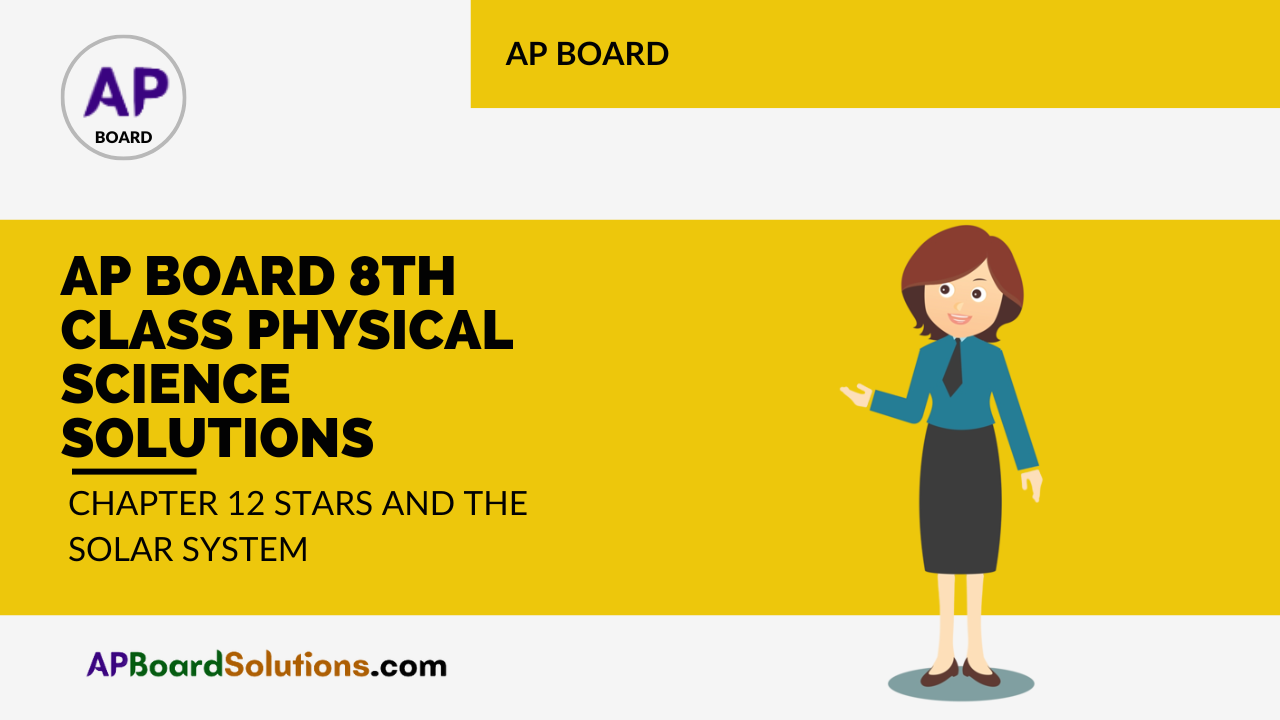
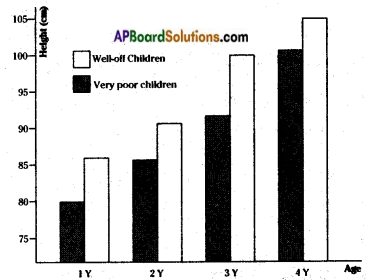
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Physical Science Solutions Chapter 11 Some Natural Phenomena Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Physical Science Solutions 11th Lesson Some Natural Phenomena
8th Class Physical Science 11th Lesson Some Natural Phenomena Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
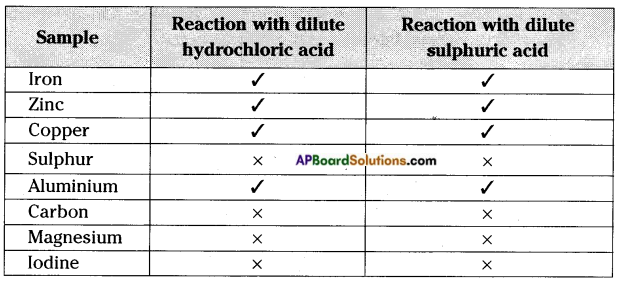
Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
A) A Plastic scale
B) A copper rod
C) An inflated balloon
D) A Woollen cloth
E) Piece of wood
Answer:
(B) A copper rod
![]()
Question 2.
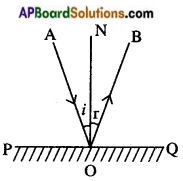
When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
A) and the cloth both acquire positive charge.
B) becomes positively charged while cloth has a negative charge.
C) and the cloth both acquire negative charge.
D) becomes negatively charged while cloth has a positive charge.
Answer:
(B) becomes positively charged while cloth has a negative charge.
Question 3.
Identify ‘True’ or ‘False’ sentences among the following:
A) Like charges attract each other. (T/F)
B) A charged glass rod attract a charged plastic straw. (T/F)
C) Lightning conductor cannot protect a building from lightning. (T/F)
D) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance. (T/F)
Answer:
A) False
B) True
C) False
D) False
Question 4.
Sometimes, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winter. Explain.
Answer:
Charge is developed on the sweater because of friction. We can observe discharge of the charge while taking off the sweater which produce the crackling sound.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Answer:
The reason is that the charged object lose charge to the earth through our body that means it is transferred its charge to earth. The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing.
Question 6.
Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answer:
The destructive energy of earthquake is measured in richter scale. Yes, it would be recorded by seismograph when earthquake measures 3 on the richter scale. It does not cause any damage to human life, generally we unable to felt its effect.
Question 7.
Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Answer:
Precautions to be taken to protect ourselves from lightning.
- Staying in a house or building of low height.
- If we are travelling in a bus or car, then we are safe inside the car or bus provided doors and windows are closed.
- If we are in a forest taking shelter under shorter trees than taller trees is a good idea during the thunder storm.
Question 8.
Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by a charged balloon?
Answer:
A charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon having same type of charge because both are having same kind of charges and like charges repel each other. Whereas an uncharged balloon attracted by a charged balloon because charged balloon induces opposite charge on uncharged balloon. We already know unlike charges attract each other. So the uncharged balloon is attracted by a charged balloon.
![]()
Question 9.
List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to occur?
Answer:
The three states are
- Jammu & Kashmir State (Mainly Kashmir)
- Whole north east states like Tripura, Manipur, etc.
- Rajasthan.
Question 10.
Does your habitation lie in earthquake prone area? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, my habitation lie in earthquake prone area because 1 am living in delta region of Krishna which is placed in seismic zone III. So it has chances of possibility of earthquake. (If the answering person is not living in Chittoor, YSR Kadapa, Nellore districts and Krishna and Godavari delta region then the answer is No.)
Question 11.
Which place in Andhra Pradesh experiences earthquakes most of the time?
Answer:
Badrachalam and Kothagudem are the places where there is a possibility of earthquake most of the time. Chittoor, Kadapa, Nellore and Krishna and Godavari delta region also have greater possibility of earthquake because they lie in zone-111.
Question 12.
When does a piece of matter have a “charge?”
Answer:
When a piece of matter rubbed with another piece of matter, the piece of matter acquire charge due to friction.
E.g.: Rub the refill vigorously with a piece of polythene and if we bring piece of paper that can be attracted by refill due to development of charge.
Question 13.
What happens if two objects having same charge brought close to each other? What happens if two objects having different charges are brought close? Can you give an example for this.
Answer:
Two objects having same charge repel each other and two objects having different charge attract each other.
E.g. A balloon rubbed with woollen cloth repelled by another balloon rubbed with woollen cloth because both will acquire same type of charge.
A balloon rubbed with a woollen cloth attracted by a refill rubbed with a polythene sheet because both will acquire different type of charge.
![]()
Question 14.
Give two examples of effects in your daily life caused by transfer of charges.
Answer:
Two examples in daily life:
- Earthing
- Lightning
Question 15.
Inflate two balloons and rub both of them with a cloth first and then with different material. Will they attract each other in both cases?
Answer:
No, they will not attract each other. Both will repel each other. The reason is both ballons rubbed with same material acquired same charge in the both the cases.
Question 16.
Which country in the world is frequently affected by earthquakes? Collect the information and photographs on the recent earthquake in Japan.
Answer:
The country in the world which frequently affected by earthquakes is Japan. Pictures of earthquake affected areas in Japan in 2012.
Photographs of earthquake:
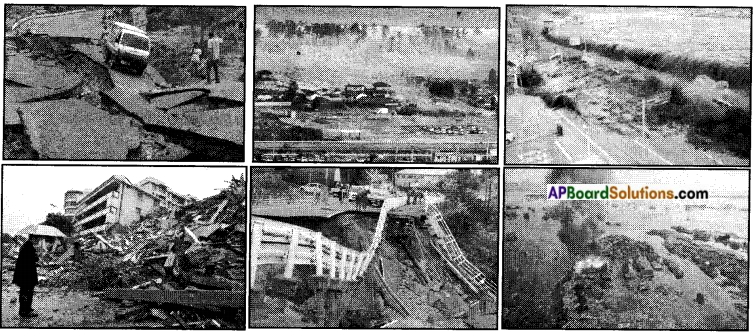
Information about earthquake:
- Lot of people killed due to earthquake.
- Lot of people killed not only due to earthquake but tsunami caused by earthquake.
- Lot of property loss took place.
- Most of the people in Japan lost their jobs and livinghood.
- They suffered emotionally also by losing their relatives, parents and children.
- Lot of effect felt on their economy.
- It effected the tourism of Japan.
![]()
Question 17.
Find out if there is an organization in your area which provides relief to those suffering from natural disaster. Enquire about the type of help they render to the victims of earthquake. Prepare a brief report on the problems of the earthquake victims.
Answer:
In India National Disaster Force provides relief for disaster victims.
Problems of earthquake victims:
- Death: Many times, the people who support a family socially and economically dies. This causes most of the other members of the family to either fight their way through, or restart their lives from the bottom of the food chain.
- Destroyed Structures: If the members of the family survive, then they could still be short of a home. The earthquake would have caused the destruction of their house and because of that, they would be left homeless.
- No food or water: In the aftermath of an earthquake, people see whether all the pipelines, roads, etc. are in good shape or order. If the pipes are broken, then water scarcity begins. If the roads are broken, then food supplies cannot be transported, later causing problems in food scarcity.
- Electricity : With inadequate supply of electricity, the debris and rubble will take a lot of time and if people are under it then they may die before the rubble is removed.
- Illnesses: After the destruction of many buildings, the sewer pipes will also break and open, causing spread of disease everywhere.
Help render by relief organisation:
- They minimize the death of people.
- They provide drinking water and food for victims.
- They provide shelter for earthquake victims.
- They provide medical facility for earthquake victims.
Question 18.
How do you relate the energy release during the collision of fault lines during earthquake to the atmospheric variation on the surface of the earth?
Answer:
An earthquake effects the atmosphere by creating amounts of debris and dust which will add to the air that we breathe. Earthquakes can also trigger volcanoes which will release tonnes of ashes and other debris into the atmosphere. This can sometime cause the blocking out of the sun, air pollution and are increased amount of carbon in the air.
Question 19.
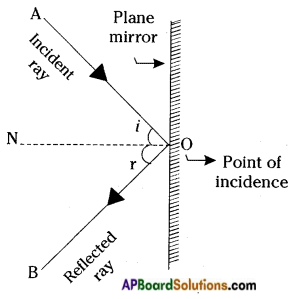
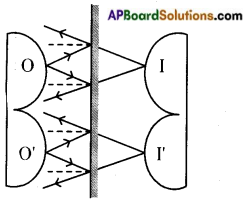
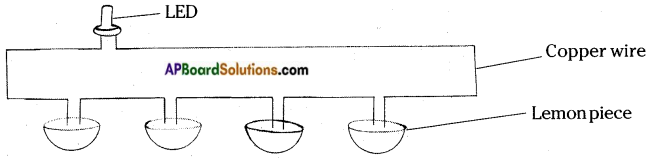
Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Answer:
The instrument used to detect a charged body is electroscope.
Description of Electroscope:
Take an empty jam bottle. Take a piece of cardboard slightly bigger in size than the mouth of the bottle. Pierce a hole in it, so that a metal paper clip could be inserted. Open out paper clip as shown in the figure. Cut two strips of aluminium foil about 4 x 1 cm each and hang them on the paper clip.

Insert the paper clip having the strips of aluminium foil into the cardboard lid so that it is perpendicular to it. This entire device works as a electroscope.
Procedure to detect a charged body ,by using a electroscope:
Charge a refill and make it touch the end of the paper clip. The aluminium foils move away from each other the reason that the strips of aluminium foil receive the same charge from the charged body through the paper clip and strips carrying similar charges repel each other and hence they move apart. This proves electroscope is useful in detecting a charged body.
![]()
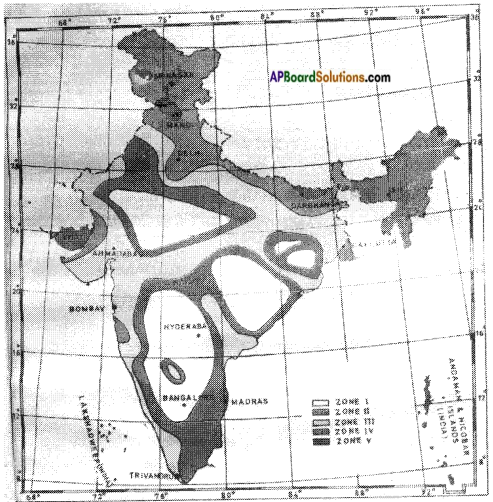
Question 20.
Colour seismic zones in India out line map.
Answer:
Question 21.
Prepare a model of seismograph.
Answer:
Preparation of model:
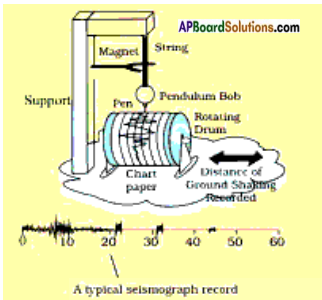
Take a pendulum and which is attached to support. This acts as vibrating system. A pen is attached to this vibrating system. Place a rotating drum covered with a paper just below the pen. When earthquake occurs the pen records the seismic waves on a paper which move under it.
Question 22.
How do you appreciate the efforts of scientists to develop an instrument to assess the intensity and source of earthquake?
Answer:
The efforts of scientists to develop an instrument to assess the intensity and source of earthquake is thoroughly appreciated because they provide assessment of earthquake and what are the rescue measurements to be taken by government and private organizations and also provide preventive measurements that would be taken when earthquake occurs. So these scientists providing life for people and their services are thoroughly appreciated.
Question 23.
Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake occurs. What precautions would you take to protect yourself?
Answer:
- I find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees and over head powerlines and I drop to the ground.
- If I am in a car or bus, I do not come out and I ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot. I do not come out of the car or bus till the tremors stop.
![]()
Question 24.
The weather department has predicted that a thunder storm is likely to occur at on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Answer:
No, I would not carry umbrella during thunderstorm because the metallic rod attached to the umbrella attracts the charge developed in thunderstorm and charge may carry through umbrella and possibility of electric shock. So it is not a good idea to carry umbrella during lightning.
Question 25.
If earthquake occurs in your area what will you do?
Answer:
- I will protect myself by covering head with helmet or cushion and hide in a safe place, such as under table.
- I will not run outside because roof tiles and glass may fall on me.
- Major after shocks can come after smallest earthquake so I calmly extinguish any nearby flames.
- Earthquake can wrap buildings, especially apartment buildings making it impossible to open doors and escape. So I open doors and windows to secure an escape route.
- I will be careful with broken glass.
- Once I come outside I will not return to house.
- I will avoid phone calls.
Question 26.
What are the measures you would take in your house when an earthquake occurs?
Answer:
- I would take shelter under a table and stay there till the shaking stops.
- I would stay away from tall and heavy objects that may fall on me.
- If I would be in the bed then I would not get up and I protect my head with a pillow.
8th Class Physical Science 11th Lesson Some Natural Phenomena Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Effect of rubbing:

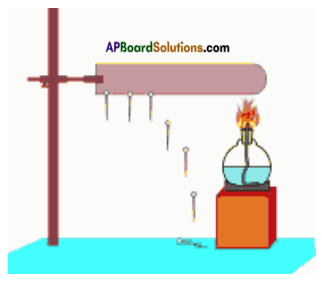
Take a used ball-pen refill and bring it near small pieces of paper.
The refill should be close enough but not touch the pieces of paper.
a) Check what happens to the paper pieces?
Answer:
They remain in the same position.
Now, rub the refill vigorously with a piece of polythene. Bring it close to small pieces of paper.
b) What is your observation. Take care that the rubbed end is not touched by your hand or with a metallic object.
Answer:
My observation is paper piece is attracted towards refill.
Now, take a comb and move it through dry hair a few times. Take the comb near small pieces of paper and check what happen.
The papers are attracted by comb.
Take an inflated balloon and rub it against your clothes. Bring the balloon close to small pieces of paper.
The paper pieces are attracted by balloon.
Take a drinking straw and rub it against a smooth wall or against your cloths, then bring it near pieces of paper.
![]()
c) What do you observe?
Answer:
The papers are not attracted by drinking straw.
d) Are they able to attract bits of paper after being rubbed?
Answer:
No, they are not attract bits of paper.
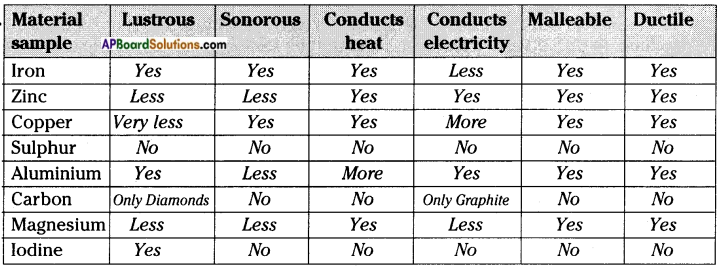
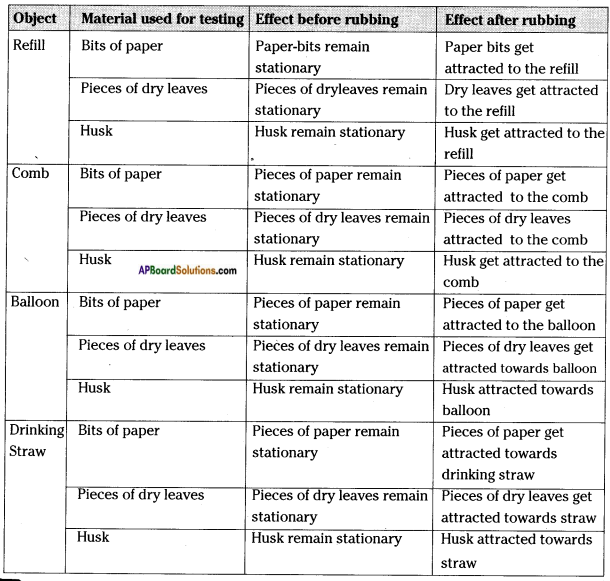
Repeat the activity by rubbing each one of the above mentioned objects (refill, comb, drinking straw, balloon) and use small pieces of dry leaf, husk, etc. as testing materials. Record your observation in table.
e) What can we infer from the above activity?
Answer:
When you rub material some material tend to attract pieces of paper.
f) Do objects like refill or comb attract pieces or paper only after rubbing?
Answer:
Yes, they attract pieces of paper only after rubbing.
g) Do all objects show this property?
Answer:
No, all the objects does not show this property.
h) Can we rub a comb against our palm and make it attract the paper bits?
Answer:
Yes, the paper bits are attracted to the palm due to friction charge is developed on the hand.
![]()
Lab Activity
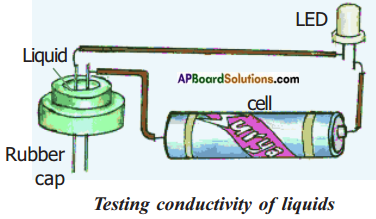
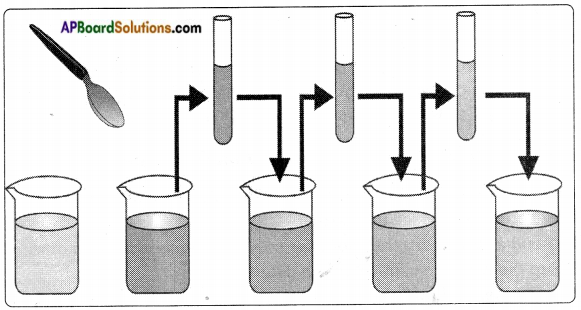
Conduct an experiment of find the effects of charged bodies which have been rubbed by different materials.
Aim: To find effects of charged bodies which have been rubbed by different materials.
Materials required: A ball pen refill, a balloon, a comb, an eraser, a steel spoon, polythene sheet, plain paper, woollen cloth, etc.
Procedure:
Rub the above objects against materials listed in table. In each case, bring the rubbed object near small pieces of paper and note whether they attract pieces of paper or not. Record your observations in table by writing ‘yes’ or ‘no’.
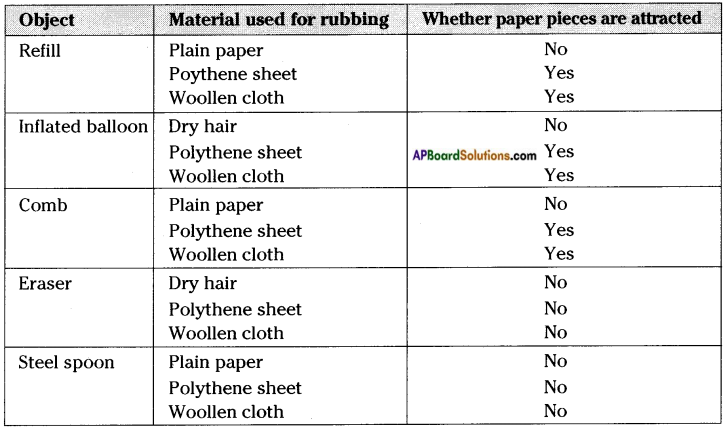
a) What do you conclude from above table?
Answer:
Some objects like refill, comb when rubbed with specific materials able to attract light objects like bits of paper. But some objects like steel spoon do not attract pieces of paper even after rubbing.
b) Why don’t some materials attract pieces of paper even after rubbing ?
Answer:
The reason is some material acquire charge when we rub them and some may not acquire charge so they do not attract pieces of paper.
Activity – 2
Question 2.
Understanding types of charges:
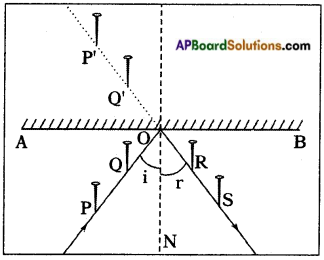
Inflate two balloons and hang them in such a way that they do not touch each other. Rub both the balloons with woollen cloth and release them.
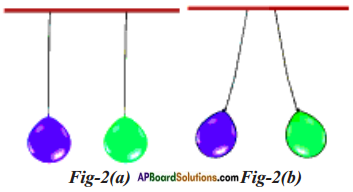
a) What do you observe?
Answer:
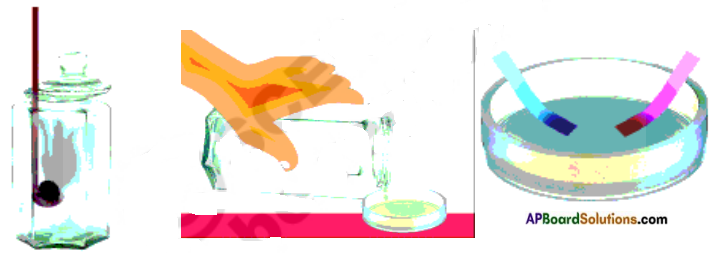
They repel each other. Take a refill and rub it with a polythene sheet. Keep it gently in a plastic tumbler. Take another refill and also rub it with the same polythene sheet.
Bring the second refill near the first one in the tumbler. Take care that you do not touch either of the rubbed portions on the refill with your hand.
b) Is there any effect on the first refill in the tumbler? Do they attract each other or repel each other?
Answer:
Yes, there is effect on the refill in the tumbler. They repel each other.
![]()
c) Now take a rubbed balloon near the rubbed refill in the tumbler and check the action. Do they attract each other or repel each other.
Answer:
They attract each other.
In the first two parts of the above activity, two objects that were made of the same material have brought near to each other after being rubbed with some appropriate material.

In the third part, objects made of different materials were brought near to each other after being rubbed with some material.
Let us summarise our observations carefully.
- A balloon rubbed with woollen cloth repelled another balloon of the same type.
- A refill rubbed with polythene repelled another refill rubbed with similar material.
- A ballon rubbed with woollen cloth attracted by a refill rubbed with polythene sheet.
d) What can we conclude from these observations?
Answer:
Some charged objects are attracted and some charged objects are repelled with each other.
e) Does the repulsion between charged balloons indicate that they possess similar charge?
Answer:
Yes, they possess similar charge.
f) Does the attraction between charged balloon and a charged refill indicate that they possess different charges?
Answer:
Yes, they possess different charges.
g) Does this activity remind you some of experiments that you have done in “Playing with Magnets” Chapter of class VI?
Answer:
Yes, we know that magnets attract objects made up of magnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt, etc.
We also know that unlike poles magnet attract each other and like poles repel each other.
h) Can we say that something similar is happening in above activities?
Answer:
Yes.
i) Does it indicate that the charge on the balloon is of a different kind from the charge on the refill?
Answer:
Yes, it indicate they are different charges.
j) Can we say that there exist two kinds of charges?
Answer:
Yes, there exists two kinds of charges.
k) Can we also say that the charges of same kind repel each other, while charges of different kinds attract each other?
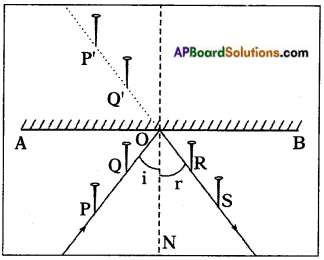
Answer:
Yes, it is convention to call the charge acquired by a glass rod when it is rubbed with silk cloth positive and charge acquired by a silk cloth is negative.
It is observed that when a charged glass rod is brought near a charged plastic straw which is rubbed with polythene sheet, there is attraction between the two.
![]()
l) What do you think about the kind of charge on the plastic straw?
Answer:
The plastic straw would carry negative charge.
m) Is your guess correct or wrong? Discuss with your teacher.
Answer:
My guess is correct because opposite charges attract each other which I confirmed by discussing with my teacher.
Activity – 3
Question 3.
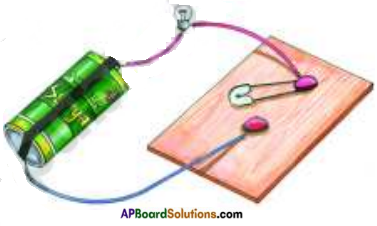
Conduct an experiment to find out the presence of charge on a body.
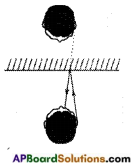
Make a small ball of thermocol. Collect thin silver foil used to decorate sweets.
Wrap this thin silver foil to cover the thermocol ball and suspend it from a stand with the help of thread as shown in figure.
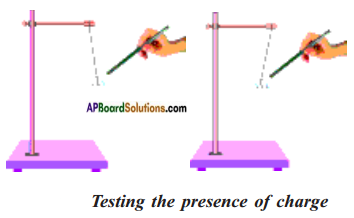
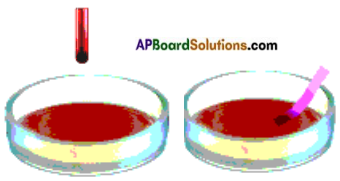
Bring a glass rod which is rubbed with a silk cloth near the suspended ball.
a) What happens ? Does it get attracted towards the glass rod or move away from it?
Answer:
It will attracts towards glass rod.
Now touch the silver foil on the thermocol ball with charged glass rod. Remove the glass rod from the ball and against rub it with silk cloth and bring it close to the suspended ball.
b) What do you observe?
Answer:
The suspended ball moves away from the glass rod.
c) What could be the reason for this change in movement of the ball?
Answer:
In the above activity when a charged body brought near an uncharged body it induces an opposite charge in it and hence it get attracted by the glass rod.
In the second case we have charged the thermocol by touching it with a charged glass rod. Hence when we brought the glass rod near the ball, as both of them have similar charge the ball gets repelled by the glass rod.
From the above activity we can conclude that attraction is not a sure test to know the presence of charge on a body.
Activity – 4
Question 4.
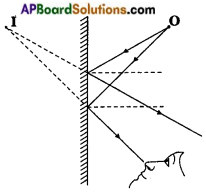
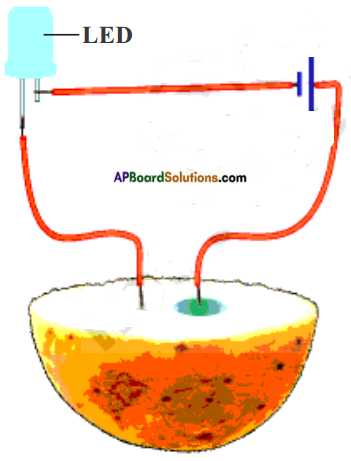
Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Take an empty jam bottle. Take a piece of cardboard slightly bigger in size than the mouth of the bottle.
Pierce a hole in it so that a metal paper clip could be inserted.

Open out paper clip as shown in the figure.
Cut two strips of aluminium foil about 4 cm x 1 cm each and hang them on the paper clip.
Insert the paper clip having the strips of aluminium foil in to the cardboard lid so that it is perpendicular to it as shown in the figure.
Change a refill and make it touch the end of the paper clip. Observe what happens.
a) Is there any effect on the strips of aluminium foil?
Answer:
Yes.
![]()
b) Do they repel each other or attract each other?
Answer:
They repel each other.
c) Now bring other charged bodies and make them touch the end of the paper. Do the foil strips behave in the same way in all cases?
Answer:
Yes, it behave in the same way in all cases.
d) Can this apparatus be used to detect the presence of charge on a body or not?
Answer:
Yes, it is used to detect the presence of charge on a body.
e) Can you explain why the strips repel each other?
Answer:
The strips of aluminium foil receive the same charge from the charged refill through the paper clip. The strips carrying similar charges repel each other and hence they move apart.
This device can be used to test whether an object is carrying charge or not. This device is known as electroscope. In the above activity you can observe that electric charge can be transferred from a charged object to another through a metal conductor.
Touch the end of the paper clip gently with hand and you will find a change in the foil strips they move closer and come back to their original state.
f) Why does it happen?
Answer:
The reason is that the foil strip lose charge to the earth through your body. We say that the foil strips are discharged.
The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing.
Activity – 5
Question 5.
Collecting information about the damages caused by earthquakes:
Ask your parents about the huge damages to life and property caused by these earthquakes. Collect a few pictures showing the damage caused by these earthquakes from newspapers and magazines of those days.
Prepare a short report on the suffering of the people during the earthquakes.
Answer:
Report: It caused damage to human life and property on a hugescale. Due to tsunami thousands of people died in the coastal areas of Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu. People lost their shelter.
a) What is an earthquake?
Answer:
An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of earth lasting for a very short period of time. It is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
![]()
b) What happens when it occurs?
Answer:
When it occurs it can cause damage to human life and property on a huge scale.
c) What can we do to minimize its (earthquake) effects?
Answer:
People living in seismic zones, where the earthquakes are more likely to occur, have to be specially prepared. The buildings in these zones should be designed so that they can with stand major tremors.
Steps to be taken in building construction:
- In highly seismic areas, the use of mud or timber is better than heavy construction material.
- Keep roofs as hieght as possible. In case the structure falls, the damage will not be heavy.
- It is better if the cupboards and shelves are fixed to the walls so that they do not fall easily.
- Be careful where you hang wall clocks, photoframes, water heaters, etc. so that in the event of earthquake, they do not fall on the people.
- Since some buildings may catch fire due to an earthquake, it is necessary that all buildings, especially tall buildings have fire fighting equipment in working order.
Measures to be taken in a house when earthquake occurs.
- Take shelter under a table and stay there till shaking stops.
- Stay away from tall and heavy objects that may fall on you.
- If you are on bed, do not get up. Protect your head with a pillow.
Measures to be taken outdoors when earthquake occurs.
- Find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees and overhead power lines. Drop to the ground.
- If you are in a car or a bus, do not come out. Ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot. Do not come out till the tremors stop.
Activity – 6
Question 6.
Locating the tsunami affected areas in the map:
Take an outline map of the world. Locate the eastern coast and Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. Mark other countries around the Indian Ocean which could have suffered damage.
Collect accounts of the devastation caused by the tsunami in India from your parents, or other elders in the family or in the neighbourhood.
Answer:
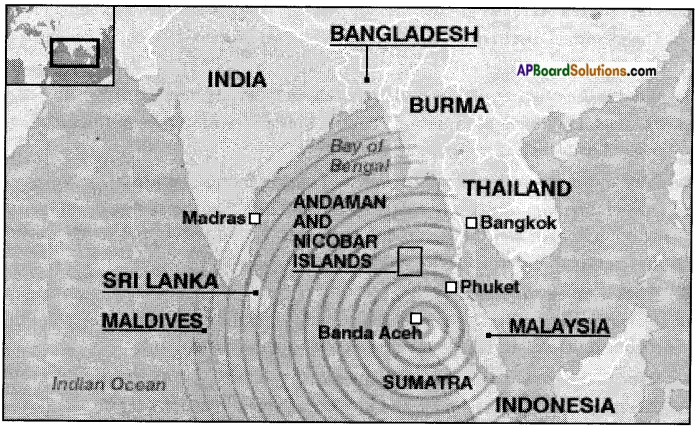
Devastation due to tsunami:
- Loss of lives, families and friends.
- Loss of properties.
- Loss of jobs and living.
- Emotional challenge.
- Loss of livestock.
- Dramatic or drastic changes to a whole community’s routine living.
- Negative impact on the affected regions, economy.
- Negative impact to the affected region’s tourism.
![]()
To the environment:
- Alternation to seaside terrain.
- Minor deforestation in the area effected by the tsunami.
- Wild life casualities.
- The sea will be temporarily littered with debris after the tsunami.