Telangana SCERT 8th Class Biology Study Material Telangana Pdf 4th Lesson Reproduction in Animals Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Biology 4th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Reproduction in Animals
Question 1.
Differentiate between:
a) Sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction
b) Gametes and zygote
c) External fertilization and internal fertilization
d) Viviparous and oviparous animals
Answer:
a)
| Sexual reproduction | Asexual reproduction |
| 1. Involves one or two organisms. | 1. Involves a single organism |
| 2. Male and Female gametes are formed. | 2. No production of gametes. |
| 3. Involves fusion of male and female gametes. | 3. No fusion of gametes. |
| 4. More chances of appearance of new characters in the offspring. | 4. Offspring is identical to the parent. |
| 5. More chance of gene variation. | 5 Less chance of gene variation. |
b)
| Gametes | Zygote |
| 1. Specialised cells produced by reproductive organs are called gametes. | 1. Fusion of gametes produce zygote. |
| 2. These are haploid in nature. | 2. This is diploid in nature. |
| 3. Consists of single set of chromosomes. (genes) | 3. Consists of two sets of chromosomes. |
c)
| External fertilization | Internal fertilization |
| 1. Fusion of male and female gametes (sperms and ova) occurs outside the body of the organism is called External Fertilization. | 1. Fusion of male and female gametes occur inside the body of the organism is called Internal Fertilization. |
| 2. Usually occurs in aquatic (water) animals like fish and frog. | 2. Usually occurs in terrestrial (land) animals. |
d)
| Viviparous | Oviparous |
| 1. The animals which give birth to their offsprings are called viviparous. | 1. The animals which lay eggs are called oviparous. |
| 2. These animals have epidermal hair on their skin and external ears. | 2. These animals do not have epidermal hair or external ears. |
![]()
Question 2.
Compare the reproduction in Hydra and Amoeba. Note down the differences in your notebook.
Answer:
| Hydra | Amoeba |
| 1. Hydra performs an asexual reproduction by means of ‘budding’. | 1. Amoeba performs asexual reproduction by means of binary fission. |
| 2. There may be one or more bulges, called buds. | 2. After the nucleus gets matured it starts dividing. |
| 3. New individuals develop from the buds seen. | 3. After the complete division of the nucleus the body of amoeba divides into two. |
| 4. In a specific period the buds detach from the parent. Thus the parent becomes existent. | 4. A single parent forms to two daughter amoebae. Thus the parent becomes non existent. |
Question 3.
Why do fish and frog lay more number of eggs whereas cow and human beings usually give birth to only one at a time?
Answer:
- Fish and frog lay more number of eggs where as cow and human beings usually give birth to young, one at a time. It is because the development of embryo takes place in open environment with greater exposure to life threatening circumstances and continuous enemy attack.
- Propagation of new organisms become difficult for fish and frog if they produce less number of reproducing cells.
- Reproductive system has undergone evolutionary change in animals, from fishes to mammals. These evolutionary changes influenced the structure and function of organs of reproduction.
![]()
Question 4.
Can animals produce offsprings even without formation of zygotes, how? Explain with suitable example.
Answer:
- In some animals formation of gametes and fusion of male and female gametes do not take place.
- Thus they produce off-springs without formation of zygotes.
- Such a process of reproduction is called Asexual Reproduction.
- If by chance an earthworm is cut across into two bits the head end is capable of developing the part to become a full earthworm.
- Hence we can say asexual reproduction in earthworm takes place by means of regeneration.
Question 5.
How can you identify the animal is viviparous or oviparous?
Answer:
- Viviparous animals can be identified by observing them giving birth to young ones. We can observe that viviparous animals posssess epidermal hair on their skin and external ears.
- Oviparous animals can be identified as they lay eggs. The animals that lay eggs do not have epidermal hair or external ears.
Question 6.
What am l?
Answer:
a. I am formed by the fusion of male and female gametes.
Answer:
Zygote is formed by the fussion of male and female gametes.
b. I am a gamete that has a tail and travel to fuse with female gamete.
Answer:
Spermatozoan (Sperm) is a gamete that has a tail and travel to fuse with female gamete.
c. I am a fully developed embryo inside a mother’s body.
Answer:
Foetus is the fully developed embryo inside a mothers body.
![]()
Question 7.
State the reason why most of the terrestrial animals’ fertilization takes place internally.
Answer:
In order to perform internal fertilization, it is necessary for the sperm to reach ovum or egg inside the body of the female. Animals in which fertilization is internal have some arrangements for ensuring that the sperm enters the body of the female. Reproductive organs’ secretions also facilitate internal fertilization. This type of fertilization occurs in terrestrial animals. Eg.: Insects, snakes, lizards and mammals
Question 8.
Observe the following figures and write the functions of them.
Answer:

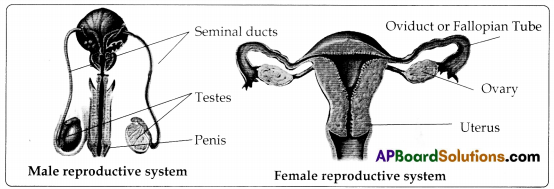
Figure – 1:
Testes of males: It is the reproductive organ of males. It produces spermatozoan
(Sperms) during copulation. It secretes a hormone called testosterone.
Figure – 2:
Ovary with fallopian tube : Ovary is the female reproductive organ. It produces ova. The fallopian tube receives ova from ovary. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube.
Figure – 3:
Spermatozoan (Sperm): Male reproducing cell (gamete) is called spermatozoan (sperm). These are produced by testes of males. It involves in fertilization with ovum.
Figure-4:
Fusion of ovuni and sperm : The given figure is fertilized egg. Fusion ot male and female gametes is called fertilization. After fertilization the egg or ovum transforms into zygote.
![]()
Question 9.
a. By taking help of the given words label the following life cycle. (eggs, adult, pupa, larva)
b. Explain the process of metamorphosis in housefly by taking help from the given diagram.
Answer:
Metamorphosis :
The marked change in the form (appearance) of an animal during development is called Metamorphosis.
The life history of house fly consists of egg, larva, pupa and imago stages.
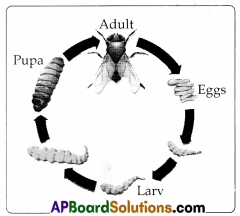
Egg : The egg is white and cylindrical on one side, it has two ribbon like longitudinal thickenings. They hatch in about 24 hours into larvae.
Larva : The larva is known as a maggot. It is white in colour. The body of the larva has 13 segments. It has a mouth and feeds on organic matter.
Pupa : The fulls’ grown larva moves to a dry place in the dung and changes into a pupa. The pupa is dark brown in colour and barrel shaped week the pupa changes into an adult or imago.
Question 10.
Match the following:
A) Oviparous ( 2 ) 1. Tadpoletoadult
B) Metamorphosis ( 1 ) 2. Birds
C) Embrov ( 4 ) 3. Fertilisation outside the body
D) External fertilization ( 3 ) 4. Developed Zygote
Answer:
A – 2, B – 1, C – 4, D – 3
Question 11.
What would happen if all the organisms stop the process of reproduction?
Answer:
- We can’t imagine the nature, if all the organisms would stop the process of reproduction.
- If the new individuals of any species are not added by the process of reproduction a stage will come when that species will disappear.
- know that different species of living organisms die due to various reasons.
Hence the important life process Reproduction helps in replacement of the species that die. - Reproduction allows an increase in total number of species under suitable conditions.
![]()
Question 12.
Kavitha found a tadpole in a pond. She collected it carefully and put it in an aquarium supposing it as a fish. After some days what did she find and why?
Answer:
- Kavitha collected a tadpole of frog as if she predicted that it was a fish.
- After some days she found a young frog with small tail.
- The tadpole undergoes a series of rapid changes which transform it into a young frog.
- This process of series of changes in the life history of frog is called meta morphosis’.
- Tadpole larva is quite different from young tailed frog in shape and structure.
- Tadpole resembles fish with gills whereas young tailed frog with limbs.
- Kavitha could not recognise as it is not a fish before putting in an aquarium.
Question 13.
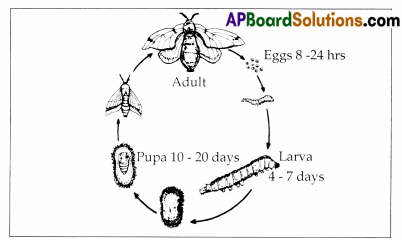
Collect information from your library or from other sources like internet and discuss the life cycle of honey bee in the symposium at your school.
Answer:
The life history of honey bee consists of eggs, larva, pupa and adult.
Egg: The queen bee lays fertilized eggs in hatches of 4-16 in the comb. The eggs are purely white and slightly curved. The eggs are hatched into larvae. It takes one to three days for the eggs to develop into larvae. The fertilized eggs develop into either workers or virgin queens.
Larva : The larva usuaHv has 13 segments with a pair of spiracles in each segment. They have no eyes or legs. Larvae hatch from eggs in three to four days. The duration of the larval stage is 4-7 days. After that they develop into pupas.
Pupa: Pupae exist in the hive. Worker bees nourish the pupae. Each pupa is grown in the nest comb nest. The pupa lasts for 10-20 days. After that it is developed into adult. (Pupa – Singular, Pupac = Plural)
Adult : Development varies among queens, workers and drones. Queens emerge from their cells in 16 days; workers in 21 days and drones in 24 days.
Question 14.
Sketch the diagrams of male and female reproductory systems?
Answer:
Question 15.
Draw labelled diagram of life history of frog and identify forms of herbivores.
Answer:
Tadpole larva: Tadpole larva resembles a small fish. It develops a mouth, a three pairs of external gills and a tail. The jaws
have teeth. It feeds on plants. Hence the tadpole larva of frog is considered herbivore unlike adult frog. The adult frog feeds on small insects or crustaceans. It is a carnivore.

Question 16.
How would you appreciate Ritwik’s work when he kept back the pigeon squab in the ventilator? If you were in Ritwik’s place what would you do?
Answer:
- Ritwik is much attracted to nature. He is the lover of birds and animals. He tried to save the squab.
- He did apply his idea to make comfortable atmosphere for the squab.
- If I were in Ritwik’s place I would have done the same thing what he had done.
- I can convey the value of sustenance of birds and animals and their lives to my friends, near and dear ones. Everyone should conserve bio-diversity.
![]()
Question 17.
Fill in the blanks.
a) Animals which give birth to babies are called ……………..
b) In human’s foetus develops in ……………..
c) Ovum is released from ……………..
d) Tadpole is the primary stage of ……………..
e) Budding, binary fission are reproductive methods ……………..
Answer:
a) Viviparous
b) Uterus
c) fallopian tube
d) frog
e) asexual
TS 8th Class Biology 4th Lesson Reproduction in Animals Intext Questions
Question 1.
Names of some animals are listed below.
Observe carefully and fill the table.
Deer, Leopard, Pig, Fish, Buffalo, Giraffe, Frog, Sparrow, Lizard, Crow, Snake, Elephant, Cat.
Answer:
| S. No | Animals that have external ears | Animals that do not have external ears |
| Deer, Leopard, Pig, Buffalo, Giraffe, Elephant, Cat. |
Fish, Frog, Sparrow, Lizard, Crow. |
Question 2.
Read the names of animals given below and try to fill the table given below.
Cow, rat, crow, pig, fox, lion, camel, duck, frog, elephant, buffalo, pigeon, cat, peacock, lizard.
You can also add a few more animals to this list.
Answer:
| SI. No. | Name of animals | Presence of external ears (Yes/No) |
Presence of epidermal hairs on the skin/feathers on their wings |
| 1. | Cow, rat, | Yes | hairs on the skin |
| 2. | Crow, hen | No | feathers on their wings |
| 3. | Pig, fox | Yes | hairs on the skin |
| 4. | Duck, pigeon, peacock | No | feathers on their wings |
| 5. | Frog | No | no hair, no feathers |
| 6. | Elephant | Yes | hair on the skin, no feathers |
| 7. | Buffalo, cat | Yes | hairs on the skin |
Question 3.
Is epidermal hair seen in those animals whose ears are visible outside?
Answer:
Epidermal hair is seen in the animals whose ears are visible outside.
![]()
Question 4.
Do animals that have epidermal hair give birth to young ones or lay eggs?
Answer:
Animals that have epidermal hair give birth to young ones.
TS 8th Class Biology 4th Lesson Reproduction in Animals Activities
Activity – 1: Observation of Budding in Hydra:
Question 1.
Recall what you observed in the first slide? Compare Slide 1 & 2 to observe which part of its body develops a swelling? Observe the second and third slidel picture now well and say.
Answer:
The slide li shows the slight development of bulge or bud from the parent body.
No such a bulge is seen in slide I. Whereas in the III slide there is complete formation of offspring that is ready to detach from the parent.
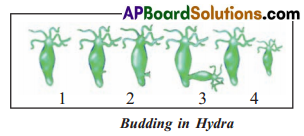
a) What are you observed in slide/picture 1, 2 and 3?
Answer:
- The pictures or slides from 1 – 4 reveal the process of budding in hydra.
- In the slide I of hydra is in mature stage. In the II slide hydras outer surface forms a buIgin structure from tissues.
- That bulge or bud expands its body and forms tentacles on its terminal region. The entire bud looks like parental one.
b) What is the main difference between slides 1 and 2 as well as 3 and 4?
Answer:
- In the slide 1 of hydra shows matured stage.
- In the 2nd slide hydra produces a small bulge or bud from its terminal body part.
- The 3rd slide shows parent hydra with fully developed bud that is ready to detach. Over a period of time the bud detaches from parent and behaves like mature individual, which is shown in 4th slide.
c) What does the swelling (bulge) develop into?
Answer:
The swelling or bulge or bud develops into an off-spring or daughter individual.
![]()
d) Write the similarities and differences between budding in yeast and hydra according to your observations and diagrams given in the text.
Answer:
| Yeast | Hydra |
| Similarities | |
| 1. Formation of bulge during | 1. Formation of bulge or bud during |
| budding. | budding. |
| 2. Budding is common type of asexual reproduction. | 2. Budding is a common type of asexual reproduction. |
| Differences | |
| 3. A soft zone appears in the wall of vegetative cells. |
3. The body wall of the parent bulges out. |
| 4. Small buds bulge out from the soft zone. | 4. Bulging area gradually increases in size. |
| 5. Matured bud pinches off into a daughter cell. |
5. The developed bud separates from the parent. |
Activity -2: Observation of Binary fission in Amoeba:
Question 1.
Observe the given diagram carefully and fill the following table.
Answer:
Changes in the nucleus/body structure
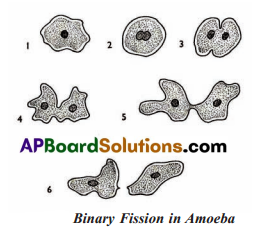
- 1st diagram : Amoeba is a unicellular organism. Prominent nucleus is present in the centre of the cell.
- 2nd diagram: The nucleus of amoeba elongates lengthwise.
- 3rd diagram : The nucleus divides transversely into two daughter nuclei. In the mean time a constriction appears in the middle of the body.
- 4th diagram: The constriction starts deepening in the body of amoeba.
- 5th diagram: The constriction deepens and divides the body into two daughter amoebae.
- 6th diagram : The daughter amoebae are separated from each other and lives independently.
a. Are budding and fission the only methods of asexual reproduction in animals?
Answer:
Budding and fission are not the only methods of asexual reproduction; there are two other methods:
They are 1. Regeneration. Eg: Earth worm, starfish.
b. Now write a note on where male and female gametes are produced in plants. Illustrate with a diagram.
Answer:

Male flower and its parts:
- Colour of the flower
- Sepals (calyx)
- Petal (corolla)
- Androecium – stamens – male reproductive organs
- Pollen grains (yellow colour)
Female flower and its parts:
- Pedicel (stalk of the flower)
- Thalamus
- Gynoecium (pistil) with ovules which are inside the ovary.
- Ovary, style and stigma.
c. Look at the flow chart given below and fill in the blank.
Answer:
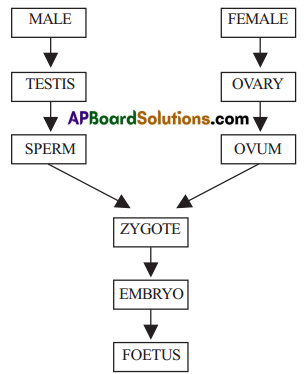
d. Can you say what would happen if fusion of sperm and ova stop?
Answer:
Fertilization stops and as a result zygote formation stops.
Finally the creation of new organism stops.
![]()
e. Can you explain why animals give birth to their babies?
Answer:
Giving birth to young ones by adult animals is called reproduction.
Reproduction is essential to replace the species that die and allow an increase in total numbers of the species under suitable conditions.
The producers of reproduction ensure continuation of race and the perpetuation of characterestics of the species and particularly the parental organisms.
f. Observe the diagram of the female reproductive system and say where an ovum and sperm have a chance of fusion?
Answer:
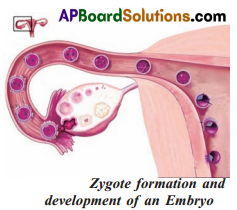
Ovum and sperm have a chance of fusion in the fallopian tube for fertilization.
Activity – 3: Observation of ResembLance in Parents & Children
Divide your class into 4 or 5 groups. See that all groups have at least 5-6 members. Collect photos of parents of all the members. Now compare the faces of your friends with their parents. See what parts of your friend’s face resemble his/ her mother or father. Table given below will help you to note the similar and dissimilar characters.
Fill the table:
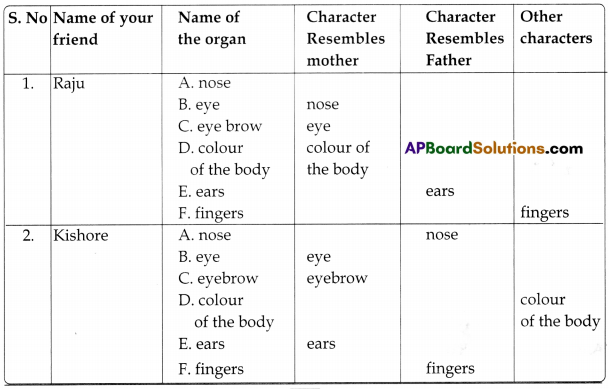
Project Work:
Go to a nearby pond or a slow flowing stream where usually sewage stagnates during rainy season. Collect few eggs of a frog with the help of wide mouthed bottle as shown in the Figure. While collecting eggs, take care that the clusters of eggs are not disturbed and isolated.
Answer:
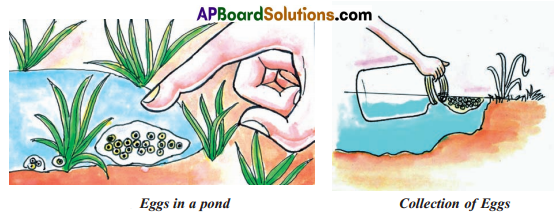

1. How many days did it take for the eggs to hatch?
Answer: It takes 5 – 6 days for the eggs of frog to hatch.
2. How does the tadpole look like?
Answer: The tadpole larva of frog looks like fish.
3. When did you find gill slits in a tadpole?
Answer: We found gill slits on 7th day of development of embryo in a tadpole larva of frog.
![]()
4. On which dates did you observe the following:
- Heart : 2nd week of tadpole development
- Intestine : After 2nd week
- Bones : 18th das’
- Rectum : 20th day
- Hind limbs : 28th day
- Fore limbs : 30th day
Now try to answer the following questions:
1. When did gill slits disappear?
Answer: The third week of development of tadpole larva.
2. When did the tail completely disappear?
Answer: After third week of development of tadpole larva.
3. How many days did it take for a tadpole to transform into an adult frog?
Answer: It takes nearly 18 days for a tadpole to transform into an adult frog.
4. Write a note on what you have learnt about external fertilization. We see that external fertilization in frog takes place in water.
Answer:
External fertilization is seen in frogs life history. Water is the medium for fusion of male and female gametes. Water currents facilitate fertilization. But some gametes may fail to fertilize.
5. Give some examples of other animals in which external fertilization takes place in water.
Answer: Fish is good example.
TS 8th Class Biology 4th Lesson Reproduction in Animals Important Questions
Question 1.
What is the meaning of squab?
Answer:
Baby pigeon is called squab.
Question 2.
What are viviparous animals?
Answer:
The animals which give birth to young ones or offsprings are called viviparous.
Question 3.
What is sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction is basically the fusion of the male reproductive cell and the female reproductive cell.
![]()
Question 4.
What is ovum? What is sperm?
Answer:
The female reproductive cell is called ovum (egg). The male reproductive cell is called sperm.
Question 5.
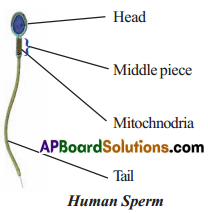
explain the structure of sperm.
Answer:
Sperms are microscopic and single celled. Each sperm has a head, a middle piece and a tail. The head bears a nucleus. It gets energy from mitochondria present in the middle tube. It swims in the semen with the help of tail.
Question 6.
What is embryo?
Answer:
Fertilized zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a hail of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs in the body. This developing structure is called embryo.
Question 7.
What is foetus?
Answer:
When the embryo develops fully and all other parts are distinct, it is called a foetus.
Question 8.
What is “pregnancy period’?
Answer:
The period from zygote to fully developed foetus is called ‘Pregnancy period’.
Question 9.
What are bisexual animals?
Answer:
Animals which carry both male and female reproductive organs are called
bisexual animals or hermaphrodite.
Question 10.
Where do we find budding and binary fission?
Answer:
Budding is observed in Hydra and binary fission is observed in Amoeba.
Question 11.
Write brief note on cloning.
Answer:
- Cloning is the production of an exact copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism.
- Cloning of an animal was successfully performed for the first time by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland.
- They successfully cloned a sheep named Dolly. Dolly was born on 5th July 1996 and was the first mammal to be cloned.
![]()
Question 12.
Kshitija saw a medical camp on her way home. She went near the doctor and asked the purpose of the camp. The doctor told her that he is cutting some part of the sperm ducts of males by operation and tying again with a string.
Answer:
i) What would happen if the sperm ducts are removed?
Answer:
If the sperm ducts are removed males naturally lose their capacity of producing spermatozoans (spems) during copulation with females.
ii. What is the purpose of doing so?
Answer:
Cutting sperm ducts of males is one of the contraceptive methods to control the population.
Purpose of cutting sperm ducts is to restrict the fusion of sperm (male gamete) with ovum (female gamete) after mating of male and female animals.
iii. How are females operated for this purpose?
Answer:
Tying of the fallopian tube with string inside the female body restricts release of ovum from the reproductive organs and prevents fertilization.
Question 13.
Write about artificial fertilization technique. (or)
Alternative method for pregnancy due to blocking of oviducts in women. (or)
Write a brief note on IVE technique.
Answer:
- IVF or In vitro fertilization is a technique that has been invented for artificial pregnancy.
- This technique is widely used for the women who are affected with blocking of oviducts.
- Sperms cant reach the eggs for fertilization in such women.
- In such cases doctors collect freshly released egg and sperms and keep them outside of the body for fertilisation.
- In case fertilization occurs, the zygote is allowed to develop for about a week and then it is placed in mothers uterus.
- Complete development takes place in the uterus and the body is born like other body.
- Babies born through this technique are called test tube babies.
Question 14.
What are Bisexual animals or hermaphrodites? (Or) Write a short note on hermaphrodites.
Answer:
Some animals like earthworms are neither male nor female. They carry both male and female reproductive organs. Such animals are called bisexual animals’ (also called hermaphrodite).
![]()
Question 15.
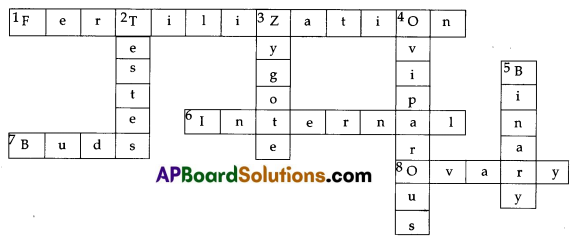
Complete the cross-word puzzle using the hints given below
Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilization in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of Hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilized egg.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission
Answer:
Question 16.
What happens if a couple gives birth to more than two babies? Is it necessary to control population why?
Answer:
If every couple gives birth to more than two babies the population increases rapidly. It will bring serious consequencies of financial and food crisis.
- Lack of shelter, scarcity of food, increase in unemployement may affect the society.
- Rapid population growth may affect the depletion of natural resources and affect the biodiversity and environment. Therefore it is necessary to control population. Decrease in population brings survival of future generations.
Question 17.
What are the questions do you ask to your Biology teacher to know about cloning in animals?
Answer:
- How is cloning done in animals?
- What are the advantages of cloning?
Question 18.
You have already observed the following permanent slides under microscope in your laboratory.
Answer:

Answer the following questions:
1. Name the animal in the picture.
Answer:
Hydra
2. What type of reproduction is this?
Answer:
Budding in Hydra. It is an asexual reproduction.
![]()
Question 19.
Madhu collected the following information about animals and tabulated. Answer the following questions based on the information.
Answer:
| Name of the animal |
Appears external ears | having hair on the skin feathers on the wings |
| Frog Buffelow Rat Hen |
No Yes Yes No |
No hair Hair on the skin Hair on the skin Feathers on the wings. |
Now answer the questions :
1. How can you say Frog and Lizard lay eggs?
Answer:
They have no hair on their body. They are oviparous.
2. How the reproduction takes place in the animals which have hair on the skin and having external ears?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction takes place i.e., mating of male and female animals.
Question 20.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
1. The diagram belongs to which system?
Answer:
Human beings female reproductive system.
2. Label the parts A, B, C.
Answer:
A. Fallopian tube
B. Ovary
C. Uterus
3. Which part releases the Ovum?
Answer:
Ovary
4. Where does the Ovum enter?
Answer:
Fallopian tube
Diagram:
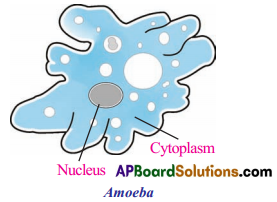
Question 1.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Amoeba.
Answer:
Question 2.
Draw the stages showing budding in Hydra.
Answer:

Question 3.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of human sperm?
Answer:
Question 4.
Draw the labelled diagram of Ovum of frog.
Answer:
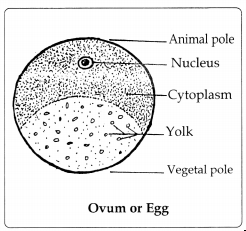
Question 5.
Draw the life cycle of Frog.
Answer:

Choose the correct answers :
Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
Find out the viviparous organism ( )
A) Frog
B) Insect
C) Rat
D) Fish
Answer:
C) Rat
Question 2.
Oviparous animal ( )
A) Lizard
B) Monkey
C) Camel
D) Man
Answer:
A) Lizard
![]()
Question 3.
Example of unicellular organism ( )
A) Hydra
B) Sponge
C) Star fish
D) Amoeba
Answer:
D) Amoeba
Question 4.
Zygote is formed due to the fusion of …. ( )
A) male gamete
B) egg
C) both A & B
D) none of the above
Answer:
C) both A & B
Question 5.
Male reproductive organs are ( )
A) testes
B) ovaries
C) ova
D) pistil
Answer:
A) testes
Question 6.
Seminal ducts are seen in ( )
A) Female reproductive system
B) Male reproductive system
C) Bisexual system
D) Both A & B
Answer:
B) Male reproductive system
![]()
Question 7.
The completion of pregnancy period in woman ( )
A) 200 – 300 days
B) 270-280 days
C) 290 – 360 days
D) 250- 400 days
Answer:
B) 270-280 days
Question 8.
In vitro fertilization helps in the development of ( )
A) Sexual reproduction
B) Asexual reproduction
C) Binary fission
D) Test tube babies
Answer:
D) Test tube babies
Question 9.
In the word metamorphosis ‘meta’ means ( )
A) Beyond
B) Form
C) Structure
D) Life
Answer:
A) Beyond
Question 10.
The successfully cloned sheep ( )
A) Snoopy
B) Dolly
C) Tiger
D) Pigeon
Answer:
B) Dolly
Question 11.
Cloning of an animal was successfully performed for the first time by
A) Gregor Mendel
B) Louis Pasteur
C) Ian Wilmut
D) Harvey
Answer:
C) Ian Wilmut
![]()
Question 12.
The first cloned Dolly was born on ( )
A) 7th July 1997
B) 5th July 1996
C) 6th July 1998
D) 5th July 1995
Answer:
B) 5th July 1996
Question 13.
The transformation of the larva into adult through drastic changes. ( )
A) Fertilization
B) Grafting
C) Metamorphosis
D) Cloning
Answer:
C) Metamorphosis
Question 14.
The animal which is not oviparous ( )
A) Turtle
B) Lizard
C) Rat
D) Parrot
Answer:
C) Rat
Question 15.
Find out non-related pair ( )
A) Calyx – Sepals
B) Corolla-Petals
C) Androecium – Stames
D) Gynoecium – Anther
Answer:
D) Gynoecium – Anther
Question 16.
List – I —- List – Il
1) Hydra — A) Budding
2) Amoeba — B) Binary fission
3) Deer — C) Sexual reproduction
A) 1-a, 2-c, 3-b
B) 1-a, 2-b, 3-c
C) 1-b, 2-a, 3-c
D) 1-c, 2-a, 3-c
Answer:
B) 1-a, 2-b, 3-c
Question 17.
Tumbler is a larvae of ( )
A) Housefly
B) Mosquito
C) Cockroach
D) Frog
Answer:
B) Mosquito
![]()
Question 18.
Cloning is successfully perfomed by ( )
A) Ian Wilmut
B) Jannadellas
C) Watson & Crick
D) Dorothy
Answer:
A) Ian Wilmut
Question 19.
The function of male and female gamets ( )
A) Conjugation
B) Fission
C) Fertilization
D) Budding
Answer:
C) Fertilization
Question 20.
Find out the missing words.
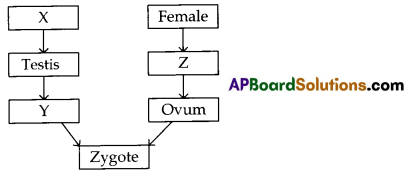
A) X – male, Y – sperm, Z – ovary
B) X – male, Y – sperm, Z – stamen
C) X-ovarv,Y-male, Z-sperm
D) X-male,Y-ovary ,D-sperm
Answer:
A) X – male, Y – sperm, Z – ovary
Question 21.
Observe the diagram, and label the missed part

A) ovary
B) collar
C) middle piece
D) Nucleus
Answer:
C) middle piece
Question 22.
Human beings are viviparous. Identify the oviparous among these
A) Snake
B) Horse
C) Whale
D) Dolphin
Answer:
![]()
Question 23.
Fill the flow chart
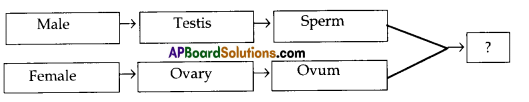
A) Embryo
B) Zygote
C) Foetus
D) None of these
Answer:
A) Embryo
Question 24.
Vivek collected frog eggs from the pond water. ( )
A) They are round, red and float
B) They are round, black and submerge
C) They are green, lump and float
D) They are round, black, lump and float
Answer:
D) They are round, black, lump and float
Question 25.
The main function of the tail in the sperm is ( )
A) Movement
B) Energy
C) Excretion
D) Food supply
Answer:
A) Movement