SCERT AP Board 7th Class Social Solutions 8th Lesson Industrial Revolution Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Studies Solutions 8th Lesson Industrial Revolution
7th Class Social Studies 8th Lesson Industrial Revolution Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Correct the false sentences:
Under the putting-out system:
a) Spinners took cotton to the weavers.
Answer:
Correct statement: A cloth trader purchased cotton from a supplier and carried it to the spinners.
b) Unlike in the guild system traders controlled what product was to be made.
Answer:
Correct statement: Unlike in the guild system the capitalists controlled what product was to be made.
c) All work was done by the same group of people.
Answer:
Correct statement: Different activities could be done in different parts of the country by different groups of people.
Under the Guild system:
a) All small farmers were allowed to learn to weave.
Answer:
Correct statement: All small farmers were forced to learn to weave.
b) Weavers determined the prices and quality of the products.
Answer:
Correct statement: Capitalists determined prices and quality of the products.
![]()
Question 2.
Putting out a system is better than factory-based production of textiles. Do you agree?
Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Every system has its own merits and demerits.
Inputting out system different activities of the production could be done in different parts of the country. It consumes a lot of time and it is very much expensive. But in factory system production is carried on in one place called factory. This factory system is time-saving and less expensive when compared to the putting-out system. Inputting – out system every worker and craftsman get employment. But in factory system machines can do the work of several workers at the same time and therefore lakhs of people are expelled from the factories. Thus it leads to unemployment and unrest among the people. In putting out a system the craftsmen and workers control the whole process of production. But in the factory system, the factories are owned and managed by the capitalists. This widens the financial gap between the capitalists and owners. Thus it leads to unrest among the labourers.
Question 3.
If Kruthika argues “Railways in India were built only for the benefit of the people by the colonial rulers”, how can you counter this statement?
Answer:
No. It is not true. The English built railways not only for the benefit of Indian people, but to transport raw material to Indian ports and manufactured goods of England from Indian ports into the country. To transport cheap labour from villages to cities, and to transport their troops fast and easily to the nooks and corners of the country to link up all their trading centres in all parts of the country British established railways in India.
Question 4.
How will an increase in the wages of the workers affect industrial production?
Answer:
- The workers cannot work with complete skills if they are not paid properly.
- They cannot satisfy their basic needs with meagre wages.
- If their pay is increased they can work for more time with enthusiasm.
- It results in an increase in production.
- Then the capitalists won’t mind the increase in their expenditures.
- Thus the increase in wages leads to an increase in production.
![]()
Question 5.
Why did factory owners pay low wages and force workers to work for long hours?
Answer:
Nowadays all facilities of production are owned and managed by capitalists. They invested money in workers, raw materials and machines. In this system, workers worked for wages. When the machines were introduced very few people were required to work on machines, all the rest would be expelled. So there are a lot of surplus workers available at hand for the capitalists. And the labourers are prepared to work even with meagre wages. Thus the capitalists who are aimed to get more and more profits to force the workers to work at low wages and they are forced to work for long hours under the whip.
Question 6.
Why do you think the working conditions in factories should be improved?
Answer:
The following steps are necessary for labourers.
- Working hours should be reduced.
- Minimum wages should be fixed.
- An insurance scheme should be launched.
- Holidays must be given to the labourers and industrial workers. In 1881 steps were taken for the welfare of the labour class and industrial workers.
- Major changes swept industries with the coming of machines.
- Machines could be worked by even unskilled persons. Thus skilled artisans were no longer required.
- In their place, a large number of women and children were employed and made to work for meagre wages.
- These conditions should be improved.
Question 7.
Why is it necessary for the government to enact laws to improve the working conditions in factories?
Answer:
The early factories were dreadful places of work. Industrial work had to face several hardships. They are
- They had to work for more than 12 hours a day.
- Machines could be worked by even unskilled people. So they were expelled from their jobs.
- A large number of women and children were employed and made to work for meagre wages.
- The children under 14 years of age were given hard jobs like pulling and pushing heavy loads and working near dangerous machines.
- The workers were forced to live in makeshift houses and shelters.
- Their areas of residence had little sanitation and their houses lacked proper ventilation and health facilities.
- Accidents, diseases and epidemics were common in their slums.
So it is very much necessary for the governments to enact laws to improve the working conditions.
![]()
Question 8.
Why are children not allowed to work in factories?
Answer:
The Indian Constitution provides the Right against exploitation as a fundamental right.
Article 24 prohibits the employment of children in hazardous work as in some factories and mines. The Directive Principles prescribe that
- the tender age of the children shall not be abused.
- children are not forced by economic necessity to enter vocations unsuited to their age and strength.
- children are given opportunities and facilities to develop in a healthy manner and in conditions of freedom and dignity and
- childhood is protected against exploitation. Under the Children’s Right to Protection, the children are free from all forms of exploitation, abuse, inhuman or degrading treatment and neglect. So the children should not be employed in factories.
Question 9.
The transport system helps the industry justify this statement in the context of Industrialisation.
Answer:
Yes. It is true. The transport system helps the industry. Cheap and proper transportation is one of the most necessary infrastructures for Industrialisation. After the Industrial revolution industrial production increased so much. They needed raw material in large quantities. The countries did not have the raw material needed for the industry. For example, the cotton needed for producing cloth was grown in India and America. So the English had to import the cotton. In the same way, industrial production increased so much that it had to be sold in other countries. Thus transport is needed to import raw materials and export the manufactured goods to other countries. To carry the cheap labour from the villages to the urban areas the transport is needed. Thus we can justify the above statement ‘Transport system helps the industry’.
Question 10.
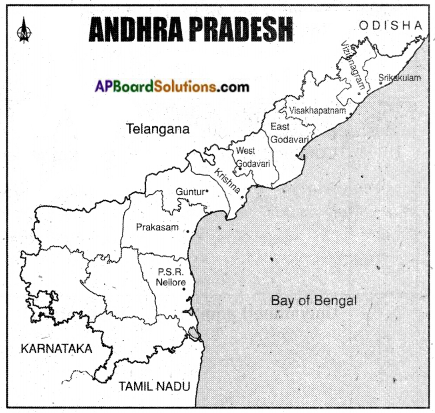
Locate the following places on the world map.
a) England b) Portugal c) France d) Spain
Answer:
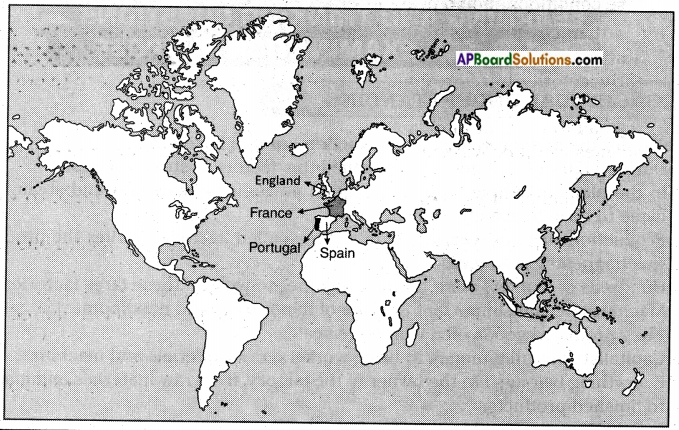
![]()
Question 11.
Read the para ‘Urbanisation and slums on page 82 and comment on it.
Urbanisation and slums: Industrial revolution led to a gradual shift of people from villages to towns. Industries and other urban activities gave people livelihood. As people moved to towns that were newly emerging, they settled down in makeshift houses and shelters which were cramped and had little sanitation or other facilities. Accidents, diseases and epidemics were common. Most workers’ residential areas lacked proper ventilation, health and sanitation facilities. Slums became a common scenario in towns and cities, especially near the factories and mines. At the same time, distinct quarters came up for the rich and the powerful which were well provided in terms of open spaces, sanitation, water supply, roads and other facilities. Slowly people fought for civil rights and the conditions of the worker’s quarters also improved.
Answer:
Industrialisation led to urbanisation. Slums are caused due to urbanisation. It is very difficult to provide health, sanitation, and shelter facilities to the growing population in urban areas. Public amenities like water, roads, and education are also should be provided. The same condition is present in urban areas even today also.
Project Work
Question 1.
You may recall the lesson on agriculture and trade in Class VI. Compare the nature of farmers and traders in Andhra Pradesh with traders in Britain or Europe. You can use a few criteria and tabulate.
Answer:
The traders in Europe were international traders. They earned many profits. They purchase raw materials and market finished goods.
But our traders are local traders. They earn small profits. They purchase the finished goods and sell them with a little margin.
![]()
Question 2.
Do you know any child working in a factory or shop? If you find, how do you respond?
Answer:
Yes. If I find it, I will immediately respond to the concerned authorities to take action against child labour.