Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Question Paper May 2019 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Question Paper May 2019
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 60
Section – A (10 × 2 = 20)
Note :
-
- Answer all questions.
- Each question carries two marks.
- All are Very Short Answer Type Questions.
Question 1.
What is “dispersion” ? Which colour sets relatively more dispersed ?
Answer:
Dispersion: The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours, on passing through a prism is called dispersion of light. The deviation is maximum for violet colour.
Question 2.
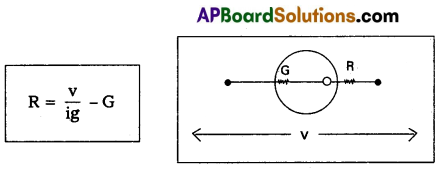
How do you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter ?
Answer:
A high resistance is connected in series to the moving coil galvanometer, then it converts to voltmeter.
![]()
Question 3.
If the Earth’s magnetic field at the equatOr is about 4 × 10-5T, what is its approximate magnetic dipole moment?
Answer:
Given, BE = 4 × 10-5T; r = 6.4 × 106m; m ?
BE = \(\frac{\mu_0}{4 \pi} \quad \frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{r}^3}\)
4 × 10-5 = \(\frac{4 \pi \times 10^{-7}}{4 \pi}\) × \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\left(6.4 \times 10^6\right)^3}\)
m = 4 × 102 × (6.4 × 106)3
∴ m = 1.05 × 1023 Am2 ≈ 1 × 1023 AM2.
Question 4.
Magnetic lines form continuous closed ioops. Why?
Answer:
Magnetic lines of force always start from north pole and forming curved path, enter south pole and travel to north pole inside the magnet. Thus lines of force are forming closed loops.
Question 5.
What is the phase difference between A.C. emf and current in the following ? Pure resistor, pure inductor and pure capacitor.
Answer:
- In pure inductor, current lags behind the e.m.f. by an angle of π/2 (or) 90°.
- In pure capacitor, current leads the e.m.f. by an angle π/2 (or) 90°.
Question 6.
What are the applications of microwaves ?
Answer:
- Microwaves are used in Radars.
- Microwaves are used for cooking purposes.
- A radar using microwaves can help in detecting the speed of automobile while in motion.
Question 7.
What is the de Broglie wavelength associated with an electron, accelerated through a potential difference of 100 volts ?
Answer:
Accelerating potential v = 100v. The de broglie wavelength λ is
λ = h/p = \(\frac{1.227}{\sqrt{\mathrm{v}}}\) nm
λ = \(\frac{1.227}{\sqrt{100}}\) = nm = 0.123 nm.
The de-brogile wavelength associated with an electron on this case is of the order of x-ray wavelengths.
Question 8.
What is “work function” ?
Answer:
The minimum energy required to liberate an electron from photometal surface is called work function, Φ0.
Question 9.
How is a battery connected to a junction diode in i) forward and ii) reverse bias ?
Answer:
- Inp – n junction diode, if p – side is connected to positive terminal of a cell and n – side to negative terminal, it is called forward bias. ’
- In a p – n junction diode p – side is connected to negative terminal of a cell and n – side to positive terminal, it is called reverse bias.
Question 10.
Define modulation why is its necessary ?
Answer:
Modulation: The process of combining low frequency audio signal with high frequency carries wave is called modulation.
Necessary: Low frequency signals cannot transmit directly, to reduce size of the antenna and to avoid mixing up of signal from different transmitters modulation is necessary.
![]()
Section – B (6 × 4 = 24)
Note :
- Answer any six of the following questions.
- Each question carries four marks.
- All are Short Answer Type Questions.
Question 11.
Explain the formation of a mirage.
Answer:
In a desert, the sand becomes very hot during the summer time and it rapidly heats the layer of air which is in its contact. So density of air decreases. As a result the successive upward layer is denser then tower layer.
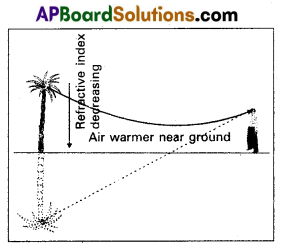
When a beam of light travelling from the top of a tree enters a varer layer, it is refracted a way from the normal. As a result at the, surface of layer of air, each time the angle of incidence increase and ultimately a stage is reached, when the angle of incidence becomes greater than the critical angle between the two layers, the incident ray surfers total internal reflection. So, it apears as inverted image of the tree is formed and the same looks likes a pool of water to the observer.
Question 12.
Explain Doppler effect in light. Distinguish between red shift and blue shift.
Answer:
Doppler effect in light: The change in the apparent frequency of light, due to relative motion between source of light and observer. This phenomenon is called Doppler effect.
The apparent frequency of light increases when the distance between observer and source of light is decreasing and the apparent frequency of light decreases, if the distance between source of light and observer increasing.
Doppler shift can be expressed as, \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{v}}\) = \(\frac{-v_{\text {radical }}}{C}\)
Applications of Doppler effect in light:
- It is used in measuring the speed of star and speed of galaxies.
- Measuring the speed of rotation of the sand.
Red shift : The apparent increase in wavelength in the middle of the visible region of the spectrum moves towards the red end of the spectrum is called red shift.
Blue shift: When waves are received from a source moving towards the observer, there is an apparent decrease in wavelength, this is called blue shift.
Question 13.
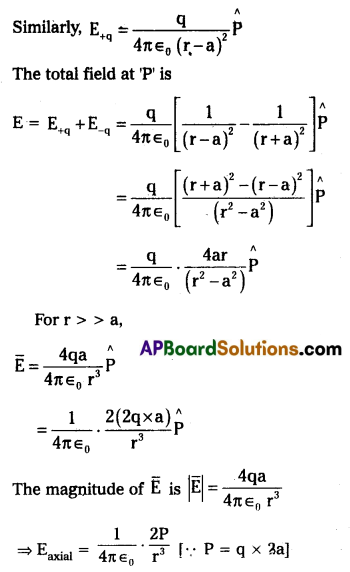
Derive an expression for the intensity of the electric field at a point on the axial line of an electric dipole.
Answer:
Intensity of the electric field at a point on the axial line of an electric dipole : Let us consider an electric dipole as, a pair of equal and opposite point charges +q and -q, separated by a distance ‘2a’ and its dipole moment is P.
Let the point ‘p’ be the distance ‘r’ from the centre of the dipole on the side of the charge ‘q’.
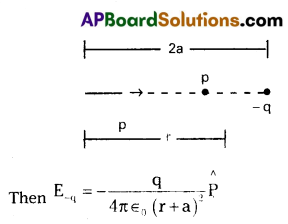
Where P̂ is the unit vector along the dipole axis from – q to +q.
Question 14.
Derive an expression fór the electric potential due to a point charge.
Answer:
Expression for the electric potential due to a point charge:
1) Electric potential at a point is defined as the amount of workdone in moving a unit +ve charge from infinity to that point.
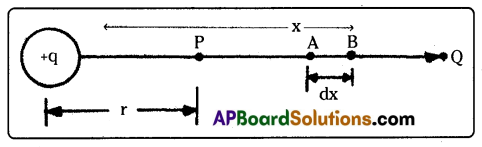
2) Consider a point P at a distance r from the point charge having charge + q. The electric field at P = E = \(\frac{Q}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0 x^2}\).
3) Workdone in taking a unit +ve charge from B to A = dV = – E.dx (-ve sign shows that the workdone is +ve in the direction B to A, whereas the potential difference is +ve in the direction A to B.
4) Therefore, potential at P = The amount of workdone in taking a unit +ve charge from infinity to P.
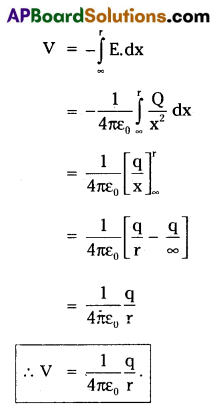
![]()
Question 15.
Derive an expression for the magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron.
Answer:
Consider an electron revolving in a circular orbit of radiiis r with speed v and frequency v.
If the electron cross a point P on the circle in every revolution, then distance travelled by electron to complete one revolution = 2πr.
No. of revolutions in one second (v) = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{2 \pi \mathrm{r}}\)
The electric current (i) = \(\frac{\text { charge }}{\text { time }}\) = charge × frequency
i = e × \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{2 \pi \mathrm{r}}\)
∴ Magnetic dipole moment (M) = iA (∵ N = 1)
M = \(\frac{\mathrm{ev}}{2 \pi \mathrm{r}}\) × πr2 (∵ A = πr2)
M = \(\frac{\text { evr }}{2}\).
Question 16.
Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co – axial solenoids.
Answer:
Let us consider two solenoids as shown in figure. The length of primary coil be ‘l’ and area of cross section A. Let N1 and N2 are the total number of turns in the primary and secondary solenoids. Let nt and n2 be the number of turns per unit length n1 and n2 be the current in primary coil.
∴ Magnetic field inside the primary coil (B) = µ0n1I
B = µ0\(\frac{\mathrm{N}_1}{l}\).I ………….. (1)
Magnetic flux through each turn of primary coil,
ΦB = \(\overline{\mathrm{B}} \cdot \overline{\mathrm{A}}\) µ0\(\frac{\mathrm{N}_1}{l}\).I ………….. (2)
The same magnetic flux is linked with the secondary coil.
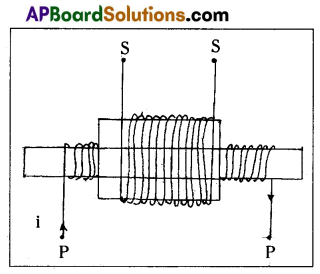
∴ Total magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil,
= µ0\(\frac{\mathrm{N}_1}{l}\) i × A × N2 …….. (3)
If M be the mutual inductance of the two coils, the total flux linked with the secondary is Mi,
∴ Mi = \(\frac{\mu_0 \mathrm{~N}_1 \mathrm{~N}_2 \mathrm{iA}}{l}\) …………. (4)
⇒ M = \(\frac{\mu_0 N_1 N_2 \mathrm{~A}}{l}\) ………….. (5)
⇒ M = \(\frac{\mu_0 \mathrm{~N}_1 \mathrm{~N}_2\left(\pi \mathrm{r}^2\right)}{l}\) ……… (6)
Question 17.
Explain the different types of spectral series.
Answer:
The following are the different types of spectral series observed in the spectrum of hydrogen atom.
1. Lyman series: The spectral lines corresponding to transition from outer energy levels n2 = 2, 3, 4 … ∞ to first orbit n1 = 1 constitute lyman series. The wave number of different lines are given by.
\(\bar{v}=\frac{1}{\lambda}=R\left[\frac{1}{1^2}-\frac{1}{n_2^2}\right]\)
2. Balmer series : The spectral lines corresponding to n2 = 3, 4, 5, …… ∞ to n1 = 2 constitute Balmer series. The wave number of different lines are given by,
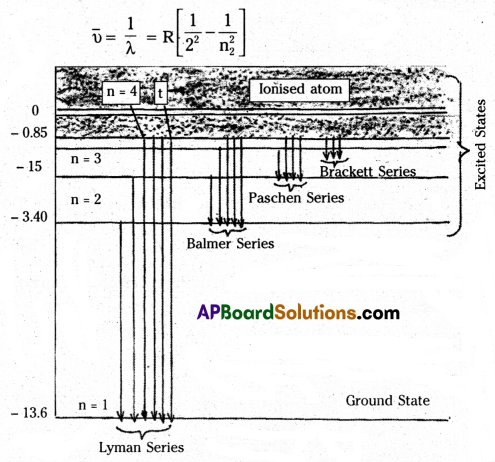
3. Paschen series : The spectral lines corresponding to n2 = 4, 5, 6, ….. to n1 = 3 constitute Paschen series. The wave number of different lines are given by,
\(\bar{v}=\frac{1}{\lambda}=\mathrm{R}\left[\frac{1}{3^2}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{n}_2^2}\right]\)
4. Brackett series : This series corresponding to transitions from n2 = 5, 6, 7 … ∞ to n1 = 4. The wave numbers are given by,
\(\bar{v}=R\left[\frac{1}{4^2}-\frac{1}{n_2^2}\right]\)
5. Pfund series : The series corresponding to transitions from n2 = 6, 7, 8 … ∞ to n1 = 5. The wave numbers are given by,
\(\bar{v}=R\left[\frac{1}{5^2}-\frac{1}{n_2^2}\right]\)
![]()
Question 18.
What is rectification ? Explain the working of a full wave rectifier.
Answer:
Rectification : The process of converting an alternating current into a direct current is called rectification. The device used for this purpose is called rectifier.
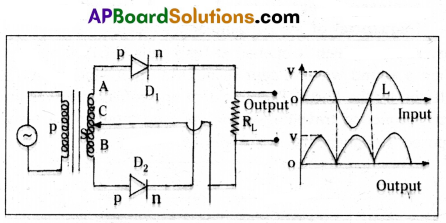
- A full wave rectifier can be constructed with the help of two diodes D1 and D2.
- The secondary transformer is centre tapped at C and its ends are connected to the P regions of two diodes D1 & D2.
- The output voltage is measured across the load resistance RL .
- During positive half cycles of ac, the diode D1 is forward biased and current flows through the load resistance RL. At this time D2 will be reverse biased and will be in switch off position.
- During negative half cycles of ac, the diode D2 is forward biased and the current flows through RL. At this time D1 will be reverse biased and will be in switch off position.
- Hence positive output is obtained for all the input ac signals. The efficiency of a rectifier is defined as the ratio between the output dc power to the input ac power.
η = \(\frac{P_{d c}^{\prime}}{P_{a c}}\) = \(\frac{0.812 R_L}{r_f+R_L}\)
The maximum, efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2%.
Section – C (2 × 8 = 16)
Note:
- Answer any two of the following questions.
- Each question carries eight marks.
- All are Long Answer Type Questions.
Question 19.
a) Explain the formation of stationary waves in an air column enclosed in open pipe. Derive the equations for the frequencies of the harmonics produced.
Answer:
A pipe, which is opened at both ends is called open pipe. When a sound wave is sent through a open pipe, which gets reflected by the Earth. Then incident and reflected waves are in same frequency, travelling in the opposite directions are superimposed, stationary waves are formed.
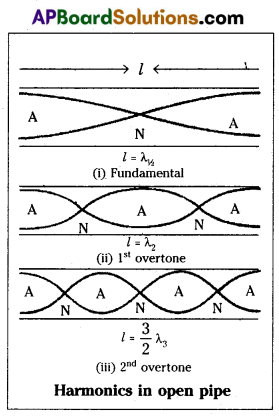
Harmonics in Open pipe : To form the stationary wave in open pipe, which has two antinodes at two ends of the pipe with a node between them.
∴ The vibrating length (l) = half of the wavelength (\(\frac{\lambda_1}{2}\))
l = \(\frac{\lambda_1}{2}\) ⇒ λ1 = 2l
Fundamental frequency υ1 = \(\frac{v}{\lambda_1}\)
where v is velocity of sound in air υ1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{2 l}\) ………… (1)
For second harmonic (first overtone) will have one more node and antinode than the fundamental.
If λ2 is wavelength of second harmonic l = \(\frac{2 \lambda_2}{2}\) ⇒ λ2 = l
If ‘υ2‘ is frequency of second harmonic then
υ2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\lambda_2}\) = \(\frac{\mathbf{v} \times 2}{2 l}\) = 2υ1
υ2 = 2υ1 ………… (2)
Similarly for third harmonic (second overtone) will have three nodes and four antinodes as shown in above figure.
If λ3 is wave length of third harmonic l = \(\frac{3 \lambda_3}{2}\)
λ3 = \(\frac{2 l}{3}\)
If ‘υ3‘ is frequency of third harmonic then
υ3 = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\lambda_3}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{v} \times 3}{2 l}\) = 3υ1
υ3 = 3υ1 ………. (3)
Similarly we can find the remaining or higher harmonic frequencies i.e. υ3, υ4 etc, can be determined in the same way.
Therefore the ratio of the harmonic frequencies in open pipe can be written as given below.
υ : υ1 : υ2 = 1 : 2 : 3 ………….
b) A closed pipe 70cm long is sounded. If the velocity of sound is 331 m/s. What is the fundamental frequency of vibration of the air column ?
Answer:
l = 70 cm
= 70 × 10-2m
v = 331 m/s
v = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{4 l}\)
= \(\frac{331}{4 \times 70 \times 10^{-2}}\)
= 118.2 HZ.
Question 20.
a) State the working principle of potentiometer. Explain with the help of circuit diagram how the potentiometer is used to determine the Internal resistance of the given primary cell.
Answer:
Wfcrking principle of potentiometer: The potential difference across a length of the potentiometer wire is directly propor-tional • to its length (or) when a steady current is passed through a uniform wire, potential drop per unit length or potential gradient is constant,
i.e., ε ∝ l ⇒ ε = Φl
where Φ is potential gradient.
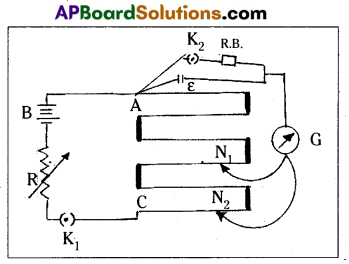
Measurement of internal resistance (r) with potentiometer:
- Potentiometer to measure internal resistance (r) of a cell (ε) is shown in diagram.
- The cell (emf ε) whose internal resistance (r) is to be determined is connected across a resistance box (R.B) through a key K2.
- With key K2 open, balance is obtained at length l1(AN1).
Then ε = Φl1 → (1) - When key K2 is closed, the cell sends a current (I) through the resistance box (R.B)
- If V is the terminal potential difference of the cell and balance is obtained at length l2(AN2. Then V = Φl2 → (2)
- \(\frac{(1)}{(2)}\) ⇒ \(\frac{\varepsilon}{\mathrm{V}}=\frac{l_1}{l_2}\) → (3)
- But ε = I (r + R) and V = IR. This gives
\(\frac{\varepsilon}{V}\) = \(\frac{(\mathrm{r}+\mathrm{R})}{\mathrm{R}}\)
\(\frac{l_1}{l_2}\) = (\(\frac{r}{R}\) + 1) [∵ from (3)]
∴ r = R(\(\frac{l_1}{l_2}\) – 1)
b) Two bulbs, whose resistances are in the ratio 1 : 2 are connected in parallel to a source of constant voltage. What . will be the ratio of power dissipation in these.
Answer:
Given, R1 : R2 = 1 : 2
In parallel series,
power, P = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\)
⇒ P ∝ \(\frac{1}{R}\) [∵ V is constant)
⇒ \(\frac{P_1}{P_2}=\frac{R_2}{R_1}\) = \(\frac{2}{1}\)
⇒ P1 = P2 = 2 : 1
![]()
Question 21.
a) Explain the principle and working of a nuclear reactor with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Principle : A nuclear reactor works on the principle of achieving controlled chain reaction in natural uranium 238U enriched with 238U, consequently generating large amounts of heat.
A nuclear reactor consists of :
1) Fuel
2) Moderator
3) Control rods
4) Radiation shielding
5) Coolant
1) Fuel and Clad : In reactor the nuclear fuel is fabricated in the form of thin and long cylindrical rods. These group of rods treated as a fuel assembly. These rods are surrounded by coolant, which is used to transfer of hear produced in them. A part of of the nuclear reactor which used to store the nuclear fuel is called the core of the reactor. Natural uranium, enriched uranium, plutonium and uranium-233 are used as nude fuels.
2) Moderator: The average energy of neutrons relased in fission process is 2meV. They are used to slow down the velocity of neutrons. Heavy water or graphite are used as moderating materials in reactor.
3) Control rods : These are used to control the fission rate in reactor by absorbing the neutrons. Suitable shielding such as steel, lead, concrete etc., are provided around the reactor to absorb and reduce intensity of radiations to such low levels that do not harm the operating personnel.
4) Coolant: The heat generated in fuel elements is removed’ by using a suitable coolant to flow around them. The coolants used are water at high pressures, molten sodium etc.
Working : Uranium fuel rods are placed in the aluminium cylinders. The graphite moderator is placed in between the fuel cylinders to control the holes of graphite block. When a few 235U nuclei undergo fission fast neutrons are liberated. These neutrons pass through the surrounding graphite moderator aud loose their energy to become thermal neutrons. These thermal neutrons are captured by 235U. The heat generated here is used for heating suitable coolants which in turn heat water and produce steam. This stem is made to rotate steam turbine and there by drive a generator of production for electric power.
b) If one microgram of \(\) is completely destroyed in an atom bomb, how much energy will be released ?
Answer:
Mass, m = 1 µgn
= 10-6 × 10-3kg
= 10-9kg
From, E = mc2
= 10-9 × (3 × 108)2
F = 9 × 107 J