Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2019 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2019 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Note: Answer any two questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is transport? What are the benefits of transport?
Answer:
Introduction:
Transport is the physical distribution means of moving goods and persons from one place to another. Transport creates place utility and time utility of goods by moving them from different centers of production to the places of consumption. Transportation would help businessmen to reach consumers. In simple language, transportation can be defined as “a means through which goods are transferred from one place to another”.
Benefits of Transport:
1. Movement of Goods:
The first important function of transport is the movement of goods. The raw materials have to move from their sources to the factory and manufactured goods have to move from the factory to the consuming areas.
2. Transport Enhances the mobility of labor and capital:
An efficient network of transport services encouraged the movement of people from one place to another. Labor can migrate to a place where they can get better job opportunities.
3. Creation of Place Utility:
Transport creates a place utility of goods. It moves goods from these places where they are abundant to those places where they are scarce.
4. Specialization and Division of Labour:
Transportation facilitates the optimum utilization of the national resources of the country. For example petroleum resources of Arab countries, watches of Switzerland, etc.
5. Creation of Time Utility:
Transportation creates time utility in various ways. With the advancement of technology, transportation time is being shortened. This helps in lesser inventory costs.
6. Stability in Prices:
Goods can be transported from the places where the goods are abundant to the places where scarcity exists. In this way, prices are equalized throughout the country.
7. Contribution to National Income:
Transportation also contributed to the national income of a nation. For example, our railways.
8. Economies of Large-Scale Production:
Transport has helped the development of large-scale industries. Transport, procure raw materials, labor, and sell the finished goods.
9. Improve the Standard of Living:
With the help of transport, we can get a wide variety of goods at reasonable prices, which improves the standard of living.
10. National Defence:
Transport strengthens the national defense transport system. During the war period, all the personnel, materials, and equipment can be moved rapidly to the border areas.
![]()
Question 2.
Define stock exchanges and explain their functions.
Answer:
Introduction:
The stock exchange is a financial barometer of the country, which deals in long-term finance. A stock exchange is an institution that provides a platform for buying and selling existing securities. It provides a connecting link between people who want to dispose of their investment because they need cash and people who wish to invest because they have surplus cash available.
Definition:
According to the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, stock exchange means any house of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating, or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities.
Functions of a Stock Exchange:
The stock exchanges provide many useful services to the corporate sector and the investor. The following are some of the important functions of a stock exchange.
1. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities:
The basic function of a stock exchange is the creation of a continuous market where securities are bought and sold. It gives investors the chance to disinvest and reinvest. This provides both liquidity and easy marketability to already existing securities in the market.
2. Pricing of Securities:
Share prices on a stock exchange are determined by. the forces of demand and supply. A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. Such a valuation provides important information to both buyers and sellers in the market.
3. Safety of Transaction:
The membership of a stock exchange is well-regulated and its dealings are well-defined according to the existing legal framework. This ensures that the investing public gets a safe and fair deal on the market.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
A stock exchange is a market in which existing securities are resold or traded. Through this process savings get channelized into their most productive investment avenues. This leads to capital formation and economic growth.
5. Spreading of Equity Cult:
The stock exchange can play a vital role in ensuring wider share ownership by regulating new issues, better trading practices, and taking effective steps in educating the public about investments.
6. Providing Scope for Speculation:
The stock exchange provides sufficient scope within the provisions of law for speculative activity in a restricted and controlled manner. It is generally accepted that a certain degree of healthy speculation is necessary to ensure liquidity and price continuity in the stock market.
Question 3.
Describe the rights and responsibilities of a consumer as per CPA 1986.
Answer:
The government of India provided the following Six rights to all consumers under the Consumer Protection Act (CPA):
- Right to Safety: According to this right the consumers have the right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services that are hazardous (dangerous) to life and property.
- Right to Information: According to this right the consumer has the right to get information about the quality, quantity, purity standard, and piece of goods and services.
- Right to choice: According to this right every consumer has the right to choose the goods or services of his or her liking. The suppliers should not force the customer to buy a particular brand only.
- Right to consumer education: According to this right it is the right of the consumer to acquire knowledge and skills to be informed to the customer to know their rights and take actions.
- Right to seek Redressal: According to this right, the customer has the right to get compensation or seek redressal against unfair trade practices or any other exploitation.
Responsibilities:
- Be quality-conscious: To put a stop to adult creation and corrupt practices of the manufacturers and traders, every consumer must be conscious of the quality of products they buy such as 1st, Agmark, Hallmark, etc.
- Beware of misleading advertisements: The advertisement often exaggerates the quality of products. Hence, the consumers should not rely on the advertisement and carefully check the product or ask the users before making purchases.
- Responsibility to inspect a variety of goods before making a section: The consumer should inspect a variety of goods before buying the goods and services. For this purpose, he/she should compare their quality, price, durability, after-sales service, etc.
- Collection of Transaction: The consumer should insist on valid documentary evidence like a cash memo or invoice; relating to the purchase of goods or availing of any services and preserve it carefully.
- Consumers must be aware of their rights: The consumer must be aware of his rights and exercise them while buying goods and services.
- Complaint for Genuine Grievances: If a consumer is dissatisfied with the product/services, he can ask for redressal of grievances. In this regard, he must file a proper claim with the company first. If the company does not respond then he can approach the forums.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Note: Answer any four questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Explain any five functions of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
Introduction:
The word entrepreneur is derived from the French verb “Entrepredre”, which means to undertake”. The entrepreneur is associated with a person who starts his own, new and small business.
Definition:
According to P.F. Drucker, an entrepreneur is one who “searches for change, responds to it and exploits opportunities, and the innovation is the specific tool of an entrepreneur”.
Functions of Entrepreneur:
1. Formation of New Producing Organisation:
An Entrepreneur makes arrangements for factors of production required for setting up a production process. He selects one of the processes which is most suitable. According to J.B.Say, the function 6f a producer/entrepreneur is to rationally combine the forces of production into a new producing organization.
2. Decision Making:
Every activity of the business requires decision-making. The entrepreneur has to make decisions every day which have an impact on the working of his enterprise. He makes various decisions regarding the following:
- Ascertaining the objective of the enterprise
- Sources of finance
- Product mix
- Pricing policies
3. Innovation:
Innovation is an important function of an entrepreneur. Innovation means the introduction of new methods in the process of production or the introduction of improvements in the existing methods. Innovative entrepreneurs are essential for rapid industrialization and economic development.
4. Management:
An entrepreneur performs managerial functions such as formulation of production plans, providing raw materials, physical facilities, and production facilities, and organizing and managing sales.
5. Risk Bearing:
The entrepreneur has to pay all the factors of production in advance. He guarantees interest to creditors, wages to labor, and rent to the landholders. There are changes that he may be rewarded with a handsome profit or he may suffer a heavy loss. An entrepreneur undertakes the responsibility for loss that may arise due to unforeseen contingencies in the future.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the role of entrepreneurship in economic development.
Answer:
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship is the ability to identify an investment opportunity and to organize an enterprise to contribute to real economic growth. According to D. C. MC. Clelland entrepreneurship is doing things in a new and better way and decision-making under the conditions of uncertainty.
Role of Entrepreneurship in Economic Development:
The role of entrepreneurship in economic development varies from economy to economy depending upon its material resources, industrial climate, and the responsiveness of the political system to the entrepreneurial function. The important role that entrepreneurship plays in the economic development of an economy is given below:
- Entrepreneurship promotes capital formation by mobilizing the idle savings of the public.
- Entrepreneurship provides immediate large-scale employment.
- Entrepreneurship promotes balanced regional development.
- Entrepreneurship helps to reduce the concentration of economic power.
- Entrepreneurship stimulates the equitable redistribution of wealth, income, and political power in the interest of the country.
- Entrepreneurship encourages the effective mobilization of capital and skills that might otherwise remain unutilized.
- Entrepreneurship induces backward and forward linkages which stimulate the process of economic development in the country.
- Entrepreneurship also promotes the country’s export trade i.e., an important ingredient to economic development.
Question 6.
What is International Trade? Write various types of International trade.
Answer:
International Trade:
A trade that takes place with other countries is called International Trade”. It is also known as “Foreign Trade” or “External Trade”. International trade is the process of transferring goods produced in one country to the consumers in another country.
Types of International Trade:
International Trade can be divided into 3 types such as (a) Import Trade (b) Export Trade and (c) Entrepot Trade.
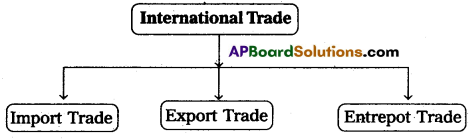
(a) Import Trade:
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in goods and services into the port of the country. When goods are purchased from smother country is called Import Trade. For Example, India imports electronic products from China.
(b) Export Trade:
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship goods and services out of the port of a country. When goods are sold to a trader in another country is called export trade. For Example: India is a major exporter of diamonds to other countries.
(c) Entrepot Trade:
When goods are imported from one country to exported the same to another country is called “Entrepot Trade.” It is also called “Re-export trade”. For example: India imported oil seeds from America and exported the same to Malaysia.
Question 7.
Write the Objectives of SEZ.
Answer:
Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws that are more liberal than a country’s economic laws. The main aim of the SEZ is to attract larger foreign investments. It is intended to make SEZ engines for economic growth. The SEZ Act was passed by parliament in May 2005.
Objectives:
- Generation of additional economic activity.
- Promotion of exports of goods and services.
- Promotion of investment from domestic and foreign sources.
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Development of infrastructure facilities.
- To exempt import duties and service tax.
Question 8.
Write the facets of electronic banking.
Answer:
The delivery of bank service to a customer at his home or office by using electronic tools and electronic channels is called “Electronic Banking”. The different facets of e-banking are explained below:
1. A.T.M:
A.T.M. means Automated Teller Machines. It is popularly known as “Any Time Money Machine”. The customer gets fast cash withdrawals, transfers, payment of bills, or cash deposits through A.T.M. Banks issue ATM cards (Debit cards) to each customer with the help of which he draws cash from A.T.M.
2. Tele Banking (Home Banking):
Customers can perform several transactions from their telephone, such as customers can check balances and statement information, transferring funds from one account to another paying certain bills, ordering statements or checkbooks, etc.
3. E-mail Banking:
Customers may communicate with the bank by electronic mail or e-mail. The most frequently used service is sending account statements periodically to the client’s mailbox.
4. Network Banking or Online Banking:
Internet or online Banking is a facility provided by banks that enables the user to execute bank-related transactions through the Internet. The account holder need not personally visit a bank.
5. Mobile Banking:
The delivery of bank services to a customer through a mobile phone is called “Mobile Banking”, mobile banking can take the form of SMS Banking GSM SIM TOOL Kit, and WAP.
![]()
Question 9.
The distinction between primary and secondary markets.
Answer:
| Primary Market (New Issue Market) |
Secondary Market (Stock Exchange Market) |
| 1. There is the sale of securities to investors by new companies or new issues by existing companies. | 1. There is the trading of existing shares only. |
| 2. Securities are sold by the company to the investors directly or through an intermediary. | 2. Ownership of existing securities is exchanged between investors. The company is not involved at all. |
| 3. In the primary market the flow of funds is from savers to investors, i.e., the primary market directly promotes capital formation. | 3. The secondary market enhances the liquidity of shares, i.e., indirectly promotes capital formation. |
| 4. In this market only the buying of securities takes place but securities cannot be sold here. | 4. Both buying and selling of securities can take place on the stock market. |
| 5. Prices of securities are determined and decided by the management of the company. | 5. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of the securities. |
| 6. In the primary market there is no fixed geographical location. | 6. Secondary markets are located at specified places for trading activities. |
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Write any two types of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
1. Innovating Entrepreneurs:
This type of entrepreneur introduces new goods, inaugurates new methods of production, discovers new markets, and reorganizes the enterprise. Such entrepreneurs can work only when a certain level of development is already achieved and people look forward to change and improvement.
2. Imitative Entrepreneurs:
Imitative entrepreneurs do not innovate the changes themselves, they only imitate techniques and technology innovated by others. These entrepreneurs adopt the methods and techniques already successfully executed by innovating entrepreneurs.
Question 11.
Explain any one characteristic of an entrepreneur.
Answer:
Innovation: Innovation is an important characteristic of an entrepreneur. Innovation means the introduction of new methods in the process of production or the introduction of improvements in the existing methods. Innovation helps in increasing production and reducing costs of production.
Question 12.
Who is a Retailer?
Answer:
A trader who is engaged in Retail Trade is called a Retailer. He purchases goods from wholesalers and sells them in very small quantities to ultimate consumers. He is an intermediary between the wholesaler and consumers. A retailer is the last link in the chain of distribution of goods.
Question 13.
Double Insurance.
Answer:
Double insurance means purchasing more than one policy for the same subject. When a person purchases two are more policies for his property, he cannot claim the same amount as that of loss from different companies. If a person gets two or more policies in his life, he can claim the amount on all these policies.
Question 14.
Recurring Deposit.
Answer:
A recurring Deposit Account is open to encourage regular savings, particularly for the fixed-income group. Money in these accounts is deposited in monthly installments for a fixed period. It is repaid depositor along with interest on maturity.
Question 15.
SENSEX.
Answer:
“SENSEX” is the benchmark index of the BSE, which was launched in 1986. It is made up of 30 of the most actively traded stocks in the market, so it is also called “BSE-30”. SENSEX represents 13 sectors of the economy with a base year of 1978-89 and a value of base year was 100.
Question 16.
Capital Market.
Answer:
A Capital Market is a market that deals with long-term funds. A capital market is an institutional arrangement through which long-term funds both debt and equity are raised and invested. Equity shares, preference shares, debentures, bonds, etc. are the main instruments traded in the capital market.
Question 17.
District Forums.
Answer:
The District Forums are established by the state government. The district forum consists of a chairman and two other members one of whom shall be a woman. If the value of goods or services and the compensation claimed do not exceed ₹ 20 lakhs, then we can file a written complaint before the district consumer forum. If a consumer is not satisfied with the decision of the district forum, he can appeal before the state commission within 30 days of the Order.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
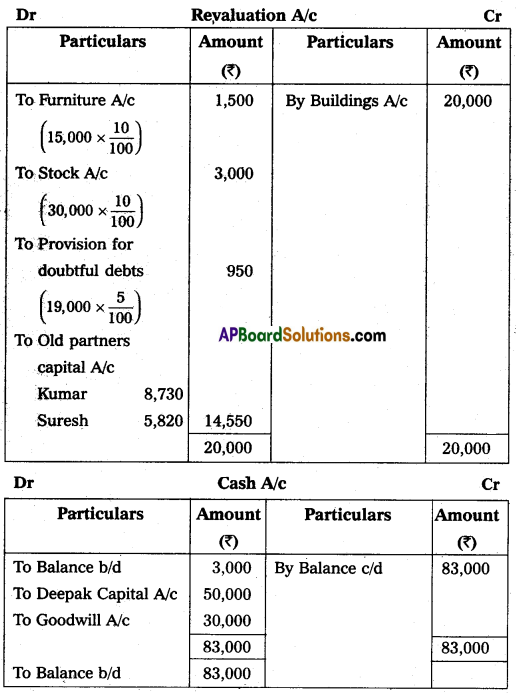
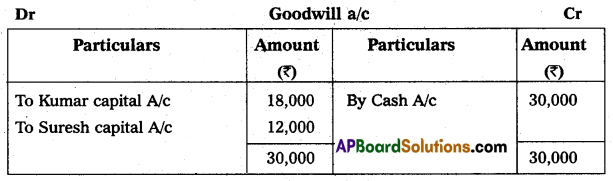
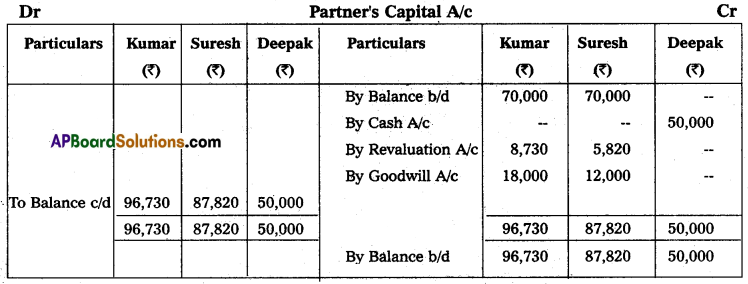
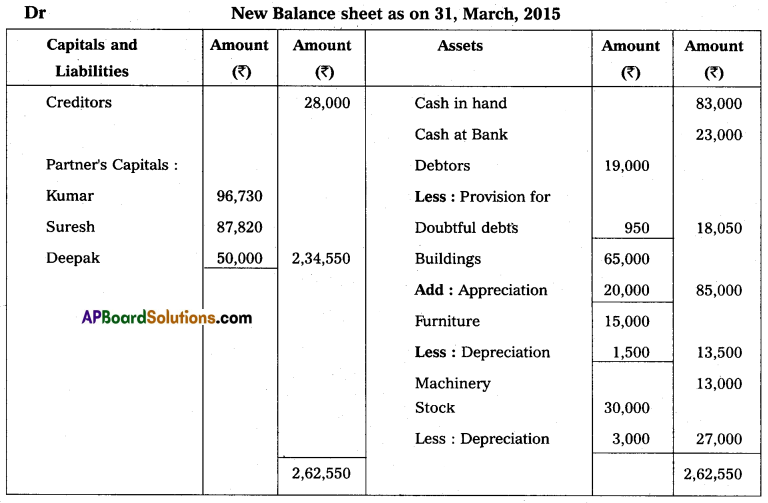
Kumar and Suresh are partners sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively. Their Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2015, was as under:
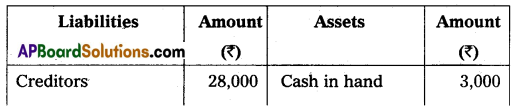
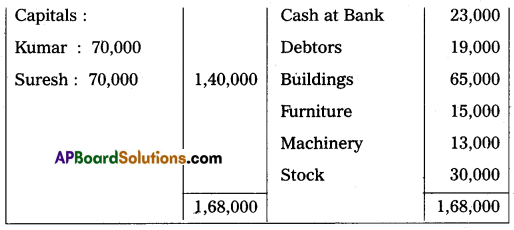
On that date, they admit Deepak into partnership for 1/3 share in future profit on the following terms:
1. Furniture and stock are to be depreciated by 10%.
2. Building is appreciated by ₹ 20,000.
3. A 5% provision is to be created on Debtors for doubtful debts.
4. Deepak is to bring in ₹ 50,000 as his capital and ₹ 30,000 as goodwill.
Make necessary Ledger Account and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Note: Answer any one of the following questions.
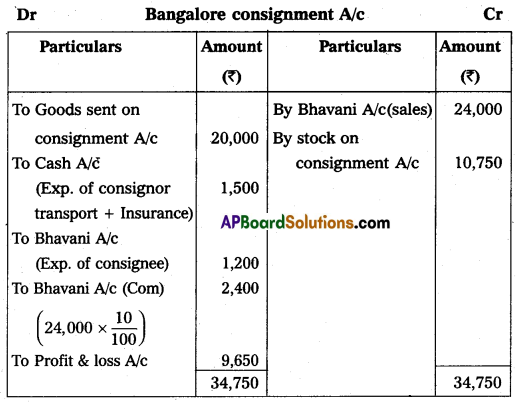
Question 19.
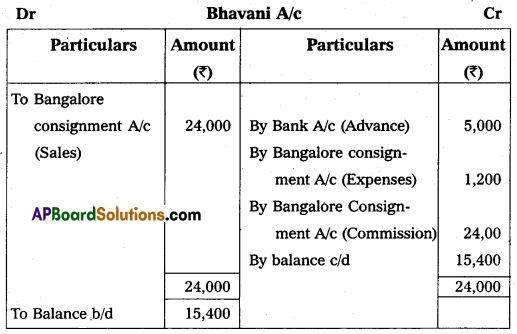
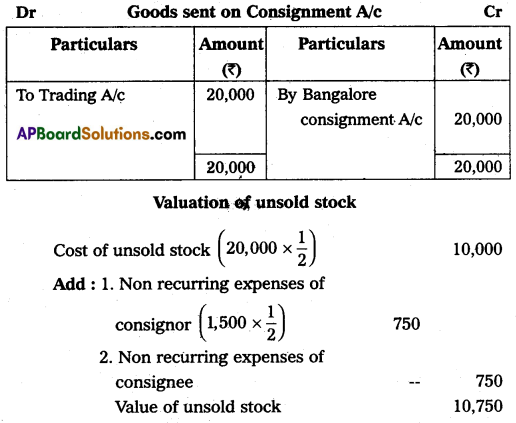
Vijaya of Vijayawada consigned goods worth ₹ 20,000 to his agent Bhavani of Bangalore on consignment. Vijaya spent ₹ 1,000, on transport, and ₹ 500 on insurance. Bhavani sent ₹ 5,000 as advance. After two months Vijaya received the account sales as follows:
(1) Half of the goods were sold for ₹ 24,000.
(2) Selling expenses were ₹ 1,200.
(3) 10% commission on sales.
Give ledger accounts in the books of Vijaya.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
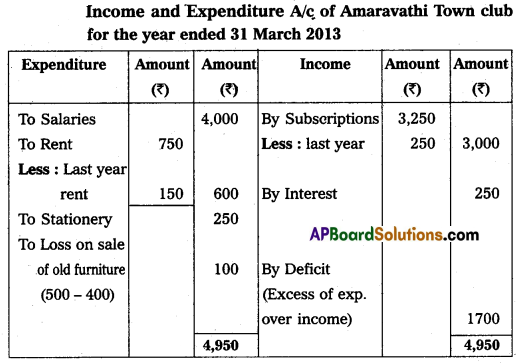
Amaravathi Town Club Provided Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31 March 2013. Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c.
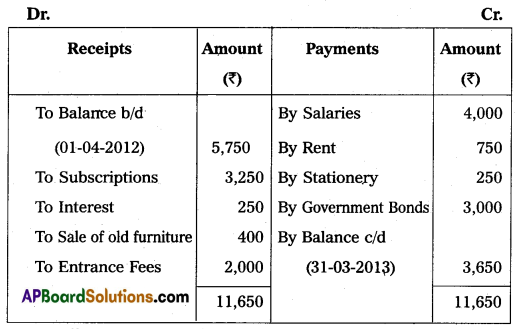
Adjustments:
1. Subscriptions include 1250 received for last year.
2. Rent includes ₹ 150 paid for last year.
3. Book value of furniture sold ₹ 500.
4. The entrance fee is to be capitalized.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Note: Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
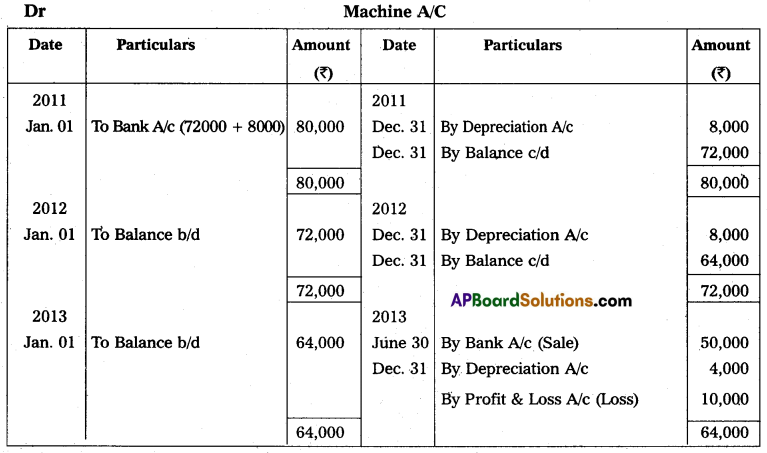
Sireesha Traders purchased a secondhand machine for ₹ 72,000 on 1st January 2011 and spent ₹ 8,000 on repairs and installed the same. Depredation is written off at 10% p.a. on the straight-line method. On 30th June, 2013 the machine was sold for ₹ 50,000. Prepare machinery accounts assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year.
Answer:
Question 22.
Satyam sold goods to Sivam worth ₹ 9,000 on 1st June, 2013 and drew a bill for 2 months for the same amount. Sivam accepted the bill and returned it to Satyam. Satyam endorsed the bill to his creditor Sundaram on 1st July 2013. The bill was honored on the due date. Pass necessary journal entries in the books of Satyam.
Answer:
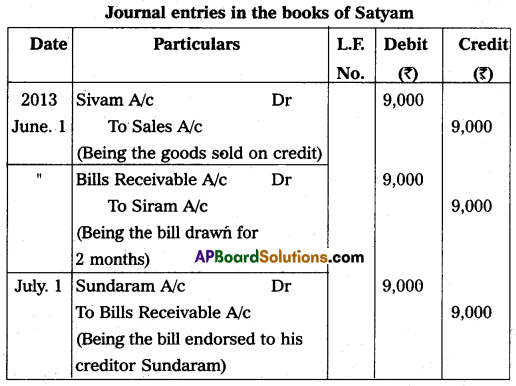
Note: On the Due Date (Aug 04, 2013) the bill is honored. So there is No Entry.
Question 23.
Explain the categories of share capital.
Answer:
Categories of share capital are given below:
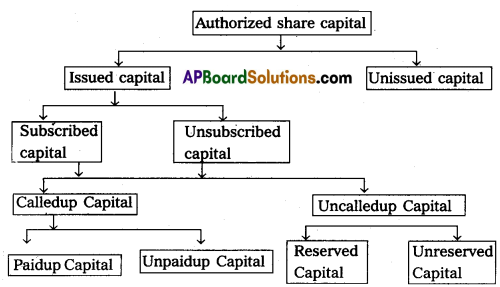
1. Authorized Capital:
Authorized Capital is the amount of share capital that a company is authorized to issue to the public by the Memorandum of Association. It is also called as “Nominal Capital” or “Registered Capital”.
2. Issued Capital:
Issued capital is part of the authorized capital which is issued to the public for subscription.
3. Subscribed Capital:
Subscribed capital is the part of the issued capital which has been subscribed by the public. This capital can be equal to or less than the issued capital.
4. Called up Capital:
Called-up capital is the part of the subscribed capital which is called up by the company to pay on the allotted shares.
5. Uncalled Capital:
Uncalled capital is that portion of subscribed capital that is not called up by the company on the shares allotted.
6. Paid-up Capital:
It is the portion of the capital called up, which is paid by the shareholders.
7. Unpaid Capital:
Unpaid capital is part of the called-up capital but not paid by the shareholders. It is also called as called-in-arrears.
8. Reserve Capital:
A company may reserve a portion of its uncalled capital to be called only in the event of the winding up of the company. Such an uncalled amount is called the “Reserve Capital” of the company.
![]()
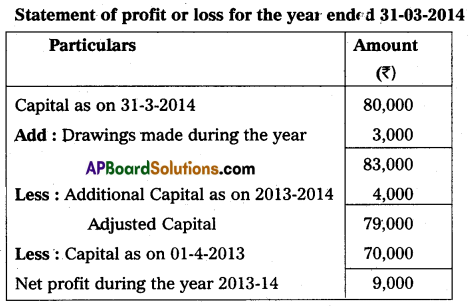
Question 24.
Mr. X keeps books in the single-entry system. Find the profit from the following particulars:
Capital on 31-03-2014 – ₹ 80,000
Capital on 01-04-2013 – ₹ 70,000
Additional capital as of 2013-2014 – ₹ 4,000
Drawings made during the year – ₹ 3,000
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each:
Question 25.
Days of Grace.
Answer:
For making the payment of the bill, the drawee is allowed three extra days after the normal due date. Such 3 days are known as ‘Days of Grace’.
Question 26.
Write any two causes of depreciation.
Answer:
- Wear and Tear: When the fixed assets are put to use in the business operations the value of such assets may decrease such a decrease in the value of assets is said to be due to wear and tear.
- Physical Forces: When the assets are exposed to the forces of nature like weather, winds, rains, etc., the value of such assets may decrease even if they are not being put to any use.
Question 27.
Del credere commission.
Answer:
To avoid the risk of Bad debts the consignor provides an additional commission known as “Del credere Commission” to the consignee Del credere Commission is paid at a predetermined percentage of Gross sales proceeds.
Question 28.
Legacy.
Answer:
An Amount received by nonprofit organizations as per the will of a deceased person is called a “Legacy”. It is treated as capital income and should be shown on the liabilities side of the Balance sheet.
Question 29.
X and Y are partners sharing profit and losses in the 1 : 2 ratio. They have decided to admit ‘Z’ by giving him 1/4 share in future profits. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio.
Answer:
The old ratio X and Y is 1 : 2
Assume total profit is 1
The new partner ‘Z’s share = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Remaining share of profit = 1 – \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
X’s new share = Remaining Share × Old Share
= \(\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Y’s new share = Remaining Share × Old Share
= \(\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{2}{3}\)
= \(\frac{2}{4}\)
∴ New Ratio of X, Y and Z = \(\frac{1}{4}: \frac{2}{4}: \frac{1}{4}\) = 1 : 2 : 1.
Question 30.
What is an equity share?
Answer:
The equity shares are also called “Ordinary shares” According to section 85 of the Companies Act 1956, an equity share is a share that is not a preference share. In other words, the shares which do not enjoy any preferential right in the payment of dividends or repayment of capital are called equity shares.
Question 31.
Ready to use.
Answer:
Ready to use is accounting software which is suitable for small organisations where the frequency or volume of accounting transactions is very low. Ready-to-use accounting software installation cost is low and easier to learn. This software’s level of secrecy is low and the software is prone to data fraud.
![]()
Question 32.
What is meant by a single-entry system?
Answer:
According to R.N. Carter, “Single entry cannot be termed as a system, as it is not based on any scientific system like Double Entry System, for this purpose, a single entry is nowadays known as preparation of accounts from incomplete records”.