These AP 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions 15th Lesson National Liberation Movements in the Colonies will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Social 15th Lesson Important Questions and Answers National Liberation Movements in the Colonies
10th Class Social 15th Lesson National Liberation Movements in the Colonies 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by “Pan Africanism”?
Answer:
- Pan Africanism is an idea that promotes the unity of all African peoples irrespective of country or tribe.
- One key person in this regard was Kwame Nkrumah.
Question 2.
Write down the ill effects of reckless oil extraction in Nigeria.
Answer:
- Environment got polluted.
- The Mangrove forests have been destroyed.
- Crops have been destroyed through contamination of ground water and soils.
- Local fish production was declined.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention any two reasons for not establishing sustainable Democracy in Nigeria.
Answer:
- Civil War
- Military Rule
- Support of Multi-National Oil Corporations
Question 4.
Why was the Civil war started in Nigeria?
Answer:
The Civil war was started in Nigeria because a just and democratic balance could not happen. Soon Civil war started in Nigeria. The corruption of rulers and Multi-National Oil Corporations suppressed human rights in Nigeria.
Question 5.
Why did America interfere into the Vietnam war?
Answer:
America interfered into Vietnam war because it was worried that communists would become powerful in Vietnam.
Question 6.
What were the twin tasks of Nigerian nationalists?
Answer:
The twin tasks of Nigerian nationalists were:
- Fighting the British
- Unifying the diverse and conflicting ethnic group of Nigeria.
Question 7.
Why did US intervene in the Vietnam War?
Answer:
With the help of the Ho Chi Minh government in the north, the NLF fought for the unification
of the country. The US watched this alliance with fear. Worried about communists gaining power, it decided to intervene decisively, sending in troops and arms.
(OR)
To arrest the spread of Communism from Vietnam, US intervene in the Vietnam war.
Question 8.
How did the oil extraction affect agriculture in Nigeria?
Answer:
Spills destroy crops and aqua culture through contamination of the ground water and soils.
![]()
Question 9.
Oil spillage from oil wells in Nigeria had several impacts on its ecosystem. Write any two such impacts.
Answer:
- Large tracts of the mangrove forests, which are especially susceptible to oil have been destroyed.
- Spills destroy crops and aquaculture through contamination of the groundwater and soils.
- Drinking water is also frequently contaminated, and a sheen of oil is visible in many local bodies of water. (any two)
Question 10.
Who was Ken Saro Wiwa?
Answer:
Ken Saro Wiwa was an eminent human rights activist and environmentalist and was executed by the military government despite international protests.
Question 11.
Who is regarded as the founder of Modern China?
Answer:
Sun Yat-sen is regarded as the founder of modern China.
Question 12.
When was a republic established in China?
Answer:
The Manchu empire was overthrown and a republic was established in 1911 under Sun Yat-sen who is regarded as the founder of modern China.
Question 13.
Who ruled China at the turn of the 20th century?
Answer:
The emperors of the Manchu dynasty ruled China at the turn of the 20th century.
Question 14.
What was the programme of Sun-Yat-sen?
Answer:
The programme of Sun Yat-sen was called the three principles – (San min chui)
San means – nationalism
Min means – democracy
Chui means – socialism
Question 15.
Who were called warlords?
Answer:
Regional military powers of China were called warlords. China came to be controlled by them.
![]()
Question 16.
What happened on 4th May 1919 in China?
Answer:
On 4th May 1919, an angry demonstration was held in Beijing to protest against the decisions of the Versailles peace conference.
Question 17.
What was called the May Fourth Movement?
Answer:
Despite being an ally of the victorious side led by Britain, China did not get back the territories seized from it by Japan. The pro-test became a movement, called the “May- Fourth Movement”.
Question 18.
What emerged as major forces striving to unite China and bring stability?
Answer:
The Guomindang and the Chinese Commu¬nist Party emerged as major forces striving to unite the country and bring stability.
Question 19.
Where was the social base of Guomindang?
Answer:
The Guomindang’s social base was in urban areas.
Question 20.
When was Peking University established?
Answer:
Peking University was established in 1902.
Question 21.
What were the four virtues that the women had to cultivate?
Answer:
Chastity, appearance, speech, and work.
Question 22.
What was the practice of foot-binding?
Answer:
Foot-binding was a cruel practice of not allowing women to have fully grown feet.
Question 23.
Who invaded China in 1937?
Answer:
Japan invaded China in 1937.
Question 24.
When had the CCP (Chinese Communist Party) been founded?
Answer:
The CCP had been founded in 1921, soon after the Russian Revolution.
![]()
Question 25.
Why did Lenin go on to establish the Comintern?
Answer:
Lenin went on to establish the Comintern in March 1918 to help bring about a world government that would end exploitation.
Question 26.
Who emerged as a major CCP leader?
Answer:
Mao Zedong.
Question 27.
Where can Mao Zedong’s radical approach be seen?
Answer:
Mao Zedong’s radical approach can be seen in Jiangxi, in the mountains, where they camped from 1928 to 1934, secure from Guomindang attacks.
Question 28.
What was the three-fold strategy of the French?
Answer:
- Improving irrigation network.
- Encouraging landlords and
- Facilitating the marketing of agricultural produce.
Question 29.
Who was called ‘colons’?
Answer:
The French citizens living in Vietnam were called colons.
Question 30.
Who established Vietnam Cong San Dang (the Vietnamese Communist Party)?
Answer:
Ho Chi Minh established Vietnam Cong San Dang.
![]()
Question 31.
Who took power in North and South Vietnam?
Answer:
Ho Chi Minh and the communists took power in the north.
An old emperor took power in the south who was soon ousted by Ngo Dinh Diem.
Question 32.
How was the new era of land reforms after 1954 in North Vietnam?
Answer:
- After 1954 a new era of land reforms was started in North Vietnam.
- The land of the landlords was confiscated and distributed among the land-hungry landless peasants and poor peasants.
Question 33.
What is Agent Orange and why is it so-called?
Answer:
Agent Orange is a defoliant plant killer, so-called because it was stored in drums marked with an orange band.
Question 34.
Name some chemical weapons used by the US.
Answer:
- Napalm
- Agent Orange and
- Phosphorous Bombs
Question 35.
Explain the formation of Nigeria.
Answer:
The country we know as Nigeria today was actually created by the British by bringing together distinct regions inhabited by different tribal groups around the Niger river system.
Question 36.
How is the region of river Niger?
Answer:
The region of river Niger is one of the most populous countries of Africa, which has been suffering from different kinds of colonial rule.
Question 37.
Expand NNDP.
Answer:
The Nigerian National Democratic Party.
![]()
Question 38.
Expand A.G.
Answer:
Action Group.
Question 39.
When did Nigeria become independent?
Answer:
Nigeria became independent on 1st October, 1963.
Question 40.
When did Nigerians elect a democratic government?
Answer:
Nigerians elected a democratic government in 1999.
Question 41.
When was oil discovered in the Niger Delta?
Answer:
Oil was discovered in 1950s in the Niger Delta.
10th Class Social 15th Lesson National Liberation Movements in the Colonies 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write about the May Fourth movement in China.
Answer:
- On 4th May 1919, an angry demonstration was held in Beijing to protest against the decisions of the Versailles peace conference.
- Despite being an ally of the victorious side led by Britain, China did not get back the territories seized from it by Japan.
- The protest became a movement, called the “May Fourth Movement”.
- The revolutionaries called for driving out of foreigners, who were controlling the country’s resources, to remove inequalities and reduce poverty.
![]()
Question 2.
Study the map given below and answer the question that follows.
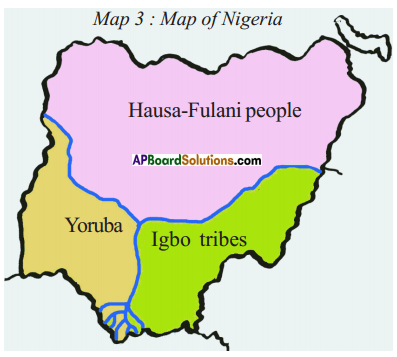 How were the British able to implement their ‘divide and rule’ policy in Nigeria?
How were the British able to implement their ‘divide and rule’ policy in Nigeria?
Answer:
- There are three major tribal groups in Nigeria.
- Hausa-Fulani,
- Yoruba,
- Igbo.
- The British were able to implement the divide and rule policy in Nigeria by encouraging competition and conflict among these three groups.
Question 3.
How did the education system in Vietnam contribute to the emergence of nationalist ideas?
Answer:
- In Vietnam, teachers and students did not blindly follow the curriculum given by the French.
- While teaching, Vietnamese teachers quietly modified the text and criticized what was stated.
- The students were inspired by patriotic feelings.
- The primary objective of the students who went to Japan for modern education was to drive out the French from Vietnam.
Question 4.
Why does the oil spillage from oil wells have a major impact on the ecosystem?
(OR)
What are the environmental problems faced by independent Nigeria?
Answer:
- Oil spillage from oil wells has a major impact on the ecosystem.
- Large tracts of the mangrove forests, which are especially susceptible to oil have been destroyed.
- Spills destroy crops and aquaculture through contamination of the groundwater and soils.
- Drinking water is also frequently contaminated, and a sheen of oil is visible in many local bodies of water.
- Offshore spills, which are usually much greater in scale, contaminate coastal environments and cause a decline in local fish production.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the impact of over-extraction of oil in Nigeria?
Answer:
Destruction of mangrove forests destroyal of :
- Ecosystem
- Crops
- Agriculture
- Soil
- Water contamination
- The decline in fish production
- Cause for cancer
Question 6.
Explain the ‘Pan Africanism’.
(OR)
What do you know about Pan Africanism?
Answer:
- Pan Africanism is an idea that promotes the unity of all African peoples irrespective of country or tribe.
- One key person in this regard was Kwame Nkrumah.
Question 7.
Observe the below map and answer the following questions.
1. Which country colonized Nigeria?
Answer:
The country of Nigeria was colonized by the British.
2. South-eastern Nigeria was dominated by which tribe?
Answer:
The South-Eastern part of Nigeria is dominated by Igbo tribes.
Question 8.
How can you appreciate the role of teachers in the Emergence of Vietnamese Nationalism?
Answer:
I appreciate the teachers by the following reasons.
- Blindly they did not follow the curriculum given by the French.
- Teachers quietly modified the text and criticized what was stated.
Question 9.
Based on the chart given below answer the question.
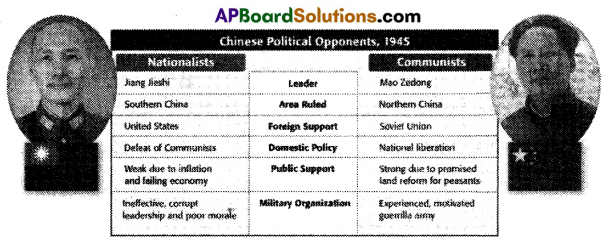 Which aspect of the Communist approach do you think led to Mao’s victory? Explain.
Which aspect of the Communist approach do you think led to Mao’s victory? Explain.
Answer:
Strong due to promised land reform for peasants.
The above aspect introduces equality among all and distributes the lands to landless poor confiscated from rich landlords.
With this programme majority of people enjoy their own lands and lived happily without pressure.
![]()
Question 10.
What do you know about Chiang Kai-shek?
Answer:
After the death of Sun, Chiang Kai-shek emerged as the leader of the Guomindang as he launched a military campaign to control the ‘warlords’, regional leaders who had usurped authority and to eliminate the communists. He sought to militarise the nation. The people, he said, must develop a ‘habit and instinct for unified behavior’.
Question 11.
What were the evil practices against women in China?
Answer:
- Practice of foot-binding.
- The subordination of women and
- Equality in marriage
- Four virtues:
- Chastity,
- Appearance,
- Speech and
- Work and
- Length of hemlines were also prescribed
Question 12.
What were the two crises faced by rural China?
Answer:
Rural China faced two crises:
- Ecological, with soil exhaustion deforestation and floods and
- A socio-economic one caused by exploitative land-tenure systems, indebtedness, primitive technology and poor communications.
Question 13.
What was the massive effort to spread literacy?
Answer:
A massive effort for setting up adult peasant schools to spread literacy and political education was undertaken along with the land reforms. This was also accompanied by the setting up of primary schools for both young children and adults in all the villages.
Question 14.
Why did the standard of living for the peasant’s decline in Vietnam?
Answer:
The colonial economy in Vietnam was primarily based on rice cultivation and rubber plantations owned by the French and few Vietnamese elites. Bonded labour was widely used in the rubber plantations. The French did little to industrialize the economy. In the rural areas landlordism, spread and large landlords took over the lands of small peasants and made them work as tenant farmers. As a result, the standard of living for the peasants declined.
![]()
Question 15.
What were the conditions of the peasants in Vietnam who rented the land of landlords?
Answer:
The peasants who rented the land of landlords had to pay rent in both share of produce and also by working on the fields and homes of the landlords and also pay different kinds of taxes imposed at will by the landlords. This forced them to borrow rice and money from the landlords and push them further into debt bondage.
Question 16.
Why did the Vietnamese students go to Japan in early 20th century?
Answer:
In early 20th century, Vietnamese students went to Japan to acquire modern education. For many of them, the primary objective was to drive out the French from Vietnam, overthrow the puppet emperor and re-establish the Nguyen dynasty that had been deposed by the French.
Question 17.
What was the impact of the Great Depression of the 1930s?
Answer:
The Great Depression of the 1930s had a profound impact on Vietnam. The prices of rubber and rice fell, leading to rising rural debts, unemployment, and rural uprising. The French put these uprisings down with great severity, even using planes to bomb demonstrators.
Question 18.
What were the challenges faced by the New Republic of Vietnam?
Answer:
The new republic faced a number of challenges. The French tried to regain control by using the emperor, Bao Dai, as their puppet. Faced with the French offensive, the Vietminh were forced to retreat to the hills. After eight years of fighting, the French were defeated in 1954 at Dien Bien Phu and over 16000 French soldiers and officers were taken, prisoners.
Question 19.
Write about China at the turn of the 20th century.
Answer:
At the turn of the 20th century, China was ruled by emperors of the Manchu dynasty, which had become powerless to defend the interests of China vis a vis the western colonial powers. These powers had carved out their ‘spheres of influence’ in different parts of China and had forced the emperors to give them economic and political concessions like low import taxes, immunity from Chinese laws, maintaining armed forces, etc. Both the common people and administrators of the empire were unhappy with this state of affairs. There were several revolts by the people and attempts at reform by the administrators.
![]()
Question 20.
Why did the Guomindang fail?
Answer:
- The Guomindang, despite its attempts to unite the country, failed because of its narrow social base and limited political vision.
- A major plank in Sun Yat-sen’s programme – regulating capital and equalizing land was never carried out because the party ignored the peasantry and the rising social inequalities.
- It sought to impose military order rather than address the problems faced by the people.
Question 21.
‘Mao was unlike other leaders’ – Why?
Answer:
- Mao stressed the need for an independent government and army.
- He had become aware of women’s problems and supported the emergence of rural women’s associations.
- He promulgated a new marriage law that forbade arranged marriages, stopped purchase or sale of marriage contracts and simplified divorce. So Mao was unlike other leaders.
Question 22.
Write about the Peoples Republic of China government.
Answer:
- The Peoples Republic of China government was established in 1949.
- It was based on the principles of the ‘New Democracy’, an alliance of all social classes opposed to landlordism and imperialism.
- Critical areas of the economy were put under government control.
- Once in power the CCP carried out large-scale land reform measures which meant taking away the land of landlords and distributing them among poor peasants.
- The new government also managed to enact laws to protect women, their rights and the abolition of polygamy.
- This enabled women to assume new roles and enjoy equal status vis a vis men in various
fields.
Question 23.
Read the paragraph and answer the following question.
The Great Depression of the 1930s had a profound impact on Vietnam. The prices of rubber and rice fell, leading to rising rural debts, unemployment and rural uprising. The French put these uprisings down with great severity, even using planes to bomb demonstrators.
Why did the fall in price of rice lead to the rise of rural indebtedness?
Answer:
- Two-thirds of the rice production in Vietnam is exported.
- By that time it was the third-largest exporter of rice in the world.
- Great depression of 1929-30 has a great negative impact on Vietnam.
- The prices of Rice and Rubber has fallen drastically and there is rise in rural indebtedness.
10th Class Social 15th Lesson National Liberation Movements in the Colonies 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the reforms implemented after the formation of democracy in China?
Answer:
- The Peoples Republic of China was based on the principles of the ‘New Democracy’, an alliance of all social classes opposed to landlordism and imperialism.
- Critical areas of the economy were put under government control.
- They carried out large scale and reform measures.
- They took away the land of landlords and distributed among poor peasants.
- The new government also managed to enact laws to protect women, their rights and abolition of polygamy.
- This enabled women to assume new roles and enjoy equal status vis a vis men in various fields.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the role of schooling played in Vietnam national movements.
(OR)
Explain the role of education in the national movement by taking Vietnam as an example.
Answer:
- The teachers did not blindly follow the curriculum given by the French.
- While teaching, Vietnamese teachers quietly modified the text and criticised what was stated.
- Students fought against the colonial government’s efforts to prevent the Vietnamese from qualifying for white-collar jobs.
- They were inspired by patriotic feelings and the conviction that it was the duty of the educated to fight for the benefit of society.
Question 3.
Explain the policies followed by the French in Vietnam.
Answer:
- French colonial rule influenced all aspects of Vietnamese life.
- The French were keen to develop Vietnam as an exporter of rice.
- They improved irrigation net work by building canals.
- They encouraged landlords and facilitated marketing of agricultural produce.
- The French did little to industrialise the economy.
- Vietnamese peasants became entrenched in a cycle of debt.
- There was no access for all to get good education.
- All the higher education was in French only.
Question 4.
How were the Land reforms implemented in China?
Answer:
Land reforms of China.
- Land reforms were launched in 1950-51.
- The major steps involved were,
- Identification of all village inhabitants.
- Confiscation of all village lands and redistribution of land lord’s land and other productive property.
![]()
Question 5.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
Racism became common in the British colonial empire in late 19th and early 20th centuries. Educated Africans were excluded from the civil service, and there was discrimination against African entrepreneurs. At the same time, the authorities from ruling country gave control to the tribal chiefs and elite and promoted them.
Answer:
The given paragraph is about Racial Discrimination between the Black and the White people. It is related to Africa. One more point is that tribal chiefs were given control and the government promoted them.
Nigeria is an African country. It was a colony of the British. The British created Nigeria by bringing together different regions around the Niger river system where people of different tribes lived.
Before bringing all together, they faced many problems. Hausa-Fulani, Igbo and Yoruba tribes were there. Due to long years of missionary activity, many people still practice tribal religious beliefs.
The British implemented their divide and rule policy. A section of the people were educated and developed. If all the people were united in Nigeria, then the British would face the problem. The British always wanted to divide the Vietnamese based on colour or religious practices. That Was what the Britishers followed in India to divide Indians. All the Indians came together and fought against the British. Then the Britishers encouraged the Muslims to form a separate party for Muslims. They emphasised that Indian National Congress was the party of Brahmins and of upper caste. Gradually Hindus and Muslims were separated and so the national movement was weakened.
Now all the Independent countries should give equal opportunities to all and equality is to be maintained. There will be no racial discrimination at any level.
Question 6.
“America was very cruel in the Vietnam war” – Comment.
Answer:
- America behaves very wild manner on Vietnam.
- America with the fear of Communism to stop the spread of Communism in Vietnam, it declared war on Vietnam.
- It uses chemical bombs and weapons like Agent Orange – B 52s. and Napalm.
- Agent Orange destroyed plants & trees and made the land barren for a long time.
- Phosphorous bombs – destroyed many villages and decimated jungles.
- Civilians died in large numbers.
- Thousands of troops were used by America.
- Due to cruelty of America, America got agitation from world wide and from their mother land also.
- Finally, America made a peace settlement and withdrawn from the war.
Question 7.
Answer the questions with the help of the given information.
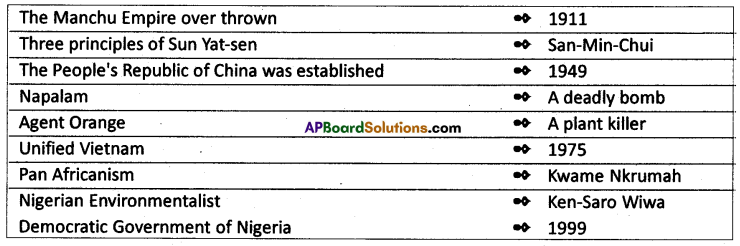 a) Which nation was ruled by the Manchu Dynasty?
a) Which nation was ruled by the Manchu Dynasty?
Answer:
China was ruled by the Manchu dynasty.
b) Who is considered as the ‘founder of modern China’?
Answer:
Sun-Yat-Sen was regarded as the founder of modern China.
c) Who was an eminent Human Rights activist and environmentalist of Nigeria?
Answer:
Ken – Saro- Wiwa was an eminent Human Rights activist and environmentalist of Nigeria.
d) What is meant by the Pan Africanism?
Answer:
- Pan Africanism is an idea which promotes the unity of all African peoples irrespective of country or tribe.
- One key person in this regard was Kwame Nkrumah.
![]()
Question 8.
Read the given paragraph and write your Opinion.
The coastal environment of Nigeria has been disturbed because of reckless oil extraction by foreign oil companies. Oil spillage from oil wells has a major impact on the ecosystem.
Answer:
The given paragraph emphasises that the coastal environment of Nigeria has been disturbed because the oil companies extracted more than their share. It is talking about the consequences of over spillage of oil.
Over spillage of oil has various negative consequences:
Oil spillage from oil wells has a major impact on the ecosystem. Large areas of the mangrove forests, which are especially susceptible to oil, have been destroyed. This is mainly because oil is stored in the soil and re-released annually. Around 5-10% of Nigerian mangrove ecosystems have been destroyed either by clearing or oil. Spills destroy crops and aqua culture through contamination of the groundwater and soil. Drinking water is also frequently contaminated, and sheen of oil is visible in many local bodies of water. Even if there is no immediate health effect of this water contamination, it can cause cancer in the long term. Offshore spills, which are usually much bigger in scale, contaminate the coastal environments and cause a decline in the local fish production.
If the same is continued the whole world be affected. Oil is a natural resource. So natural resources are to be saved.
Question 9.
“The United States approach in Vietnamese’s struggle was brutal.” Do you agree with this statement? Why? Why not?
Answer:
“Yes, I agree with this statement. Because:
- Until 1950’s Vietnamese were under the control of French.
- And in some years it was under control of Japan.
- People were suffered with high rents and taxes.
- They did not get proper food also.
- Ho-Chi-Minh’s idea land distribution in North Vietnam provide something to them and they lived happily.
- So the North Vietnam peasants fulfilled their long cherished dream.
- At the same manner South Vietnam people also wished that reforms introduced in that area and established Communism and get happy life.
Conclusion: But America brutally declare war on them to fulfill its desire.
Question 10.
Read the following paragraph given below and answer the questions.
Agent Orange: The Deadly Poison
Agent Orange is a defoliant, a plant killer, so called because it was stored in drums marked with an orange band. Between 1961 and 1971, some 11 million gallons of this chemical was sprayed from cargo planes by US forces. Their plan was to destroy forests and fields, so that it would be easier to kill if there was no jungle cover for people to hide in. Over 14 percent of the country’s farmland was affected by this poison. Its effect has been staggering, continuing to affect people till today. Dioxin, an element of Agent Orange, is known to cause cancer and brain damage in children and according to a study, is also the cause of the high incidence of deformities found in the sprayed areas.
The tonnage of bombs, including chemical arms, used during US intervention (mostly against civilian targets) in Vietnam exceeds that used throughout the Second World War.
a) What is Agent Orange ?
Answer:
Agent Orange is a defoliant, a plant killer.
b) How does Agent Orange affect the children?
Answer:
Agent Orange causes cancer, brain damage and deformities in children.
c) Why did they destroy forests and fields?
Answer:
That it would be easier to kill if there were no forests and fields cover for people to hide in.
d) Do you think America was justified in using chemical weapons and civilian population and forests?
Answer:
No, it was not justified.
![]()
Question 11.
What do you know about the administration of Chiang Kai-shek?
Answer:
- Chiang was a conservative and he encouraged women to cultivate the four virtues of ‘chastity,
appearance, speech and work’ and recognize their role as confined to the household. - He also tried to suppress the trade union movement to encourage factory owners.
- The Guomindang was failed because of its narrow social base and limited political vision.
- A major plank in Sun-Yat-sen’s programme – regulating capital and equalising land – was never carried out because the party ignored the peasantry and the rising social inequalities.
- It sought to impose military order rather than address the problems faced by the people.
Question 12.
How was the French education system in Vietnam?
Answer:
- The French colonisers like the British were convinced that the people of the colony were uncivilised and the objective of their rule was to bring the benefits of modern civilisation. Education was seen as one way to civilize the ‘natives’.
- The French needed an educated local labour force but they feared that education might create problems.
- Once educated, the Vietnamese may begin to question colonial domination.
- Even though Vietnamese language was taught in the primary level, all higher education was in French.
- Only the Vietnamese elite -comprising a small fraction of the population – could enroll in the schools and only a few among those admitted ultimately passed the school-leaving examination.
Question 13.
Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions.
The Manchu empire was overthrown and a republic established in 1911 under Sun Yat-sen (1866-1925) who is regarded as the founder of modern China. He came from a poor family and studied in missionary schools where he was introduced to democracy and Christianity. He studied medicine but was greatly concerned about the fate of China. He studied the problems of China and worked out a programme of action. His programme was called the Three Principles (San min chui). These were: “nationalism”- this meant overthrowing the Manchu who were seen as a foreign dynasty, as well as other foreign imperialists; “democracy” or establishing democratic government; and “socialism” regulating industries and land reforms to distribute land to the landless peasants. Even though the Manchu dynasty was overthrown and a republic was declared, the republican government led by Sun-Yat-sen could not consolidate itself. The country came to be controlled by regional military powers called “warlords”.
a) Why was Sun Yat-sen regarded as the founder of modern China?
Answer:
Because he established a republic in China by overthrowing the Manchu empire.
b) What were the Three Principles?
Answer:
San min chui (Nationalism, Democracy, Socialism)
c) What is meant by Nationalism here?
Answer:
Nationalism meant overthrowing the Manchu who were seen as foreign dynasty as well as other foreign imperialists.
d) What is meant by Socialism?
Answer:
Regulating industries and land reforms.
e) Who were war lords?
Answer:
The regional military powers were called warlords.
Question 14.
Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions.
Japan attacked and occupied much of China between 1937 and 1945. They tried to impose a barbaric colonial militaristic rule over China which had a disastrous impact on the Chinese society and economy. Both Guomindang and CCP now tried to join forces to fight Japanese occupation. After the surrender of Japan to the US in August 1945, Guomindang and CCP engaged with each other in an all out warfare for control over China. Eventually CCP was successful in establishing its rule over mainland China while Guomindang was forced to set up its government on the island of Taiwan.
a) How was the Japanese rule over China?
Answer:
It was a barbaric colonial militaristic rule.
b) Name the two political parties.
Answer:
Guomingdang and CCP.
c) To whom did Japan surrender?
Answer:
Japan surrendered to the US.
d) Which party was successful?
Answer:
The CCP was successful.
e) Which party established rule in Taiwan?
Answer:
The Guomindang.
![]()
Question 15.
Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions.
The French were keen to develop Vietnam as an exporter of rice and for this purpose they adopted a threefold strategy – improving irrigation network, encouraging landlords and facilitating marketing of agricultural produce like rice and rubber. The French began by building canals and draining lands fa the Mekong delta to increase cultivation. The vast system of irrigation works – canals and earthworks – built mainly with forced labour, increased rice production and allowed the export of rice to the international market. Vietnam exported two- thirds of its rice production and by 1931 had become the third largest exporter of rice in the world. This was followed by infrastructure projects (roads and railways) to help transport goods for trade, move military garrisons and control the entire region. Construction of a trans- Indo-China rail network that would link the northern and southern parts of Vietnam and China was begun.
a) Why were the French keen to develop Vietnam?
Answer:
Because it was an exporter of rice.
b) What was the other crop?
Answer:
Rubber plantations.
c) Which Delta was developed?
Answer:
The Mekong Delta was developed.
d) exported two-thirds of its rice production.
Answer:
Vietnam.
e) Who developed Vietnam?
Answer:
The French developed Vietnam.
Question 16.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
This phase of struggle with the US was brutal. Thousands of US troops arrived equipped with heavy weapons and tanks and backed by the most powerful bombers of the time – B52s. The wide spread attacks and use of chemical weapons – Napalm (a deadly bomb which caused intense damage to humans), Agent Orange (which destroyed plants and trees and made the land barren for a long time), and phosphorous bombs – destroyed many villages and decimated jungles. Civilians died in large numbers.
a) Which struggle was brutal?
Answer:
The struggle with the US was brutal.
b) What were B52s?
Answer:
B52s were powerful bombers.
c) What was “Napalm’?
Answer:
It was a chemical weapon.
d) Which was used on forest areas?
Answer:
Agent Orange was used on forest areas.
e) How were phosphorous bombs?
Answer:
They destroyed many villages and decimated jungles, civilians died in large numbers.
![]()
Question 17.
Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions.
Nigerian nationalism had the twin task of fighting the British and also welding the. very diverse and conflicting ethnic groups. The national movement was stronger in the more developed south rather than in the north and this created a north-south divide. Even in the south, nationalism was plagued by ethnic conflict between the Yoruba and the Igbos. By the 1950s these three regions also had their own anti-colonial movements led by regional parties: the conservative Northern People’s Congress (NPC) in the north; the National Council for Nigeria and the Cameroons (NCNC) in the east, and the Action Group (AG) in the west.
a) What were the two tasks?
Answer:
- Fighting the British
- Welding the very diverse and conflicting ethnic groups.
b) In which region was the national movement stronger?
Answer:
It was strong in south.
c) What were the two tribes?
Answer:
Yoruba and Igbos.
4) Expand NPC.
Answer:
Northern People’s Congress.
e) Expand AG.
Answer:
Action Group.
Question 18.
Read the passage and answer the following question.
The effect of the war was felt within the US as well. Many were critical of the government for getting involved in a war that they saw as indefensible.
How do you appreciate the role of the people of the USA in ending the war?
Answer:
- Vietnam was a small country.
- The USA was very brutal in the war.
- It used even chemical weapons.
- The effects of the war was felt within the US as well.
- When youth were drafted for the war, the anger spread.
- People opposed the war.
- They questioned the government’s policy.
- Finally the people were instrumental in ending the war.
- A peace settlement was signed in Paris in 1974.
![]()
Question 19.
Read the following text and interpret it.
Pan Africanism
Pan Africanism is an idea which promotes the unity of all African peoples irrespective of country or tribe. This unity was to be used not only to fight colonialism and racial discrimination, but also to build unity among tribes and communities inhabiting the continent based on principles of equality, social justice and human dignity. One key person in this regard was Kwame Nkrumah, a freedom^ghter from Ghana.
Answer:
- Africa was colonized by the European imperialistic powers and different tribes were residing in Africa.
- The European powers plundered the resources of Africa both the mineral and agricultural resources.
- Slave trade was also carried in this region.
- Pan Africanism promoted the idea of the unity of all the Africans.
- It helped them to fight against colonization and racial discrimination.
- Pan Africanism has a higher sphere and it breaks the limits of nationalism.
- It unites all the tribes living on the continent based on the principles of equality, social justice and human dignity.
Question 20.
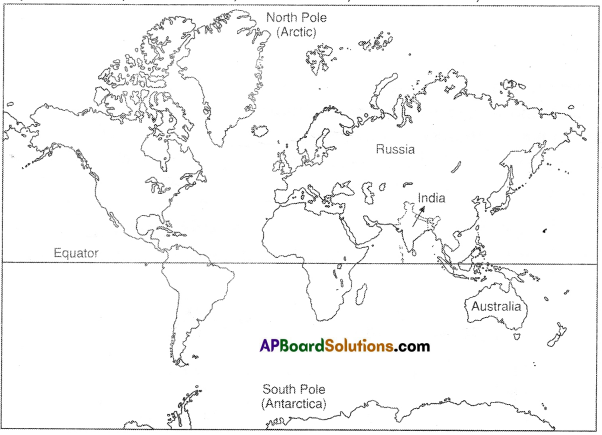
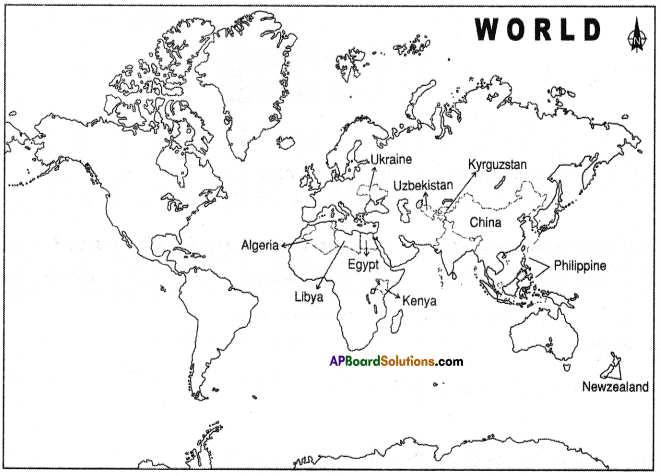
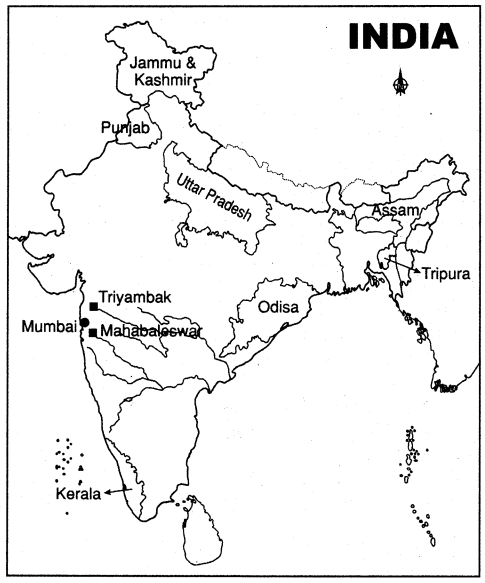
Locate the following on the outline map of the world.
- China
- USA
- Vietnam
- France
- Nigeria
- Russia
Answer:
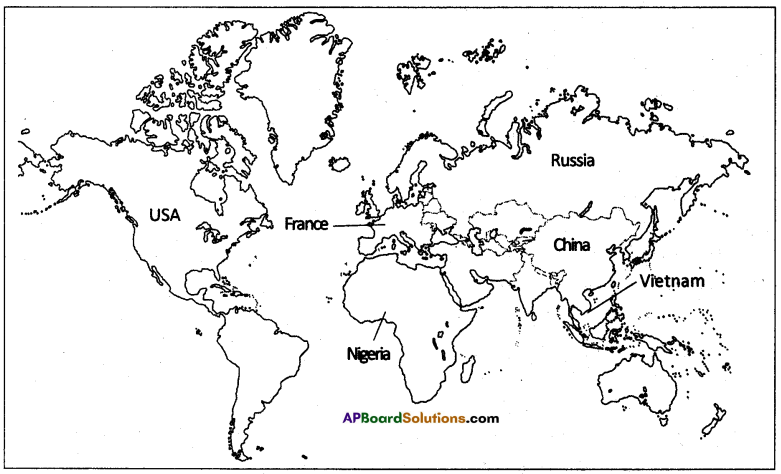
![]()
Question 21.
Locate the following in the given map of world.
1) The third largest exporter of rice in the world.
Answer: Vietnam
2) These country people were called colons.
Answer: France
3) Manchu dynasty rule this country.
Answer: China
4) Yoruba people are belongs to this country.
Answer: Nigeria
5) America used agent orange on this country.
Answer: Vietnam
6) Washington
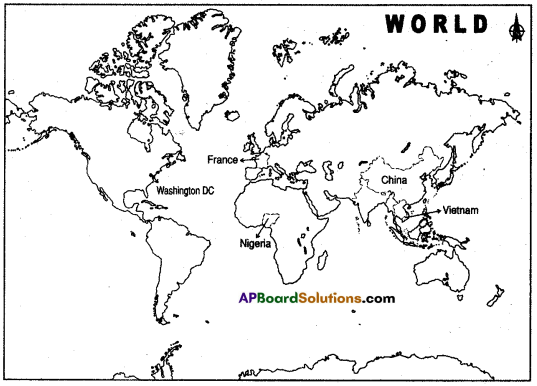
![]()





 Answer:
Answer:

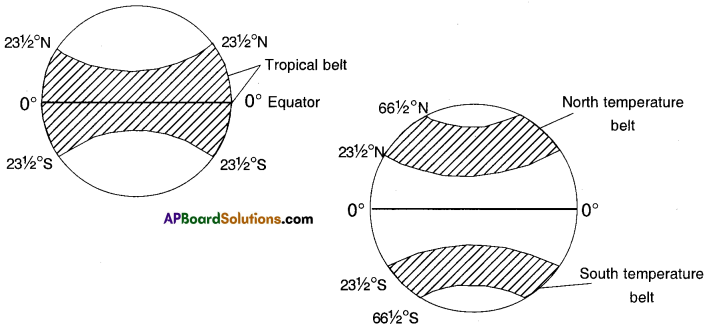
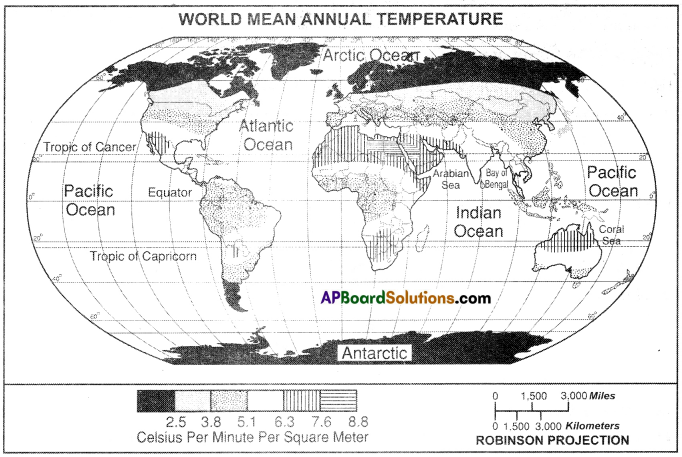 1. What is the line to south of equator?
1. What is the line to south of equator?
 Answer:
Answer: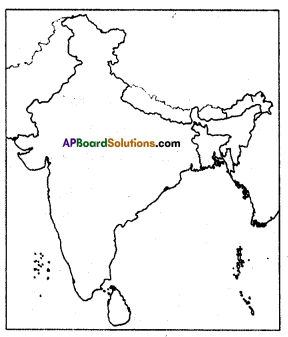
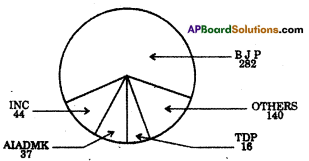
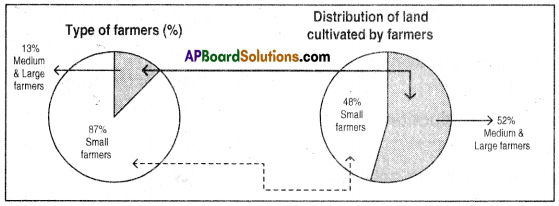
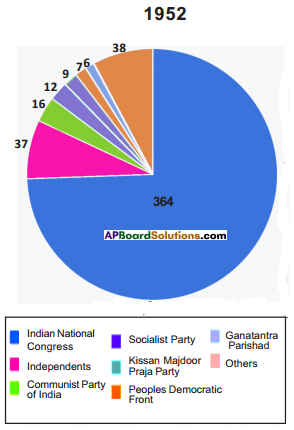 1. Which political party secured less seats ?
1. Which political party secured less seats ?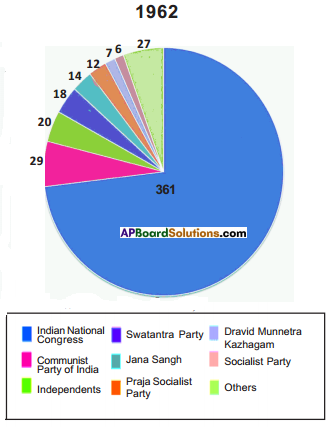
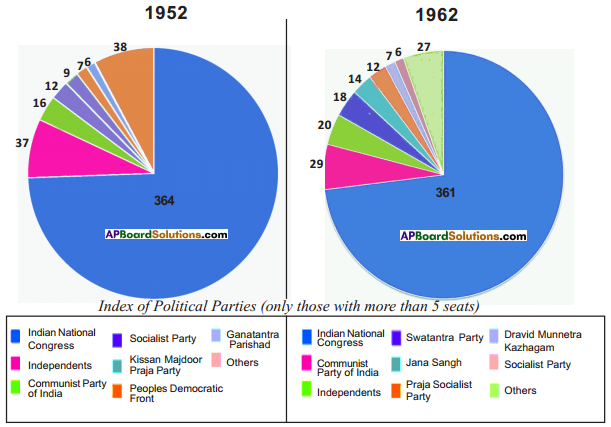 Compare the above Pie diagrams.
Compare the above Pie diagrams.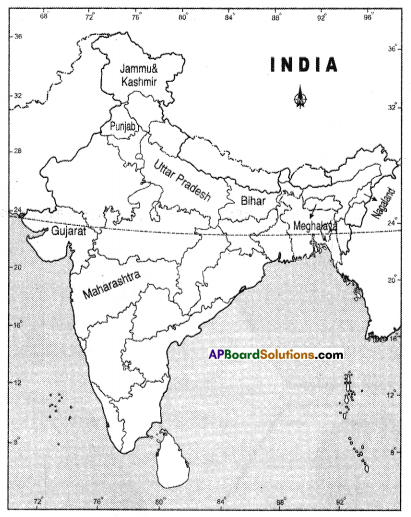


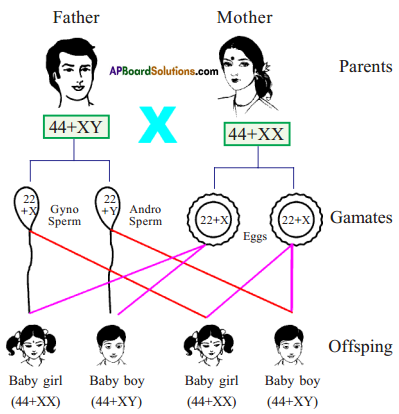
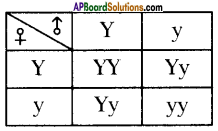
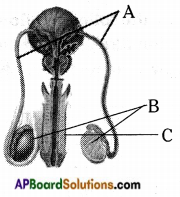
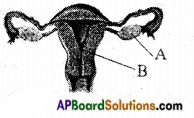
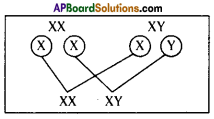 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?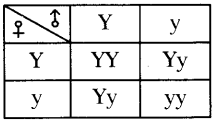 (OR)
(OR)

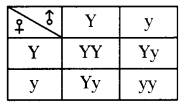
 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.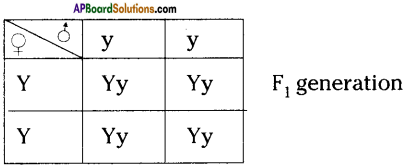 All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.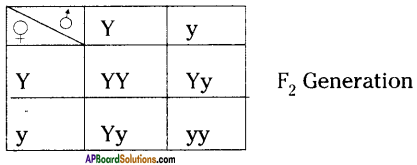 In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.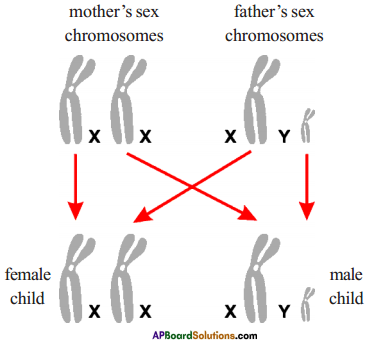 Answer:
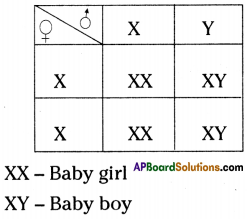
Answer: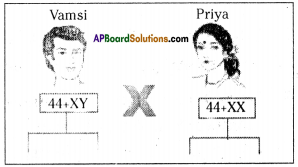 a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.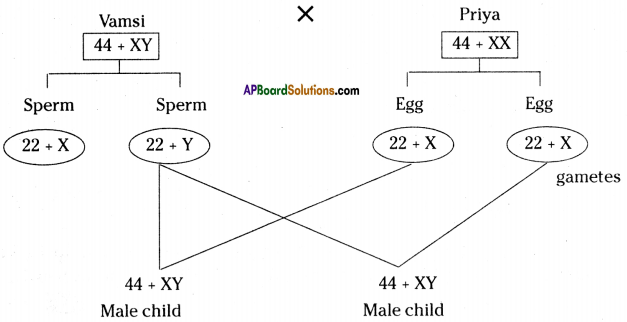 b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?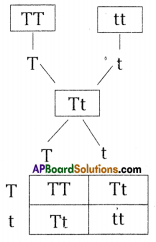 i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?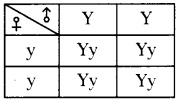


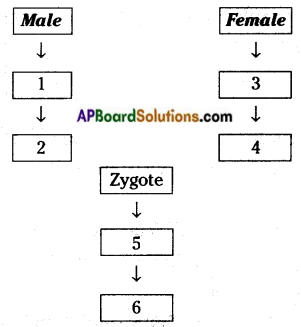
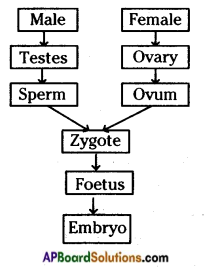
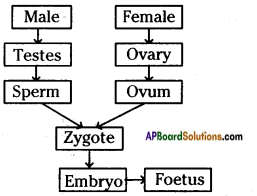


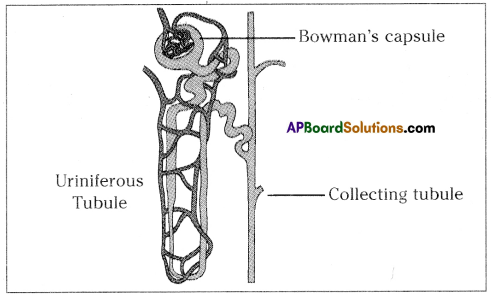
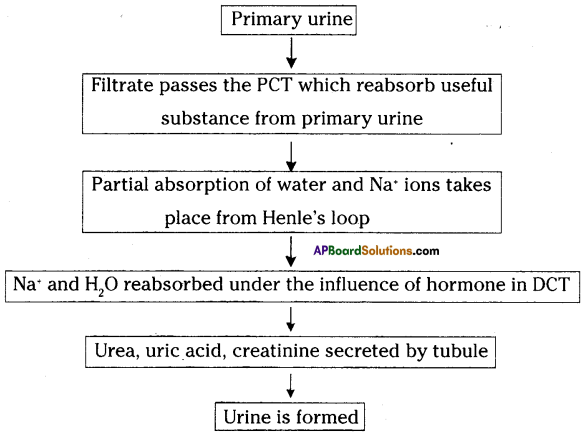
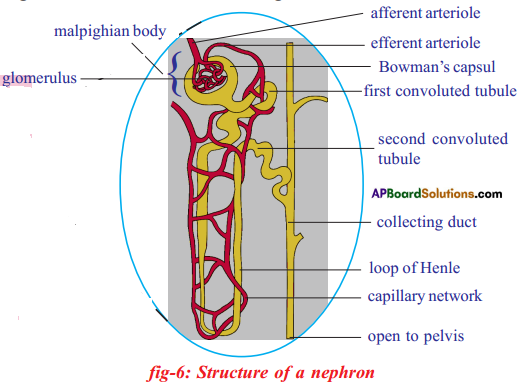
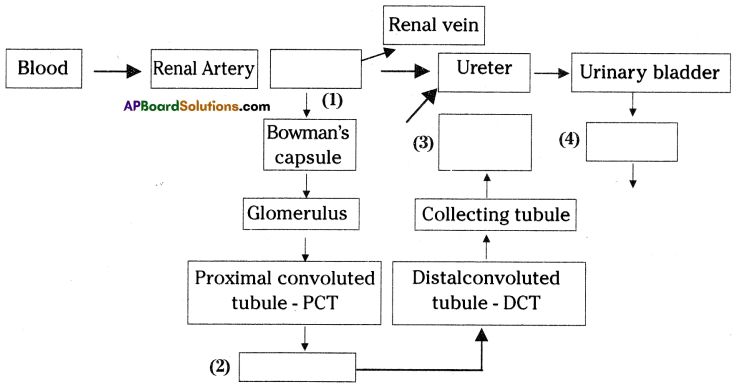
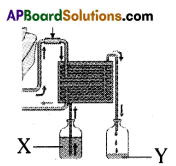 The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.
The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.