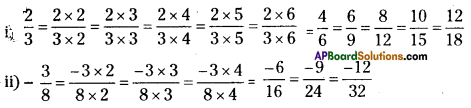These AP 7th Class Social Important Questions 8th Lesson Bhakthi – Sufi will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class Social 8th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Bhakthi – Sufi
7th Class Social 8th Lesson Bhakthi – Sufi 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Bhakti?
Answer:
Bhakti means a path of loving devotion to a particular deity.
Question 2.
What is the main characteristic of the Bhakti Movement?
Answer:
Universal Brotherhood and equality of all in the society.
Question 3.
When did Bhakti movement became popular in all religions?
Answer:
In the medieval period the path of Bhakti became more popular in all religions.
Question 4.
Who started the Bhakti Movement?
Answer:
Bhakti movement was started by Adi Shankaracharya.

Question 5.
Who lead the Bhakti movement in North India?
Answer:
Ramananda, Kabir, Ravidas, Surdas, Mira Bai, etc.
Question 6.
Who spread the Bhakti movement in Tamilnadu?
Answer:
Alwars and Nayanars spread Bhakti movement in South India, mainly in’Tamilnadu.
Question 7.
Write a few words about Shankaracharya.
Answer:
- Shankaracharya was born in Kaladi of Kerala.
- He became a saint at the age of 5.
- He preached Advaita Philosophy.
- He established four Shakthi Peethas in all the four corners of India.
Question 8.
Names of Shakthi Peethas.
Answer:
- Badri in the North.
- Srungeri in the South.
- Puri in the East and
- Dwaraka in the West.
Question 9.
Name the works of Shankaracharya.
Answer:
Shankaracharya wrote Viveka Chudamani, Soundaryalahari, Sivanandalahari, Atmabodha, etc.
Question 10.
Define Dwaita Philosophy.
Answer:
According to Dwaita Philosophy, the world is not an illusion but a reality. Brahman, Atman and matter are unique in nature.
Question 11.
What is the idealogy of Vajlabhacharya?
Answer:
Vallabhacharya idealogy is known as Suddhadvaita.
Question 12.
What was the Cardial quote of Sant Ravi Das?
Answer:
Santa Ravi Das cardial quote was “Hari is in all and all in Hari”.
Question 13.
Who was the founder of Sikh religion?
Answer:
Guru Nanak was the founder of Sikh religion.

Question 14.
Write about the teachings of Guru Nanak.
Answer:
The most famous teaching attributed to Guru Nanak are :
- There is only one God.
- That all human beings can have direct access to God.
- He taught that everyone is equal, regardless of caste or gender.
Question 15.
Write about Molla.
Answer:
- Molla is also called Mollamamba.
- She is a Telugu poet.
- She wrote Ramayana in Telugu.
Question 16.
Write a few words about Annamayya.
Answer:
- Tallapaka Annamacharya came from Tallapaka village of Kadapa district.
- He is known as Padakavita pithamaha.
- He wrote 32,000 Keerthanas in praise of lord Venkateswara.
Question 17.
Define Sufi movement.
Answer:
- The Sufi movement was a socio-religious movement in Islam.
- The Sufis emphasised on an egalitarian society based on universal love.
Question 18.
What is the impact of Sufi movement?
Answer:
- Sufi’s travelled all over the country to reach the poor and rural communities.
- They preached in the local languages.
- They lived a modest simple life.
7th Class Social 8th Lesson Bhakthi – Sufi 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain about Saguna and Nirguna Bhakthi.
Answer:
- The gunas are a key concept in nearly all schools of Hindu philosophy.
- These three gunas are called: Sattva (goodness, calmness, harmonious), Rajas (passion, activity, movement) and Tamas (ignorance, inertia, laziness).
- All of these three gunas are present in everyone and everything.
- Attributing these gunas to the God is Saguna Bhakthi.
- Worshipping the god without these Gunas is Nirguna Bhakthi.
Question 2.
What is the impact of the Bhakti Movement on the Medieval Indian society?
Answer:
- The most important social impact of the Bhakti movement was that the followers of the Bhakti movement rejected caste discrimination.
- This movement encouraged religious tolerance.
- The bhakti saints preached religous tolerance and monotheism.
- A spiral of harmony developed among different sections of the society.
- It tried to develop humanitarian attitude.

Question 3.
What are the salient features of Sufism?
Answer:
The salient features of Sufism :
- There is only one God. All are children of God.
- To love a fellow human being is to love God.
- Devotional music is one of the ways to reach the presence of God.
- Sufi believes WahdatTul-Wujud which means worship for a single God.
7th Class Social 8th Lesson Bhakthi – Sufi 8 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Appreciate Sufi movement.
Answer:
Sufi Movement:
The Sufi movement was a socio-religious movement in Islam. The Sufis emphasised on an egalitarian society based on universal love. The word Sufi is derived from an Arabic word Saf. Saf means purity / clean. The Sufi saints were always in meditation and they led a simple life. They wore woollen clothes.
The salient features of Sufisim :
- There is only one God. All are children of God.
- To love ones fellow men is to love God.
- Devotional music is one of the ways to move nearer to God.
- Sufi believes Wahdat-ul-Wujud means worship for a single God.
Question 2.
Why Hindus worship many forms of God while there is only one form of God in Islamism?
Answer:
- Hindus worship many Gods. But all the Gods are not human beings, they are energies.
- The common man cannot understand or pray the immortal forms. So the rishis of Hinduism gave names to certain energies and physical shape.
- Later due to lack of knowledge the energies are forgotten by the common people and the physical forms and names only recorded in their minds.
- It also can be said that these energies are in subtle form in human bodies.
So Hindus worship many forms of God. But they also have only one Universal Supreme Being, PARAMATMA.

Question 3.
What are the inferences from the poetry of Bhakti and Sufi saints about the existing social order ?
Answer:
Inferences from the Poetry of Bhakti and Sufi saints about the existing social order:
- Bhakti movement and Sufi movement influenced the life style, cultural practices and traditions of people.
- The saints and their followers resented caste, religious inequalities that prevailed in society.
- Dignity of labour enhanced the recognition of the people in Agriculture, Handloom, Art crafts etc.
- Inspiration of Bhakti movement lead to the formation of new kingdoms.
1) Vijayanagara kingdom was established with the inspiration of Swami Vidyaranya.
2) The Maratha kingdom by Shivaji with the inspiration of Samardha Ramadas.
- Bhakti movement enhanced the essence of local languages. The saints of Bhakti movement composed songs and poems to attract common man easily. This enhanced the literature in regional languages.
Ex : Writings of Akkamahadevi, Meera Bhajans, Tiruppavai of Godadevi.
- The sufi saints propagated the principles of monotheism (belief in one God) simple way of worship and protested superstitions.
- Sufi saints propagated their principles in poems and songs. Music has great prominence in praising God. Ex : Quwwali.
- Simplicity, disciplined life dedication towards Islam etc. Attracted the society towards Sufism.
AP Board 7th Class Social 8th Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Bhakthi – Sufi
I. Multiple Choice Questions
1. The Bhakti Movement reached its prominence in _______ century.
A) 5th
B) 6th
C) 7th
D) 8th
Answer:
D) 8th
2. Saguna Bhakti means ___________ .
A) Worshipping god with form
B) Worship of the divine as formless
C) A & B both
D) None
Answer:
A) Worshipping god with form
3. Nirguna Bhakti means ________ .
A) Worshipping god with form
B) Worship of the divine as formless
C) A & B both
D) None
Answer:
B) Worship of the divine as formless

4. The Bhakti movement was started by _________ .
A) Adi Shankaracharya
B) Ramanujacharya
C) Madhwacharya
D) Nimbarka
Answer:
A) Adi Shankaracharya
5. Alwars and Nayanars spread Bhakti movement in _________ .
A) Andhra Pradesh
B) West Bengal
C) Odisa
D) Tamilnadu
Answer:
D) Tamilnadu
6. Tukaram, Namdev, Samartha Ramadas belongs to _________ .
A) Assom
B) Punjab
C) Maharashtra
D) Kerala
Answer:
C) Maharashtra
7. Alwars were ______ saints
A) Sufi
B) Vaishnava
C) Saiva
D) All the above
Answer:
B) Vaishnava
8. Nayanars were ______ saints.
A) Saiva
B) Vaishnava
C) A & B both
D) None
Answer:
A) Saiva
9. Which of the following saint belongs North India?
A) Mira Bai
B) Shankardev
C) Basaveswara
D) Tukaram
Answer:
A) Mira Bai
10. Sankaracharya was born in ______ .
A) Perumbudur
B) Kaladi
C) Palani
D) Ooty
Answer:
B) Kaladi
11. Shankaracharva preached _______ .
A) Advaita
B) Dvaita
C) Visisthadvaita
D) Dvaita-Dvaita
Answer:
A) Advaita
12. Who established Shakthi Peethas?
A) Ramanuja
B) Madhwa
C) Shankaracharya
D) Basaveswara
Answer:
C) Shankaracharya

13. Shankaracharva attained nirvana at the age of ______ .
A) 12
B) 60
C) 32
D) 50
Answer:
C) 32
14. Ramanuiacharva was born in ______ .
A) Kaladi
B) Sri Perumbudur
C) Prayag
D) Chittor
Answer:
B) Sri Perumbudur
15. Ramanuja preached ______ .
A) Vishishtadwaita
B) Dwaita
C) Adwaita
D) All the above
Answer:
A) Vishishtadwaita
16. Madhwacharva promoted ______ philosophy.
A) Advaita
B) Dvaita
C) Vishishtadvaita
D) All the above
Answer:
B) Dvaita
17. He hailed from a Telugu family
A) Basaveswara
B) Ramananda
C) Vallabhacharya
D) Ramanuja
Answer:
C) Vallabhacharya
18. Who popularised the Veerasaivism?
A) Basaveswara
B) Ramananda
C) Molla
D) Shankaracharya
Answer:
A) Basaveswara
19. Basaveswara’s famous quote was
A) God is one
B) All men are equal. There is no caste or sub-caste
C) Unity of god
D) All the above
Answer:
B) All men are equal. There is no caste or sub-caste
20. Ramananda was born at
A) Kaladi
B) Prayag
C) Sri Perumbudur
D) Odisa
Answer:
B) Prayag

21. Kabir was brought up by a Muslim weaver named
A) Niru
B) Guru
C) Siru
D) None
Answer:
A) Niru
22. Kabir became a disciple of
A) Ramanuja
B) Ramanand
C) Adi Shankara
D) Vallabhacharya
Answer:
B) Ramanand
23. Sant Ravidas lived at
A) Banares
B) Prayag
C) Chittod
D) Kaladi
Answer:
A) Banares
24. Mira Bai became a devotee of
A) Sri Krishna
B) Rama
C) Hanuma
D) All the above
Answer:
A) Sri Krishna
25. Guru Nanak was born at
A) Lahore
B) Talwandi
C) Prayag
D) Banares
Answer:
B) Talwandi
26. Guru Nanak followers were known as :
A) Buddhists
B) Jains
C) Sikhs
D) Sufis
Answer:
C) Sikhs
27. Namdev was a devotee of
A) Nanak
B) Kabir
C) Ramanuja
D) Vithoba of Pandharpur
Answer:
D) Vithoba of Pandharpur
28. Jnaneswar used ______ to convey his thoughts.
A) Sanskrit
B) Marathi
C) Hindi
D) Telugu
Answer:
B) Marathi
29. Molla wrote Ramayana in ______ language.
A) Telugu
B) Sanskrit
C) Hindi
D) Marathi
Answer:
A) Telugu

30. ______ was a great Sufi saint of India.
A) Khwaja-Pir-Mohammad
B) Nizam-Ud-Din-Auliya
C) Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti
D) Shaikh Niamat Ullah
Answer:
C) Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti
II. Intext – Bits – Fill in the Blanks
1. Bhakti means …………….. devotion to a particular deity.
2. Saguna bhakti means …………….. .
3. Nirguna Bhakti means …………….. .
4. Bhakti movement was started by …………….. .
5. Basaveswara isfrom …………….. .
6. Ramananda is from …………….. .
7. Guru Nanak Dev isfrom …………….. .
8. Shankaradev is from …………….. .
9. Shankaracharya became a saint at the age of …………….. .
10. Shankaracharya was considered the greatest reformer of …………….. .
11. Ramanujacharya was a philosopher and …………….. .
12. Ramanujacharya was born in …………….. year.
13. Ramanujacharya wrote a commentary on the Brahma Sutras popularly known as …………….. .
14. Madhwacharya was born on the west coast of …………….. .
15. Vallabhacharya idealogy is known as …………….. .
16. Vallabhas teachings are also known as …………….. .
17. Basaveswara literary works are named …………….. .
18. The credit forthe spread of N/aishnava religion in Northern India goes to …………….. .
19. Ramananda adopted …………….. to spread his teachings.
20. Kabir advocated …………….. .
21. Sant Ravidas cardial quote was …………….. .
22. …………….. was another important woman saint of the medieval times.
23. Chaitanya Mahaprabhu is also known as …………….. .
24. Shankara deva is the saint of …………….. .
25. Guru Nanak was born in …………….. year.
26. Namdev was born in a …………….. family.
27. Jnaneswar wrote his commentary on the Bhagawadgita called …………….. .
28. Molla is also called …………….. .
29. Tallapaka Annamacharya is popularly known as …………….. .
30. Annamayya is known as ……………..
31. The sufi movement was a …………….. movement fn Islam.
32. The word Sufi is derived from an Arabic word …………….. .
33. Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti was born in …………….. .
34. Moinuddin Chishti Dargah is located at …………….. in India.
35. Farid-ud-din Ganj-i-Shakar is known as …………….. .
36. ‘Saf means …………….. .
Answer:
- a path of loving
- Worshipping God with form
- Worshipping God without form
- Adi Shankaracharya
- Karnataka
- North India
- Talwandi near Lahore
- Assom
- 5
- Sanatana Dharma
- Social reformer
- 1017CE
- Sri Bhasya
- Karnataka
- Suddhadvaita
- Pushlimarga or the Path of Grace
- Vachanas
- Ramananda
- Hindi
- All are equal before God
- Hari is in all and all in Hari
- Mira Bai
- Sri Gauranga
- Assam
- 1469 AD
- Tailor
- Bhagavat Deepika
- Mollamamba
- Annamayya
- Padakavitha Pithamaha
- Socio-religious
- Sal
- 1143 AD
- Ajmer in Rajasthan
- Baba Farid
- Purity/clean
III. Match the following
1.
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Sankaracharya |
A) Visishtadvaita |
| 2. Ramanujacharya |
B) Pushtimarga |
| 3. Madhwacharya |
C) All men are equal |
| 4. Vallabhacharya |
D) Dvaita |
| 5. Basaveswara |
E) Advaita |
Answer:
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Sankaracharya |
E) Advaita |
| 2. Ramanujacharya |
A) Visishtadvaita |
| 3. Madhwacharya |
D) Dvaita |
| 4. Vallabhacharya |
B) Pushtimarga |
| 5. Basaveswara |
C) All men are equal |
2.
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Mira Bai |
A) Sankeerthanas |
| 2. Molla |
B) Fraternity of men |
| 3. Annamayya |
C) Sri Krishna |
| 4. Guru Nanak |
D) Telugu |
Answer:
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Mira Bai |
C) Sri Krishna |
| 2. Molla |
D) Telugu |
| 3. Annamayya |
A) Sankeerthanas |
| 4. Guru Nanak |
B) Fraternity of men |
3.
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Namdev |
A) Sufi saint |
| 2. Jnaneswar |
B) Seistan in Persia |
| 3. Moinuddin Chishti |
C) Bhagavat Deepika |
| 4. Baba Farid |
D) Vithoba of Pandharpur |
Answer:
| Group-A |
Group-B |
| 1. Namdev |
D) Vithoba of Pandharpur |
| 2. Jnaneswar |
C) Bhagavat Deepika |
| 3. Moinuddin Chishti |
B) Seistan in Persia |
| 4. Baba Farid |
A) Sufi saint |
Do You Know?
7th Class Social Textbook Page No. 18
The two types of bhakti are Saguna Bhakti and Nirguna Bhakti. Saguna Bhakti means worshipping God with form, Nirguna Bhakti means worshipping God without form.
7th Class Social Textbook Page No. 20
The Brahma Suthras is a Sanskrit text. Attributed to the sages Badarayana or Vyasa. It is also known as Vedanta Sutra.

7th Class Social Textbook Page No. 24
Moinuddin Chishti Dargah is located at Ajmer. Rajasthan in India. The shrine has the grave of the revered saint, Moinuddin Chishti.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()