Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions 8th Lesson Applied Biology which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions 8th Lesson Applied Biology
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What factors constitute dairying?
Answer:
The factors of dairying are
- Breeding, feeding and management of milk animals.
- Production, processing and marketing of milk and milk products on economic basis.
Question 2.
Mention any two advantages of inbreeding.
Answer:
Advantages of inbreeding:
- Inbreeding increases homozygosity and helps to produce a pure line of animals.
- Helps in the accumulation of superior genes and elimination of undesirable genes.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between out-cross and cross-breed.
Answer:
- Outcross: It is mating of animals of same breed but having no common ancestor on either side of pedigree for 4-6-generation. The offspring of such a cross is outcross.
- Cross breed: In this method superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed. The offspring of such a mating is cross breed.
Question 4.
Define the terms layer and broiler. [TS MAY-22] [AP MAR-15,17]
Answer:
- Layers are birds which are exclusively raised for the production of eggs.
- Broilers are birds which are raised only for their meat. They are raised only upto 8 or 10 week and sent to market.
Question 5.
What is apiculture? [TS MAR-15, 17] [AP MAR-17,20]
Answer:
- Apiculture is Beekeeping.
- It is the maintenance of bee-hives for the production of honey and wax.
Question 6.
Distinguish between a drone and worker in a honey bee colony. [TS MAR-19]
Answer:
| Drone bee | Worker bee |
| 1) A drone is a male haploid honey bee. 2) Drone donot have stringers. 3) Drone’s life span is short. 4) Drone is bigger than worker bee but smaller than queen bee. 5) Its primary role is to mate with fertile queen. |
1) A worker bee is a sterile diploid female bee. 2) Worker bees have stringers. 3) They live for two to three months. 4) Worker bees are smaller than drones 5) They secrete wax, build hexagonal cells of hive, collect nectar, manufacture and store honey, gather pollen and make propolis. |
Question 7.
Define the term Fishery.
Answer:
Fishery: Fishery is an occupation (industry) for catching, processing, storing and selling of fish or shell fish or any other aquatic animals for human consumption.
Question 8.
Differentiate aquaculture and pisciculture. [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
| Aquaculture | Pisciculture |
| The culturing of fish and other aquatic organism (prawn, lobster, oysters etc.,) under regulated conditions for better production is called aquaculture. | The culturing and breeding of fin fish under regulated conditions is called pisciculture. |
Question 9.
Explain the term hypophysation. [AP MAR-16] [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
- Hypophysation (or) induced breeding is an artificial breeding.
- Pituitary extract or ovaprim is injected into brood fish which are induced for seed production.
Question 10.
List out any two Indian carps and two exotic carps. [TS MAR-17]
Answer:
- Indian carps: Catla catla and Labeo rohita
- Exotic carps: Grass carp and silver carp
Question 11.
Mention any four fish by-products. [TS MAY-22] [AP,TS MAR-19]
Answer:
Fish by-products:
- Shark liver and cod liver oil
- Omega 3 fatty acids in saldines and salmon.
- Fish guano – fertiliser from waste fish
- Isinglass – prepared from air bladder and used in the clarification of wines.
![]()
Question 12.
How many amino acids and polypeptide chains are present in insulin? [AP MAR-19]
Answer:
- 51 amino acids are present in insulin.
- 21 amino acids form polypeptide chair A
- 30 amino acids form polypeptide chain B
Question 13.
Define the term ‘vaccine’. [APMAR-16]
Answer:
- Vaccine: A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease.
Typically, a vaccine contains weakened or killed disease causing organisms.
Sometimes proteins of micro organisms are also used. - Ex: Sabin’s oral polio vaccine
Question 14.
Mention any two features of PCR.
Answer:
- PCR is Polymerase chain reaction that help early diagnosis of disease
- PCR helps to detect very low amounts of DNA by amplification.
- PCR is now used to detect HIV in suspected cases.
- PCR is used to detect mutations in suspected Cancer patients.
Question 15.
What does ADA stand for? Deficiency of ADA causes which disease?
Answer:
- ADA stands for Adenosine DeAminase.
This enzyme is very important for immunity system to function. - ADA deficiency causes severe combined immuno deficiency(SCID).
Question 16.
Define the term transgenic animal.
Answer:
- Transgenic animal: Transgenic animals are the animals that have their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extragene in addition their own genome.
- Ex: Emphysema can be treated by a-1 antitrypsin (human protein)
Question 17.
What is popularly called ‘Guardian Angel of Cell’s Genome’? [APMAR-20] [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
- P53 gene, a tumor suppressing gene is called Guardian Angel of cells Genome, because it guards the integrity of the DNA.
- It stops the cell cycle at ‘G1 check point’ and helps repair the damaged DNA.
Question 18.
List out any four features of cancer cells.
Answer:
Features of cancer cells:
- Cancer cells actively grow and divide continuously.
- Cancer cells can easily detach themselves and migrate (metastasis) to new locations.
- Cancer cells lose the property of contact inhibition’
- Cancer cells do not undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death)
- Cancer cells attract blood vessels from their surrounding.
Question 19.
How do we obtain radiographs?
Answer:
- Photographs developed using X-rays are called radiographs or Skiagraphs.
- A beam of X-rays is projected on the body parts in concern. X-rays that pass through body parts are recorded on a photographic film. It is observed on a fluorescent screen.
- Dense bones absorb more radiation and appear more white. Soft parts allow the rays to pass through them and look greyish. Calcifications appear white and lungs appear black.
Question 20.
What is tomogram? [AP MAY-22]
Answer:
- Tomogram: It is a 3-D cross-sectional picture of the part of the body seen on CAT scan.
CAT scan is a medical imaging method using several beams of x-rays. - It is used to locate blood clots, tumors, fracture in the head, density of bones.
Question 21.
MRI scan is harmless-justify.
Answer:
- MRI Scan: MRI means Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
It uses magnetism, radio waves and computer to produce body images. - MRI does not use ionising radiation as used in X-rays.
So MRI scanning is a very safe procedure.
![]()
Question 22.
What is electocardiography and what arc the normal components of ECG? [AP MAR-15]
Answer:
- Electro cardiography(ECG) is a procedure for recording electrical changes in the heart.
- The normal components of ECC are:
(i) Waves (P,Q, R, S and T waves)
(ii) Intervals (P-R; Q-T; R-R intervals)
(iii) Segments (S-T segment) (iv) Complexes (QRS complex)
Question 23.
What docs prolonged P-R intervalindicate?
Answer:
- The normal P-R interval is 0.12 to 0.2 sec.
- Prolong P-R interval indicates delay in conduction of impulses from S.A node to A.V.Node.
Question 24.
Differentiate between primary and secondary antibodies.
Answer:
- Primary antibodies react with antigens of interest.
- Secondary antibodies react with primary antibodies.
Question 25.
Which substances in a sample are detected by direct and indirect ELISA respectively?
Answer:
- Direct ELISA Test is used to detect Antigens [AP MAY-22]
- Indirect ELISA Test is used to detect Antibodies.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the various methods employed in animal breeding to improve livestock?
Answer:
There are two methods of breeding. 1. Inbreeding 2. Outbreeding
1) Inbreeding: It is the crossing of animals of the same breed. Superior males and superior females of the same breed are selected and mated.
- A superior female is which produces more milk.
- A superior male is which gives rise to better offspring.
- The progeny are evaluated and the superior of them are used for mating.
Inbreeding is of two types:
a) Close breeding: It is the crossing male parent with its female offspring or crossing of female parent with its male offspring.
b) Line breeding (cousin muting): It is the crossing of closely related animals but not close as close breeding.
It leads to upgrade the desired commercial character.
2) Out breeding: It is crossing of unrelated animals. It is of three types
a) Out crossing: Mating of animals of same breed but have no common ancestor or either side for 4-6 generations. The offspring of such a mating is called out cross.
It is the best method to improve milk production and growth rate.
It often helps to out come inbreeding depression.
b) Cross breeding: It is a cross between superior male of one breed with superior female of another breed. The offspring of such a mating is a cross breed.
Ex: Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing ‘Bikaneri ewes’ with ‘Marino rams’.
c) Inter specific hybridisation: In this method the male and female belong to two different closely related species. The progeny may get the desired characters of both parents.
Ex: Mule is produced by crossing male donkey and female horse.
Hinny is produced by crossing female donkey and male horse.
Such offsprings are generally sterile. Mule has economic value.
![]()
Question 2.
Define the term ‘breed’. What are the objectives of animal breeding?
Answer:
1) Breed: A breed is a group of animals related by descent and similar in most characters like appearance, features, size etc., .
2) Objectives of Animal breeding: Animal breeding is an important aspect of animal husbandry. It aims at increasing the yield of animals. It also aims at improving desirable qualities of animals and their produce.
Objectives of breeding:
- To produce disease-resistant animals.
- To increase the quality and quantity of milk, meat, wool etc.,
- Improving the growth rate
- To enhance (prolong) productive life by improving livestock through gene manipulation.
- Early maturity
- Economy of feed.
Question 3.
Explain the role of animal husbandry in human welfare.
Answer:
- The human population is growing leaps and bounds. With traditional methods of farming and animal husbandry, it is difficult to meet the food needs of growing population.
- So, the application of biological principles will become crucial to increase the food production.
- Animal husbandry is the agricultural practice of breeding and raising live stock such as buffaloes, cows, pigs, horses, cattle, sheep, camels goats etc.,
- These animals and bees have been used by man for their products such as honey, silk, wax, meat, pork, hydes, wool etc.,
- It has become necessary to improve the live stock and also the quality and quantity of their produce.
- To meet the demand new breading methods like Multiple ovulation and embryo transfer methods and artificial insemination production of transgenic animals are developed.
- Poultry has been developed to such an extent. India stands thrid in egg production.
- Still there is much to be done in the field of animal husbandry to provide quality food products for the growing human population.
Question 4.
List, out the various steps involved in MOET.
Answer:
MOET: It is Multiple ovulation and Embryo transfer method. Generally at a time a cow can deliver one or two calves. But with this methods 6-8 embryos are formed at a time.
The procedure is as follows:
Step 1: A cow is injected with hormones like FSH activity.
Step 2: It induces follicular maturation and super ovulation. Instead of one egg the cow produces 6-8 eggs per cycle.
Step 3:The cow is either mated with an elite bull or artificially inseminated.
Step 4:The embryos at the stages 8-32 cells are recovered non surgically and transferred to surrogate mother (cows).
- The genetic mother is again ready for MOET. This technology is usefiill for cattle, sheep, rabbits, buffaloes etc.,
- High milk yielding breeds, high quality meat, yielding bulls are produced in this method and the herd size also increases in faster rate.
Question 5.
Write short notes on controlled breeding experiments.
Answer:
Controlled Breeding experiments: Sometimes normal breeding may not give desired result. Elite bulls may not be available.
In such cases two latest methods are used to improve live stock.
1) Artificial insemination (AI): It is a technique in which semen is collected from superior bulls and introduced into female reproductive tract when the female is in heat.
- The semen can be stored frozen and can be transferred to the place of need.
- The advantage of AI is it permits the dairy farmer to get desired quality of breed he wants.
- It improves genetic context of the cattle and can control Venereal diseases.
- He can use semen of different elite bulls and improve his herd of cattle.
- In India at SALON there is a breeding centre where top quality frozen semen of pure exotic bulls is available.
2) Multiple Ovulation and Embryo transfer (MOET): To increase the size of herd with good quality cattle MOET is used. The cow is injected with FSH like hormones to release more ova (6-8). The ova are fertilized by semen of superior bulls by artificial inseminated.
- The embryos at 8-32 cell stages are recovered non surgically and transferred surrogate cows.
- This technology is used to increase the herd size with good quality animals.
Question 6.
Explain the important components of poultry management
Answer:
Important Components of poultry management:
1) Selection of good breeds which are disease free and can thrive in any climate.
Hybrid layers used in India are BV-300, Hyline, Poona pearls etc.
The broilers used in India are Hubbard, Vencobb etc.
![]()
2) Feed management: Balanced diet is essential for maximum yield. The layers are fed with brooder mash, grower mash, prelayer and layer mash at different stages.
The broiler are fed with prestarter mash, starter mash and finish mash at different stages.
3) Health care management: Young birds are vaccinated against viral diseases Ranikhet, Marek and Gumboro. Antibioitcs are used for bacterial diseases fowl cholera, infectious coryza and chronic respiratory disease.
There must be continuous look out for fungal diseases like Brooder’s pneumonia, aflatoxicosis and Thrush.
4) Proper hygiene and safe farm conditions ensure better produce.
Question 7.
Discuss in brief about ‘Avian Flu’. [TS MAY-22] [AP MAR-20]
Answer:
1) Avina Flu: It is an important and dangerous viral disease affecting poultry birds and also man.
2) Causative Organism: Bird flue is caused by avian flue virus H5N1. It can start a world wide epidemic (pandemic disease).
3) Mode of lnfection: Simply by touching contaminated surfaces. Infected birds release the virus through saliva and faeces for about 10 days.
4) Symptoms:Humans infected by H5N1 show typical flu like symptoms, dry cough with phlegm diarrhoea, breathing difficulty, fever, headache sore throat and body pains.
5) Prevention:
- Consumption of undercooked chicken to be avoided.
- Poultry people use protective clothes and wear masks.
- Complete culling (elimination) of infected birds either by burning or burying.
Question 8.
Explain in brief about queen bee.
Answer:
Queen Bee: Queen bee is the only fertile female of the colony.
- She is the largest bee of the colony.
- Her business is only to produce eggs.
- She is diploid, fertile female.
- She lives about for five years.
- She takes only one nuptial flight and receives sperms from a drone.
- She stores the sperms in spermathecae and utilizes them through out life.
- She fertilizes some eggs with sperms which turnout to be worker sterile female.
- She releases few eggs and doesnot fertilize them.
- The unfertilized eggs develop parthenogenetically into males, (arrhenotoky).
- So males are haploid.
- The larvae are fed by royal jelly for 4 days and later with bee bread.
- Only one larva which destines to become queen is fed by royal jelly continuously until metamorphosis.
Question 9.
Honeybees are economically important-justify. [TS MAY -22] [AP MAR-16]
Answer:
Economic Importance of Honey bees:
Honey bees produce honey, beeswax, propolis, venom. They are best pollinators.
- Honey: It is a rich source of fructose, glucose, vitamins, minerals and water.
- Bee’s wax is used in the preparation of cosmetics, polishes and candles.
- Propolis is used in the treatment of wounds and bums.
- Bees’ venom is used in treatment of arthritis.
- Bees’ are the pollinators of our crop plants such as sunflower, Brassica, apple and pear. In view of the above aspects, we claim that Honey bees are economically important insects.
Question 10.
What are the various factors required for bee keeping.
Answer:
Factors required for successful Bee-keeping:
- Knowledge of different types of honey bees, their nature and habits.
- Selection of a suitable location for keeping beehives.
- The first colony is small with the queen and small group of workers.
- Management of hives in different seasons.
- Knowledge of handling and collection of honey and bees wax.
![]()
Question 11.
Fisheries have carved a niche in Indian economy-explain.
Answer:
Economic Importance of Fishes:
1) Fish meat is easily digestible protein. It is a good source of proteins, vitamins A and D, mineral and iodine. Fishes have good export value.
2) By Products:
- Shark and cod liver oils have vitamins A&D. They contain Omega 3 fatty acid (sardine and salmon) fish oil is used soap industry and also as lubricant.
- Fish guano: Fertilizer is prepared from scrap fish.
- Shagreen is the dried skin of shark used to polish furniture.
- Isinglass is a gelatinous substance used in clarification of wines. Isinglass is prepared from air bladders.
Pisciculture, prawn culture, crabs, oysters earn foreign exchange from exports.
Thus fisheries have carved a niche in the Indian economy.
Question 12.
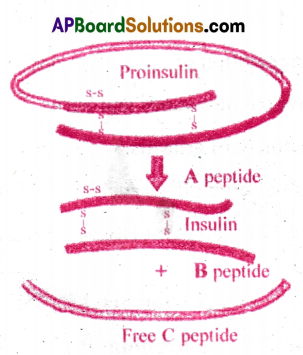
Explain in brief structure of Insulin. [APMAR-15]
Answer:
Structure of Insulin:
- Insulin is a protein hormone secreted by P cells of pancreas.
- Human insulin is made up of 51 amino acids in two polypeptide chains.
- ‘A’ chain consists 21 amino acids and ‘B’ chain consists of 30 amino acids.
- The two chains are held together by disulphide linkages.
- Insulin is primarily synthesized as a prohormone which contains an extra stretch called ‘C peptide’.
Question 13.
Define vaccine and discuss about types of vaccines.
Answer:
Vaccines: Vaccine is a biological preparation which improves immunity to a particular disease. The term ‘Vaccine’ was coined by Edward Jenner.
The vaccine may contain weekend or killed organisms or toxins or proteins of disease-causing microorganisms.
Following are biotechnologically produced vaccines.
1) Attenuated whole agent vaccines: It contains disabled or weekend live micro organisms. Mostly they are antiviral. Eg: Vaccines against yellow fever, measles, rubella, mumps and bacterial diseases like typhoid.
2) Inactivated whole agent vaccines: They contain killed whole microbes. Eg: Influenza, Cholera, Bubbonic plague, polio, hepatitis A, rabies and sabin’s polio vaccine. At present SABIN’s oral polio is popular.
3) Toxoids: They contains exotoxins of certain microbes. Eg: Diphteria and Tetanus vaccines . The vaccine is injected into the body. The body immune system reacts and produces antibodies. The memory cells remember the antigen.
Whenever the microbes enter the body in their virulent form, the body immediately kill them with the help of antibodies. The vaccines prepare the body immunity to fight against disease successfully. .
Question 14.
Write in brief the types of genetherapy.
Answer:
Genetherapy is the insertion of genes into cells and tissue to treat a disease. The gene therapy is in an incipient stage and its operation is much complicated.
Basic Technique: A normal gene is introduced into the genome to supplement (counter) the abnormal gene. The vector transfers the therapeutic gene into the target cell.
a) Germlinc gene therapy: In this type of gene therapy, functional genes are introduced into sperm or ovum and integrated into the DNA (genome). This change is heritable. But it is not easy as said. This therapy is still in ’infant stage’.
b) Somatic line therapy: in this type the normal gene is inserted to somatic cell of the patient. The change that takes place is temporary and not heritable. The insertion of gene may takes place either outside the body (ex-vivo) or inside the body (in-vivo). The first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4 year girl in 1990 to treat Adenosine de amenase deficiency (ADA).
This deficiency cause serious combined immuno deficiency (SCID).
The deficiency may be cured by bone marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy. In either case it is not a complete cure.
![]()
Genetically modified DNA can be inserted into a cell by transfection or by gene guns. Synthetic oligodeoxy nucleosides are used to inactivate the disease causing genes (silencing the genes).
Question 15.
List out any four salient features of cancer cells.
Answer:
Cancer is a syndrome characterized by uncontrolled, unrestricted, purposeless cell division due to failure of cell cycle regulation.
The salient feature of Cancer cells
1) Lack of contact inhibition: Normal cells stop cell division and cell mobility when they are in close contact. This is called ‘contact inhibition’. Cancer cells lack this property hence they continue to grow and divide.
2) Lack of cadherins: Cadherins are absent in Cancer cells. Hence they can detach and cause metastasis.
3) Immortalisation: If the DNA is damaged in normal cells, they can repair the damage in time. If they fail to repair the damaged DNA they undergo programmed cell death called apoptosis. But cancer cells do not undergo apoptosis.
4) Angiogenesis: In a fast-growing cancer tumor, in order to get more 02 and nutrients, tumors attract more blood vessels from their surrounding matrix. This is called angiogenesis.
Question 16.
Explain the different types of cancers. [TS MAR-15, 17]
Answer:
Based on the origin, cancers are classified as follows:
- Carcinoma: Cancer of epithelial tissue or cells. It is the most common type of cancer.
- Sarcoma: Cancer of connective tissue.
- Leukemia: A liquid tumor. It is the cancer of bone marrow resulting in unrestricted production ofW.B.C [Leukemia-white blood]
- Lymphoma: Cancer of the Lymphatic system
- Familial cancer: Cancers that are inherited from parents or grandparents.
- Sporadic cancer: Cancers that occur without any family history.
Question 17.
Write about the procedure involved in MRI.
Answer:
MRI: MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
- It is a diagnostic radiology technique. MRI does not use ionizing radiation as in X-rays.
- It is a very safe procedure.
- It produces detailed pictures of organs, soft tissues, bones and any other structure of the body.
- MRI scanner is a giant circular magnetic tube.
- The patient is placed on a movable bed that moves into the magnetic ring.
- Human body is mainly composed water which contains protons.
- The magnet creates a strong magnetic field. Body protons align with the direction of magnetic field. A second radio frequency electromagnetic field turned on for a brief period.
- The protons of different parts of body release different energy, which can be detected by MRI scanners.
- Accordingly there is a contrast between images of different tissue based on their water content.
- The information received is processed by a computer and an image is generated.
- The images are transferred to a photographic film.
- Sometimes radio contrast agents like gadolinium are used to increase accuracy.
Question 18.
Write briefly about different waves and intervals in an ECG.
[AP MAR-19] [TS MAY-17]
Answer:
E.C.G: ECG stands for electrocardiograph.lt records electrical changes in the heart.
12 Sensors are placed at 12 places and the leads are connected to ECG machine.
I) Waves:
- P-Wave: It represents atrial systole.
Its duration is 0.1 sec.
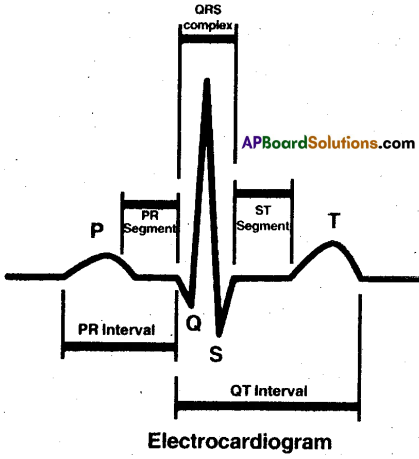
- QRS complex wave: It represents ventricular systole. Its duration is 0.08 to 0.1 sec.
Q wave is a small negative wave R wave is a tall positive wave S wave is a small negative wave. - T- wave: It is a positive wave.
Its duration is 0.2 sec.
![]()
II) Intervals: Electrocardiogram
- P-R interval: It is the time between onset of P wave and onset of Q wave.
Its duration is 0.12 to 0.2 sec. - Q-T interval: It is the interval between onset of Q wave and the end of T wave.
It depends on heart rate. Its duration is 0.4 sec.
If the heart beat is faster then the interval is shorter. - R-R interval: It is the duration of one cardiac cycle. Its duration is 0.8 sec.
Question 19.
Discuss briefly the process of indirect ELISA. [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a fundamental tool of clinical immunology. Indirect ELISA is done to detect antibodies in the serum of the patient.
HIV test is an indirect ELISA.
Protocol:
- It is used to detect anti HIV antibodies.
- A known antigen (Ex: HIV antigen) is added to the ‘well’
- Patients antiserum is added
- Antibodies in the patient’s antiserum are bind to the antigen coated on the surface of the ‘well’
- Enzyme linked anti human immune serum globulins (ant HISGs) are added. They bind to antibodies that are already linked to antigens.
- Enzyme’s substrate is added and the reaction produces a visible colour which is measured by spectrophotometer.
- ELISA cannot be used as confirmation test for HIV. It can be false positive and false negative under certain circumstances.
Question 20.
Write short note on EEC. [AP MAY-22]
Answer:
1) EEC: It is Electro Encephalography.
- It records the electrical activity of the brain. Leads are placed all over the scalp and connected to EEG machine.
- EEG is used to diagnose epilepsy coma, brain death and sleep disorders.
2) Wave: The waves recorded in EEG consists of
- Synchronized waves common in normal healthy people and
- Desynchronized waves relating to certain neurological conditions.
They are ALPHA, BETA, THETA AND DELTA waves.
3) Alpha waves: They are rhythmical 8-13 cycles/sec. They are seen in drowsy people with closed eyes.
4) Beta waves: They are at high frequency of 13-40 cycles/sec. Their amplitude is low. The patient is mentally very active and tense.
5) Delta waves: The frequency is very low 3 cycles/sec. They have high amplitude. They are common in early childhood in awaken condition. In adults they occur in deep sleep.
If there is brain tumor, epilepsy and mental depression they occur in awaken adults.
6) Theta waves: The frequency 4 to 7 cycles/sec. They are common irt children less than 5 years of age. They are found in adult during emotional stress.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write in detail about out breeding.
Answer:
Outbreeding:
- Since times unknown man has been domesticating animal and conducting experiments in breeding animals to meet his requirements.
- Inbreeding and out breeding are two methods of breeding.
- Inbreeding sometimes-express harmful recessive alleles.
- The animals are subjected to inbreeding depression.
- To overcome these drawbacks of inbreeding man has started out breeding methods which proved to be successful.
- Out breeding is breeding of unrelated animals it is of three types.
a) Outcrossing
b) Cross Breeding
c) Inter specific hybridisation.
![]()
a) Out Crossing:
- In this type of breeding the animal are selected from the same breed but there was no common ancestors in either line for 4-6 generations.
- The offspring of such a mating is called outcross. It is the best method of breeding for low milk-yielding animals and for animals having low growth rate.
- Some times a single out cross helps to over come inbreeding depression.
b) Cross Breeding:
- In this type of breeding, super males of one breed is crossed with super females of another breed.
- The offspring of such a mating is called cross breed.
- The desirable characters of the two breeds appear in cross breed.
- The cross breeds are used for commercial production and to develop stable breeds which are superior to the existing breeds. Eg: Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams in Punjab.
c) Interspecific Hybridisation:
- In this type of breeding the male and female animal belong to two different related species.
- The offspring gets desirable characters of both the parents but they will be sterile.
Eg: A male donkey (Jackass) is crossed with female horse (mare). The offspring is called mule. - Mule is tenaceous hard worker especially used to carry people and luggage in ghat roads and mountains.
- Similarly when a male horse is mated with a female donkey the offspring hinny is produced. Hinny is also sterile. It is not as popular as mule.
Question 2.
Explain in detail clinical inferences from ECG.
Answer:
1) ECC and Clinical Inferences:
- ECG means Electrocardiogram or Electrocardiograph.
- Electrocardiography is a procedure to record the electrical changes that take place in the heart.
- The ECG contains series of waves. Complexes and intervals.
- 12 sensors (leads) are placed around the chest and at various location where there is superficial artery.
- The leads are connected the ECG machine.
Waves, intervals and clinical inferences:
2) P Wave: It represents atrial systole i.e., the electral impulse passing through atrial wall.
- Its normal duration is 0.1 sec.
- Clinical Inference: Enlarged p wave indicates enlarged atria..
3) QRS Complex: It represents ventricular systole.
Q Wave: It is a small negative wave.
R Wave: It is a tall positive wave.
S wave: It is a negative wave.
The normal duration of QRS complex waves in about 0.08 to 00.1 sec.
Clinical Inference: Variations in duration of amplitudes indicate disorders like bundle branch block.
4) T wave: It is a positive wave. It represents ventricular repolarisation (diastole).
Its duration is 0.2 sec.
Clinical Inference: Tall T wave indicates hyperkalemia (High potassium levels, daingerous). Small, flat or inverted wave indicates hypokalemia (very low potassium levels in blood also dangerous) may lead sudden cardiac arrest.
5) PR Interval: It is the interval between onset of P wave and one set of Q wave.
Its normal duration is 0.12 to 0.2 sec.
Clinical Inference: Prolonged PR interval indicates delay in conduction of impulse from SA node to AV node. It means the heartbeat is slow. It is called Brady cardia.
If the PR interval is short it indicates fast beating heart. It is called tachycardia.
6) QT Interval: It is the interval between the on set of Q wave and the end of T wave. It represents electrical activity in ventricular muscle.
QT interval is dependent on the heart rate. The faster the heart rate the shorter the interval.
Its normal duration is 0.4 sec.
Clinical Inference: Prolonged QT interval indicates myocardial infarction and hypothyroidism. Myocardial infarction is heart attack. Hypothyroidism is less thyroxin in blood. Short QT interval indicates hypercalcemia (having more Ca in blood.)
7) ST Segment: It is the time between end of S wave and onset of T wave. It is the Zero I voltage period.
Clinical Inference: Elevated ST segment also indicates myocardial infarction.
Thus ECG indicates the abnormal function of heart if any.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Average annual milk yield per cow in India is about
1. 160 liters
2. 170 liters
3. 150 liters
4. 100 liters
Answer:
2. 170 liters
Question 2.
Birds raised only for their meat are called
1. Layers
2. Broilers
3. Chickens
4. Fowls
Answer:
2. Broilers
Question 3.
Chemically insulin is a
1. Protein
2. Carbohydrate
3. Fat
4. None
Answer:
1. Protein
Question 4.
DNA amplification is done by
1. Molecular assay
2. genetic assay
3. Nuclear assay
4. PCR technology
Answer:
4. PCR technology
Question 5.
ECG records
1. Volume changes of heart
2. Structural changes of heart
3. Magnetic changes of heart
4. Electrical changes of the heart
Answer:
4. Electrical changes of the heart
Question 6.
Fish meat is the rich source of
1. Chlorine
2. Fluorine
3. Bromine
4. Iodine
Answer:
4. Iodine
Question 7.
Gene therapy allows
1. Amplification of gene defect diagnosed in a child
2. Replication of gene defect diagnosed in a child
3. Multiplication of gene defect diagnosed in a child
4. Correction of gene defect diagnosed in a child
Answer:
4. Correction of gene defect diagnosed in a child
Question 8.
HIV in suspected cases can be detected by
1. PCR
2. Blood test
3. MAB
4. Hybridoma
Answer:
1. PCR
![]()
Question 9.
Inbreeding contributes to
1. Homozygosity
2. Hterozygosity
3. Homoline
4. Heterosis
Answer:
1. Homozygosity
Question 10.
The first transgenic cow is
1. Rosie
2. Dolly
3. Rosette
4. Dolloid
Answer:
1. Rosie
Question 11.
Commercial silk is obtained from
1. Cocoon/pupa
2. Caterpiller
3. Adult moth
4. Both egg and adult moth
Answer:
1. Cocoon/pupa
Question 12.
In poultry, the disease coryza is caused by
1. Bacteria
2. Protozoan
3. Virus
4. Fungi
Answer:
1. Bacteria
Question 13.
Costliest type of bulls in India is
1. Ongole
2. Amul
3. Murrah
4. Shahli
Answer:
1. Ongole
Question 14.
In dairy farming, the milk yield depends parimarily on the
1. Quality of feed
2. Quality of breeds
3. Quality of fodder
4. Management of fodder
Answer:
2. Quality of breeds
Question 15.
The largest egg production state in India is
1. Uttar Pradesh
2. Andhra Pradesh
3. Punjab
4. Haryana
Answer:
2. Andhra Pradesh
Question 16.
Father of modern poultry in India is
1. Dr. B.V.Rao
2. Dr.M.Swaminathan
3. Dr.Kurian
4. Dr. S.V.Rao
Answer:
1. Dr. B.V.Rao
Question 17.
In poultry, broilers are fed with
1. broodermash, chick mash, grower mash
2. Prestarter mash, starter mash, finish mash
3. Brooder mash, chick mash, starter mash
4. Pre starter mash, brooder mash
Answer:
2. Prestarter mash, starter mash, finish mash
![]()
Question 18.
Protein efficiency ratio of egg is
1. 1.7
2. 4.5
3. 2.2
4. 3.2
Answer:
2. 4.5
Question 19.
The other name for bee keeping is
1. Apiculture
2. Sericulture
3. Comb culture
4. Aquaculture
Answer:
1. Apiculture
Question 20.
In a bee colony, workers are
1. Fertile femals
2. Diploid males
3. Sterile males
4. Sterile females
Answer:
4. Sterile females
Question 21.
The life span of the queen been of bee colony is
1. one day
2. one year
3. five days
4. five years
Answer:
4. five years
Question 22.
In honey bee colony, the short lived bees are
1. Queen
2. Worker bees
3. Drones
4. Diploid female
Answer:
3. Drones
Question 23.
Honey bees those having poisonous stings are
1. Male
2. Queen
3. Worker
4. Both queen and worker
Answer:
3. Worker
Question 24.
The capture of fishes from the sea is known as
1. Marine fishery
2. Fresh water fishery
3. Inland fishery
4. Shell fishery
Answer:
1. Marine fishery
![]()
Question 25.
Culture fishery is referred to as
1. Aquaculture
2. Aquaphomics
3. Aquatics
4. Aquatide
Answer:
1. Aquaculture
Question 26.
Shark and cod liver oils are good source of
1. Vitamin A and E
2. Vitamin A and D
3. Vitamin B and E
4. Vitamin A and B
Answer:
2. Vitamin A and D
Question 27.
The omega 3 fatty acids of fish oil will reduce
1. Vitamins
2. Cholesterol
3. Minerals
4. Hormones
Answer:
2. Cholesterol
Question 28.
Human insulin is brand named as
1. Instalin
2. Humulin
3. Periling
4. Hypilin
Answer:
2. Humulin
Question 29.
Human insulin is madeup of
1. 52 amino acids
2. 51 amino acids
3. 50 amino acids
4. 61 amino acids
Answer:
2. 51 amino acids
Question 30.
Number of amino acids in chain A of insulin is
1. 21
2. 30
3. 20
4. 31
Answer:
1. 21
Question 31.
The most common adjuvants used during vaccination are
1. Calcium adjuvants
2. Aluminium Adjuvants
3. Chloride Adjuvants
4. Megnesium Adjuvants
Answer:
2. Aluminium Adjuvants
Question 32.
Small Pox was eradicated by
1. Intensive sensitization programme
2. Intensive antibody issue programme
3. Intensive vaccination programme
4. Intensive health check up programme
Answer:
3. Intensive vaccination programme
![]()
Question 33.
Oral polio vaccine is an example of
1. Attenuated whole agent vaccine
2. Inactivated whole agent vaccine
3. Toxiods
4. Toxicoids
Answer:
2. Inactivated whole agent vaccine
Question 34.
Toxoid refers to
1. Inactivated exotoxins of microbes
2. Inactivated Endotoxins of microbes
3. Whole protein of activated microbe
4. Whole DNA of activated microbe
Answer:
1. Inactivated exotoxins of microbes
Question 35.
Technique used in early diagnosis of diseases is
1. PCR technology
2. DNA technology
3. PCR and DNA technology
4. X-ray method
Answer:
1. PCR technology
Question 36.
The insertion of genes into an individual’s cells and tissues to treat a disease is called
1. Gene technique
2. Gene modification
3. Gene therapy
4. gene manipulation
Answer:
3. Gene therapy
Question 37.
ADA deficiency causes
1. SCID
2. SICD
3. SIID
4. SCCD
Answer:
1. SCID
Question 38.
First clinical gene therapy is on
1. ADA deficiency
2. ABB deficiency
3. AAD deficiency
4. DAD deficiency
Answer:
1. ADA deficiency
Question 39.
α-1 antitrypsin is used to treat
1. Metasema
2. Polysema
3. Emplysema
4. Colysema
Answer:
3. Emplysema
![]()
Question 40.
The leading killer disease in the world is
1. AIDS
2. Cancer
3. TB
4. Jaundice
Answer:
2. Cancer
Question 41.
In Cancer, an abnormal proliferation of cells is called
1. Neoblast
2. Neuroblast
3. Epiblast
4. Neoplasia
Answer:
4. Neoplasia
Question 42.
Cancers are caused chiefly due to failure of
1. cell division
2. nuclear reorganization
3. cell cycle regulation
4. cell metabolism
Answer:
3. cell cycle regulation
Question 43.
Carcinogenic rays are
1. X-rays
2. Infra red rays
3. Infra blue rays
4. Ultra-yellow rays
Answer:
1. X-rays
Question 44.
Cancers of bone marrow are
1. Leukemia
2. Sarcoma
3. Carcinoma
4. Lymphoma
Answer:
1. Leukemia
Question 45.
The types of stem cells found in mammals are
1. Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells
2. Foetus stem cells, Umbilical stem cells
3. Bone marrow stem cells, spleen stem cells
4. Skin stem cells, Liver stem cells
Answer:
1. Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells
![]()
Question 46.
Embryonic stem cells are
1. Mono potent
2. Pleuri potent
3. Uni potent
4. Morula
Answer:
2. Pleuri potent
Question 47.
Adult stem cells are otherwise referred to as
1. Reproductive stem cells
2. Somatic stem cells
3. Embryonic stem cells
4. Totipotent stem cells
Answer:
2. Somatic stem cells
Question 48.
X-rays film provide
1. Mono axial representation
2. 2D representation
3. 3D representation
4. HD representation
Answer:
2. 2D representation
Question 49.
CAT means
1. Computerized Axial Tomography
2. Computerized Anatomical tomography
3. Central Axid Tomography
4. Centre Appendicle Tomography
Answer:
1. Computerized Axial Tomography
Question 50.
MRI means
1. Morphological Resonance Image
2. Metastatic Resonance Image
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
4. Multiple Radiographic Imaging
Answer:
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Question 51.
In an ECti, normal duration of T waves
1. 0.1 sec
2. 0.2 sec
3. 0.08 sec
4. 0-0 sec
Answer:
2. 0.2 sec
Question 52.
EEC studies are useful in analyzing
1. Insomnia
2. Bradycardia
3. Trachycardia
4. Myocardial infraction
Answer:
1. Insomnia
![]()
Question 53.
In EEG, Delta waves frequency is
1. 4 and 7 cycles per second
2. 13-40 cycles per second
3. 8-13 cycles per second
4. Less than 3 cycles per second
Answer:
4. Less than 3 cycles per second
Question 54.
ELISA is a method used mainly to detect the presence of specific
1. Antibodies or antigens
2. Immunity or inheritance
3. Heredity or variation
4. Autoimmunity or antibodies
Answer:
1. Antibodies or antigens
Question 55.
Which of the following increases yield & improves quality of milk
1. Selection of good breeds having high yielding potential
2. Disease resistance breeds
3. Proper housing with Adequate water, ventilation, suitable temperature
4. All the above
Answer:
4. All the above
Question 56.
When a jackass (male donkey) is crossed with a mare (female horse), it leads to the production of
1. A fertile mule
2. A sterile hinny
3. A sterile mule
4. A sterile colt
Answer:
3. A sterile mule
Question 57.
The progenitors that are formed in bone marrow and differentiated else where, are
1. Pre-NK cells
2. Pre-Erythroblasts
3. Pre-T cells
4. Myeloblasts
Answer:
3. Pre-T cells
Question 58.
An example of liquid tumor is
1. Glioblastoma
2. Adenocarcinoma
3. Chondrosarcoma
4. Myelocytic leukemia
Answer:
4. Myelocytic leukemia
Question 59.
Crossing of unrelated pure breeding animals of different traits within the same breed is called
1. Cross breeding
2. Out crossing
3. Close breeding
4. Species hybridization
Answer:
1. Cross breeding
![]()
Question 60.
The *P* wave in an EGG indicates
1. Atrial Depolarization
2. Repid venticular Depolarization
3. Absolute Refractory period
4. Repolarization of the ventricles
Answer:
1. Atrial Depolarization
Question 61.
Identify the tumor suppressor genes from the following
1. Oncogenes
2. p53 gene
3. Pseudogenes
4. 5 RY gene
Answer:
2. p53 gene
Question 62.
In EEG, the waves which are quite low in frequency and having high amplitude are
1. Theta waves
2. Delta waves
3. Beta waves
4. Alpha waves
Answer:
2. Delta waves
Question 63.
Biochemical procedure used to detect human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) is
1. WIDAL
2. CAT
3. MRI
4. ELISA
Answer:
4. ELISA
Question 64.
Human insulin is being commercially produced from a transgenic species of
1. Escherichia
2. Mycobactgerium
3. Rhizobium
4. Saccharomyces
Answer:
1. Escherichia
Question 65.
Antihuman immunoglobulins are also called as
1. Secondary antibodies
2. First primary antibodies
3. Second primary antibodies
4. Anti human immunogens
Answer:
1. Secondary antibodies
![]()
Question 66.
Which of the following technique is used to diagnose neurological and sleep disordes?
1. ECG
2. EKG
3. CT scan
4. EEG
Answer:
4. EEG
Question 67.
Biological response modifiers which activate the immune system of the patient and help in destroying tumors are
1. Monoclonal antibodies
2. interferons
3. Taxol
4. Methotexate
Answer:
2. interferons
Question 68.
Salk’s vaccine (IPV) contains
1. Attenuated poliomyelitin virus
2. Inactivated polio toxins
3. Inactivated polio virus
4. Surface antigenes of polio virus
Answer:
3. Inactivated polio virus
Question 69.
In mammals, including humans, insulin Is synthesized as a/an
1. Pro-enzyme
2. Active enzyme
3. Active hormone
4. Pro-hormone
Answer:
4. Pro-hormone
Question 70.
Pituitary extracts containing these are used to induce release of spawn for seed production
1. FSH and LH
2. LTH and estrogen
3. Ovaprim
4. All the above
Answer:
1. FSH and LH
Question 71.
Diploid larvae fed with bee bread develops into
1. Sterile males
2. Fertile males
3. Sterile females
4. Fertile females
Answer:
3. Sterile females
![]()
Question 72.
Identify the wrong statement
1. Bird flu is caused by avian influenza virus H5N1
2. It is not a pandemic disease
3. Avian flu spreads simply by touching contaminated surfaces
4. Birds affected by Avian flu release virus through faeces and saliva
Answer:
2. It is not a pandemic disease
Question 73.
Cartilagenous fishes are not generally considered as food fishes because
1. They possess spiny scales
2. Their skeleton is cartilayenous
3. They store urea in their blood
4. They store oil in their liver
Answer:
3. They store urea in their blood
Question 74.
In which product of biotechnology, only the protein part of the micro organisms is used
1. Antibodies
2. Enzymes
3. Vaccines
4. All the three
Answer:
3. Vaccines
Question 75.
interferons are antiviral
1. a-interferons
2. β – interferons
3. γ-interferons
4. All the three
Answer:
4. All the three
Question 76.
Monoclonal antibodies are produced in
1. Southern blotting technique
2. Colony hybridisation technique
3. Hybridoma technology
4. Western blotting technique
Answer:
3. Hybridoma technology
Question 77.
The feature of malignant tumour but absent in benign tumour is
1. Matastasis
2. Haemostasis
3. Homeostasis
4. Somatostasis
Answer:
1. Matastasis
Question 78.
Which of the following statements on Cancer are correct
I. Cancer is a group of syndromes that arc caused by mutations in somatic cells.
II. Cancer cells are characterised by indefinate growth, transformation and metastasis.
III. Tumour suppressor genes are recessive.
1. All are correct
2. I and II are correct
3. II and III are correct
4. I and III are correct
Answer:
2. I and II are correct
![]()
Question 79.
Which one of the following is not a primary lymphoid organs
1. Bone marrow
2. Thymus
3. Bursa of Fabricus
4. Spleen
Answer:
4. Spleen
Question 80.
Stem cells of the skeletal muscles are
1. Pericytes
2. Satellite cells
3. Podocytes
4. Intercalated cells
Answer:
2. Satellite cells
Question 81.
A queen Honey Bee lays eggs of
1. One type from which all castes develop
2. Two types, one forming queen and workers and second forming drones
3. Three types forming queen, drone and workers
4. Unfertilized eggs die while fertilized ones form all castes.
Answer:
2. Two types, one forming queen and workers and second forming drones