Students must practice these AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Important Questions 3rd Lesson Business Services to boost their exam preparation.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Important Questions 3rd Lesson Business Services
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define banking. Explain the functions of the banking.
Answer:
The word ‘bank’ is derived from French word ’Bancus’ which means a ‘bench’. A bank is an institution which deals with money and credit.
According to Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949, banking means “the accepting for the purpose of lending or investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by cheque, draft or otherwise”.
The basic functions of banks are classified as primary and secondary functions.
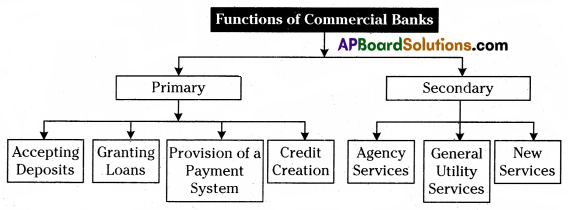
A) Primary Functions:
1. Accepting Deposits: Banks accept deposits from public.
- Fixed Deposit Account: Customer deposits money for a fixed period and can be withdrawn only on maturity. The rate of interest on this account is higher than the other types of deposits. They are also called “Time Deposits”.
- Current Deposit Account: These accounts are more suitable to the traders and businessmen because money can be deposited into and withdrawn from the bank number of times. No interest is paid on these accounts. They are also called Demand Deposits.
- Saving Deposit Account: The aim of these accounts is to encourage small savings of the public. Certain restrictions are imposed on the deposits and number of withdrawals and the amount to be withdrawn.
- Recurring Deposit Account: The purpose of these accounts is to encourage regular savings by the fixed income group. A fixed amount is deposited in monthly installments for a fixed period. It is repaid to the depositor along with interest on maturity. The rate of interest is nearly same as on fixed deposits.
2. Granting Loans: Commercial banks grant loan which is accepted through the deposits. The different form of granting loans are –
- Money-at-Call and Short Notice: These loans are granted for one day to fourteen days. These loans are inter bank loans.
- Cash Credit: The bank agrees to lend money to the borrower up to certain limit. The amount is credited to customer account. Customer draws the money as and when he needs. Interest is charged only on the actual amount drawn.
- Loans: Loan is given for a fixed period at an agreed rate of interest. Loan is granted against security of property.
- Overdraft: The bank provides overdraft facility to its customers through which they allowed to withdraw more than their deposits. Interest is charged on bank overdraft amount.
- Discounting Bill of Exchange: The bill holder may be in urgent need of cash before maturity period, he may sell the bill to bank at less than actual amount.
3. Provision of a Payment System: The depositor directs the bankers to make payment to the payee through cheque.
4. Credit Creation: Banks have the ability to create credit many times more than the deposits.
B) Secondary Functions: In addition to the main functions, banks provide various banking services.
1. Agency Services:
- Banks help their customers in transferring funds from one place to another through cheques, drafts, etc.
- Banks collect and pay various credit instruments like cheques, bill of exchange, promissory notes, etc.
- Banks undertake purchase and sale of various securities like shares, bonds, debentures, etc. on behalf of their customers.
- Banks preserve the wills of their customers and execute them after death.
2. General Utility Services:
- Banks issue a letter of credit and help in Foreign Trade.
- Banks issue traveller cheques to travel without fear.
- Banks provide safe deposit lockers facilities for the safe custody of valuables.
- Acceptance and collecting foreign bills of exchange.
3. New Services:
- Free cheque book,
- Anywhere banking,
- Free internet banking.
Question 2.
Discuss the principles of Insurance. [May ’22; Mar. ’17 (AP)]
Answer:
Insurance means protection against risk of loss. It provides compensation against any loss damaged due to the happening of an event. It is a contract between two parties- insurer and insured. The following are the principles of insurance.
1. Insurable interest: A person cannot enter into a contract of insurance unless he has insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Without insurable interest the contract of insurance will be treated as a gambling contract.
Ex: A person has an insurable interest on his own life and also in the wife’s life.
2. Utmost good faith: A contract of insurance is based on utmost good faith. Both the parties must disclose all the facts relating to subject matter of insurance; otherwise the contract between the parties becomes void.
Ex: A person who had suffered from T.B in the past had not disclosed in the proposal form; later on the insurer comes to know of the fact, the contract is void.
3. Indemnity: Indemnity means security against risk of loss. According to this principle, the insured may not collect more than the actual loss in the event of damage. The insured gets only the loss suffered from the insurer, but not profits. This principle applies to contract of fire and marine insurance but not to life insurance contracts.
4. Subrogation: According to this principle, the insurer after compensating the loss of insured goods the right of ownership on damaged goods is shifted from insured to the insurer. This principle is not applicable to the life insurance.
Ex: Mr ‘A’ insured car Rs. 2,00,000 with an insurance company. Later it was met with an accident and ‘irreparable’. The insurance company paid the full value as compensation and handed over the damaged car.
![]()
5. Contribution: Sometimes goods are insured with more than one insurance company. It is double insurance. The insured can get compensation only total loss from all insurance companies put together but not total loss from each company. It is not applicable to life insurance.
Ex: Lorry was insured with X Co. & Y Co. for 2,00,000,1,00,000 respectively. Later it was met with an accident and loss is estimated at Rs. 75,000. Both companies contribute Rs. 75,000 in the ratio of 2 : 1.
6. Causa Proxima: According to this principle, the loss is caused by nearest and direct factor then only insurer will have to bear the loss.
Ex: Ship carrying sugar to another country through sea water and due to some sea animals broken the ship, sugar diluted in water. It is the nearest and direct cause, hence insured will get loss.
7. Mitigation of Loss: It is the duty of the insured to take necessary steps to minimise loss happened due to some events. Insured should not act carelessly at the time of loss.
Question 3.
Define Life Assurance Policy. What are the kinds of Life Assurance Policies?
Answer:
Nowadays human lives are always exposed to some kind of risks. Hence life insurance policy was introduced as a protection against risks. According to R.S. Sharrna “Life Insurance refers to a contract, whereby the insurer, in consideration of a premium paid either in lumpsum or in periodical installments undertakes to pay an annuity of a certain sum of money either on the death of the insured or on the expiry of a certain number of years”.
Kinds of Life Insurance Policies: Some of the popular types of Life Insurance Policies are –
a) Whole life policy: It runs throughout the life of the policy holder. Premium is low and covers high risk. The policy sum assured is payable after the death of the policy holder.
b) Endowment policy: This policy is taken up for a specific period, 10,15 or 20 years. The policy will mature on the expiry of a specific period or the death of the insured whichever is earlier. The premium is higher than whole life policy.
c) Joint life policy: A policy may be taken jointly on the lives of two or more persons. On the death of any person the policy is paid to other surviving policy holder.
d) Annuity policy: Under this policy an insured would deposit a lumpsum amount with the insurance company. The amount of policy would be paid to the insured after a specific number of years or death of the assured.
e) Children’s endowment policy: This policy is taken by a person for his children to meet the expenses of their education and marriage. A certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age.
Question 4.
What do you understand by the word Transport? Discuss the benefits and limitations of transport. [March 2019]
Answer:
Physical movement of men and goods from one place to another wherever they are required is called ‘Transportation’. It is an integral part of commerce. Transport helps the businessmen to reach consumers. Transport gives place utility and time utility.
Transportation can be defined as “a means through which goods are transferred from one place to another”.
Functions / Benefits of Transport:
1. Movement of goods: The raw materials have to move from the place of supply (sources) to the factory. The manufacture goods have to move from the factory to the consuming areas. It is only by means of transportation.
2. Transport enhances the mobility of labour and capital: Transport encourages the movement of people from one place to another. Labour can migrate to the place where they can get better job opportunities.
3. Creation of place utility: Transport creates place utility. It moves goods from those places where they are abundant to the place where they are scarce.
4. Specialization and division of labour: Transportation facilitates optimum utiliza-tion of natural resources of a country. For example – watches of Switzerland, petroleum resources of Arab countries.
5. Creation of time utility: With the advancement of technology, transport time is being shortened. So it creates time utility.
6. Stability in prices: Surplus goods are transported to the places where scarcity exists, thereby prices are equalised throughout the country.
7. Contribution to national income: The transportation also contributes towards national income of a nation. For example, our railways.
8. Economies of large scale production: Transport has helped the development of large scale industries. Transport facilitates to get raw material, labour and sell the finished goods.
9. Improves standard of living: Availability of wide variety of goods at reasonable price improves standard of living.
10. National defence: Transport strengthens national defence transport system. During war period all the personnel, material and equipment can be moved rapidly to the border areas.
Limitations:
- Cottage and small scale industries lost their glory: With transport facilities, labour is showing interest to work in big factories and cities. This has led to shortage of workers in tiny and small scale industries.
- Accidents: Improvement of transport facility has given rise to a new problem, viz., accidents.
- High urbanization: Improved means of transport has helped in creating big cities, which leads to concentration of population in cities. This gives many problems like housing, pollution and health.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the Road Transportation. Explain the kinds of roads in India. [Mar. ’17(AP)]
Answer:
Road transport is the oldest form of transport. It is suitable for short distance, door to door collection and delivery of goods. It is most suitable for perishable goods. Modes of road transport are bullock carts, tonga, rickshaws and motor vehicles.
Indian roads are classified into three types – National Highway, State Highway, District and rural roads.
Kinds of Roads in India:
a) National Highway: These roads are meant for interstate transport and movement of defence force. They also connect the state capitals, major cities, etc. The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has the responsibility of development, maintenance and operation of National Highways.
b) State Highways: These are constructed and maintained by the state governments. They join the state capital with district headquarters and other important towns.
c) District Roads: These roads are the connecting link between district headquarters and other important roads of the districts. They account for 14% of the total road length of the country.
d) Rural Roads: These roads provide links to the rural areas. These are about 80% of total length in India are categorized as rural roads.
e) Border Roads: These roads are in the northern and north eastern boundary of the country. The Border Roads Organisation constructs and maintains Border Roads, constructs roads in altitude areas and undertakes snow clearance.
f) International Highways: These are meant to promote the harmonious relationship with the neighbouring countries by providing effective links with India.
Question 6.
Explain the warehouse concept and its significance.
Answer:
The term ‘ware’ means the article of Merchandise, warehouse is a building or room for storing goods. Warehousing is the process of proper storage and handling of goods using scientific methods.
Significance:
- Some commodities are produced in a particular season only, but they are used throughout year. Hence warehouse is needed.
- Some products are produced throughout the year but their demand is seasonal. Hence to meet demand warehouses are needed.
- The companies which opt for large scale production and bulk supply warehouse is needed.
- Warehousing helps companies ensure quick supply of goods iri demand.
- Warehousing helps companies for continuous production of goods and their movement of goods.
- Warehousing helps for price stabilization of goods by supplying them to the market as per demand.
- Another important need of warehousing is for bulk breaking.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define services and goods.
Answer:
Services are those separately identifiable, intangible activities that provide satisfaction of wants and are not necessarily linked to the sale of a product or another service.
Goods are those having homogeneous, tangible and separation of production and consumption. They can be stored, and involvement at the time of delivery not possible.
Distinction between Services and Goods:
| Services | Goods |
| 1. Nature: Activity or process. Eg: Watching a movie in a cinema hall. |
A physical object. Eg: Video cassette of a movie. |
| 2. Type: Heterogeneous. |
Homogeneous. |
| 3. Intangibility: Intangible. Eg : Doctor treatment. |
Tangible. Eg: Medicine |
| 4. Inconsistency: Different customers having different demands. Eg: Mobile services. |
Different customers getting standardized demands fulfilled. Eg: Mobile phones. |
| 5. Inseparability: Simultaneous production and consumption. Eg: Eating ice cream in a restaurant. |
Separation of production and consumption. Eg: Purchasing ice cream from a store. |
| 6. Inventory: Cannot be kept in stock. Eg: Experience of a train journey. |
Can be kept in a stock. Eg: Train journey tickets. |
Question 2.
What are the advantages of E-Banking? [May 2022]
Answer:
E-Banking advantages:
- It reduces cost: The cost of banking transaction is considerably reduced. It increases the profitability of banks.
- Prompt in Service: E-Banking provides prompt service.
- Anywhere and anytime banking: E-Banking is 24 hours in a day and 7 days in a week banking service. The customer can obtain information on his account, conduct transactions from his home or office.
- Cashless banking: Handling of cash is not necessary in E-Banking.
- Global coverage: It provides global network coverage of bank services.
- Central data base: The data base of each branch is centralized. Customer can deposit, withdraw or remit money from any branch of his bank.
Question 3.
What is the Mobile Banking? What are the services that can be obtained through Mobile Banking?
Answer:
The delivery of bank services to a customer through mobile (cell) phone is called Mobile banking. Mobile banking scope is more and effective when compared to telephone banking. It can take the form of SMS banking, GSM SIM Tool Kit and WAP.
a) SMS Banking: Short messages are sent to the customer’s mobile phones. Customer receives information about his account balance after a certain operation is performed.
b) GSM SIM Tool Kit: GSM SIM Tool Kit is software. Mobile phones having GSM SIM Tool Kit software, support the special sim card and activate with the permanent bank branch. The client can use this service.
c) WAP (Wireless Application Protocol): Unlike web pages appearing on the computer monitor, WAP presents its output display on a small mobile phone. Few banks are providing this service.
Question 4.
What are the facets of electronic banking? [Mar. 2020,’19 (AP)]
Answer:
The different facets of e-banking are –
1. ATM: ATM means Automated Teller Machine. The customer gets fast cash withdrawal, transfer, payment of bills or cash deposit through ATM. They are located in bank and also in different places of city. ATM is linked to the host computer. Each customer is given debit card, which helps to withdraw cash from ATM; subject to the availability of balance in his account.
2. Tele Banking (Home Banking): Customers can perform a number of transactions from their telephone such as customer verification, account balance, transfer funds from one account to another, payment of bills, etc.
3. E-mail Banking: Bank communicates information to the customer by e-mail. Bank sends account statements periodically to the customers.
4. Network Banking or Online Banking: It is a facility provided by the banks. The customer can transact the business through internet by sitting at home. Customer need not visit bank personally.
5. Mobile Banking: The delivery of bank services to a customer through mobile (cell) phone is called mobile banking. It is more effective than Tele banking.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the term Insurance. Explain the functions of Insurance. [May ’17(AP)]
Answer:
Insurance means protection against risk of loss. It provides compensation against any loss damaged due to the happening of an event. It is a contract between two parties- insurer and insured.
Functions of Insurance:
- Providing Certainty: Insurance provides certainty of payment for the risk of loss. The insurer charges premium for providing the certainty.
- Protection: Insurance can provide protection from probable chances of loss. Insurance cannot stop the happening of a risk but can compensate losses.
- Risk Sharing: The risk of loss is shared by all the insured out of premiums.
- Assist in Capital Formation: The insurer utilises the premiums accumulated, which are invested in various income generating schemes.
Question 6.
Explain the costs and benefits of Insurance.
Answer:
Insurance provides number of advantages to the common people, trade and government.
- Provides Security: Insurance provides protection against risk of loss due to happening of events. It covers both life and non-life aspects.
- Distribution of Loss: Insurance helps to distribute the losses of any uncertain events among large number of policy holders.
- Generates Capital: Insurance is an important source of funds for capital formation. It leads to economic growth and full employment.
- Increases Efficiency: Insurance reduces the risk and increases the efficiency in business. It provides security for business community.
- Earns Foreign Exchange: Insurance provides security to the international traders, shippers and banking institutions for expansion of foreign trade. It leads to secur¬ing foreign exchange.
- Social Security: Insurance acts as an instrument to fight against evils of poverty, unemployment, old age, sickness, accidents, etc.
- Promotes Thrift: It encourages the people to go for savings a certain sum of money regularly.
- Enhancement of Credit: A trader can easily get loans from banks or financial institutions on the security of insured property.
Question 7.
What are the advantages of Life Insurance Policies? [Mar. ’18(AP)]
Answer:
- Encourages savings habit: The insured has to pay premiums to the insurance company every year. Hence it promotes habit of savings among the people.
- Policy can be mortgaged: Insured can get loans against mortgage of policy in insurance companies, financial institutions to meet emergency needs.
- Tax benefits: Policy holder is exempted from income-tax for premium paid to the insurance company.
- Protection: It provides a protection to the family members if the owner expires suddenly.
- Capital formation: It helps in capital formation and economic development of the country.
- Provides social security: Life insurance provides social security to the policy holders in the form of old age pensions, health insurance, accidents, children’s marriage, education, etc.
Question 8.
Explain the characteristics of a Marine Insurance.
Answer:
Characteristics of a Marine Insurance:
- Fundamentals of general contract: Marine insurance must have the fundamentals of general contract, i.e. insurable interest, utmost good faith, indemnity, subrogation, contribution, etc.
- Consideration: It is a contract between the insured and the insurer. Hence the insured has to pay premium amount periodically to the insurer to bear the risk.
- Coverage of insurance: Marine insurance covers a large number of risks such as sinking of the ship, burning, collusion of ships, sea dacoities, etc.
- Mode of insurance: In this insurance may be for a single journey or number of journeys or for a specific period of time.
- Indemnify the losses: The insurers guarantee to indemnify the losses caused by sea perils only.
- Condition of compensation: The insured is compensated only when the loss is occurred to the ship or cargo.
Question 9.
Define Fire Insurance. Explain characteristics.
Answer:
Sec 2 (6A) of Insurance Act, 1938 defines fire insurance as “The business of effecting, otherwise than incidental to some other class of insurance business, contract of insurance against loss by / or incidental or fire or other occurrences customarily included among the risk insured against in fire insurance policies.
Features or Characteristics:
- Contract of indemnity: The fire insurance is a contract of indemnity and the insured can get only value of goods lost or damaged.
- Lawful consideration: The consideration in the fire insurance contract is premium paid by the insured which is essential element of contract.
- Insurable interest: The insured must have insurable interest in the property insured against fire.
- Claim over residue: Ownership on damaged goods is passed on to the insurer after payment of claim to the insured.
- Cause of accident: Loss must be the outcome of fire but not other reasons.
- Utmost good faith: In fire insurance, both insured and insurer must have utmost good faith on each other.
![]()
Question 10.
Briefly state the advantages and disadvantages of Road Transportation.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Less capital: It requires less capital for construction of roads and is maintained by the government.
- Door-to-Door service: Road transport provides door delivery facilities for all concerns.
- Service to rural areas: Exchange of goods between villages and towns is possible by road transport.
- Low maintenance: The maintenance charges are much less than that of railways.
- Flexible service: Road vehicles are very flexible. The routes and timings can be adjusted to the individual requirements.
- Suitable for short distance: It is more economical and quicker for carrying goods for short distances.
- Rapid speed: Road transport reduces the effective duration of the transit.
Disadvantages:
- Less reliable: Road transport cannot be relied upon long distance during rainy or flood seasons.
- Accidents and breakdown: There are more chances of accidents and breakdowns in case of motor transport.
- Lesser speed: The speed of motor transport is comparatively slow.
- Limited carrying capacity: Load carrying capacity of road transport is limited.
- More expensive: The road transport is more expensive than railway transport for long distances.
Question 11.
State various advantages and disadvantages of Railway Transportation.
Answer:
Advantages:
- It facilitates long distances travel and transport of bulky goods.
- It is a quick and regular form of transport.
- It helps in the industrialization process of a country.
- It helps in the quick movement of goods from one place to another at the time of emergencies.
- It encourages mobility of labour for employment.
- The carrying capacity of the railways is extremely large.
Disadvantages:
- The railway requires a large investment of capital for construction, maintenance.
- It is inflexible. Its routes and timings cannot be adjusted to individual requirements.
- It cannot provide door to door service.
- Rail transport is unsuitable and uneconomical.
- It involves much time and labour.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
ATM:
Answer:
ATM means Automated Teller Machine. The customer get fast cash withdrawal, transfer, payment of bills or cash deposit through ATM. Each customer is given debit card, which helps to withdraw cash or transfer from ATM. They are located in banks and also junctions of city.
Question 2.
Online Banking:
Answer:
It is the facility provided by the banks. The customer can transact the business through internet by sitting at home. Customer need not visit bank personally.
Question 3.
Tele Banking:
Answer:
Customers can perform a number of transactions from their telephone such as verifying account balance, transferring, funds from one account to another account, payment of bills, etc.
Question 4.
Mobile Banking: [Mar. (AP) ’17]
Answer:
The delivery of bank services to a customer through mobile (cell) phorte is called Mobile Banking. It is more effective than Tele Banking.
![]()
Question 5.
Electronic Banking:
Answer:
The delivery of banks service to a customer at his office or home by using electronic delivery channels may be called Electronic Banking. Through computer various transactions like cash receipts, payments transfer of funds are done.
Question 6.
Differenciate Insurer and Insured.
Answer:
Insurer: The party who agrees to pay money on the happening of an event is known as insurer. Insurers are risk bearers.
Insured: The party who seeks protection against the risk by paying premium is called insured. He receives money as compensation.
Question 7.
What is Premium?
Answer:
Amount paid to the insurer periodically by the insured for giving protection against risk of loss.
Question 8.
Define Insurance. [May 2022]
Answer:
Insurance means protection against risk of loss. It provides compensation against any loss damaged due to the happening of some events. It is a contract between two parties insurer and insured.
Question 9.
Re-insurance: [May ’17(AP)]
Answer:
If a company undertakes more risks than its capacity, then it tries to share the risks with some other insurance company. When the insurance company insures complete or part of the risk with other insurance company, then it is called “Re-insurance”.
Question 10.
Double Insurance: [Mar. 2019, ’18 (AP)]
Answer:
When more than one insurance policy is taken on the same subject matter, it is called “double insurance”. In life insurance any number of policies can be taken out by the insured upon his life. He can collect full amount from all policies. But it is not possible in other insurances.
Question 11.
What is subrogation?
Answer:
According to this principle, the insurer after compensating the loss of insured, the right of ownership on damaged goods is shifted from insured to the insurer. This principle is not applicable to the life insurance.
Question 12.
What is proximate cause (causa proxima)?
Answer:
According to this principle, the loss is caused by nearest and direct factor (cause) then only insurer will have to bear the loss.
Question 13.
What is Insurable Interest?
Answer:
A person cannot enter into a contract of insurance unless he has insurable interest in the subject matter of the insurance. It is essential feature of insurance. Without this insurable interest, the contract of insurance will be treated as a gambling contract.
Question 14.
Endowment policy:
Answer:
Endowment policy is taken up for a specific period. The policy will mature at the expiry of a specified period or death of insured whichever is earlier. The premium is higher than whole life policy.
Question 15.
Whole life policy: [March 2020]
Answer:
It runs throughout the life of the policy holder. Premium is low and covers high risks. The policy sum assured is payable after the death of the policy holder.
Question 16.
Name the subject matters of Marine Insurance:
Answer:
There are three things involved in Marine Insurance.
- Ship or hull insurance: When the ship is insured against any type of danger, it is called “Hull insurance”.
- Cargo insurance: The goods on transhipment are known as ‘cargo’. If an insurance policy is taken against the risk of cargo, then it is cargo insurance.
- Freight Insurance: The shipping company will not get freight if goods are lost during transit. To avoid such loss, the shipping company may insure the freight to be received which is known as “Freight insurance”.
Question 17.
What is Cargo Insurance?
Answer:
The goods on transhipment are known as ‘cargo’. If an insurance policy is taken against the risk of cargo, then it is cargo insurance.
Question 18.
What is Freight Insurance?
Answer:
The shipping company will not get freight if goods are lost during transit. To avoid such loss, the shipping company may insure the freight to be received which is known as “Freight insurance”.
Question 19.
Essentials of Fire Insurance:
Answer:
The essentials of Fire insurance are a) Contract of indemnity, b) Lawful consideration, c) Insurable interest, d) Subrogation, e) Causes of accident and f) Utmost good faith.
![]()
Question 20.
National Highway:
Answer:
These roads are meant for interstate transport and movement of defence force. They are connected to the state capitals, major cities, etc. The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has the responsibility for development, maintenance and operation of National Highways.
Question 21.
Pipelines:
Answer:
Pipeline transport is used for the movement of liquid commodities such as crude oil, natural gas and petroleum products. It is a continuous movement at a relatively low cost. They are dependable, fuel efficient and involve less losses and damages. They are much economical for carrying oil.
Question 22.
Bonded warehouse: [Mar. ’18(AP)]
Answer:
Bonded warehouses are owned and operated by Port Trust Authorities. They will be located near the ports and airlines. The importers store goods until customs duties are paid.
Question 23.
The significance of warehouse:
Answer:
Significance of warehouse are:
- To supply seasonal produced commodities
- To supply seasonal demanded commodities
- Warehouses help to keep the stable prices for goods.
- Warehouses help in maintaining continuous sales.
Question 24.
Cash Credit:
Answer:
It is an arrangement made by the bank which agrees to lend money to the borrower up to a certain limit. The amount is credited to the account of the borrower. The borrower draws money as and when needs. Interest is charged only on the amount actually drawn.
Question 25.
Bill discounting:
Answer:
The holder of the bill may be in urgent need of cash before the date of maturity. He may sell the bill to his bank at lesser amount than the actual amount.
Question 26.
Recurring deposit: [March 2019]
Answer:
The depositer is required to deposit a fixed amount of money every month for a specific period, i.e. 12 months to 10 years. After the completion of the period, the customer gets back all his deposits along with the accumulated interest on the deposits.