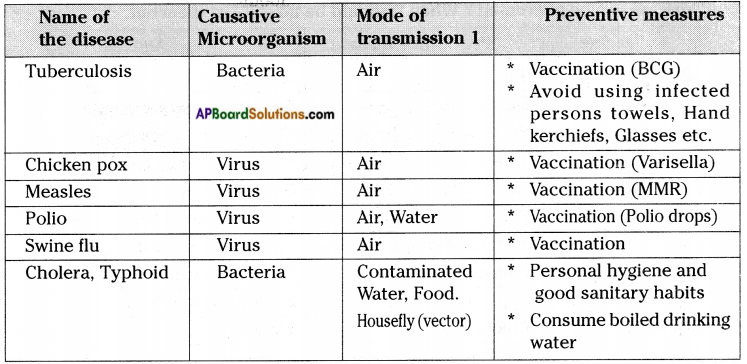
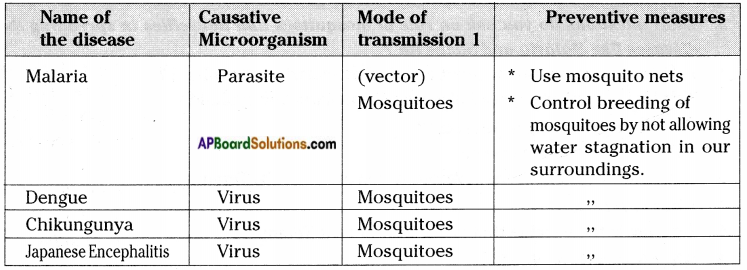
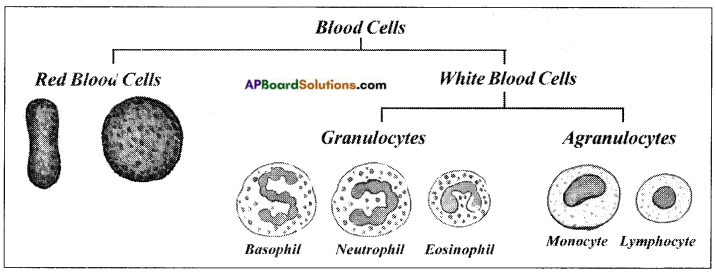
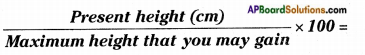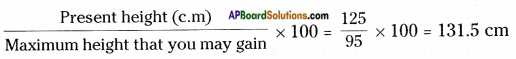AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 10 Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Solutions 10th Lesson Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing
8th Class Biology 10th Lesson Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
How does air pollution lead to water pollution?
Answer:
- Air and water are not separate problem. There is a close link between the health of air and the health of water.
- Nitrogen and chemical contaminants are two types of pollutants that harm both the air and water.
- Up to l/3rd of the nitrogen that pollutes the bay and it’s rivers comes from the air.
- Air pollution from a very large geographic area can eventually wind up in the Bay.
- Use of fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture pollutes not only air but also land and water.
- Sources of air pollution includes vehicles, industries, power plants and farm operations which lead to water pollution.
![]()
Question 2.
What steps can be taken up to control air pollution and water pollution?
Answer:
Some of the methods for controlling air pollutions are:
- Tall chimneys should be installed in all factories to reduce air pollution at the ground level.
- Better designed fuel burning equipment should be used in homes and industries so that fuel burnt completely.
- Install electrostatic precipitators in the chimneys of industries.
- Reduce vehicular emissions by using non polluting fuels like CNG (compressed natural gas)
- Use LPG for domestic use (Liquify Petroleum Gas)
- Improve the quality of fuel in automobiles and use catalytic converters in them.
- Make use of renewable alternative source of energy like solar energy, wind energy and hydro energy.
- All motor vehicles should be maintained properly so that they comply with pollution norms.
- Use unleaded petrol.
- Plant and grow, more and more trees, we can protect plants and trees. Vanamahotsav should be continued every year in July month.
Prevention and controlling of water pollution
- Toxic industrial wastes should be treated chemically to neutralize the harmful substances present in it before discharging into rivers and lakes.
- The sewage should not be dumped in to the rivers directly.
- The use of excessive fertilizers and pesticides should be avoided.
- The use of synthetic detergent should be minimized or biodegradable detergents should be used.
- Dead bodies of human beings and animals should not be thrown into rivers.
- The excreta and other garbage should be treated in a biogas plant to get fuel as well as manure.
- The water of rivers, streams, ponds and lakes should be purified or cleaned. For example Ganga action plait launched by the Indian Government.
- Trees and shrubs should bp planted along the banks of the rivers.
- There should be general Rareness among the people regarding the harmful of water pollution and the ways of prevention.
- Waste papers, plastic, waste fbod materials and rotten food and vegetables should not be thrown into open drains.
- Go for the alternate energy resources that can replenish themselves without affecting our environment.
- Reuse the materials for secondary purpose. Recycling is the next stage of reuse.
Question 3.
Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Answer:
Plants nutrients:
- Phosphates and nitrates – chemical fertilizers from agriculture run – off due to rain and industrial wastes enter into water through sewage and pollute the water.
- It helps algae to bloom, weeds to grow and bacteria is spread. As a result water turn green and cloudy and smell bad.
- Decomposing plants use up the oxygen in water, disrupting aquatic life, reducing biodiversity and even killing aquatic life.
- Thus, this enrichment of water by nutrients leading to excessive plant growth and depletion of oxygen is known as ‘Eutrophication’. This affects aquatic life badly.
![]()
Question 4.
Road side plants cannot grow properly. Find your own reasons and explain with your argument.
Answer:
- The plantation along the roads mainly includes neem, peepal, banyan, almond etc.
- It was observed that vegetation at roadside with heavy traffic and markets was much affected by vehicular emissions.
- Significant decrease in total chlorophyll and protein content was observed with reduced leaf area.
- It is concluded that plants can be uses as indicators for urban air pollution and there is need to protect the road side plants from air pollution.
- Biomonitoring of plants is an important tool to evaluate the impact of air pollution on plants.
- A study suggests that plants have the potential to serve as excellent quantitative and qualitative indices of pollution levels.
- So plants should be grown and protected.
Question 5.
Sudheer is a traffic constable. What do you think about his health? Give some suggestions to protect his health during duty period.
Answer:
- Environmental pollution place a significance role in the development of various respiratory diseases. Different particles and gases from vehicular emissions like carbondioxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur, benzene, lead, nitrogen dioxide and black smoke are the root of the problem.
- Traffic police are increasingly becoming victims of a diabetes and allergies at a younger age. Irregular work schedule were posing a challenge to the health of the police. Besides physical strain, mental stress and asymmetrical food habits are also contributing the problem.
- The traffic police men who work at busy intersections are at the highest risk of developing asthma, bronchitis, shortness of breath, sore throat, chest pain, lung cancer, eye irritation, skin ailments. Impaired hearing, excessive carboxy haemoglobin and annoyance with noise also high blood pressure and cardiovascular problems.
- On the basis of the study, pollution masks should be used by the traffic police men on duty at higher polluted junctions.
- He should be recommended better and special medical care for his protection. Various duty places for them need to be scientifically evaluated for their exposure risk.
- To protect ears from deafening noises, they can put small cotton balls in the ear and also wear ear masks for this purpose.
- Ecofriendly solar traffic booths at traffic intersections will be provided for the traffic police men. These booths contains ionisers which supress the suspended particulate matter and provide a healthy environment for a police man seated inside.
Question 6.
Write a short note on the effects of water pollution in your village. Suggest precautions.
Answer:
- Patancheru is a suburban mandal headquarters in Medak district, located about 25 km from Hyderabad. It is a major industrial hub of the state.
- It is one of the most polluted areas in India. Nearly 14 villages were badly affected by pollution related diseases like cancer, respiratory diseases and heart diseases caused by number of poisons in air, water and on land.
- The presence of pharmaceutical and chemical industries, pesticide units, steel rolling industries, distilleries releasing the pollutants like chlorine, Hydrogen sulphide, which are entering into the atmosphere.
- Most of the agricultural lands became barren. The lives of people there depend on agriculture and animal husbandry. They became helpless. Most of the people converted themselves as workers in the factories.
![]()
Question 7.
Visit a pollution check centre. Observe the process of conducting a pollution check and record your findings. You may consider the following areas your record.
Average number of vehicles checked in a certain time period, Time taken to check each vehicle, Pollutants checked for, The process of testing, Permissible limits of emission of various pollutants, Measures taken if the emitted gases are above the permissible limits.
- % Average number of vehicles checked in a certain time period.
Answer:
10-15 - Time taken to check each vehicle.
Answer:
5-7 minutes - Pollutants checked for
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, nitrogen oxide, methane, hydro carbons, sulphur dioxide, particular matter, trace elements, water vapour etc. - The process of testing:
- The test shall be carried out with the engine mounted on a test bench and connected to a dynamometer.
- The gases emission from the exhaust of the engine include hydrocarbons, carbondioxide, carbon monoxide and oxides of nitrogen.
- During prescribed sequence of warmed up engine operating conditions, the amount of the above gases in the exhaust, shall be examined continuously.
- The prescribed sequence of operations consists of a number of speed and power modes which span the typical operating range of engine.
- During each mode, the concentration of each pollutant, exhaust flow and power out put shall be determined and the measured values, weighed and used to calculate the grams of each pollutant emitted for kilowatt hour.
- Permissible limits of emission of various pollutants.
Pefrol engine
Carbondioxide 14%
Carbon monoxide 1 to 2%
Nitrogen oxide less than 0.5%
Hydrocarbons 0.5%
Sulphur dioxide possible traces
Particular matter less than 0.5%
Trace elements less than 0.5%
Nitrogen 71%
Water vapour 12%
Diesel Engine
Nitrogen 67%
Carbondioxide 13%
Water vapour 11%
Carbon monoxide less than 0.045%
Nitrogen oxide less than 0 to 1.5%
Sulphur dioxide less than 0.03%
Hydro carbons less than 0.43%
Particulate Pollutants less than 0.045%
Trace elements 0.3% - Measures taken if the emitted gases are above the permissible limits.
Answer:
The carbon particles (soot) deposited in the engine head will be checked and cleaned or the vehicle will be ceased by .R.T.O.
Question 8.
Organize a field visit to a pond/lake/river present in or near to your village with the help of your teachers.
Observations followed by discussion could focus on…. The history of the pond or lake or river, Water resources available other than that river/pond/or lake, Cultural traditions, Pollution concerns, Source of pollution, Effects of pollution on the people living by the river side as well as those living far away.
Answer:
Kolleru lake: It is a 2nd largest fresh water lake located in Andhra Pradesh located between Krishna and Godavari delta.
History: Two copper plates of the early Pallava dynasty have been found in the lake, tracing it’s history to Langula Narasimha Deva an Ganga Vanshi Odisha King. According to legend, the Gajapathi fort was located at Kolleti kota on one of the eastern islands of the lake. The enemy general “Muhammadan” general escamped at “Chiguru kota” located on the shores. In some ways the lake protected the Oriya forces. The enemy finally tried to excavate a channel, the modern day Upputeru. So that the water of the lake would empty into the sea and the level would fall so that they could attack the Gajapathi fort. The royal oriya army general sacrificed his own daughter to propitiate Gods and ensure his success against Muhammadan and her name was “Perantala Kanama”. Therefore the channel Was called perantala Kanama. “Sri Peddinti Ammavari Temple” is one of the oldest and famous temples found in Kolleru.
Water sources available other than Kolleru: Wells, taps. The lake is fed directly water from seasonal Budameru and Tammileru streams and connected to the Krishna and Godavari systems by channels.
Cultural traditions: The vast majority of the district is rural in nature. Thus the culture of the kolleru lake people is mostly conservative and traditional. The joint family system, the arranged marriages are the norms. Telugu language is spoken in this place. Pollution concerns: Kolleru lake is suffering from the unsatisfied greed of people and selfish interests of mankind who exploit the lake’s integrity. Thousands of fish tanks were dug up effectively converting the lake into a mere drain. This had great impact in terms of pollution, leading to difficulty in getting drinking water for the local people.
Source of pollution: Satellite images taken on February 9, 2001 by the Indian remote sensing satellite found that approximately 42% of the 245 km2 lake was occupied by aquaculture. While agriculture had encroached another 8.5% they were mostly rice paddies. Surprisingly no clear water could be found in the satellite image. The rest of the lake is being diminished by weeds like elephant grass and water hyacinth.
Effects of pollution on people: Thousands of fish tanks were dug up effectly leading to difficulty in getting drinking water for the local people. An adverse effect on the thousands of acres of crop in the upper reaches of water flow into the sea because of obstruction by bunds of the fish tanks that appeared illegally.
![]()
Question 9.
What is air pollution? Make a flow-chart to describe its causes and effects.
Answer:
If solid, liquid and gaseous substances are present in higher volumes than required in the air, it is harmful to air. It is called air pollution.
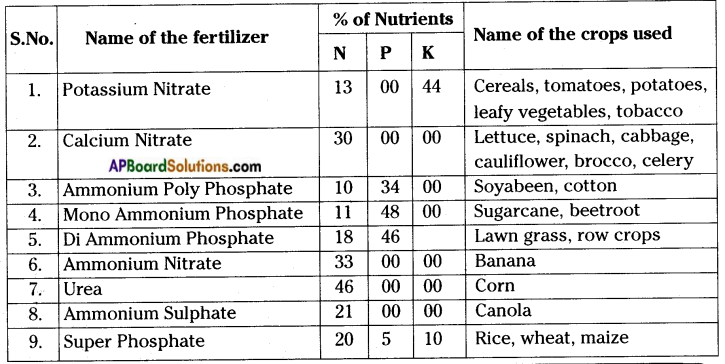
Table shows causes and effects of air pollution:
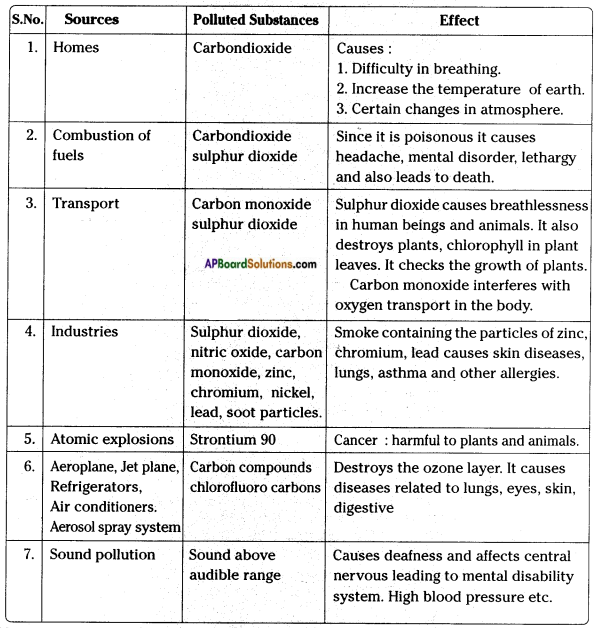
COMMON POLLUTANTS AND THEIR SOURCES
Question 10.
Clear and transparent water is always suitable for drinking. Comment.
Answer:
- No. Clear and transparent water is not always suitable for drinking.
- Water might appears clean but it may contain some disease causing micro-organisms and other dissolved impurities.
- Hence it is advised to purify water before drinking.
- Purifying can be done by water purifying systems or by boiling the water.
![]()
Question 11.
If our monument like Tajmahal is effected by air pollution, what is your advise to protect it?
Answer:
The Taj Mahal one of the seven wonders of the world is located in Agra. It is made of white marbles. The effect of pollutants like SO2, NO2, smoke, dust, soot, etc. on it has turned the marble from white to yellow.
Precautions to protect Taj Mahal:
- Switch over to cleaner fuels like CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquify Petroleum Gas)
- Use unleaded petrol in vicinity of Taj Mahal.
- Shift polluting industries to the outside of Agra city.
- Industrial pollution should be banned around the Taj Mahal.
- Limited vehicular use in a specific radius.
- An electronic board should be installed in the Taj Mahal premises, that compares current pollution levels, to the levels that deemed safe.
Question 12.
Reshma going to talk about controlling measures of soil pollution. Prepare write up for her.
Answer:
Controlling measures of soil pollution:
- Limit the use of fertilizers and pesticides.
- Awareness about biological control methods and their implementation.
- The grazing of cattle must be controlled and forest management should be done properly.
- The afforestation and reforestation must take place.
- Proper preventing methods like shields should be used in areas of wind erosion .and wind breakes.
- Remember to carry paper bags and minimising plastic bags.
- The soil binding grass must be planted and the large trees must be plant along the banks.
- Industrial waste must be dumped in the low lying areas.
- There should be a definite technic of cropping which does not allow weeds to settle on the fields.
- The mining waste must be improved along with the transportation.
- The are must not be left barren and dry.
Question 13.
To conduct a quiz program on air and water pollution, prepare five thought provoking questions.
Answer:
- What is environmental pollution?
- What are the natural disasters of pollution?
- What are the human activities that leads to pollution?
- What is the unforgettable industrial tragedy took place in Bhopal on second December
- Who is responsible for thepollution in Patancheru ? What are the interim orders, released by supreme court of India for the sake of people and environment?
- What is the sad story of River Musi?
- Can we save Taj Mahal from pollution?
What is the present situation of Taj Mahal? - Natural resources are the devine gift for us by nature. Can we keep these resources clean and healthy for the future generations? What is your role and response towards this?
![]()
Question 14.
“Use Bicycle – Avoid motor bikes and cars”. This slogan is prepared by Sravani. Prepare some more slogans on pollution.
Answer:
- Slogans towards biodiversity:
- Segregate the reusable waste.
- Don’t produce lot of waste.
- Don’t use plastic covers.
- Compost the wet waste.
- Turn the waste into compost.
- Make Compost out of fallen leaves.
- Never burn the fallen leaves of trees.
- Use bicycles if the destination is manageable.
- Plant trees in vacant places and take care to ensure their growth.
- Grow plants and protect them for fresh air and ventilation.
- Use cattle dung, organic fertilizers.
- Practice eco-friendly methods.
- Strictly follow environmental policies and laws.
- Limit the use of fire wood and use bio fuels for cooking.
- Plant a sapling on your birthday water it every day.
- Wash your hands, feet close to the trees and plants.
Question 15.
If you are a general manager of a chemical industry, what precautions would you take to control air and water pollution?
Answer:
Precautions to control air and water pollution :
- Stoppage of effluent flowing into air and water bodies immediately.
- Installing tall chimneys in factory to reduce air pollution at the ground level.
- Installing electrostatic precipitators in the chimney of industry to reduce.
- Plant and grow, more and more. Trees in the industry surroundings.
- Protecting plants and trees.
- Toxic industrial wastes should be treated chemically to neutralize the harmful substances present in it before discharging into water bodies.
- Waste water from the industry is to be filtered first to remove particulate material and stored in shallow tanks where bacterial degradation of organic compounds takes place.
8th Class Biology 10th Lesson Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing InText Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Observe this certificate try to find out answers for the following questions.
Answer:
The pollution under control certificate

a) Which department issues the pollution under control certificate?
Answer:
The pollution check up centre issues the certificate.
b) For how much time is it valid?
Answer:
It is valid for six months.
c) For which type of vehicle has it been issued?
Answer:
Motor bike, scooters, cars, bus, lorry all type of vehicles.
d) What is emission test ? What components are tested ini the pollution check up centre?
Answer:
The test conducting of the gases releasing from the vehicle is called emission test. Components tested in the pollution check up center are carbondioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, hydrocarbons, sulphur dioxide etc.
e) What will happen if carbon monoxide (CO) and hydro carbons (HQ readings are higher that the permissible limits reading ?
Answer:
If the above said gases are higher than the permissible limits reading it leads to pollution is harmful to the living organisms and hurt the health and well of living organisms.
f) Think of why there is a peed of “pollution under control certificate”?
Answer:
With a rapid increase in Ifie number of vehicles the problem of automobile pollution has assumed greater significance. The emission of smoke from motor vehicles is a major source of air pollution.
Question 2.
What will happen if harmful organisms or substances enter your body? How do you feel?
Answer:
If harmful organisms enter the body, the normal functioning of the body will be disrupted or disturbed. We feel sick.
What is air pollution ?
Question 3.
List out the gases that you know present in the air.
Answer:
The gases present in the air are nitrogen, oxygen, carbondioxide, inert gases mainly argon, and water vapour.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the four major gases in the air?
Answer:
The four major gases are nitrogen oxygen, argon and carbondioxide.
Question 5.
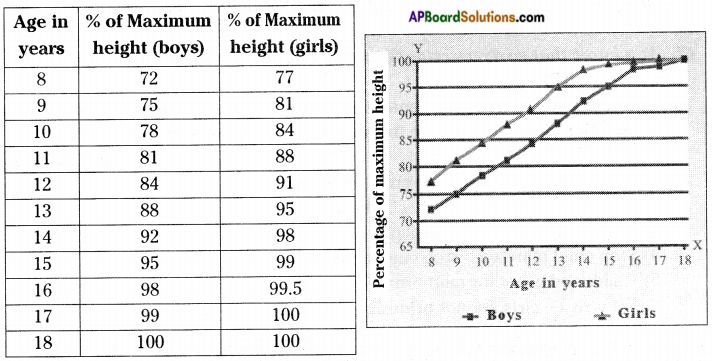
Draw a neat diagram showing the composition of air in the atmosphere arid write the percentage of gases.
Answer:
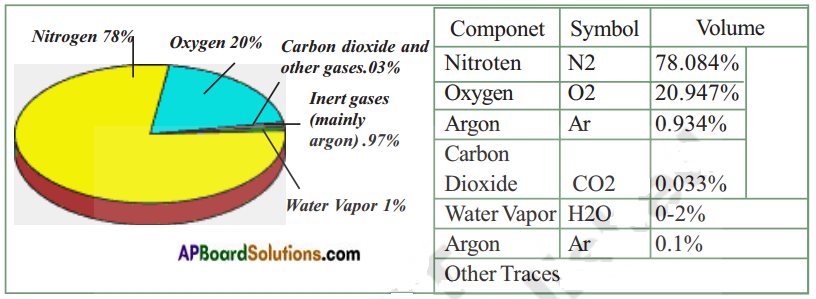
Question 6.
Collect the pictures of natural activities and human activities which leads to pollution and paste them in your record book.
Answer:




Question 7.
If a person burnt out types or dried leaves at a particular place. Where shall go the smoke and ash goes?
Answer:
The smoke and ash raise up, mixes with gases in the atmosphere which leads to pollution.
Water Pollution
Question 8.
Let us read the following news paper clipping.

Answer the following questions based on your understanding of the paper clipping.
a. What do you understand after reading the news paper clippings?
Answer:
Some areas in Nalgonda district, the water got polluted because of the chemicals dissolved in it. These chemicals are released Into the water by the oil factory, textiles, pesticide factory and steel factory.
b. What are the issues discussed in this news paper clipping?
Answer:
Total dissolved solids (T.D.S.) in water should be maximum 500. Due to pollution it is estimated that T.D.S. has reached to 10,000. The pollution in water is higher which is dangerous for use.
c. What are its causes and effects?
Answer:
The causes for the TDS: The chemical pollutants released by the factories into the water. Effects: The water becomes unfit for drinking. By using the water the crops are beeing dead.
d. How does the problem arise?
Answer:
Large amounts of chemicals discharged into the ground water leads to water pollution. Due to water pollution the problem arise in those areas.
e. Are you also facing this type of problems in your area? Can you explain reasons behind?
Answer:
Yes, I am facing this type problems in our area. Because industries are developed in our area. So population is increasing. That’s why water is polluted in our area.
![]()
8th Class Biology 10th Lesson Not For Drinking-Not For Breathing Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
NATURAL DISASTERS POLLUTION
Collect information from your school library for the following natural disasters in the world.
Answer:
Volcanic eruptions:
Deep under the earth’s surface, it’s so hot that even rock melts. Sometimes this molten rock, called ‘magma’, is pushed up to the surface. At this point it is referred to as lava. And the opening or vent that lets the lava out is a volcano. ‘
A volcano may explode violently throwing out rocks for miles around. It releases various gases and ash into the atmosphere.
Forest fires:
Forest fire is a moving combustion reaction spreading outwards in a band from it’s ignition point leaving burnt forest behind it and also called as wild fire.
It can be large uncontrolled disasters that burnt through hundred to hundred thousand acres.
Causes : Natural cause, lightening, volcanic eruptions, sparks from rocks falls and spontaneous combustion.
Pollution :
Forest fires release carbon particles (ash) into the air and pollute the air.
Sand storms and Tsunamis:
A sand storm or a dust storm is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi arid regions. They arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows, loose sand and dirt from a dry surface. Particles are transported by saltation and suspension. The Sahara where sand is more prevalent, soil type than dirt or rock.
Causes:
As a force of wind passing over loosly held particles increased, the particles of sand first start to vibrate, then to saltate. As they repeatedly strike the ground, they loosen and break off smaller particles of dust, which then begin to travel in suspension.
Tsunamis:
- Tsunami is also called as a ‘seismic sea wave’ is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water.
- Tsunami impact is limited to coastal areas. But their destructive power can be enormous, and they can effect entire ocean basin.
- The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was among the deadliest natural disasters in human history with, atleast 2,30,000 people killed or missing in 14 countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
- Tsunami causes much damage by two mechanisms. The smashing force of water travelling at a high speed and destructive power of a large volume of water draining of the land and carrying away large amount of debris with it.
- About 80% of tsunamis occur in the Pacific ocean, and there is possibility for tsunamis wherever there are large bodies of water including lakes.
![]()
Activity – 2
Question 2.
A) OIL PAPER EXPERIMENT
Answer:
Take three square pieces of white paper of 5 x 5 cm size dipped in oil. Hang these oil dipped paper at three different locations, say your backyard, your school, near a park or parking lot etc. Let it be there for 30 minutes. Observe and compare all three papers.
a) What did you found on those papers dipped in oil ?
Answer:
Some dust particles sticking to the oil paper.
b) Is there any difference observed for all the three locations ?
Answer:
Some differences are observed. The soot and ash dust particles are seen on the oil paper hung at back yard which comes from burning of wood.
More dust particles seen on the oil paper at the school and less dust particles on the oil paper which was hung near a park.
c) Try to find out the answer why this difference occurred.
Answer:
When different types of fuels are burnt they release different types of particles into air. These particles are different according to different locations.
d) Do you know where the dust particles could have come from ?
Answer:
The dust particles could have come from the effect of air pollution caused by man made resources largely affects nature.
B) HUMAN ACTIVITIES:
Name of the fuels we burnt in our daily activities including rural and urban areas.
Answer:
Petrol, diesel, wood, charcoal, tyres etc.
Activity – 3
![]()
Question 3.
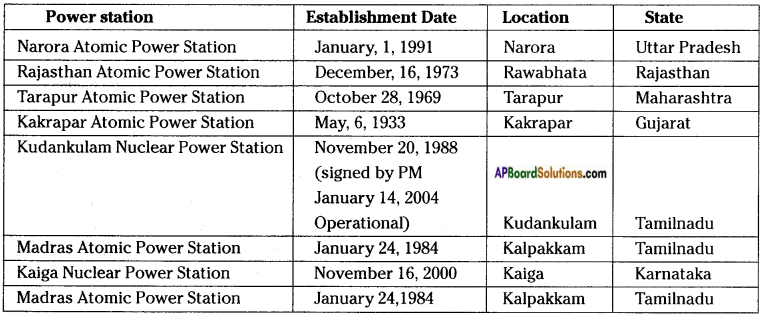
POWER GENERATION PLANTS.
Go to your school library and collect information to make a list of these power generation plants and where they are located.
Answer:
THERMAL POWER PLANTS
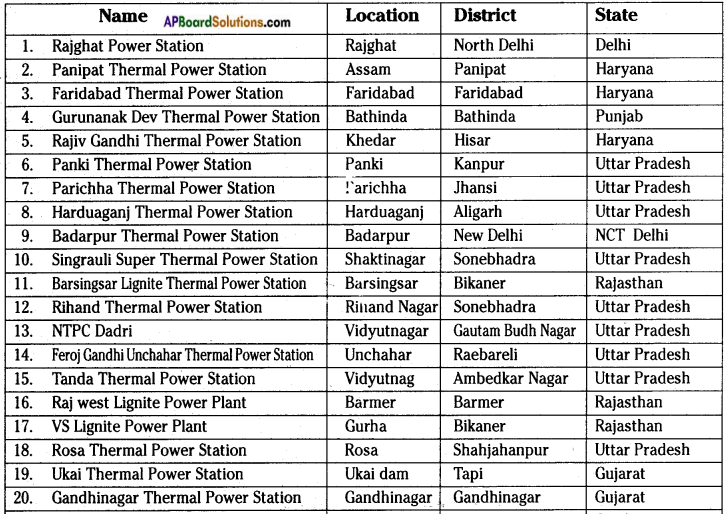
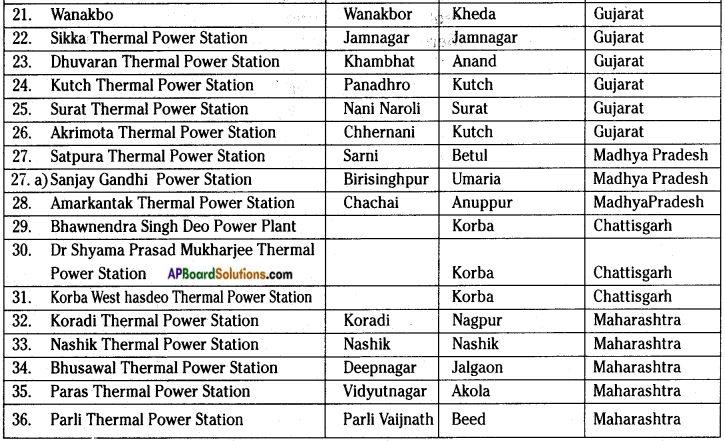
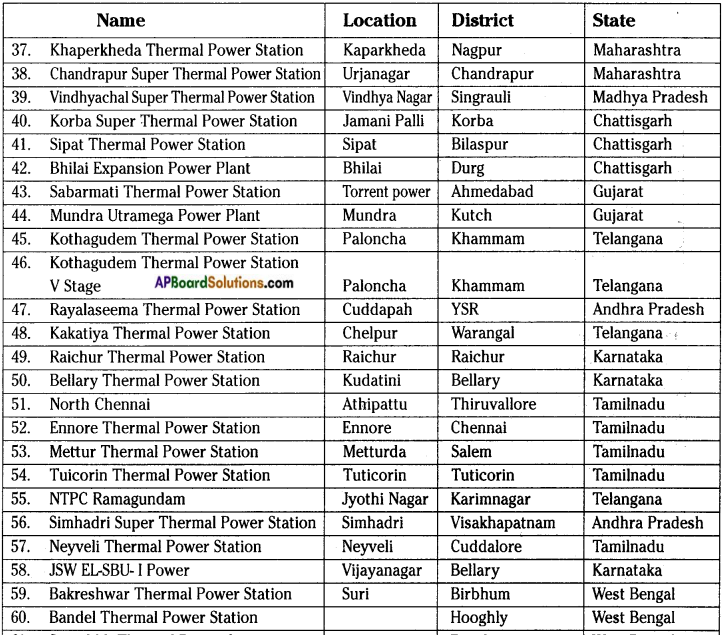
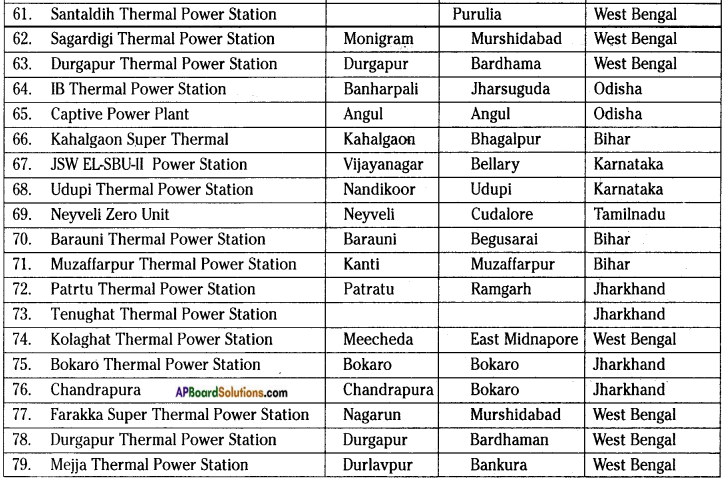
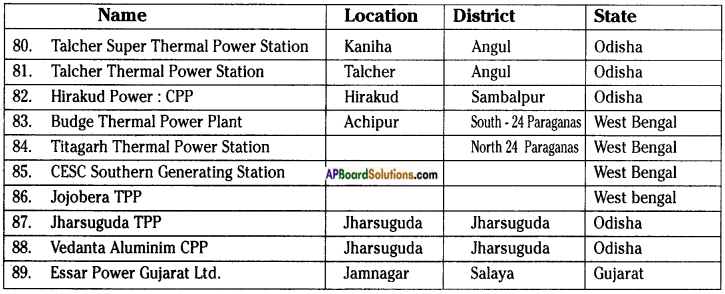
NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS
Discuss about the adverse effects of Global warming.
Answer:
Effects of Global Warming: Global warming is having measurable effects on the planet right now. They are
- Ice is melting in both polar ice caps and mountain glaciers.
- Lakes around the world, including lake superior are warming rapidly.
- Animals are changing migration patterns.
- Plants are changing the dates of activity. Ex : Leaf flash.
- Global warming increase in temperature around the world.
- The average global temperature increased 0.8°C over the post 100 years.
- Weather is changed by globed warming, some places become more hot and some more cool.
- Global warming increases the sea level. So the costal areas will sink into the sea.
- Ice is melted which increases the sea level that leeds to ocean acidification.
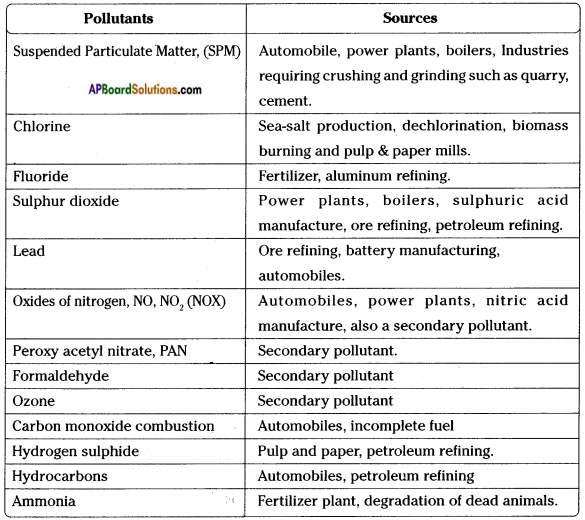
Ask your teacher about secondary pollutants why they are called so?
Answer:
Oxides of nitrogen NO, NO2 (NOx), peroxy acetyl nitrate, formaldehyde, ozone, etc., are the secondary pollutants.
Pollutants are defined as primary pollutants resulting from combustion of fuels and industrial operations and secondary pollutants, those which are produced due to reaction of primary pollutants in the atmosphere.
Activity – 4
![]()
Question 4.
FIELD VISIT:
Visit nearby factory, industry (boiled rice mill, brick making kiln, oil mill food processing mill etc.,) present in your area and observe.
- How are they polluting air and water ?
Answer:
They are releasing smoke, smooth dust particles into air and releasing waste material into water sources and polluting air and water. - Is there any green belt around the factory ? Name the trees they are growing.
Answer:
Ashoka, Gulmohar, Neem, Eucalyptus are growing around the factory. - What precautions are they taking to prevent pollution ?
Answer:
Suction devices known as vacuum pans are used to collect the pollutants from the water.
To control air pollution, ventury type wet scrubber and meeting the norms described by A.P. Pollution board -have arranged.
Lab Activity
Question 5.
POLLUTANTS:
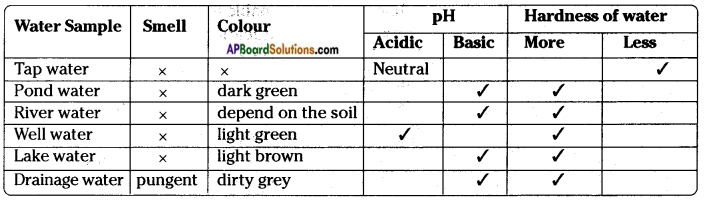
Aim: Observation of pollutants in local available water samples.
Material: Glass tumblers, water samples from tap, pond, river, well, lake, red, blue litmus papers, soap.
Procedure: Collect water samples from a tap, pond, river, well and lake. Pour each into separate glass containers. Compare these for smell, colour pH and hardness.
- pH of water samples can be determined by using litmus paper. If blue litmus paper turns to the red colour, that water sample is acidic in nature and if red litmus turns to blue, water sample is basic in nature.
- Hardness of water can be determined using soap. If water produces lesser foam it is referred as hard water.
Observations and findings:
Record your observation in the following table.
Activity – 5
Question 6.
Visit your nearby pond/lake or river and find out the material being discharged in it. Prepare a biography on it.
Answer:
As Hyderabad has grown in size and is emerging as a global mega city, its growing water requirements have been met by under taking long distance water projects over the years. These projects are dependent on Musi River. Thousands of people depend on it for their daily needs and livelihood. The Moosi has been polluted for many years.
The people living near the Musi river, throw large quantities of garbage, untreated sewage, industrial waste, dead bodies, polythene bags, hot water and statues of deities and many other materials directly in to the river. –
The ‘Musi reservoir action plan project’ was undertaken to reduce the pollution level in the river. Pollution control activities include under the project are:
- Solid waste management.
- Installation of sewage treatment plant.
- Provision of low cost sanitary facilities.
- Development of river front.
- Efforts to develop public awareness.
Ask your teacher about aerobic bacteria and write a note on it with some examples.
Answer:
An aerobic bacteria is the one that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. Bacillus, nocardic and pseudomonas space aeruginosa, myobacterium tuberculosis are some of the examples of aerobic bacteria.
Do you know oil slick on sea water ?In what way it is dangerous to aquatic life?
Answer:
Several kinds of plants and animals live in oceans. Oceans maintain equilibrium in nature. We transport several kinds of oils and fuels over seas. The spillage of these oils and fuels by accident creates a layer of oil over the surface of the sea water for hundreds of kilometers. This is called oil spill or oil slog. When it happens, air and light cannot enter the sea water and several marine creatures like fish, tortoise and other marine life forms die of asphyxiation.
Think and Discuss
![]()
Question 1.
When we go on a busy road in the evening a lot of smoke is spread in the surroundings. We get cough and feel uneasy even when we close the nose with napkins.
a) Why this type of symptoms we observe? Think about it.
Answer:
Carbon monoxide is poisonous gas combines with haemoglobin of our blood and forms carboxy haemoglobin. Due to this haemoglobin is unable to carry oxygen to various parts. This leads to respiratory problems. It causes suffd&Stion and may cause even death.
b) If these symptoms will continue, what happens?
Answer:
Air pollution is like a slow poison. The effect of air pollution are not seen immediately. But over a long period of time the pollutants present in air damage our health and property.
Question 2.
Do you find any relation between pH and hardness of water?
Answer:
No relation between pH and hardness of water. pH is scale to measure acid, base or neutral hardness is the percentage of salts dissolved in the water.
Question 3.
Which water sample is colourless?
Answer:
Tap water.
Question 4.
Which water sample is suitable for drinking and why?
Answer:
Tap water is suitable for drinking because the tap water is cleaned and chlorinated and safe for drinking.
Question 5.
Do you find any change in colour and smell of water in some water samples ? What are your reasons ?
Answer:
The colour and smell of water is due to the nature of the soil and the plants grown in the water.