Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2016 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2016 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Explain the term Insurance. Discuss the principles of Insurance.
Answer:
Insurance means protection against the risk of loss. It provides compensation against any loss or damage due to the happening of an event. It is a contract between the two parties by which one of them undertakes to indemnify the other person against a loss that may arise due to some events.
Principles of Insurance:
1. Insurable Interest:
A person cannot enter into a contract of insurance unless he has an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. It is an essential feature of insurance. Without this insurable interest, the contract of insurance will be treated as a wager or gambling contract. A person has an insurable interest in his own life or the life of his wife and a creditor has an insurable interest in the debtor.
2. Utmost Good Faith:
Insurance is based on the principle of utmost good faith. It means both the parties of the contract must disclose all the facts relating to the subject matter of insurance. If the insured does not disclose all material facts, the contract between them is void. A person who had suffered from T.B. in the past had not disclosed it in the proposal form. Later on, the insurer comes to know of this fact. He may declare the contract void.
3. Indemnity:
This is the chief principle of insurance. Indemnity means security against the risk of loss. Under this principle, the insured gets only the loss suffered by the insurer but not profits out of the contract of insurance. The principle of indemnity applies to contracts of fire and marine insurance only, but not to life insurance contracts.
4. Contribution:
Sometimes, goods are insured by more than one company. It is double insurance. The insured can get compensation only for the total from all insurance companies put together, but not the total loss from each company. The insurance companies will pay the compensation on a pro-rata basis.
5. Subrogation:
According to this principle, the insurer after compensating the loss of the insured, the right of ownership of the damaged goods is shifted from the insured to the insurance company.
Ex: Mr. X owns a scooter worth ₹ 36,000 and it was insured with an insurance company for full value. Later it was met with an accident and damaged beyond repairs. The insurance company paid the full value as compensation. Then all the rights on the scooter will be passed on to the insurance company.
6. Causa Proxima:
According to this principle, if the loss is caused by a nearest and direct factor, then only the insurer will have to bear the loss.
Ex: Biscuits in a ship are insured and are destroyed because of the seawater entered through a hole made by the mouse in the bottom of the ship and water entered into the ship. The nearest and direct cause is seawater. Hence, the insurer will have to bear the loss.
7. Mitigation of Loss:
It is the duty of the insured to take necessary steps to minimize the loss that happened due to some event. He should not act carelessly and negligently at the time of loss to the insured property.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the functions of SEBI.
Answer:
SEBI was entrusted with the twin task of both regulation and development of the securities market. It has certain protective functions.
A. Regulatory Functions:
- Registration of brokers, sub-brokers, and other players in the market.
- Registration of collective investment Schemes and mutual funds.
- Regulation of stock brokers, portfolio exchanges, underwriters, and merchant bankers, and the business of stock exchange and any other securities market.
- Regulation of takeover bids by companies.
- Calling for information by undertaking inspections, conducting inquiries, and audits of stock exchanges and intermediaries.
- Levying fee or other charges for carrying out the purposes of the Act.
- Performing and exercising such power under the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, as may be delegated by the Government of India.
B. Development Functions:
- Training for intermediaries of the securities market.
- Conducting research and publishing information useful to all market participants.
- Undertaking measures to develop the capital markets by adopting a flexible approach.
C. Protective Functions:
- Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair practices like making misleading statements, manipulations, price rigging, etc.
- Controlling insider trading and imposing penalties for such practices.
Question 3.
Who is a consumer? What are the responsibilities of a consumer?
Answer:
A consumer is the most important visitor an our premises. He is not dependent on us, we are on him. He is not an interruption to our work, he is the purpose of it. He is not an outsider to our business. He is a part of it. We are not doing him a favor by serving him. He is doing us a favor by allowing doing so. Responsibilities of a consumer.
1. Be Quality Conscious:
To put to stop adulteration and corrupt practices of the manufacturers and traders, every consumer must be conscious of the quality of the products they buy. They should look for standard quality certification marks like ISI, Agmark, Woolmark, Ecomark, Hallmark, etc. While making the purchases.
2. Beware of Misleading Advertisements:
The advertisement often exaggerates the quality of the products. Hence the consumers should not rely on the advertisement and carefully check the product or ask the users before making a purchase.
3. Responsibility to inspect a variety of goods before making a selection:
The consumer should inspect a variety of goods before buying the goods and services. For this purpose, he/she should compare their quality, price, durability, after-sales service, etc.
4. Collect Proof of Transaction:
The consumer should insist a valid documentary evidence (Cash memo/invoice ) relating to the purchase of goods or availing of any services and preserve it carefully. Such proof of purchase is required for filing a complaint. In the case of durable goods the manufacturers generally provide the warrantee/guarantee card with the product. The consumers must obtain these documents and ensure that they are duly signed, stamped, and dated. The consumer must preserve them till the warranty/guarantee period is over.
5. Consumers must be aware of their rights:
Consumers must be aware of their rights as stated above and exercise them while buying goods and services. For example, it is the responsibility of a consumer to insist on getting all information about the quality of the product and ensure himself/herself that it is free from any kind, of defect.
6. Complaint for Genuine Grievances:
As a consumer, if you are dissatisfied with the product, you can ask for redressal of your grievances. In this regard, you must file a proper claim with the company first. If the manufacturer/company does not respond, then you can approach the forums. But your claim must state the actual loss and the compensation claim must be reasonable. At no cost fictitious complaints should be filed otherwise the forum may penalize you.
7. Proper use of Product/Service:
It is expected from consumers that they use and handle the product/service properly. It has been noticed that during the guarantee period, people tend to recklessly use the product, thinking that it will be replaced during the guarantee period. This practice should be avoided.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Explain five functions of an Entrepreneur.
Answer:
The functions of Entrepreneur are:
1. Innovation:
Innovation is also different from invention. Invention implies the discovery of new ideas, new articles, and new methods, whereas innovation means the application of inventions and discoveries to make new and desired products and services that can be successfully sold in the market.
2. Risk Bearing:
Entrepreneurs in the game of business where risks and rewards are plenty will be ready to accept them.
3. Organisation and Management:
As rightly said by Alfred Marshall organization and management of the enterprise is the main function of an entrepreneur. He makes required alternations in the size of the business, its location, techniques of production, etc. The entrepreneur also undertakes managerial functions like formulation of production plans, organization of sales, and personnel management.;
4. Business Planning:
The entrepreneur must provide logical and scientific basics for planning the business operations, the need for raw materials and men, production schedules, etc. For systematic business planning, the entrepreneur must be able to formulate goals, policies, procedures, programs, and budgets.
5. Decision Making:
Another important function discharged by the entrepreneur is decision-making. He has to make decisions regarding the activities of the enterprise.
Question 5.
Explain five characteristics of Entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Characteristics of Entrepreneurs are:
- Innovation: Entrepreneurs deal with the changes. He does not continue with the old ideas.
- Risk Taking: Any new business poses a risk for entrepreneurs. They may succeed or fail. Entrepreneur takes risks.
- Self-Confidence: They have the confidence that they can change their existing position.
- Hard Work: Entrepreneurs are hard workers. Few people in our society work harder than entrepreneurs.
- Goal Setting: Entrepreneurs get happiness by setting and striving for goals. They may not always achieve those goals.
- Accountability: Entrepreneurs take success or failure in their stride.
- Leadership: Leadership represents an abstract quality of a man.
- Managerial Skills: The entrepreneur requires the managerial skill to achieve the goals of the enterprise.
![]()
Question 6.
Distinguish between Home Trade and Foreign Trade.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Home trade and Foreign trade.
| Home Trade | Foreign Trade | |
| 1. Trade | Trade carries within the country. | Trade carried with other countries. |
| 2. Currency | It does not involve any exchange of currency. | It involves the exchange of currencies. |
| 3. Restrictions | It is not subjected to any restrictions. | It is subject to many restrictions. |
| 4. Risk | Transport costs and risks are less. | Transport costs and risks are higher. |
| 5. Nature | It consists of sales, transfer, or exchange of goods within the country. | It involves the import and export of goods. |
| 6. Transport of Goods | The movement of goods depends on internal transport systems, e.g.: Roads and railways. | The movement of goods takes place usually by sea wherever possible. |
| 7. Specialisation | It helps to derive benefits of specialization within the country. | It helps all trading countries to derive the benefits of specialization. |
Question 7.
Explain the main five advantages of SEZ.
Answer:
Advantages: The following major benefits can be attributed to Special Economic Zones (SEZ).
- Employment generation: Special Economic Zones are considered to be highly effective tools for job creation.
- Economic development: India can be made a transformed economy if special economic zones are implemented properly because special economic zones are engines for economic development.
- Growth of labor-intensive manufacturing industry: The establishment of special economic zones may lead to faster growth of the labor-intensive manufacturing and service industry in the country.
- Balanced Regional Development: Special economic zones are beautifully crafted initiatives for achieving balanced regional development.
- Capacity building: Special economic zones are necessary for stronger capacity building.
- Export promotion: Special economic zones induce dynamism in the export performance of a country by eliminating
- Distortions resulting from tariffs and other trade barriers
- The corporate tax system and excessive bureaucracy.
Question 8.
Explain five benefits of Transport.
Answer:
1. Movement of Goods:
The first and most important function of transport is the movement of goods. The raw materials have to move from their sources to the factory. The manufactured goods have to move from the factory to the consuming areas.
2. Transport Enhances Mobility of Labour and Capital:
An efficient network of transport services encourages the movement of people from one place to another labour can migrate to the place where they can get better job opportunities which reduces exploitation of labour.
3. Creation of Place Utility:
It moves goods from places where they are abundant to places where they are scarce and thus creates place utility.
4. Specialisation and Division of Labour:
Transportation facilitates the optimum utilization of the natural resources of a country. For example, the petroleum resources of Arab countries, watches of Switzerland, etc.
5. Creation of Time Utility:
With the advancement of technology, transportation time is being shortened. So, it creates time utility.
Question 9.
Distinguish between the Primary Market and the Secondary Market.
Answer:
The following are the differences between the primary market and the secondary market.
| Primary Market (New Issue Market) | Secondary Market (Stock Exchange) |
| 1. There is the sale of securities to investors by new companies or new issues by existing companies. | 1. There is the trading of existing shares only. |
| 2. Securities are sold by the company to the investor directly or through an intermediary. | 2. Ownership of existing securities is exchanged between investors. The company is not involved at all. |
| 3. The flow of funds is from savers to investors i.e. The primary market directly promotes capital formation. | 3. Enhances encashment (liquidity) of shares i.e. The secondary market indirectly promotes capital formation. |
| 4. Only the buying of securities takes place in the primary market. Securities cannot be sold there. | 4. Both the buying and selling of securities can take place on the stock exchange. |
| 5. Prices of securities are determined and decided by the management of the company. | 5. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of the security. |
| 6. There is no fixed geographical location. | 6. Located at specified places. |
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Explain the meaning of Entrepreneur.
Answer:
The word entrepreneur is derived from the French verb ‘entrepredre’ which means to undertake. He is an economic agent who united all means of production, labor, capital, and land and found the value of products that result from their employment.
Question 11.
Write two types of Entrepreneurs.
Answer:
1. Adaptive or Initiative Entrepreneur:
Entrepreneurs of this type are found in underdeveloped countries. This type of entrepreneur instead of innovating new things, just adopt the successful innovations innovated by others. However, some of the innovations made by others, may not suit the needs of underdeveloped countries. In such cases, the initiative innovators may make some changes in the innovations made by innovative entrepreneurs to suit their requirements.
2. Fabian Entrepreneur:
These entrepreneurs neither fall in the innovative entrepreneur category nor the adoptive entrepreneur category. These are very cautious people. These entrepreneurs are rigid and fundamental in approach. They follow in the footsteps of their successors. They are shy to introduce new methods and ideas. Fabian entrepreneurs are no risk-takers.
![]()
Question 12.
Entrepot Trade
Answer:
When goods are imported into a country, not for consumption in that country, but for exporting them to a third country, it is known as ‘Entrepot trade’.
e.g.: India importing wheat from the U.S. and exporting the same to Sri Lanka.
Question 13.
ATM
Answer:
ATM means Automatic Teller Machine. An ATM is an unmanned device located on or off the bank premises. The. operation mechanism is that an ATM is inserted into the ATM, and the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to a processor which activates the account. It works 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. ATMs are being used to withdraw, deposit, and transfer funds.
Question 14.
Mobile Banking
Answer:
This type of service is provided free of cost to all the customers. Under this, the customer can access his bank account on the mobile screen for services such as checking the balance, ordering a demand draft, stopping payment, or viewing the last five transactions. To avail of this facility the customer is required to have a mobile phone with a WAN facility.
Question 15.
SENSEX
Answer:
BSE Sensex is called BSE-30. Since BSE has been the leading exchange of the Indian secondary market, SENSEX is an important indicator of the Indian Stock Market. SENSEX which was launched in 1986 is made up of 30 of the most actively traded stocks in the market.
Question 16.
Capital Market
Answer:
The term capital market refers to facilities and institutional arrangements through which long-term funds, both debt and equity are raised and invested. It consists of a series of channels. Through this savings of the community are made available for industrial and commercial purposes.
Question 17.
National Commission
Answer:
National Commission operates at the National level. It settles the consumer disputes in the country. The National Commission has a President, who should be a serving or retained Supreme Court Judge the commission also comprises other members of not less than four. The president and all the members of the commission are appointed by the central government. The National Commission shall have jurisdiction to entertain consumer complaints where the value of goods and services and compensation exceeds 1 crore.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
A and B share profits in the proportions of 3/5 and 2/5, their Balance Sheet on December 31, 2014, was as follows:
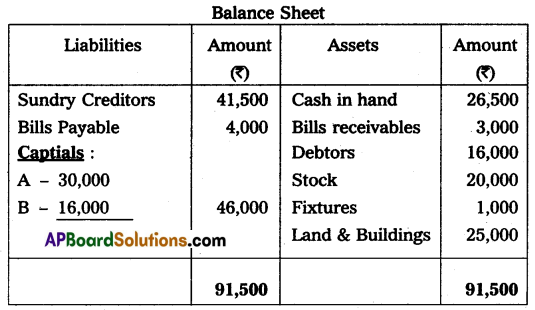
On that date ‘C’ was admitted into partnership on the following terms:
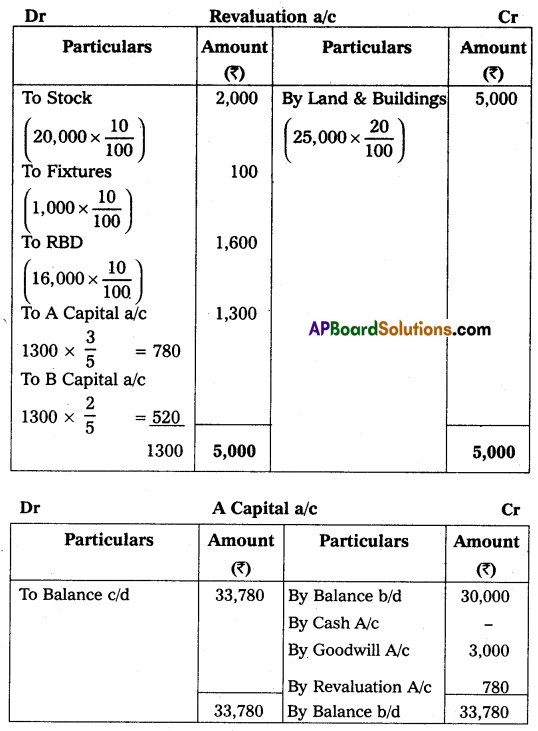
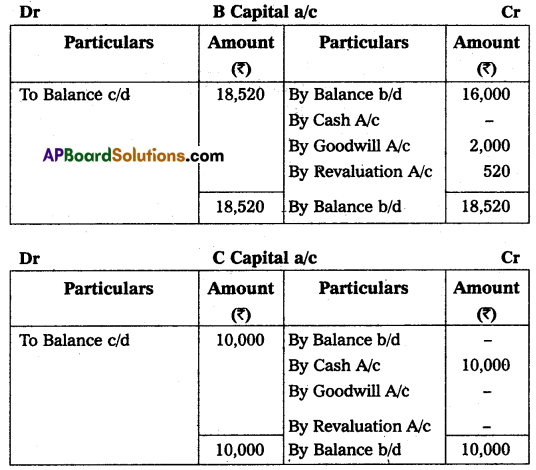
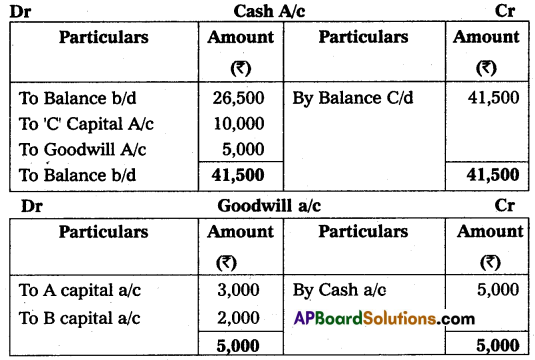
(a) That ‘C’ pay ₹ 10,000 as his Capital and ₹ 5,000 as goodwill for his 1/6 share in Profits.
(b) That stock and fixtures be reduced by 10% and 10% respectively.
(c) A provision of 10% for doubtful debts was to be created for debtors.
(d) The value of land & buildings be appreciated by 20%.
Prepare necessary Accounts and the new Balance Sheet on the admission of ‘C’.
Answer:
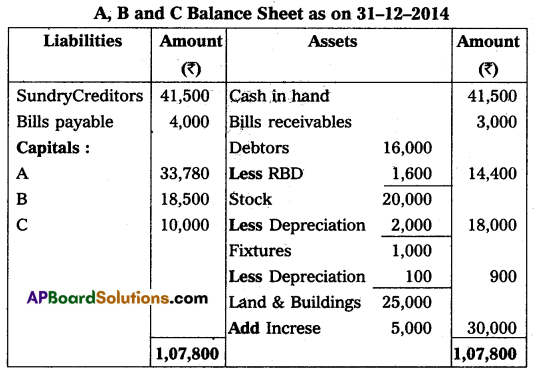
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
Krishna and Co. of Bombay consign 500 TV sets to Rama and Co. of Vijayawada. The cost of each TV set is ₹ 5,000. Krishna and Co. paid insurance ₹ 10,000 and freight ₹ 15,000. Account sales were received from Rama and Co. showing the following particulars:
(1) 400 TV sets sold each at ₹ 6,000.
(2) Advertisement expenses ₹ 20,000.
(3) Commission 10% on sales.
Rama and Co. send a bank draft for the balance due to the consignor. Show ledger accounts in the books of Krishna and Co. of Bombay.
Answer:
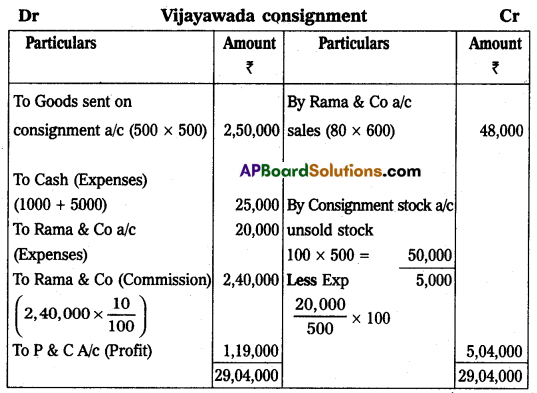
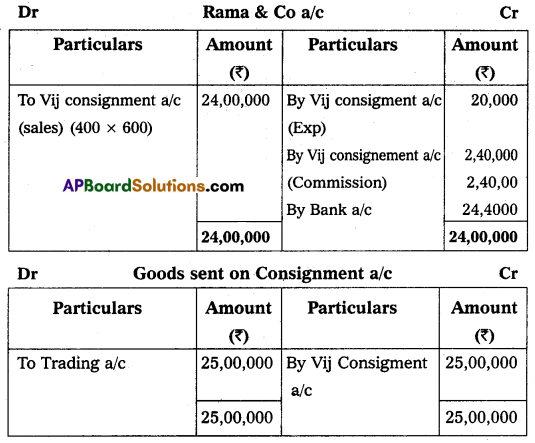
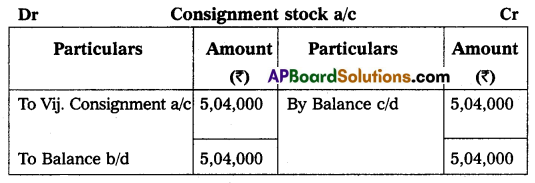
![]()
Question 20.
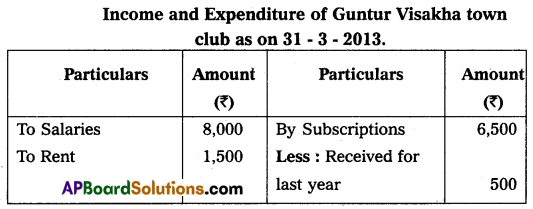
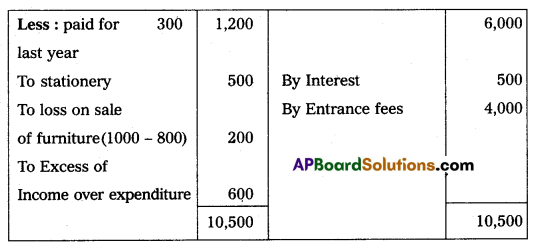
Visakha Town Club provided Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31-3-2013. Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c.
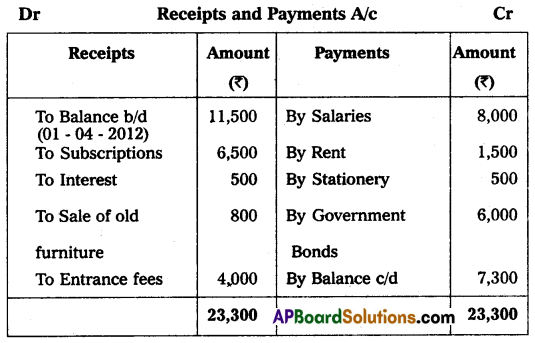
Adjustments:
1. Subscriptions include ₹ 500 received for last year.
2. Rent includes ₹ 300 paid for last year.
3. Book value of Furniture sold ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
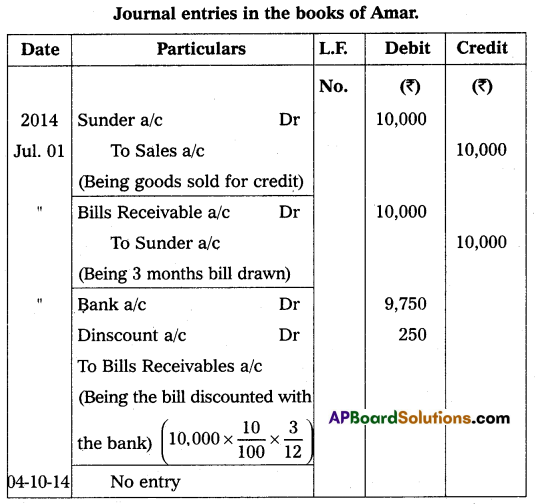
Amar sold goods for ₹ 10,000 to Sunder on credit on 1st July 2014. Amar drew a bill of exchange on Sunder for the same amount for three months. Sunder accepted the bill and returned it to Amar. Amar discounted the bill with his bank at 10% per annum on the same day. Sunder met his acceptance of maturity. Pass necessary Journal entries in the books of Amar.
Answer:
Question 22.
Suneetha Traders purchased a secondhand machine for ₹ 72,000 on 1st January 2011 and spent ₹ 8,000 on repairs and installed the same. Depreciation is written off at 10% per annum on the straight-line method. On 30th June, 2013 the machine was sold for ₹ 50,000.
Answer:
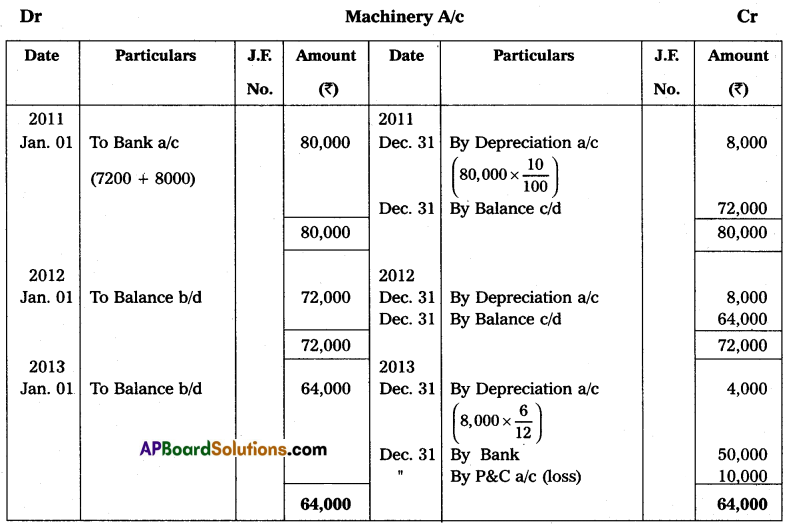
Question 23.
Explain the five categories of share capital.
Answer:
The main categories of share capital are
- Nominal (or) Registered Authorised capital: The amount of capital with which the company intends to be registered is called registered capital.
- Issued capital: A large part of the authorized capital that is offered to the public for subscription is called issued capital.
- Subscribed capital: That part of the issued capital for which applications are received from the public is called the subscribed capital.
- Called-up capital: The amount on the shares which is demanded by the company to be paid is known as called-up capital.
- Paid-up capital: That part of the called-up capital that is offered and paid by the members is known as paid-up capital.
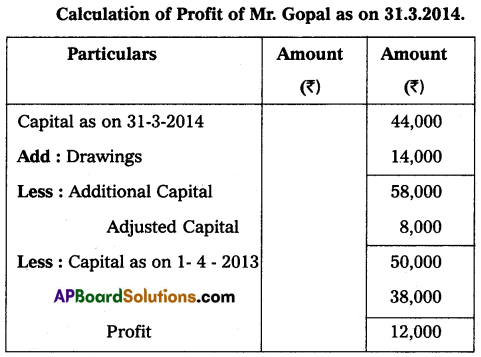
Question 24.
Mr. Gopal maintains his books on single entry method. He gives the following information:
Capital on 01-04-2013 – ₹ 38,000
Capital on 31-3-2014 – ₹ 44,000
Drawings during the year – ₹ 14,000
Additional Capital introduced during the year – ₹ 8,000
You are required to calculate profit or loss.
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
Days of Grace.
Answer:
For making the payment of the bill, the drawee is allowed three extra days after the normal due date. Such three days are known as ‘Days of Grace’, If the dire date is a public holiday previous day is the due date. If the due date is a sudden holiday, the next day is the due date.
Question 26.
What are the two causes of depreciation?
Answer:
Causes of depreciation are:
- Wear and tear
- Depletion
- Accidents
- Obsolescence
- Fluctuations
![]()
Question 27.
What is Del credere Commission?
Answer:
The consignee may sell some part of the goods on credit. When goods are sold on credit, there is always a risk of some amount of bad debt. To avoid the risk of bad debts the consignor provides an additional commission known as the Del-Credre commission to the consignee which guarantees the payment in case of a credit sale. Del credre commission is paid at a predetermined percentage of gross sale proceeds.
Question 28.
What is Legacy?
Answer:
It is the amount that a not-for-profit concern will receive as per the will of a deceased person. It should be capitalized being an item of a non-recurring nature and should be shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 29.
Partnership Deed.
Answer:
It is a document that defines the rights and liabilities of partners of the firm besides containing other matters about the conduct and management of the firm.
Question 30.
Explain the issue of shares at par (or) Face value.
Answer:
When a company issues its shares at their face value, the shares are known to have been issued at par.
Ex: The face value of the share is ₹ 100 and it is issued, for ₹ 100.
Question 31.
What is MIS?
Answer:
The computerized accounting system facilitates the real-time production of management information reports, which will help management monitor and control. The business effectively. Debtors analysis indicates the possibilities of bad debts and also the concentration of debt and its impact on the balance sheet.
![]()
Question 32.
Single Entry System.
Answer:
According to R.N. Carter, single entry cannot be termed as a system, as it is not based on any scientific system like a double entry system, for this purpose, single entry is nowadays known as the preparation of accounts from incomplete records, or single entry.