Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Question Paper May 2017 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Question Paper May 2017
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 60
Section – A (10 × 2 = 20)
Note:
- Answer all questions.
- Each question carries two marks.
- All are Very Short Answer Type Questions.
Question 1.
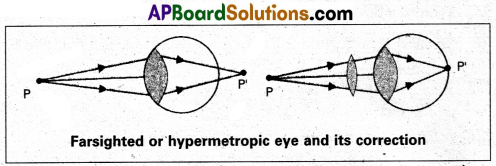
What is Hypermetropia ? How can it be corrected ?
Answer:
Hypermetropia (or) Farsightedness: The light from a distant object arriving at the eye-lens may get converged at a point behind the retina. This type of defect is called Hypermetropia.
To correct this, we interpose a convex lens (Convergent lens) between the eye and the object.
Question 2.
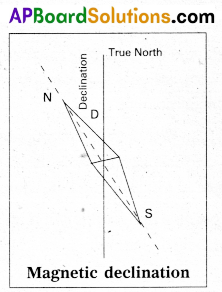
Define magnetic decÍination.
Answer:
Magnetic Declination (D) : The angle between the true geographic north and the north shown by a compass needle is called magnetic declination or simply declination (D).
Question 3.
What are the units of magnetic moment and magnetic induction ?
Answer:
The unit of magnetic moment – Ampere – metre2
The unit of magnetic induction = Weber / metre2 (or) Tesla
![]()
Question 4.
Distinguish between ammeter and voltmeter.
Answer:
| Ammeter | Voltmeter |
| 1) It is used to measure current. | 1) It is used to measure ED between two points. |
| 2) Resistance of an ideal Ammeter is zero. | 2) Resistance of ideal volt-meter is infinity. |
| 3) It is connected in series in the circuits. | 3) It is connected in parallel in the circuits. |
Question 5.
What is the phenomenon involved in the working of a transformer ?
Answer:
When a current changes in one coil magnetic flux changes in it, hence an emf is induced in near coil. This phenomenon is called mutual induction.
Question 6.
What is the de Broglie wavelength associated with an electron, accelerated through a potential difference of 100 volts ?
Answer:
λ = \(\frac{h}{P}=\frac{1.227}{\sqrt{V}}=\frac{1.227}{\sqrt{100}}\) nm
= 0.123 nm
Question 7.
Give any one use of Infrared rays.
Answer:
- Infrared radiation plays an important role in maintaining the Earthwarm.
- Infrared lamps are used in Physical therapy.
- Infrared detectors are used in Earth Satellites.
- These are used in taking photographs during the conditions of fog, smoke etc.
Question 8.
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Answer:
Kmax = \(\frac{1}{2}\) m V2max = hυ – Φ0
Question 9.
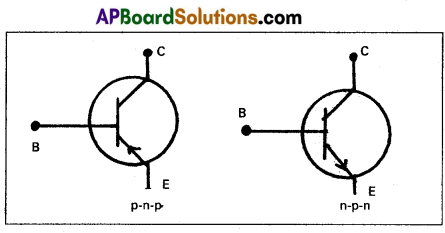
Draw the circuit symbols for p-n-p and n-p-n transistors.
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
Define modulation. Why is it necessary ?
Answer:
Modulation: The process of combining low frequency audio signal with high frequency carrier wave is called modulation.
The audio frequency signals cannot be transmitted over long distances faithfully. Therefore they are combined with high frequency waves and transmitted.
Section – B (6 × 4 = 24)
Note :
- Answer any six of the following questions.
- Each question carries four marks.
- All are Short Answer Type Questions.
Question 11.
Explain the formation of a rainbow.
Answer:
Figure shows how sun light is broken into its segments in the process and a rainbow appears. The dispersion of the violet and the red rays after internal reflection in the drop is shown in figure.
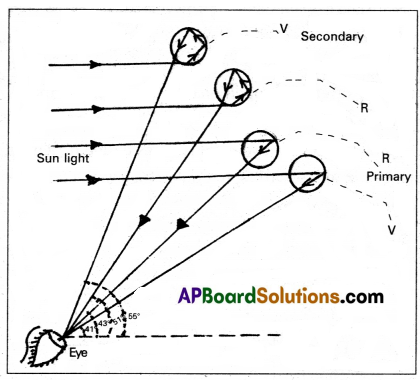
The red rays emerge from the drops of water at one angle (43°) and the violet rays emerge at another angle (41°). The large number of water drops in the sky makes a rainbow. The rainbow appears semicircular for an observer on earth.
Question 12.
Does the principle of conservation of energy hold for interference and diffraction phenomena ? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Yes; the principle of conservation of energy holds good for interference and diffraction phenomena.
In interference and diffraction, light energy is redistributed. If it reduces in one region, producing a dark fringe, it increases in another region, producing a bright fringe. There is no gain or loss of energy, which is consistent with the principle of conservation of energy.
Question 13.
State and explain Coulomb’s inverse square law in electricity.
Answer:
Coulomb’s law : “The force of attraction (or) repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges”.
Explanation : Let two point charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance r in air. According to Coulomb’s law, the force between two charges is given by
i) F ∝ q1q2
∴ F ∝ \(\frac{\mathrm{q}_1 \mathrm{q}_2}{\mathrm{r}^2}\)
F = \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \cdot \frac{\mathrm{q}_1 \mathrm{q}_2}{\mathrm{r}^2}\)
ii) F∝ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}^2}\)

where \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_0} \cdot \frac{\mathrm{q}_1 \mathrm{q}_2}{\mathrm{r}^2}\) = 9 × 109 Nm-2C-2 = Proportionality constant
ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12 C2N-1 m-2 = Permittivity in free space.
![]()
Question 14.
Derive an expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
Answer:
Consider two parallel plates A and B separated by a distance d in air. The upper plate A is given a charge +q and a lower plate B given a charge -q.
By using Gauss law, first we calculate the value of electric field E.
Consider a Gaussian surface PQRS. The flux through the ends PR and QS is zero.(∵ angle between E and ds is 90°). Electric flux through the surface PQ is zero, because inside the conductor charge is zero.
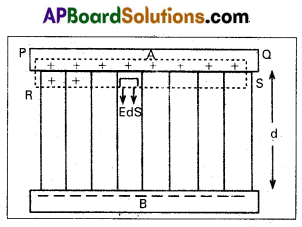
The only contribution of electric flux is due to the surface RS. Total electric flux through the entire Gaussian surface is
ΦE = \(\oint \mathrm{E} \cdot \mathrm{dS}=\oint \mathrm{EdS} \cos \theta\) (∴ Angle between E and dS is zero, i.e., θ = 0)
ΦE = \(\oint \text { E. dS }\) (∵ \(\oint \mathrm{dS}=\mathrm{A}\))
Let A be the area of each plate ΦE = E.A ……….. (1)
Applying Gauss law ΦE = \(\frac{1}{\varepsilon_0}\)q …………. (2)
From eq’s (1) and (2), EA = \(\frac{\mathrm{q}}{\varepsilon_0}\).
E = \(\frac{\mathrm{q}}{\varepsilon_0 \mathrm{~A}}\) ……….. (3)
The potential difference V between the plates can be written as
V = E.d = \(\frac{\mathrm{q}}{\varepsilon_0 \mathrm{~A}}\).d (∵ C = \(\frac{q}{V}\))
\(\frac{q}{V}=\frac{\varepsilon_0 A}{d}\)
∴ C = \(\frac{\varepsilon_0 A}{d}\)
Question 15.
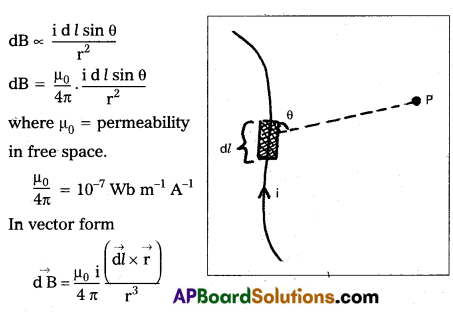
State and explain Biot-Savart law.
Answer:
Consider a very small element of length dl of a conductor carrying current (i) Magnetic induction due to small element at a point P distance r from the element.
Magnetic induction (dB) is directly proportional to
- current (i)
- Length of the element (dl)
- sine angle between r and d! and
- Inversely proportional to the square of the distance from small element to point P.
Question 16.
Describe the ways in which Eddy currents are used to advantage.
Answer:
Eddy currents are used to advantage in
i) Magnetic breaking in trains : A strong magnetic field is applied across the metallic drum rotating with the axle of the electric train. Thus large eddy currents are produced in the metallic drum. These currents oppose the motion of the drum and hence the axle of the train which ultimately makes the train come to rest.
ii) Induction Motor : Eddy currents are used to rotate the short circuited rotor of an induction motor. Ceiling fans are also induction motors which run on single phase alternating current.
iii) Electromagnetic damping: Certain galvanometers have a fixed core made of non magnetic metallic material. When the coil oscillates, the eddy currents generated in the core oppose the motion and bring the coil to rest quickly.
iv) Induction furnace,; Induction furnace can be used to produce high temperatures and can be utilised to prepare alloys, by melting the constituent metals. A high frequency alternating current is passed through a coil. The eddy currents generated in the metals produce high temperatures sufficient to melt it.
v) Analogue energy meters : Concept of eddy currents is used in energy meters to record the consumption of electricity. Aluminium disc used in these meters get induced due to varying magnetic field. It rotates due to eddy currents produced in it.
![]()
Question 17.
What are the limitations of Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom ?
Answer:
Limitations of Bohr’s theory of Hydrogen atom :
- This theory is applicable only to simplest atom like hydrogen, with Z = 1. The theory fails in case of atoms of other elements for which Z > 1.
- The theory does, not explain why orbits of electrons are taken as circular, while elliptical orbits are also possible.
- Bohr’s theory does not say anything about the relative intensities of spectral lines.
- Bohr’s theory does not take into account the wave properties of electrons.
- Question 18.
What is rectification ? Explain the working of a full wave rectifiers.
Answer:
Rectification : The process of converting on alternating current into a direct current is called rectification.
The device used for this purpose is called rectifier.
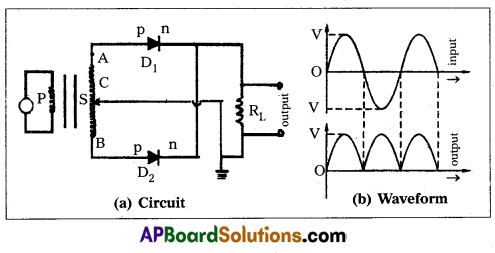
- A full wave rectifier can be constructed with the help of two diodes D1 and D2.
- The secondary transformer is centre tapped at C and its ends are connected to the p regions of two diodes D1 & D2.
- The output voltage is measured across the load resistance RL.
- During positive half cycles of ac, the diode D1 is forward biased and current flows through the load resistance RL. At this time D2 will be reverse biased and will be in switch off position.
- During negative half cycles of ac, the diode D2 is forward biased and the current flows through RL. At this time D1 will be reverse biased and will be in switch off position.
- Hence positive output is obtained for all the input ac signals.
- The efficiency of a rectifier is defined as the ratio between the output dc power to the input ac power.
η = \(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{dc}}}{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{ac}}}=\frac{0.812 \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{f}}+\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}}\)
The maximum efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2%. The device used for this purpose is called rectifier.
Section – C (2 × 8 = 16)
Note:
- Answer any two of the following questions.
- Each question carries eight marks.
- All are Long Answer Type Questions.
Question 19.
How are stationary waves formed in closed pipes ? Explain the various modes of vibrations and obtain the relations for the frequencies.
A closed organ pipe 70 cm long is sounded. If the velocity of sound is 331 m/s, what is the fundamental frequency of vibration of the air column ?
Answer:
Formation of standing waves in a closed pipe: A pipe, which is closed at one end and the other is opened is called closed pipe. When a sound wave is sent through a closed pipe, which gets reflected at the closed end of the pipe. Then incident and reflected waves are in same frequency, travelling in the opposite directions are super-imposed stationalary waves are formed.
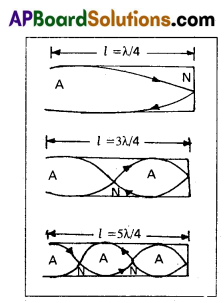
- In closed pipe one end is closed and other end is open. So antinode is formed at open end node is formed at closed end.
- The possible harmonics in vibrating air column is a closed pipe
vn = \(\frac{(2 \mathrm{n}+1) \mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ………… - In first normal mode of vibrating air column in a closed pipe, v1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) first harmonic or fundamental frequency.
- In second normal mode of vibrating air column in a closed pipe, v3 = \(\frac{3 \mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) [Third harmonic or first overtone]
- In third normal mode of vibrating air column in a closed pipe, v5 = \(\frac{5 \mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) [Fifth harmonic or second overtone]
- Therefore the ratio of the frequencies of harmonics in closed pipe can be written as
v1 : v3 : v5 = \(\frac{\mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) : \(\frac{3 \mathrm{v}}{4 l}\) : \(\frac{5 \mathrm{v}}{4 l}\)
v1 : v3 : v5 = 1 : 3 : 5
Problem :
l = 70 cm = 70 × 10-2 m
v = 331 m/s
v = ?
v = \(\frac{υ}{4 l}=\frac{331}{4 \times 70 \times 10^{-2}}\)
= 118.2 Hz.
Question 20.
State the working principle of Potentiometer. Explain with the help of a circuit diagram. How the emf of two primary cells are compared by using the Potentiometer ?
Answer:
Working principle of potentiometerThe potential difference across a length of the potentiometer wire is directly proportional to its length (or) when a steady current is passed through a uniform wire, potential drop per unit length or potential gradient is constant.
i.e. ε ∝ l ⇒ ε = Φl
where Φ is potential gradient.
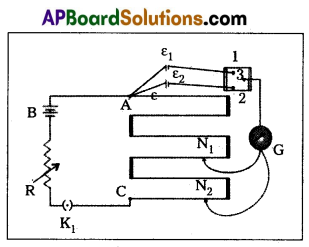
Comparing of emf of two cells ε1 and ε2 :
- To compare the emf of two cells of emf E1 and E2 with potentiometer is shown in diagram.
- The points marked 1, 2, 3 form a two way key.
- Consider first a position of the key where 1 and 3 are. connected so that the galvanometer is connected to ε1.
- The Jockey is moved along the wire till at a point N1 at a distance l1 from A, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
Then ε1 ∝ l1 ⇒ ε1 = Φl1 ……….. (1) - Similarly, if another emf ε2 is balanced against
l2 (AN2), then ε2 ∝ l2 ⇒ ε2 = Φl2 - \(\frac{(1)}{(2)} \Rightarrow \frac{\varepsilon_1}{\varepsilon_2}=\frac{l_1}{l_2}\)
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the principle and working of a nuclear reactor with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Principle : A nuclear reactor works on the principle of achieving cont;oiled chain reaction in natural Uranium 238U enriched with 235U, consequently generating large amounts of heat.
A nuclear reactor consists of
1) Fuel
2) Moderator
3) Control rods
4) Radiation shielding
5) Coolant.
1) Fuel and clad : In reactor the nuclear fuel is fabricated in the form of thin and long cylindrical rods. These group of rods treated as a fuel assembly. These rods are surrounded by coolant, whfch is used to transfer of heat produced in them. A part of the nuclear reactor which use to store the nuclear fuel is called the core of the reactor. Natural uranium, enriched uranium, plutonium and uranium – 233 are used as nuclear fuels.
2) Moderator : The average energy of neutrons released in fission process is 2 MeV. They are used to slow down the velocity of neutrons. Heavy water or graphite are used as moderating materials in reactor.
3) Control Rods : These are used to control the fission rate in reactor by absorbing the neutrons. Cadmium and boron are used as controlling the neutrons, in the form of rods.
4) Shielding: During fission reaction beta and gamma rays are emitted in addition to neutrons. Suitable shielding such as steel, lead, concrete etc are provided around the reactor to absorb and reduce the intensity of radiations to such low levels that do not harm the operating personnel.
5) Coolant: The heat generated in fuel elements is removed by using a suitable coolant to flow around them. The coolants used are water at high pressures, molten sodium etc.
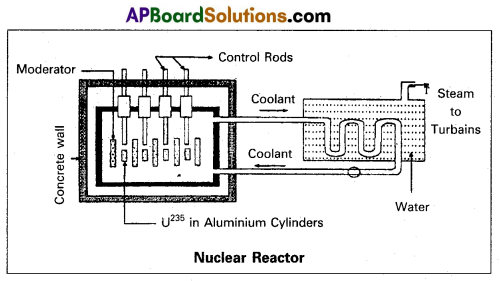
Working : Uranium fuel rods are placed in the aluminium cylinders. The graphite moderator is placed in between the fuel cylinders. To control the number of neutrons, a number of control rods of cadmium or beryllium or boron are placed in the holes of graphite block. When a few 235U nuclei undergo fission fast neutrons are liberated. These neutrons pass through the surrounding graphite moderator and loose their energy to become thermal peutrons. These thermal neutrons are captured by 235U. The heat generated here is used for heating suitable coolants which in turn heat water and produce steam. This steam is made to rotate steam turbine and there by drive a generator of production for electric power.