Access to a variety of AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity. question patterns.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2018
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section – ‘A’. Answer any six questions in
Section – ‘B’ and any two questions in Section – ‘C’. - In Section – A, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section -”’8′, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section – ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Section – ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all the questions.
Question 1.
Define osmotic pressure.
Answer:
The pressure required to prevent the inflow of solvent molecules into the solution through a semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure (71).
Question 2.
What are antibiotics ? Give an example.
Answer:
Antibiotics: The chemical substances produced by micro organisms and inhibit the growth or destroy micro organisms are called antibiotics.
(Or)
The substance produced totally or partly by chemical synthesis which in low concentration inhibits the growth (or) destroy micro organism by intervening in their metabolic process are called antibiotics. E.g. : Penicillin, Chloramphenicol etc.
![]()
Question 3.
What is PHBV? How is it useful to man?
Answer:
Poly P – hydroxy butyrate – CO – P – hydroxy Valerate (PHBV) :
It is a Copolymer of 3 -hydroxy butanoic acid and 3 – hydroxy pentanoic acid.
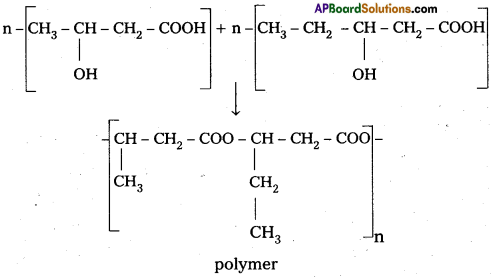
Properties & Uses :
The properties of PHBV vary according to the ratio of both the acids, 3-hydroxy butanoic acid provides stiffness and 3-hydroxy pentanoic acid imparts flexibility to copolymer. It is used in medicine for making capsules. PHBV also undergoes degradation by bacteria.
Question 4.
A solution of OuSO4 is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode.
Answer:

Question 5.
What are food preservatives ? Give an example.
Answer:
The chemical substances which prevent the spoilage of food due to microbial growth are called food preservatives. E.g.: Sodium benzoate, Salt of sorbic acid etc.
Question 6.
What is Ziegler-Natta catalyst?
Answer:
A mixture of Tri alkyl aluminium and titanium chloride is called Ziegler – Natta catalyst.
E.g. : (C2H5)3 Al + TiCl4
Question 7.
Why does NH3 act as a Lewis base?
Answer:
NH3 molecule is an electron rich hydride. It has high electron density. It donates electron pair and forms co-ordinate covalent bond with other substances. So NH3 act as a Lewis base.
NH3 + H+ → (NH3 → H+</sup)→ NH4+
Question 8.
What is flux? Give an example.
Answer:
Flux : An outside substance added to ore to lower its melting point is known as flux.
Flux combines with gangue and forms easily fusible slag.
Question 9.
Which chemical compound is formed in the brown ring test for nitrate ion? Write the formula.
Answer:
The chemical compound formed in the brown ring test for nitrate ion is [Fe(H2O)5 NO]+2.
![]()
Question 10.
What is an alloy? Give an example.
Answer:
Alloy : An intimate mixture having physical properties similar to that of the metal formed by a metal with other metals or metalloids v or sometimes a non metal is called as an alloy.
Eg.: Invar – 64% Fe, 35% Ni, Mn 8cc in traces
Nichrome – 60% Ni, 25% Fe, 15% Cr.
Section – B
Question 11.
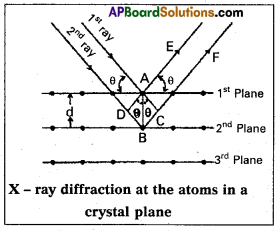
Derive Bragg’s equation.
Answer:
Derivation of Bragg’s equation : When X-rays are incident on the crystal or plane, they are diffracted from the lat¬tice points (lattice points may be atoms or ions or molecules). In the crystal the lattice points are arranged in regular pattern. When the waves are diffracted from these points, the waves may be constructive or destructive interference
Img-1
The 1st and 2nd waves reach the crystal surface. They undergo constructive interference. Then from the figure 1st and 2nd rays are parallel waves. So, they travel the same distance till the wave form AD. The second ray travels more than the first by an extra distance (DB + BC) after crossing the grating for it to interfere with the first ray in a constructive manner. Then only they can be in the same phase with one another. If the two waves are to be in phase, the path difference between the two ways must be equal to the wavelength (X)
or integral multiple of it (n λ, where n = 1, 2, 3, )
(i.e.,) nX = (DB + BC) [where, n = order of diffraction]
DB = BC = d sin θ
θ = angle of incident beam,
(DB + BC) = 2d sin θ
d = distance between the planes
nX = 2d sin θ
This relation is known as Bragg’s equation.
Question 12.
What is catalysis? How is catalysis classified ? Explain each type of catalysis with an example.
Answer:
Catalysis A substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed in the process, is called a catalyst. The action of catalyst in altering the rate of a chemical reaction is called catalysis.
Types of catalysis:
Catalysis is classified into two types as
a) Homogeneous catalysis and
b) Heterogeneous catalysis.
Homogeneous catalysis:
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in the same phase as that of reactants, is known as homogeneous catalysis.
Heterogeneous catalysis:
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in a phase different from that of the reactants is known as heterogeneous catalysis.
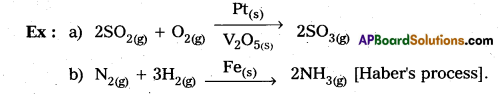
Question 13.
Explain the following with examples:
(i) Calcination
(ii) Roasting.
Answer:
Roasting : Removal of the volatile components of a mineral by heating mineral either alone (or) mixed with some other substances ‘ to a high temperature in the presence of air is called Roasting.
- It is applied to the sulphide ores.
- SO2 gast is producted along with metal oxide.
![]()
Calcination : Removal of the volatile components if a neral by heating in the absence of air is called calcination.
- It is applied to carbonates and bicarbonates.
- CO2 gas is produced along with metal oxide.
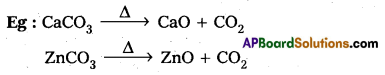
Question 14.
(a) Define mole fraction.
(b) Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 10 g of NaOH in 500 ml of solution.
Answer:
(a) Mole fraction :
The ratio of no. of moles of one component to the total no. of moles of all the components of the solution is called mole fraction. It has no units.
(b) Molarity (M) = \(\frac{\text { weight }}{\text { gmw }} \times \frac{1000}{V(\mathrm{ml})}\)
= \(\frac{10}{40} \times \frac{1000}{500}\)
= \(\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\)
= 0.5 moles/lit
![]()
Question 15.
How are XeF2 and XeF6 prepared? Write their structures.
Answer:
XeF2 and XeF6 are prepared by the following reactions
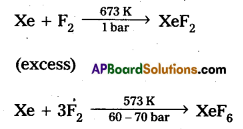
1 : 20 ratio
structure of XeF2 :
1) In XeF2 Central atom is ‘Xe’
2) ‘Xe’ undergoes sp3d hybridisation in it’s 1st excited state
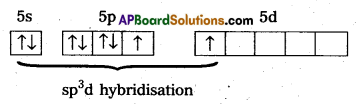
3) Shape of molecule is linear.
4) Xe form two a.bonds with two fluorines.
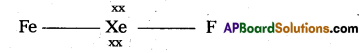
Structure of XeF6:
1) Central atom in XeFg is ‘Xe’.
2) Xe under goes sp3d3 hybridisation in it’s 3rdrd excited state.

3) Shape of molecule is distorted octahedral
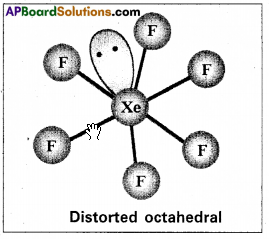
Question 16.
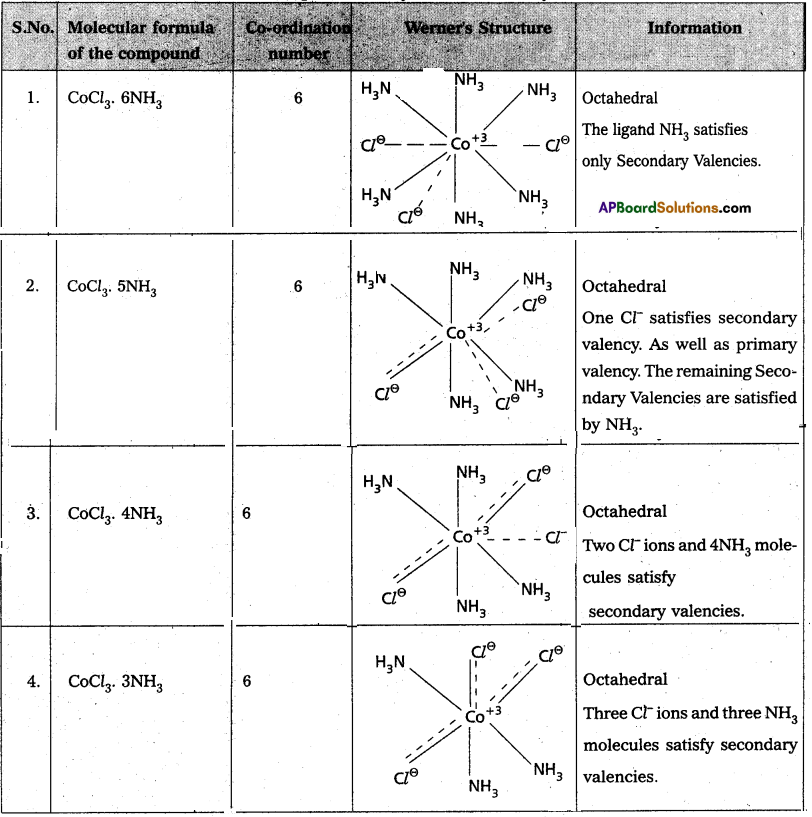
Explain Werner’s theory with example.
Answer:
Werner’s theory :
Postulates :
1) Every complex compound has a central metal atom (or) ion.
2) The central metal shows two types of valencies namely primary valency and secondary’ valency.
A) Primary valency :
The primary valency is numerically equal to the oxidation state of the metal. Species or groups bound by primary valencies undergo complete ionization. These valencies are identical with ionic bonds and are non-directional. These valencies are represented by discontinuous lines (……..) Eg. : CoCl3 contains Co3+ and 3Cl– ions. There are three Primary Valencies or three ionic bonds.
B) Secondary Valency:
Each metal has a characteristic number of Secondary Valencies. They are directed in space around the central metal. The number of Secondary valencies is called Coordination number (C.N.) of the metal. These valencies are directional in Nature.
For example in CoCl3. 6NH3
Three Cl– ions are held by primary valencies and 6NH3 mole cules are held by Secondary Valencies. In CuSO4.4NH3 complex SO42- ion is held by two Primary valencies and 4NH3 molecules are held by Secondary valencies.
3) Some negative ligands, depending upon the complex, may 1 satisfy both primary and secondary valencies. Such ligands, in a j complex, which satisfy both primary as well as secondary valencies % do not ionize.
4) The primary valency of a metal is known as its outer sphere of attraction or ionizable valency while the Secondary valencies are known as the inner sphere of attraction or coordination sphere. Groups bound by secondary valencies do not undergo ionization in the complex.
Question 17.
What are hormones? Give one example for each of the following:
i) Steroid hormones
ii) Polypeptide hormones
iii) Amino acid derivatives.
Answer:
Hormones : Hormone is defined as an “organic compound synthesised by the ductless glands of the body and carried by the blood stream to another part of the body for its function”.
Eg: testosterone, estrogen.
i) Example for steroid hormones : Testosterone, Estrogen.
ii) Example for poly peptide hormones : Insulin.
iii) Example for Amino acid derivative: Thyroidal hormones thyronine.
![]()
Question 18.
Explain the following reactions :
(a) Wurtz-Fitting reaction
(b) Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Answer:
(a) Wurtz-Fitting reaction :
A mixture of Aryl halide and alkyl halide reacts with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form alkyl arene. This reaction is known as wurtz reaction.

(b) (i) Friedel-Crafts Alkylation : Benzene reacts with alkyl halides in presence of an hydrous AlCl3 to form alkyl benzene.
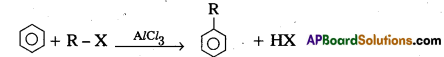
(ii) Friedel-Crafts Acylation : Benzene reacts with acyl halide in presence of an hydrous AlCl3 to form acyl benzene.
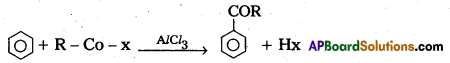
Section – C
Question 19.
Give a detailed account of the collision theory of reaction rates Of Bimolecular gaseous reaction.
Answer:
Collision theory of reaction rate bimolecular reactions salient features.
- The reaction molecules are assumed to be hard spheres.
- The reaction is postulated to occur when molecules collide with each other.
- The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
- For a bimolecular elementary reaction A + B → products
K = ZAB. eEa/RT ; = collision frequency. - All collisions do not lead to product formation.
- The collisions with sufficient kinetic energy (Threshold energy) are responsible for product formation. These are called as effective collisions.
- To account for effective collisions a factor p called to probability factor or steric factor is introduced.
K= P ZAB. eEa/RT - The proper orientation of reactant molecular lead to bond formation where as improper orientation makes them back and no product are formed.
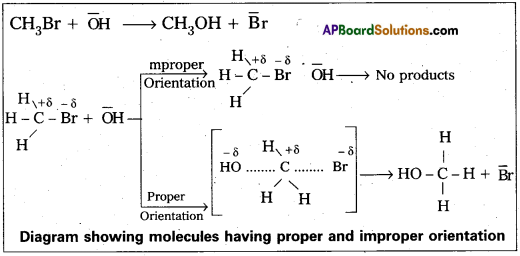
In this theory activation energy and proper orientation of the molecules to gather determine the creteria for an effective collision and hence the rate of a chemical reaction
![]()
Question 20.
a) How does ozone react with the following :
i) PbS
ii) C2H2
iii) Ag
iv) Hg.
Answer:
(i) Black lead sulphide oxidised to white lead sulphate by ozone.
Pbs + 4O3 → PbSO4 + 4O2
(ii) Acetylene undergo ozonolysis to form acetylene ozonoid followed by hydrolysis with Zn to form glyoxal.
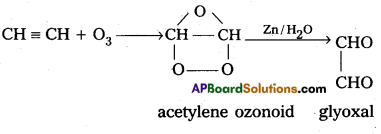
(iii) Ozone oxidises silver metal to silver oxide.
2 Ag + O3 → Ag2O + O2
(iv) Mercury loses it’s lustreness, meniscus, and sticks to the walls of container or vessel when it reacts with ozone.
2Hg + O3 → Hg2O + O2
b) How is chlorine prepared in the laboratory? Explain the reactions of chlorine with the following :
i) Cold dil. NaOH
ii) Hot con. NaOH.
Answer:
Laboratory Preparation :
In laboratory chlorine is prepared by the oxidation of HCl with MnO2.
4 HCl + MnO2 → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2↑
i) Chlorine reacts with cold dil. NaOH to form sodium hypochloride.
Cl2 + 2NaOH → NaCl + NaOCl + H2O
ii) Chlorine reacts with hot cone. NaOH to form sodium chlorate.
3 Cl2 + 6 NaOH → 5 NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
Question 21.
Explain the following reactions with suitable examples :
a) Williamson’s synthesis
b) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
c) Carbyl amine reaction
d) Diazotization.
Answer:
a) Williamson’s synthesis :
Alkyl halides reacts with sodium alkonides to form ethers. This reaction is called Williamson’s synthesis.
R – x + R’- ONa → R – 0 – R’ + Nax
Eg: Ethyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide to form Diethyl ether.
C2H5Cl + C2H5ONa → C2H5O. C2H55 + NaCl
b) Riemer – Tiemann Reaction :
Phenol reacts with chloroform in presence of base to form salicylaldehyde (O – Hydroxy benzaldehyde).
This reaction is called Riemer – Tiemann reaction.
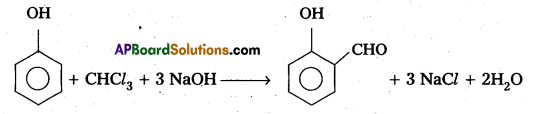
(C) Carbyl amine reaction :
Aniline reacts with chloroform in presence of alcoholic KOH to form a foul smelling compound phenyl iso cyanide. This reaction is called carbyl amine reaction (or) Iso cyanide reaction.
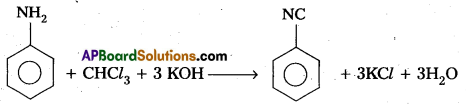
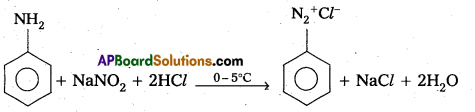
(d) Diazotisation :
Aniline reacts with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperature (0 – 5°C) to form benzene diazonium chloride. This reaction is called diazotisation.