Access to a variety of AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2020 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity. question patterns.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2020
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section – ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section – ‘B’ and any two questions in Section – ‘C’.
- In Section – A, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section -”’8′, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section – ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Section – ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all the questions.
Question 1.
What are artificial sweetening agents? Give example.
Answer:
The chemical substances which are used instead of sucrose (or) sugar are called artificial sweetening agents. E.g.: Aspertame, Alitame, saccharin. These decrease the calorific intake and at the same time several times sweeter than sucrose.
Question 2.
What is Zeigler – Natta Catalyst?
Answer:
A mixture of Tri alkyl aluminium and titanium chloride is called Ziegler – Natta catalyst.
E.g. : (C2H5)3Al + TiCl4
Question 3.
Name two most familiar antioxidants used as food additives.
Answer:
Antioxidants:
- Antioxidants are important and necessary food additives.
- Antioxidants help in food preservation by retarding the action of oxygen on food.
- Antioxidants are more reactive towards oxygen than the food material which they protecting.
- The most familiar antioxidants are Butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT) and Butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA).
- The addition of BHA to butter increases its shelf life from months to years.
- BHT and BHA along with citric acid are added to produce more antioxidant effect.
- SO2 and sulphites are useful anti Oxidants for wine and beer, sugar syrups and cut, peeled (or) dried fruits and vegetables.
![]()
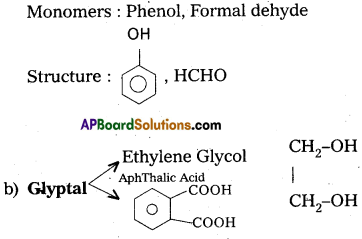
Question 4.
Write names of the monomers used for getting the polymers
(a) Bakelite
(b) Glyptal
Answer:
a) Bakelite:
Question 5.
What are colligative properties? Give any one.
Answer:
Colligative properties : The properties of dilute solutions which depends upon the no. of solute particles of solution are called colligative properties.
Question 6.
Identify the reaction order from each of the following rate constants :
(a) K = 2.3 × 10-5 L mol-1S-1
(b) K = 3 × 10-4 s-1
Answer:
i) The unit of second order rate constant is L mol-1 s-1
therefore k = 2.3 × 10-5 L mol-1 S-1 represents a second order reaction.
ii) The unit of a first order rate constant is s-1 therefore K = 3 × 10-4 s-1 represents a first order reaction.
Question 7.
What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
Answer:
By adding the cryolite to the pure Alumina, the melting point of pure Alumina is lowered (which is very high 2324K) and electrical conductivity of pure alumina is increased.
Question 8.
Why Zn2+ is diamagnetic whereas Mn2+ is paramagnetic?
Answer:
- Zn+2 electronic configuration is [Ar] 4s03d10. It has no unpaired electrons. So, it is dia magnetic.
- Mn+2 electronic configuration is [Ar] 4s03d5. It has five unpaired electrons so it is paramagnetic.
Question 9.
Complete the following:
(a) XeF4 + O2F2 →
(b) XeF2 + H2 →
Answer:
a) XeF4 + O2F2 → XeF6 + O2
b) 2XeF2 + 2H2O → 2xe + 4HF + O2
![]()
Question 10.
Give the hybridization of sulphur in the following:
(a) SO2 (b)SO3 (C)SF4 (d) SF6
Answer:
a) Hybridisation of ‘S’ in SO2 is Sp2
b) Hybridisation of ‘S’ in SO3 is Sp2
c) Hybridisation of ‘S’ in SF4 is Sp3d
d) Hybridisation of ‘S’ in SF6 is Sp3d2
Section – B
Question 11.
(a) What are amino acids? Give two examples.
Answer:
The organic compounds which contain amino (-NH2) func¬tional group and carboxyl (-COOH) functional group are called amino acids. E.g : Glycine, Alanirte etc.
(b) Write any two differences between Globular and fibrous- proteins.
| Globular proteins | Fibrous proteins |
| 1. In this proteins the chains of poly peptides coil around to give a spherical shape. | 1. In this proteins the poly peptides run parallel and are held together by hydrogens and disulphite – bondy |
| 2. These are soluble in water | 2. These are insoluble in water |
| E.g : Insulin | E.g : keratin |
Question 12.
Explain the following with one example for each:
(a) Wurtz reaction
(b) Fitting reaction
Answer:
i) Wurtz reaction : Alkyl halides react with sodium in dry ether solvent give alkanes.
![]()
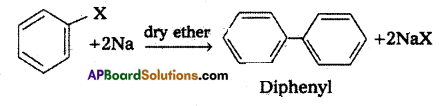
ii) Fitting reaction :
Aryl halides react with sodium in dry ether solvent to give diphenyl is called fitting reaction.
Question 13.
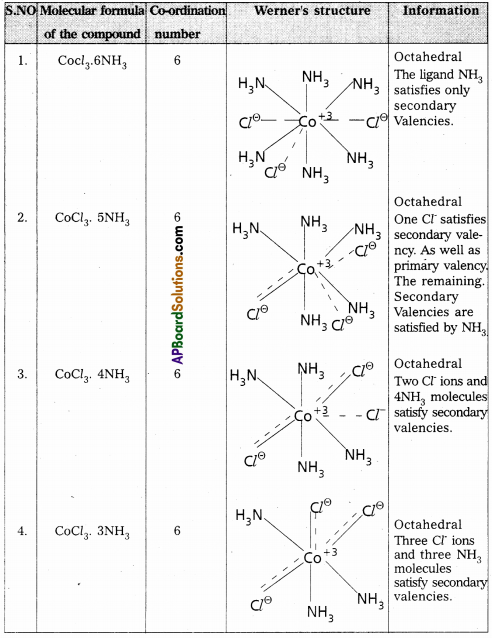
Explain Werner’s theory of co-ordination compounds with suitable examples.
Answer:
Werner’s theory :
Postulates :
1) Every complex compound has a central meted atom (or) ion
2) The central metal shows two types of valencies namely primary valency and secondary valancy.
A) Primary valency :
The primary valency is numerically equal to the oxidation state of the metal. Species or groups bound by primary valencies undergo complete ionization. These valencies are identical with ionic bonds and are non- directional. These valencies are represented by discontinuous lines (…..)
E.g. : CoCl3 contains CO3+ and 3Cl+ ions. There are three Primary Valencies or three ionic bonds.
B) Secondary Valency :
Each metal has a characteristic number of Secondary Valencies. They are directed in space around the central metal.
The number of Secondary Valencies is called Co-ordination number (C.N.) of the metal. These valencies are directional in Nature. For example in CoCl3. 6NH3
Three Cl– ions are held by primary Valencies and 6NH3 molecules are held by Secondary Valencies. In CuSO4. 4NH3 complex SO42- ion is held by two Primary Valencies and 4NH3 molecules are held by Secondary Vacencies.
3) Some negative ligands, depending upon the complex, may satisfy both primary and secondary valencies. Such ligands, in a complex, which satisfy both primary as well as secondary valencies do not ionize.
4) The primary valency of a metal is known as its outer sphere of attraction or ionizable valency while the Secondary valencies are known as the inner sphere of attraction or coordination sphere. Groups bound by secondary valencies do not undergo ionization in the complex.
Question 14.
How does PCI5 react with tha following
(a) Water
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3COOH
(d) Ag
Answer:
a) PC5 undergo hydrolysis to form phosphoric acid.
PCl5 + H2O → POCl3 + 2HCl
POCl3 + 3H2O → H3PO4 + 3HCl
b) PCl5 reacts with C2H5OH to form Ethyl chloride.
C2H5OH + PCl5 → C2H5Cl + POCl3 + HCl
c) PCl5 reacts with CH3COOH to form acetyl chloride.
CH3COOH + PCl5 → CH3COCl + POCl3 + HCl
d) PCl5 reacts with Ag to form PCl3 and AgCl
PCl5 + 2 Ag → 2 AgCl + PCl3
![]()
Question 15.
Define the following with suitable examples:
(a) Anti-ferromagnetism
(b) Frenkel defect
Answer:
a) Anti ferro magnetism :
Substances like MnO showing anti – ferromagnetism . having domain structure similar to ferromagnetic substance, but their domains are oppositely oriented and cancel out each other magnetic moment.
b) Frenkel defect:
- It is a point defect in which an atom or iron is shifted from its normal lattice position”. The ion or the atom now occupies an interstitial position in the lattice.
- This type of a defect is favoured by a large difference in sizes between the cation and anion. In these compounds co-ordination number-is low. Eg : Ag – halides, ZnS etc.
Question 16.
State Henry’s law. Calculate the mass of the non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g of octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
Answer:
Raoult’s law formula
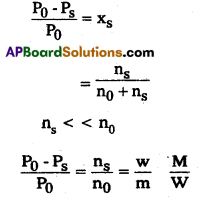
Given vapour pressure reduced to 80%, when non-volatile solute is dissolved in octane.
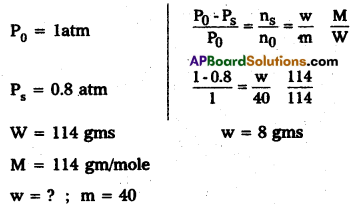
Question 17.
What is catalysis ? How is catalysis classified ? Give one example for each of catalysis.
Answer:
Catalysis:
A substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed in the process, is called a catalyst.
The action of catalyst in altering the rate of a chemical reaction is called catalysis.
Types of catalysis :
Catalysis is classified into two types as a) Homogeneous catalysis and b) Heterogeneous catalysis.
Homogeneous catalysis :
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in the same phase as that of reactants, is known as homogeneous catalysis.
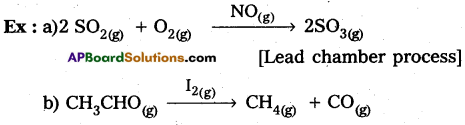
Heterogeneous catalysis :
The catalytic process in which the catalyst is present in a phase different from that of the reactants is known as heterogeneous catalysis.

Question 18.
Write any two ores of the following metals :
(a) Aluminium
(b) Zinc
(c) Iron
(d) Copper
Answer:
a) Ores of Aluminium : Bauxie – Al2 O3.2H2O
Cryolite – Na3Al F6
b) Ores of Zinc : Zinc blende – Zns
Calamine – ZnCO3
C) Ores of Iron : Haematite – Fe2O3
Magnetite – Fe3O4
d) Ores of copper : Copper Pyrites – CuFeS2
Copper glance – Cu2S.
Section – C
Question 19.
(i) Explain the following with suitable examples:
(a) Conversation of alkylhalide to ether.
(b) Conversion of phenol to salicylic acid.
Answer:
(a) Conversion of Alkyl halide to Ether
Williamson’s Synthesis : Alkyl halides reacts with sodium alkoxides to form ethers.
R-x + R1ONa → R-O-R1 + Nax
(b) Conversion of phenol to salicyclic acid :
Kolbe’s Reaction :
Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide followed by the reaction with CO2 and H+ to form salicyclic acid.
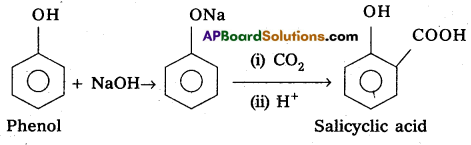
(ii) (a) How do you prepare carboxylic acid and alcohols from Grignard’s reagent? Give example.
(b) What is carbylamine reaction? Give example.
Answer:
ii) a) Preparation of carboxylic acids :
Grignard reagent on carboxyliatic followed by the hydrolysis to form carboxylic acids.
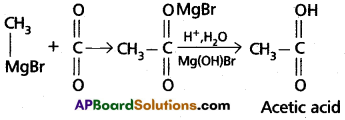
Preparation of alcohols:
Ethylalcohol is obtained by the action of Methyl magnesium bromide on formal dehyde followed by the hydrolysis.
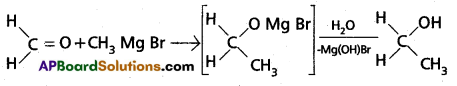
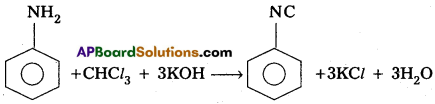
b) Carbylamine Reaction :
Aliphatic or Aromatic primary amines reacts with chloroform and alc.KOH to form Isocyanides (or) Carbylamines.
Question 20.
(i) State Faraday’s first and second laws of electrolysis. A solution of CuSO. is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathod ? ,
Answer:
t = 600 s charge = current × time = 1.5 A × 600 s = 900 C According to the reaction :
Cu(aq)2+ + 2e– = Cu(s)
We require 2F or 2 × 96487 C to deposit 1 mol or 63 g of Cu. For 900 C, the mass of Gu deposited
= (63 g mol-1 × 900 C) / (2 × 96487 C mol-1) = 0.2938 g
(ii) What is molecularity of a reaction? How is it different from the order of a reaction ? Name one bimolecular and one trimolecular gaseous reactions.
Answer:
The number of reacting species (atoms, ions or molecules) taking parts in an elementary reaction, which must colloid simultaneously to bring about a chemical reaction is called molecularity of a reaction.
NH4NO2 → N2 + 2H2O (Unimolecular)
2HI → H2 + I2 (Bimolecular)
2NO + O2 → 2NO2 ( Trimolecular)
- Molecularity has only integer values (1, 2, 3 …….)
- It has non zero, non fraction values while order has zero,1, 2, 3 and fractional values.
- It is determined by reaction mechanism, order is determined experimentally.
![]()
Question 21.
(i) How does chlorine react with
(a) acidified FeSO4?
(b) dry slaked line ?
Answer:
i) a) Acidified FeSO4:
Cl2 reacts with acidified FeSO4 and ferric iohs are formed.
2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + Cl2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2HCl
b) dry slaked line :
Chlorine reacts with dry slaked line and forms bleaching
powder Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
(ii) Describe the manufacture of H2SO4 by contact process.
Answer:
Manufacture of H2SO2 by contact process:
Manufacturing of H2SO2 involves three main steps.
Step – 1:
SO2 production : The required SO2 for this process is .obtained by burning S(or) Iron pyrites in oxygen.
S + O2 → SO2
4FeS2 + 15O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO3
Step – 2 :
SO3 formation : SO2 is oxidised in presence of catalyst with atmosphric air to form SO3 catalyst
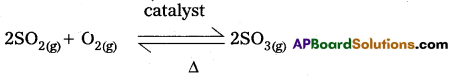
Step – 3 :
Formation of H2SO4: SO3 formed in the above step absorbed in 98% H2SO4 to get oleum (H2S2O7). This oleum is diluted to get desired concentration of H2SO4.
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4