advantages of ploughing the soil ?
Answer:
Use of ploughing :
- Water is stored deeply for a long time as the soil is soft.
- Roots penetrate into the deep and can respire well as the air enters easily into the soil.
- Friendly microorganisms and earthworms can grow well when the soil is soft.
- Some foe-micro organisms die due to the sun-rays.
![]()
Question 40.
List out the paddy varieties which are grown in different continents.
Tabulate the items.
Answer:
| S.No. | Paddy item name | Continent in which item is grown |
| 1. | Oryza Sativa | Asia |
| 2. | Oryza Glaberrima | Africa |
| 3. | Oryza Glumaepatula | America |
Question 41.
List out the paddy varieties which are grown In our state.
Answer:
Molagolukulu, Amritha Sari, Bangaru Teega, Kolleti Kusuma, Potti Basangi Musoori, Sona Musoori are some of the varieties of paddy which are grown in our state.
Question 42.
Write a short notes on harmful effects of pests on paddy crops ?
Answer:
The growing rice crop is attractive food for moths caterpillars, paddy beetles and their larvae, paddy grass hoppers and aphids. Some eat the leaves others bore through the root and stem or suck the juice from the tender rice grain.
Question 43.
Where do you find Tikka disease?
Answer:
In groundnut all leaves of the affected plant have powdery spots. Whole plant becomes wilted. This is due to fungus. This fungal disease is called ‘Tikka disease”.
Question 44.
Define Natural manure.
Answer:
The fertilizers or manure which are formed due to decomposing of plant and animal wastes.
Question 45.
Write the names of some of the artificial fertilizers?
Answer:
Urea, D.A.P, Superphosphate, Potash, which are enriched with Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potash are some of the artificial fertilizers.
![]()
Question 46.
Name the weeds which grow in paddy field.
Answer:
Garika, Wanza, Varipilla Gaddi, Sukha Bhogi, Dharaka, BuradhaThung grow along with paddy.
Question 47.
Name some weeds which grow in vegetable crop field.
Answer:
Gunugu, Gaddi chamanthi, Jeeluga are vegetable crop weeds.
Question 48.
Tabulate different weeds which are grow different crop plants.
Answer:
| S.No | Crop name | Weeds names |
| 1. | Rice (Paddy) | Garike, Wanza, Varipilla Gaddi, Sukha Bhogi, Dharaka etc. |
| 2. | Vegetables | Gunugu, Jeelugu |
| 3. | Tobacco | Pogaku Malle |
| 4. | Mirchi | Pulichinta |
| 5. | Cotton | Pulichinta |
TS 8th Class Biology 8th Lesson Production of Food from Plants Activities
Activity. 1: Crops in India
Question 1.
Observe the following map (India). List out the crops that are grown in our country.
Answer:
The crops grown in our country are Rice, wheat. jovar, pulses, sugarcane, jute, coconut, coffee, tea, cotton, chilli, groundnut etc.,
- North India: Wheat, Sugarcane in many places and tea in some places.
- Western India : Wheat, cotton.
- Eastern India: Paddy, Jute in many places and tea in some places.
- Southern India: Paddy, cotton, groundnut and coffee in many places; jowar in some places. In states of Kerala and Tamilnadu spices are grown.
![]()
Now answer the following.
a. Are there many crops that grow in most of the parts of our country What are they?
Answer:
Yes. Rice, wheat and jowar (sorghum) coconut, sugarcane etc.
b. Why are such crops grown all over the country?
Answer:
Climatic conditions are favourable for those crops.
c. From the above list, which of them are grown in your village?
Answer:
Rice and coconut.
Question 2.
Go through your social studies text book or in library, make comparative statements showing crops largerly grown in the country.
a. Country
b. State
c. District.
d. Your village
Ans.
a. Country : Rice, wheat, sugarcane, coconut, jowar.
b. State : Rice, sugarcane, coconut cheeni, tobacco, mirchi, bengal gram, black gram, red gram.
c. District : Rice, mirchi, green gram, black gram, maize, sugarcane etc.
d. Your village : Rice, green gram, black gram
.
Activity – 2: Duration of crop:
Collect information from the farmers of your village about the time period taken to grow different crops. Write the information in the table.
| Name of the crop | Duration of the crop |
| Rice | In Kharif – 3 1/2 months In Rabi – 3 1/2 – 4 months |
| Green gram | 3 months. |
| Black gram | 3 months |
| Mirchi | 3 months |
| Brinjal | 3-4 months |
| Groundnut | 4 months |
| Sugarcane | 9 months |
Activity – 3 : When do crops are grown
Question 1.
Discuss in groups and make a list of these things for the following table.
Answer:
| Season | Vegetables | Fruits | Cereals | Pulses |
| Rainy | ||||
| Winter | ||||
| Summer |
Answer:
| Season | Vegetables | Fruits | Cereals | Pulses |
| Rainy | Leafy vegetables, potato, brinjal, cucumber, tamato, brinjal | Banana, sweet lime, custard apple | Maize | Bengal gram |
| Winter | Beans, carrot, cauliflower, all leafy vegetables | Guava, banana, kamala, apple, pomagranate | Ground nut green gram black gram | |
| Summer | Brinjal, Bhendi | Banana, guava, mango, sapota |
![]()
Question 2.
Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
Answer:
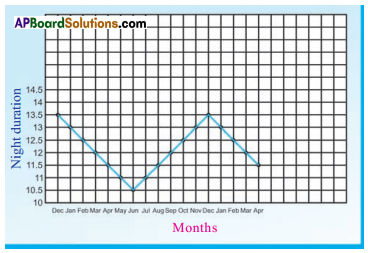
a. Why do farmers cultivate wheat crop in Rabi season?
Answer:
Rabi season facilitates hot climatic conditions for wheat.
b. What happens if it is cultivated in the month of September?
Answer:
It takes long period for growing. No flowering due to less number of hours in night duration.
c. Why farmers do not cultivate it in Kharif season?
Answer:
Because it is non flowering season for wheat, the growth period of wheat is very long.
Activity – 4 : Production of Paddy:
Question 1.
Go to your nearest farmer and collect the information for the following table.
| Paddy growing | Paddy production | Quality of seeds | |
| season | per hectare (quintals) | Size | Weight |
| Rabi | 27-50 | 4.8 mm | 1.99 gm |
| Kharif | 30-55 | 5 mm | 2 gm |
a. In which season farmers get more benefits?
Answer: In Kharif season farmers get more benefits.
b. Is there any crops which are grown in both Kharif and Rabi seasons?
Answer: Rice and soyabeans are growing both in Rabi and Kharif seasons.
c. In which seasons farmers generally get good quality of seeds?
Answer:
Both seasons give good qualities of seeds.
![]()
d. The quantity of grains is higher in Kharif, lower in Rabi. Do you agree to this? Give your reasons.
Answer:
Yes. The availability of water is more in Kharif. Climatic conditions are favourable in Kharif.
e. Do you know about third crops. Some of the places in our state growing 3rd crop also.
Answer:
Developing fish culture (aquaculture) along with paddy in our state, especially in coastal districts, is said to be third crop.
2. Read the table and answer the following.
| Country | Land under rice cultivation millions of hectare |
Total production Million metric tones |
Production per area kg/hectare |
| India | 40 | 79 | 1975 |
| China | 37 | 130 | 3534 |
| Japan | 2.5 | 16 | 6250 |
a. What is the reason for high production in Japan?
Answer:
Japan farmers follow sophisticated methods with modem devices in their agricultural fields.
b. What is the reason for low production in India?
Answer:
In India farmers face problems like availability of quality seeds, power supply, market problems.
c. Elaborate the phases of paddy cultivation?
Answer:
The following practices are used for growing paddy in the field.
1. Preparing the soil: Ploughing and saddling the soil is to be done to germinate the seeds properly and for uniform supply of water is called soil preparation for crop.
- Ploughing: Nursery is first harrowed and ploughed. The nursery might be first covered with manure and then flooded. Now-a-days different types of ploughs are widely used.
- Levelling the soil: Levellers are used to remove the ups and downs in the field. By levelling the soil water nutrients can be reached.
2. Crop harvesting : Collecting grains from the crop by cutting the matured plant is called harvesting. This is the most important task in agriculture. Harvesting is done either manually or by using machines.
![]()
3. Storage : Farmers store the food and wait for the reasonable market price. Storage of produce is an important task. There are different storage practices in our state. Eg: Cold storage, bins, godowns.
Activity – 5 : Selection of seeds:
1. Take some water in glass. Drop a fist of seeds in it. You can observe some seeds floating on water. Collect those seeds and observe with hand lens and compare with seeds that sink under the water. Write your observations in the table.
Question 1.
What are the differences you observed in both seeds?
Answer:
| Seed character | Sunken seed | Floated seed |
| Good colour | Good colour | Faded colour |
| Wrinkled and rough shaped | – | Wrinkle and rough seed |
| Smooth and round shaped | Smooth & round shape | – |
| More weight | More weight | – |
| Less weight | – | Less weight |
Question 2.
Do you know why the floated seeds are light in weight ?
Answer:
The floated seeds are light in weight because lack of nutrients in the seeds.
Activity – 6 : Germination and selection :
Question 1.
Sow the seeds in different pots and provide water uniformly, observe the growth of the plants in two pots and make a report.
a. Which seeds germinate well ? Why ?
Answer:
Round and smooth seed germinated well, because it has all the qualities with nutrients for germination.
b. Which seeds do not germinate properly? Why?
Answer:
Wrinkled and less weighted seeds do not germinate properly. Nutrients are necessary for proper germination.
c. Were all seeds tested like this ?
Answer:
Yes.
![]()
d. Do you know how the paddy seeds germinate?
Answer:
Paddy seeds are soaked in water before sowing in the field. When they contact with water they germinate.
Question 2.
Observe a sprout of paddy. Can you say which part becomes root? Which part becomes shoot in the picture ?
Answer:
Radicle region gives root and coleoptile part (Plumule) gives leaves and stem.
Activity – 7 : Seeding Methods
Question 1.
Collect information from the nearby farmers and fill in the table.
Answer:
| Seeding by dispersal | Sowing with hands | Seeding with seed drill |
| Green gram | Ground nut | Ground nut |
| Black gram | Coconut | Sunflower |
| Rice | Sugarcane | Cotton |
| Coriander | Beans | Maize |
| Amaranth | Sweet potato |
Question 2.
Why are the seedlings are replanted at proper distances?
Answer:
For uniform distribution of water, sunlight and fertilizers.
Question 3.
Do all the crops grow when replanted ? Why not?
Answer:
No. Root formation is not favourable.
Activity – 8 : Crops and diseases:
Question 1.
Form a group with 4 to 5 of your classmates, visit near by field, discuss with farmers about diseases affected by, and how to control them. If you do not know the name of the disease, write Its local name or its characters.
| S.No. | Name of the farmer | Crop grown | Observed diseases | Name of the pesticides used | Results | Remarks |
| 1. | Ramu | Groundnut | Tikka | Carbondizime | Spreading of disease stops | Uninfected leaves not affected |
| 2. | Keshav Rao | Sugarcane | Redrot | Carbondizime cane | Disease stops |
Eradication seen |
| 3. | Krishna | Rice | Blast of Rise | Tricyclozol | Infection stops |
Remaining crop not affected |
| 4. | Suryam | Citrus | Canker | Blitox & steptocyclin | Patches disappear |
Plants become normal |
| 5. | Vinod | Mirchi | Necrosis | Pifronil | disease stops | Crop looks normal |
a. Do all the farmers use the same pesticides for same crop?
Answer:
No. All the farmers do not used the same pesticide.
b. Is there any disease that you find in all fields?
Answer:
No. Different crops are affected with different diseases.
c. Where do they buy pesticides?
Answer:
They buy pesticides from agricultural fertilizers market.
![]()
d. What are the appliances used to spray pesticides ?
Answer:
They use sprayer, dishes, shop water drum etc.
e. Did you find any other living organisms dying along with pests due to pesticides. What are they ?
Answer:
Yes, butterflies, some birds etc.
Activity – 9 Identification of pests
Question 1.
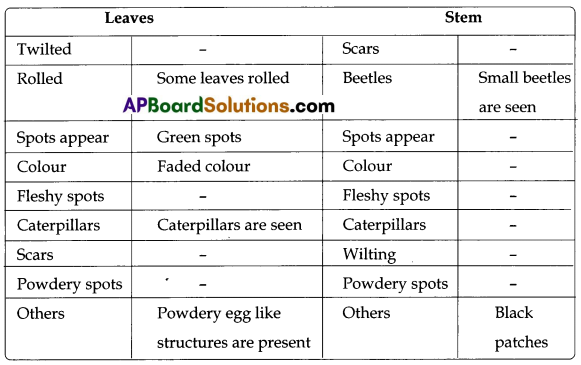
Observe the plants in a nearby field or in your school garden. Closely observe the leaves and stems to collect the following information.
Name of the plant/crop : …………………….
Place : …………………………
| Leaves | Stem | ||
| Twilted | Scars | ||
| Rolled | Beetles | ||
| Spots appear | Spots appear | ||
| Colour | Colour | ||
| Fleshy spots | Fleshy spots | ||
| Powdery spots | Powdery spots | ||
| Caterpillars | Caterpillars | ||
| Scars | Wilting | ||
| Others | Others | ||
a. Do all the leaves of plant have spots? Draw the leaf with those spots.
Answer:
Only some leaves have spots.

b. What is the reason for the leaves which have cutting edges?
Answer:
Caterpillar eats the leaves.
c. Do you find any twilled leaves with insects? How are they?
Answer:
No, rolled leaves are seen.
d. Are the scars on the stems is the same as spots on leaves?
Answer:
No.
![]()
e. Collect powdery substance of the spots on leaves and observe under microscope. Write down what you observed.
Answer:
Powdery egg like structures contain eggs of the insect.
Name of the plant/crop: Citrus
Place : School compound.
Activity – 10 : Pest controlling practices:
In your village farmers control pests by using different pesticides and insecticides for different crops. For this they use different practices. Ask your elders the names of pesticides that they use in the following pest controlling practices.
1. Spraying
2. Dusting
3. Put is the soil
4. Burning, picking are also the practices where they use these
5. Bio pesticides
Answer:
- Spraying : Malathian, Monocrotofos on green gram and black gram fields.
- Dusting : Neem powder and diazinon on the mirchi field.
- Put in the soil : Infected plants are put in the soil to restrict the diseases. Eg : cotton
- The infected leaves of lemon, grape are burnt to stop the diseases.
- Bio pesticides: Neem powder.
Activity – 11: When should farmers irrigate the field?
Consult the farmers and fill the table with the information on how and when they provide water to various crops.
| Name of the crop | Stages of providing water |
| Paddy | |
| Ground nut | |
| Sugarcane | |
| Bhendi | |
| Cucumber | |
| Beans |
Answer:
| Name of the crop | Stages of providing water |
| Paddy | Nursery bed, plantation, flowering, fruiting |
| Ground nut | Sowing seeds, seedling, fruiting |
| Sugarcane | Sowing seeds, seedling, mature |
| Bhendi | Watering every day until harvesting. |
| Cucumber | Watering, every day |
| Beans | Watering, every day |
![]()
a. Are all the crops provided with equal amount of water ?
Answer:
No, all the crops are not provided with same amount of water.
Activity – 12 : How is weeding done ?
Ask your nearby farmers and know the weeds that grow in different crops. Make a table.
Answer:
| S.No. | Crop plant | Weed names |
| 1. | Paddy | Garika, voodha, thunga, bhogi etc. |
| 2. | Vegetables | Gaddi chamanthi, pichi thotakura |
| 3. | Green gram | Bangarutheega |
| 4. | Black gram | Bangarutheega |
| 5. | Mirchi | Pulichinta |
| 6. | Cotton | Puli chinta |
Activity – 13:
Find out the methods of harvesting in and around our village and fill in the table.
Answer:
| Name of the crop | Type of harvesting | Tools used |
| Paddy | Cutting | Sickle (manual) |
| Green gram | Cutting | Sickle (manual) |
| Ground nut | Plucking | Manual (hands) |
| Paddy | Cutting | Modern harvester |
Diagram:
1.

TS 8th Class Biology 8th Lesson Production of Food from Plants Important Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by summer preparation of the soil ? What are the advantages of summer preparation.
Answer:
Preparing the soil by ploughing during summer before Kharif season is called summer preparation of the soil.
Advantages of summer preparation of soil:
- Soil particles in the field become loose. As a result air and water easily enter among the soil particles.
- Soil becomes soft and prevent water from sinking for a long tissue.
- Useful bacteria, farmer’s friend earthworm grows very well in loosely ploughed soil.
- Harmful microbes, weeds die due to hot summer aeration after ploughing.
![]()
Question 2.
Prepare a flow chart showing process of cultivating rice.
Answer:
The flow chart showing process of cultivating rice.

| Sprinkler | Drip irrigation |
| 1. No water wastage is seen. 2. All the field is irrigated with this method |
1. No water wastage is seen. 2. All the field is irrigated in this method |
Question 5.
This diagram shows the means of irrigation in Giddaluru village. Answer the given questions with the help of the diagram.
Answer:

a. Which means of water resources are used minimum by farmers?
Answer:
Water from rivers and canals.
b. If we use borewells indiscriminately what would be the consequence?
Answer:
Ground water resources will decrease. The soil will become dry.
![]()
Question 6.
Farmers should use natural fertilizers having known its benefits.
What suggestions will you give regarding this?
Answer:
The following suggestions are important.
- Natural fertilizers do not pollute the soil.
- They add nutrients to the soil.
- They cause no harm to the plants.
- They increase water holding capacity in the soil.
- Less processing is needed while applying natural fertilizers.
Question 7.
Observe the adjacent figure and answer.

a. Name the type of fertilizer in the figure?
Answer:
Green manure.
b. What type of chemicals are present in it?
Answer:
Nitrogen, Phosphorous and potash.
c. What does 20-5-10 represent?
Answer:
20 %Nitrogen. 5 % Phosphorous and 10% Potash
d. Will you gain or lose by using this type or fertilizers?
Answer:
We will gain more yield by using this fertilizer.
Choose the correct answers:
Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
Find out long term crops ( )
A) Green gram, black gram
B) Jowar, red gram
C) Mango, jowar
D) Sapota, black gram
Answer:
B) Jowar, red gram
Question 2.
One of the following is short term crop: ( )
A) Jowar
B) Red gram
C) Sugarcane
D) Black gram
Answer:
D) Black gram
![]()
Question 3.
The duration for short term crops: ( )
A) 100 days
B) 180 days
C) 100-180 days
D) 50-150 days
Answer:
A) 100 days
Question 4.
In some plants flowering takes place after producing ( )
A) 2 leaves
B) 3 leaves
C) 7-9 leaves
D) 50 leaves
Answer:
C) 7-9 leaves
Question 5.
If you cultivate wheat in July, the period it takes for growing ( )
A) 6-10 weeks
B) 8- 10 weeks
C) 5-8 weeks
D) 5- 10 weeks
Answer:
B) 8- 10 weeks
Question 6.
Flowering will be more in these plants when night duration is more than 12 1/2 hours ( )
A) Maize
B) Cotton
C) Both A & B
D) Sugar cane
Answer:
C) Both A & B
![]()
Question 7.
Wheat is cultivated in this season ( )
A) Kharif
B) Rabi
C) Both A & B
D) Summer
Answer:
B) Rabi
Question 8.
Rice variety grown in America ( )
A) Oryza Sativa
B) Orvza Glaberrima
C) Oryza Glumaepatula
D) Oryza Arizona
Answer:
C) Oryza Glumaepatula
Question 9.
Amrita sari, Bangaaru teega, Kolleti kusuma, Basangi are varieties of ( )
A) rice
B) wheat
B) beans
D) raagulu
Answer:
A) rice
Question 10.
Sprouted seed ( )
A) Coleoptile
B) Tree
C) Zygote
D) Worts
Answer:
A) Coleoptile
Question 11.
One of the following is not an inorganic pesticide: ( )
A) Arsenic
B) Zinc
C) Aldrin
D) Fluorine
Answer:
C) Aldrin
Question 12.
The pesticides usually dusted or sprayed: ( )
A) Endosuiphan
B) Diazonin
C) Chlordane
D) Both A & B
Answer:
D) Both A & B
Question 13.
The grasshopper seen in Kharif season: ( )
A) Deccan wingless grasshopper
B) Korean bird grasshopper
C) Both A & B
D) Tibetin wingless grasshopper
Answer:
A) Deccan wingless grasshopper
Question 14.
Pulichinta weed is commonly not seen in this field ( )
A) Mirchi
B) Cotton
C) Tobacco
D) Both A & B
Answer:
C) Tobacco
Question 15.
This is not a vegetable crop weed: ( )
A) Gunugu
B) Gaddi chamanti
C) Pogakumalle
D) Dharaka
Answer:
C) Pogakumalle
![]()
Question 16.
Flesh and blood of our country: ( )
A) Industries
B) Agriculture
C) Deforestation
D) Jhoom farming
Answer:
B) Agriculture
Question 17.
This is a dangerous practice: ( )
A) Farming in the desert
B) Farming among houses
C) Harvesting in the desert
D) Harvesting on the roads
Answer:
D) Harvesting on the roads
Question 18.
Supply of water to crops at regular intervals ( )
A) Cultivation
B) Irrigation
C) Harvest
D) Sowing
Answer:
B) Irrigation
Question 19.
Simple tool used to remove weeds: ( )
A) Sickle
B) Plough
C) Hoe
D) Seed drill
Answer:
C) Hoe
Question 20.
Instrument used for spraying weedicide: ( )
A) Sprayer
B) Cultivator
C) Plough
D) Combine
Answer:
A) Sprayer
Question 21.
The father of Indian green revolution: ( )
A) H.G. Khorarta
B) M.S. Swaminathan
C) J.C. Bose
D) T.S. Venkatraman
Answer:
B) M.S. Swaminathan
Question 22.
The process of loosening of the soil is called ( )
A) Tilling
B) Harvesting
C) Spraying
D) Weeding
Answer:
A) Tilling
![]()
Question 23.
Which is pesticide? ( )
A) 2.4-Dichiorophenoxyacetic acid
B) Malathion
C) Metachior
D) Chloroform
Answer:
B) Malathion
Question 24.
Seed drill is used for ( )
A) Harvesting
B) Cleaning the seed
C) Sowing
D) Weeding
Answer:
C) Sowing
Question 25.
Rabi crop is harvested in ( )
A) January
B) March
C) October
D) September
Answer:
C) October
![]()
Question 26.
Maize grows well during ( )
A) June
B) January
C) April
D) September
Answer:
A) June
Question 27.
The agricultural instrument used for removal of weeds is ( )
A) Sickle
B) Khurpa
C) Seed drill
D) Plough
Answer:
B) Khurpa
Question 28.
Transplantation of seedling is done in ( )
A) Coffee
B) Cocoa
C) Rice
D) Mango
Answer:
C) Rice
Question 29.
Compost is a ( )
A) Manure
B) Fertilizer
C) Pesticide
D) Weedicide
Answer:
A) Manure
Question 30.
BHC (Benzene hexachioride) is a ( )
A) Weedicide
B) Fertilizer
C) Fungicide
D) Pesticide
Answer:
D) Pesticide
Question 31.
The chemical substances rich in nutrients are called ( )
A) Fertilizers
B) Weedicides
C) Pesticides
D) Herbicides
Answer:
A) Fertilizers
![]()
Question 32.
The process of separation of grain from the chaff after harvesting is known as ( )
A) Tilling
B) Thrashing
C) Spraying
D) Weeding
Answer:
B) Thrashing
Question 33.
The soil matter formed by decayed organic matter is called ( )
A) Pesticide
B) Fertilizer
C) Humus
D) Biocide
Answer:
C) Humus
Question 34.
The plant that gives flower any time during the year ( )
A) Wheat
B) Mango
C) Tamarind
D) Soyabean
Answer:
D) Soyabean
Question 35.
The process of growing crops ( )
A) Horticulture
B) Agriculture
C) Aquaculture
D) Paddy harvesting
Answer:
B) Agriculture
Question 36.
Essential factors for growing crops ( )
i) Soil ii) Water iii) Chemicals
A) i
B) iii
C) i, ii
D) All
Answer:
C) i, ii
Question 37.
If you want to know about production of paddy, what information you have to collect?
i) Paddy growing season
ii) Production per hectare
iii) Quality of seeds
A) i
B) ii
C) iii
D) All
Answer:
D) All
![]()
Question 38.
Rice cultivated largest area in the world ( )
A) China
B) Australia
C) India
D) Pakistan
Answer:
C) India
Question 39.
The word Oryza was coined by ( )
A) Linnaeus
B) Harvey
C) Theoprastus
D) Aristotle
Answer:
A) Linnaeus
Question 40.
The instrument which helps to sow seeds: ( )
A) Modem tractor
B) Paddy planter
C) Hand
D) Seed drill
Answer:
D) Seed drill
![]()
Question 41.
Dithane M – 45 and Eldrine are ( )
A) Fertilizers
B) Pesticides
C) Herbicides
D) All
Answer:
B) Pesticides
Question 42.
The insects that suck plant juices: ( )
A) Mosquitoes
B) Houseflies
C) Tick & Mites
D) Aphides
Answer:
D) Aphides
Question 43.
Find out the mis-matched pair: ( )
A) Tikka – Groundnut
B) Cankir – Citrus
C) Redrot – Paddy
D) Smut – Jowar
Answer:
C) Redrot – Paddy
Question 44.
Urea, DAP, Potash are ( )
A) Fertilizers
B) Pesticides
C) Herbicides
D) All
Answer:
A) Fertilizers
Question 45.
One hectare is equal to ( )
A) 1.4 acres
B) 2.4 acres
C) 3. 4 acres
D) All
Answer:
B) 2.4 acres
![]()
Question 46.
Observe a,b statements ( )
a) crop production is based on flowering of plant
b) flowering of plants depends on duration of night
A) a,b are correct
B) a is correct, b is wrong
C) a is wrong, b is correct
D) a, b are wrong
Answer:
A) a,b are correct
Question 47.
Arrange the order of agricultural practices: ( )

A) 1,2,3,4
B) 1,4,2,3
C) 2,3,4,1
D) 1,3,2,4
Answer:
B) 1,4,2,3
Question 48.
Choose the vegetable crop in rainy season ( )
A) Tomato
B) Raddish
C) Mango
D) Birnjal
Answer:
A) Tomato
Question 49.
Find out the winter season fruit ( )
A) Apple
B) Orange
C) Mango
D) Custard apple
Answer:
B) Orange
Question 50.
Write the sentences in a correct order.
1) Applying manure
2) Preparing the soil
3) Facilitate water
4) Sowing of seeds
A) 1,2,3,4
B) 2,4,1,3
C) 3,1,4,2
D) 3,1,2,4
Answer:
A) 1,2,3,4
![]()
Question 51.
Usage of machinery in Agriculture leads to …………………..
A) Wastage of time
B) Waste of money
C) Increase of labour
D) Labour do not lose their jobs
Answer:
A) Wastage of time
Question 52.
Number of paddy varieties cultivated in our country
A) 1 dozen
B) 2 dozens
C) 3 dozens
D) 4 dozens
Answer:
B) 2 dozens
Question 53.
…………. is not an artificial fertilizer ( )
A) Degradable waste
B) Urea
C) Ammonium phosphate
D) Ammonium Nitrate
Answer:
A) Degradable waste