Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 9th Lesson Principles of Inheritance and Variation which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 9th Lesson Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the cross between the F1 progeny and the homozygous recessive parent called? How is it useful? [TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-17, 15]
Answer:
- Such a cross is called ‘Test cross’
- This cross is used to determine the genotype of the test organism.
Question 2.
Do you think Mendel’s laws of inheritance would have been different if the characters that he chose were located on the same chromosome?
Answer:
Yes, because the genes for characters located on the same chromosome inherit and do not follow the law of independent assortment of Mendel.
![]()
Question 3.
Who proposed the Chromosome theory of Inheritance? [AP MAR-17, 19] [TS 20] [AP, TS MAY-22]
Answer:
Sutton and Boveri.
Question 4.
Define true breeding. Mention its significance. [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
- True breeding: Continuous self pollination is called true breeding.
- Significance: It shows the stable trait inheritance and expression for several generations.
Question 5.
Explain the terms phenotype and genotype. [TS MAY-22] [AP, TS MAY-17] [AP MAR-16]
Answer:
- The physical appearance of a character is called Phenotype
- The genetic makeup of an individual is called Genotype.
Question 6.
What is point mutation? Give an example.
Answer:
- A mutation that occurs due to a change in a single base pair of DNA is called point mutation.
- Ex: Sickle cell anemia.
Question 7.
A person has to perform crosses for the purpose of studying inheritance of few traits/ characters. What should be the criteria for selecting the organisms?
Answer:
- Genetically dissimilar organisms with desirable traits.
- Short life cycle
- Should be bisexual.
- Should be self pollinated and cross pollinated.
- More number of offsprings.
- Should have contrasting characters.
- They should be grown easily & crossed easily.
Question 8.
Inorder to obtain F1 generation, Mendel pollinated a pure breeding tall plant with pure breeding dwarf plant. But to get the F2 generation, he simply self pollinated F1 plants. Why?
Answer:
- Continuous cross pollination leads to heterozygosity with less yield.
- To keep the F1 hybrid is homozygous condition, he self pollinated F1 hybrids.
Question 9.
How are alleles of a particular gene differ from each other? Explain its significance.
Answer:
- Alleles a pair of genes located on homologous chromosomes representing a character.
- Heterozygous alleles of a gene differ from each other as one is dominant and other one is recessive.
- The dominant gene is expressed in next generation whereas the recessive gene remains suppressed.
- The DNA codings determine distinct traits that can be passed from one generation to next generation.
![]()
Question 10.
In a monohybrid cross between red and white flowered plants, a geneticist got only red flowered plants. On self-pollinating these F1 plants, he got both red and white flowered plants in 3:1 ratio. Explain the basis of using RR and rr symbols to represent the genotype of plants of parental generation.
Answer:
- Genes which code for a pair of contrasting characters are called alleles.
- They are similar in homozygous condition.
- Conventionally we use Capital letter for dominant character and small letters for recessive character.
- RR symbol is used to represent genotype of pureline red flowered plants.
- rr symbols is used to represent pureline of white flowered plants.
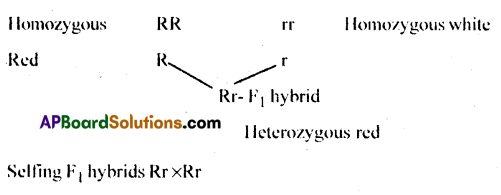
Question 11.
What is the genetic nature of wrinkled phenotype of pea seeds? [AP MAR-15]
Answer:
r r is the genotype of wrinkled phenotype of pea seeds.
Question 12.
What will be the phenotypic ratio in the offsprings obtained from the following crosses. [TS M-I6]
a. Aa x aa
b. AA x aa
c. Aa x Aa
d. Aa x AA
Answer:
a. 1:1
b. 3:1
c. 3:1
d. 1:1
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
In a Mendelian monohybrid cross, the F2 generation shows identical genotypic and phenotypic ratios. What does it tell about nature of alleles involved? Justify your answer. [TS 20]
Answer:
It tells us about incomplete dominance which results in an intermediate expression.
When RR (Red) is crossed with white (rr)

Apparent blending of two colours occurs due to incomplete dominance and pink colour, an intermediate expression is obtained.
F2 generation – Selling of F1 hybrids.
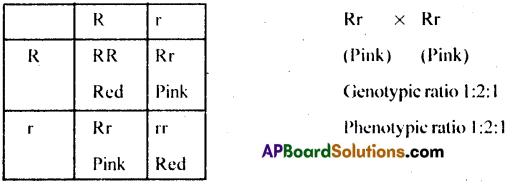
In this case, both genotypic and phenotypic ratio is same.
Question 2.
Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for the experiment by Mendel. [TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-19] [AP, TS MAR-17]
Answer:
Mendel selected garden pea for his experiments due to the following advantages:
- It has many contrasting characters.
- It can be grown and crossed easily.
- It has bisexual flowers containing both female and male flowers
- It can be self-pollinated conveniently.
- It has a short life cycle and produces large number of off springs.
- It has less number of chromosomes
- Experiments may be conducted in simple laboratory conditions.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate between the following: [AP 20]
a) Dominant and Recessive
b) Homozygous and Heterozygous
c) Monohybrid and Dihybrid
Answer:
a) The character which is expressed in F1 generation is called dominant character and which is unexpressed is called recessive character.
b) An individual having two similar or identical genes for a single character is called homozygous.
An individual having two dissimilar genes for a single character is called heterozygous.
c) Monohybrid cross: The cross made between two individuals differing in one character is called Monohybrid cross.
Dihyhrid cross: The cross made between individuals differing in two characters.
Question 4.
Explain the law of Dominance using a monohybrid cross. [AP MAY-17] [AP MAR-15, 19]
Monohybrid cross: The cross made between two individuals differing in one character is called Monohybrid cross.
In the hybridization experiment Mendel crossed tall and dwarf pea plants to study the inheritance of one gene. Based on his observation on monohybrid crosses, Mendel proposed Law of Dominance.
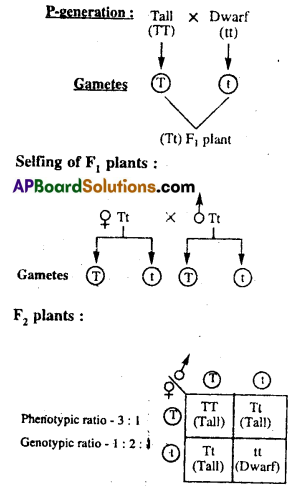
Law of Dominance:
- Characters are controlled by discrete units called factors.
- Factors occur in pairs.
- In a dissimilar pair of factors, pertaining to a character, one member of the pair, dominates (dominant) the other (recessive).
- The law of dominance is used to explain the expression of only one of the parental characters in a ‘monohybrid cross’ in the F1 generation and the expression of both in the F2 generation. It also explains the proportion of 3:1 obtained at the F2 generation.
Question 5.
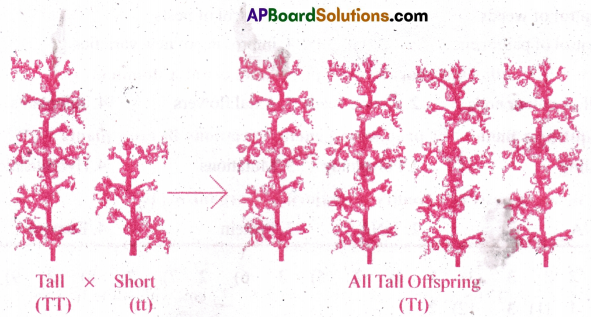
Define and design a test-cross. [AP,TS MAY-22] [AP,TS MAR-16]
Answer:
- Test crossr: Crossing between F1 individuals with the recessive parent is called test cross.
- It is used to test whether an individual is homozygous or heterozygous.
- A monohybrid test cross gives a phenotype rafio of 1:1
- A dihybrid test cross gives a ratio of 1:1:1:1
Question 6.
Using a Punnet square, work out the distribution of phenotype features in the first filial generation after a cross between a homozygous female and a heterozygous male for a single locus.
Answer:
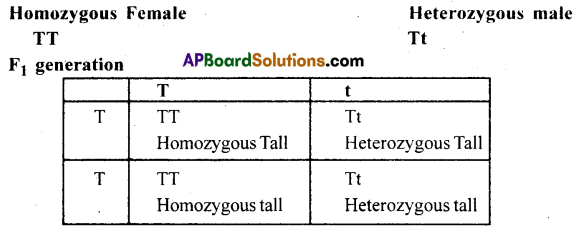
Homozygous Tall: Heterozygous tall =1:1
Genotypic ratio is 1:1.
All plants show phenotypically dominant.
![]()
Question 7.
When a cross is made between tall plants with yellow seeds (TtYy) and tall plant with green seeds (Ttyy) what proportion of phenotype in the offspring is expected to be (a) Tall & green (b) dwarf & green
Answer:
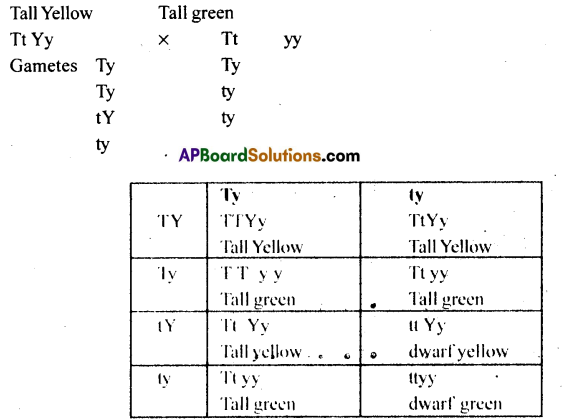
Phenotypic ratios
(i) Tall & green =3/8
(ii) Dwarf & green =1/8
Question 8.
Explain the following terms with examples.
(a) Co-dominance (b) Incomplete dominance [TS MAY-17] [TS MAR-15].
Answer:
(a) Co-dominance:
- Co-dominance: It is the phenomenon in which both the genes are equally dominant.
- The character of both genes is well expressed in the next generation.
- So, in F1 generation, regeneration resemble both parents.
- Ex 1: Different types of red blood cells that determine ABO blood grouping in human beings.
- Ex 2: Seed coat pattern and size in Lentil plants.
- Lentil is a major grain legume crop in North America.
- A cross is made between pure – breeding spotted lentils and pure breeding dotted lentils.
- It produced heterozygotes that are both spotted and dotted.
- The F1 hybrids show the phenotypic features of both parents.
- It shows that neither the spotted nor the dotted allele is dominant or recessive to the other.
(b) Incomplete dominance: [TS MAY-22]
- Incomplete Dominance: It is the phenomenon in which neither of the genes is completely dominant or completely recessive.
- Ex: The inheritance of flower colour in the dog flower (Snapdragon or Antirrhinum).
- In a cross between homozygous red flowered (RR) and white flowered plants (rr), the F1 (Rr) was Pink.
- When the F1 was self pollinated, the F2 resulted in 1 (RR) Red: 2 (Rr) Pink: 1 (rr) white.
- Here genotypic ratios were exactly as in Mendelian monohybrid cross, but phenotypic ratio had changed from 3:1 to 1:2:1.
- It was because of the incomplete dominance of ‘R’ over ‘r’ and this made it possible to distinguish Rr as Pink from RR (red) and rr (white).
- Thus the Phenotypic and genotypic ratios in F2 progeny are the same, that is 1:2:1.
Question 9.
Write a brief note on chromosomal mutations and gene mutations. [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
1) Chromosomal mutation: A change in the number or structure of chromosome is called chromosomal mutation.
- Loss or gain of a segment of DNA results in alteration in chromosomes.
- Alteration in chromosomes results in abnormalities (or) aberrations.
- Ex: It is commonly observed in Cancer cells.
2) Gene Mutation:
- A change in a single base pair of DNA is called gene mutation.
- It is also called as point mutation.
- Ex: Sickle cell anemia in humans.
![]()
Question 10.
How was it concluded that genes are located on chromosomes?
Answer:
1) Morgan hybridised yellow bodied and white eyed females to brown bodied red eyed males and intercrossed F1 progeny.
2) He observed that two genes did not segregate independently of each other and F2 ratio deviated very significantly from the 9:3:3:1 ratio.
3) He saw quickly that when the two genes in a dihybrid cross were situated on same chromosome, the proportion of parental combinations was much higher than the non parental type.
4) He attributed this to the physical association or linkage of two genes and coined the term linkage and the term recombination to describe the generation of non parental gene combination.
5) He also found that, even when genes were grouped on same chromosome, some genes were tightly linked and some genes were loosely linked.
6) Alfred Sturtevant used frequencj of recombination between gene pairs on the same
chromosomes as a measure of distance between genes and mapped their positions on the chromosome.
Question 11.
A plant with red flowers was crossed with one having yellow flowers, if F1 showed all flowers in orange colour, explain the inheritance.
Answer:
- Apparent blending of red and yellow colours is made orange colour due to incomplete dominance which resulted in an intermediate expression.
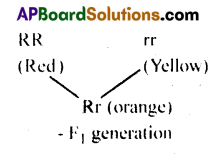
- Here dominant red colour is not completely dominant over the yellow colour. It results the other colour that is orange.
- Intermediate expression is due to incomplete dominance of either red alLeles or yellow alleles.
- So blending of two colours red and yellow resulted in orange colour.
Question 12.
Define law of Segregation and law of independent Assortment.
Answer:
a) Law of Segregation: It states that the two alleles of a gene often present together in a heterozygous state, donot fuse, but remain distinct and segregate during meiosis so that each gamete carries only one gene.
Law of segregation is based on the results of monohybrid cross. It is postulated by Mendel . It is also known as law of purity of gametes.
b) Law of independent Assortment: It states that when the plants differ from each other in two or more pairs of contrasting characters, the inheritance of one pair of factors is independent of the other pair of factors.
Law of Independent assortment is based on the results of dihybrid cross.
It is also postulated by Mendel as a Second Law.
![]()
Question 13.
In peas, tallness is dominant over dwarfness and violet colour of flowers is dominant over the white colour. When a tall plant bearing violet flowers was pollinated with a dwarf plant bearing white flowers, different phenotypic groups were obtained in the progeny in numbers mentioned against them:
Tall, Violet = 138 Tall, White = 132 Dwarf, Violet =136 Dwarf, White =128
Mention the genotypes of the two parents and of the four offspring types.
Answer:
In a pea plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness and violet flowers are dominant over white flowers.
Tall plant with violet flowers is crossed with dwarf plant with white flowers.
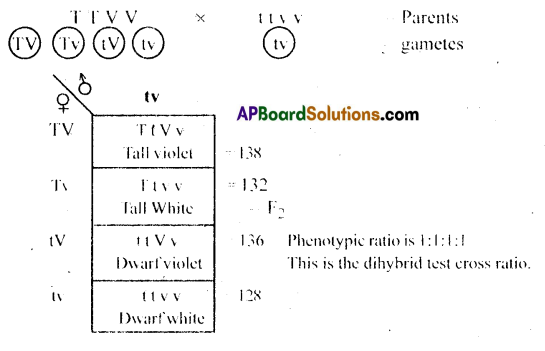
Question 14.
How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the view point of genetical studies?
Answer:
- Chromosomes are composed of chromation madeup of DNA and histone proteins.
- DNA is a long string of numerous nucleotide pairs linked together
- Genes are structures of DNA that contain code to make protein.
- Thus both chromosomes and genes are similar from the point of genetic studies.
Question 15.
With the help of an example differentiate between incomplete dominance and dominance.
Answer:
| Incomplete Dominance | Co-dominance |
| 1) It is a condition when one allele of a gene is not completely dominant over the other allele and results in the heterozygotes having phenotype different from dominant & recessive homozygotes. | 1) The phenomenon in which both alleles dominate nor recessive tP other. Characters of both genes will be expressed in next generation. |
| 2) Ex: Cross between Red flower (RR) and white flowered plants (rr) results in pink flowered plants. | 2) Ex: Cross between is spotted lentils and dotted lentils produced heterozygote both spotted and dotted lentils.d |
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
In a plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness and red flower is dominant over white. Starting with parents work out a dihybrid cross. What is standard dihybrid ratio? Do you think the values would deviate if the two genes in question are interacting with each other.
Answer:
Parent generation
Tall Red × dwarf white
TT RR ttrr
gametes TR tr
F1 generation TtRr- Tall Red
F2 generation Tt Rr × TtRr
Possible gametes TR, Tr, tR, tr
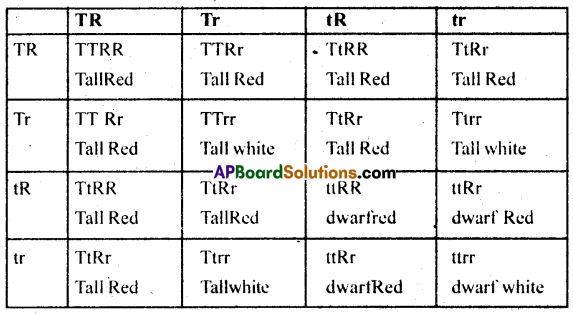
Tall Round : Tall white: dwarf Red: dwarf white
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Standard Dihybrid ratio Phenotype 9:3:3:1
Genotypic Ratio = 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
If two genes in question are interacting with one another, surely the values will deviate.
![]()
Exercise
Question 1.
Mendel crossed pea plants producing round seeds with those producing wrinkled seeds. From a total of 7324 F2 seeds, 5474 were round and 1850 were wrinkled. Using the symbols K and r for genes, predict the: .
a. the parental (p) genotypes
b. the gametes
c. F1 progeny
d. The cross between F1 hybrids.
e. genotypes, phenotypes, genotypic frequency, phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
Answer:
a. The parental genotypes are — RR, rr (homozygous)
b. The gametes are R and r
c. F1 progeny — Rr
d. Cross between F1 hybrids are Rr x Rr
e. Genotypes are —3 Phenotypes are — 2 Genotypic frequency —1:2:1 Phenotypic ratio —3:1
Question 2.
The following data was obtained from an experiment on peas. The grey coloured seed is dominant over white coloured seed. Use the letter G for grey and g for white traits. Predict genotypes of the parents in each of the following crosses.
Parent Progeny
Grey white
a. Grey x white 164 156
b. Grey x grey 59 19
c. White x white 0 100
d. Grey x grey 180 0
Answer:
Genotypes of parents:
a. Grey x white
Gg x gg
b. Grey x grey
Gg x Gg
c. White x White
gg x gg
d. Grey x grey
Gg x GG
Question 3.
In tomatoes red fruit colour (R) is dominant to yellow (r), suppose a tomato plant homozygous for red is crossed with one homozygous for yellow. Determine the appearance of the following.
a. The F1
b. F2
c. The offspring of a cross of the F( back to the red parent
d. the offspring of a cross of the Ft back to the yellow parent.
Answer:
a. Appearance in F1 are — all Red (Rr)
b. Appearance in F2 are — 3:1 (3 Red, 1 yellow)
c. The appearance of the offsprings of a cross of the F1 back to the red parent are — All red (homozygous red and Heterozygous red)
d. The appearance of the offsprings of a cross of the F1 back to the yellow parent are — Red and yellow in 1:1 ratio.
Question 4.
In pea, axillary position of flowers (T) is dominant over its terminal position (t). Coloured flowers (C) are dominant to white flowers (c). A true breeding plant with coloured flowers in axils is crossed to one with white terminal flowers. Give the phenotypes, genotypes and expected ratios of F1, F2 back cross and test cross progenies. What genotypic ratio is expected in the F1 progeny?
Answer:
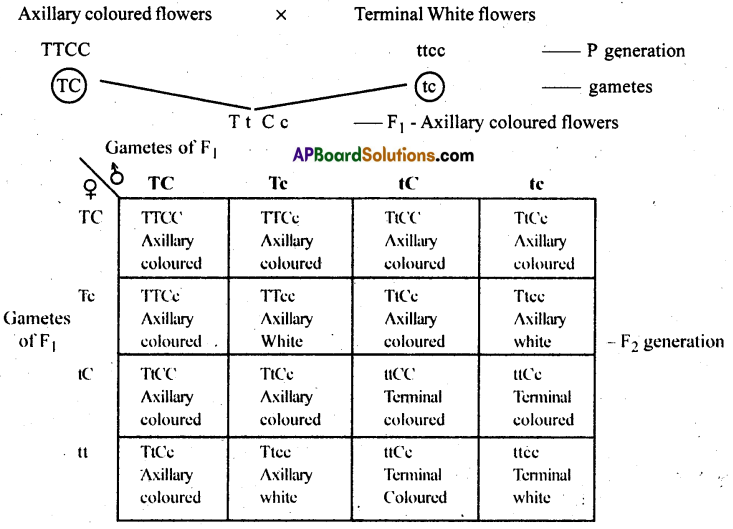
- All F1 hybrid phenotypes are —Axillary coloured flowers
- All F1 hybrid genotypes are — TtCc
- The phenotypic ratio of F2 — 9:3:3:1
- The genotypic ratio of F2— 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
![]()
Dihybrid Test cross: It is across made between F1 hybrid and recessive parent.
The ratio is 1:1:1:1.
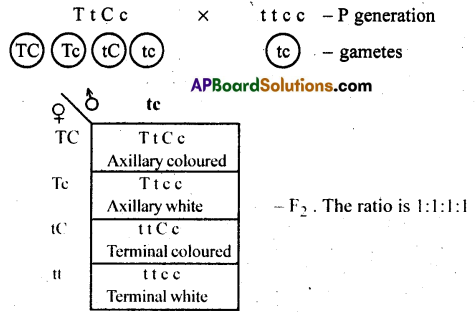
Dihybrid back cross: It is across made between F1 hybrid and dominant parent. The resultant young ones are all axillary coloured flowers.
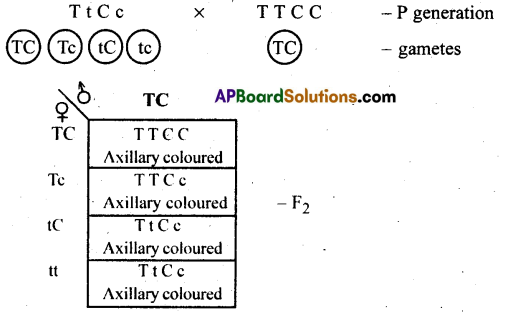
Question 5.
In summer squash, a plant with white flowers and disc-shaped fruits is crossed to a plant with yellow flowers and sphere shaped fruits. The F1 hybrids had white flowers and disc-shaped fruits. Which phenotypes are dominant? Give the genotypes ol the parents and the hybrids. If these hybrids are selfed and 256 progeny are obtained. What would be the frequencies of the various phenotypes.
Answer:
a. The dominant phenotypes are – dominant flowers white (W), recessive flowers yellow (Y) dominant fruit disc shaped (D), recessive fruit sphere shaped (d) dominant phenotypes – White flowers with disc shaped Suits.
b. The genotypes of parents – WWDD (white flowered disc shaped fruits)
– wwdd (yellow flowered sphere shaped fruits)
c. The genotype of hybrids is — WwDd (white flowered disc shaped Suits)
d. The frequencies of various phenotypes is — 9:3:3:1
Question 6.
Give the ratios of the following:
a. Monohybrid test cross
b. Dihybrid test cross
e. F2 phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross d. F2 phenotypic ratio of dihybrid cross
c. F2 genotypic ratio of monohybrid cross and
d. F2 genotypic ratio of dihybrid cross
Answer:
a. Monohybrid test cross ratio is — 1:1
b. Dihybrid test cross ratio is—1:1:1:1
c. F2 phenotypic ratio of Monohybrid cross — 3:1
d. F2 phenotypic ratio of dihybrid cross — 9:3:3:1
e. F2 genotypic ratio of Monohybrid cross — 1:2:1
f. F2 genotypic ratio of dihybrid cross — 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
Question 7.
A diploid organism is heterozygous for 4 loci. How many types of gametes can it produce?
Answer:
Two types of gametes.
Question 8.
What is crossing over? In which stage of cell division crossing over occurs? What is its significance?
Answer:
The exchange of chromatids between two non-sister chromatids leading to genetic recombination is called crossing over. It occurs during pachytene substage of meiosis.
Significance:
- Crossing over causes genetic recombination and genetic variations.
- It is essential for natural selection and evolution.
Question 9.
“Genes contain the information that is required to express a particular trait”. Explain.
Answer:
In the hybridisation experiments carried out by Mendel, he crossed tall and dwarf pea plants to study the inheritance of one gene. Only one of the parental traits was expressed in the F1 generation, while at the F2 stage both the traits were expressed in the proportion on 3:1. The contrasting traits did not show any blending at either F1 or F2 stage.
Based on these observations, Mendel proposed that something was being stably passed down, unchanged, from the parent to offspring through the gametes, over successive generations. He called these things as factors. Nowadays, we call them genes. Genes therefore, are the units of inheritance. They contain the information that is required to express a particular trait in an organism.
![]()
Question 10.
For the expression of trails genes provide only the potentiality and the environment provides the opportunity. Comment on the veraeity of the statement.
Answer:
- At times the environmental variations like temperature, humidity, plays an important role in expressing the same genotype into different phenotypes.
- The phenotype of an organism is the result of the interaction of a genotype with the environment. In this regard both factors are necessary for the expression of a trait.
- Because of environmental variations such as amount and kind of fertilizers and type of soil in crop plants, in breed lines can be obtained., They differ phenotypically.
- For eg: Sweet potatoes grow in soil rich in potassium are round and fleshy but when this element is scarce, they become long and spindle shaped.
- Another example is the effect of hair colour in Himalayan rabbit. The colour of hair is white in hot conditions. The white hair on a small area of back of this rabbit was pulled out and the animal is allowed to grow in cold room. The hair that grew under cold conditions was black.
- This proves that genes provide potentiality for the expression of the trait and environment provides opportunity.
Question 11.
Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would he the distribution of phenotypic features in F( generation for a dihy brid cross?
Answer:
Linkage is the presence of two or more genes on a chromosome as a result of which the genes tend more often to be inherited together. For example a cross between yellow body, white eyes and wild type parent in Drosophila will produce wild type and yellow white progenies. It is because yellow bodied and white eyed genes are linked. Therefore, they are inherited together in progenies.
Question 12.
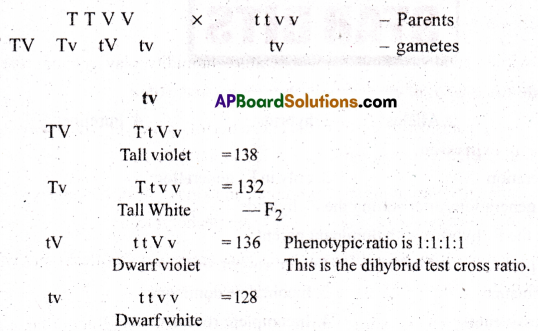
In peas, tallness is dominant over dwarfness and violet colour of flowers is dominant over the white colour. When a tall plant bearing violet flowers was pollinated with a dwarf plant bearing white flowers, different phenotypic groups were obtained in the progeny in numbers mentioned against them:
Tall, Violet = 138
Tall, White – 132
Dwarf, Violet =136
Dwarf, White = 128
Mention the genotypes of the two parents and of the four offspring types.
Answer:
In a pea plant tallness is dominant over dwarfness and violet flowers are dominant over white flowers.
Tall plant with violet flowers is crossed with dwarf plant with white flowers.
Question 13.
How do genes and chromosomes share similarity from the view’ point of genetical studies?
Answer:
- Chromosomes are composed of chromation madeup of DNA and histone proteins.
- DNA is a long string of numerous nucleotide pairs linked together
- Genes are structures of DNA that contain code to make protein.
Thus both chromosomes and genes are similar from the point of genetic studies.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Genes which code for a pair of contrasting characters are called
1. Factors
2. Alleles
3. hybrids
4. Purelines
Answer:
2. Alleles
Question 2.
Dwarf character is expressed
1. only in F1 generation
2. only in F2 generation
3. in subsequent generations after selfing the F1 hybrids
4. After crossing the F1 hybrids with dominant parent
Answer:
3. in subsequent generations after selfing the F1 hybrids
Question 3.
In Snapdragon plant, the inheritance of flower colour indicates
1. Complete dominance
2. Incomplete dominance
3. Complete recessiveness
4. Incomplete recessiveness
Answer:
2. Incomplete dominance
Question 4.
The law of independent assortment is applicable to
1. Monohybrid cross
2. dihybrid cross
3. back cross
4. test cross
Answer:
2. dihybrid cross
Question 5.
In Drosophila, the genes for body colour and eye colour are present on
1. Autosomes
2. Y chromosome
3. X chromosome
4. Sat chromosome
Answer:
3. X chromosome
![]()
Question 6.
The method of gene mapping of the chromosomes was developed by
1. Alfred Hershey
2. Alfred sturtevant
3. Franklin stahl
4. Marshall Nirenberg
Answer:
2. Alfred sturtevant
Question 7.
In a point mutation
1. Entire set of chromosomes is altered
2. A change in single base pair of DNA occurs
3. Some portions of chromosomes are lost
4. New portionis are added to chromosomes
Answer:
2. A change in single base pair of DNA occurs
Question 8.
Sickle eell anemia is caused due to
1. Delection
2. Insertions
3. Single base alterations
4. Polyploidy
Answer:
3. Single base alterations
Question 9.
In agriculture, mutations are useful for
1. Control of weeds
2. Control of pests
3. Control of pathogens
4. improving of new varieties
Answer:
4. improving of new varieties
Question 10.
Which of the following characters of pea plants is not a dominant one
1. Yellow colour pods
2. Round seeds
3. Axial flowers
4. Tall plants
Answer:
1. Yellow colour pods
Question 11.
The quickest method of producing genetic variations in crop plants is
1. Selfing
2. Polyploidy
3. Mutations
4. Hybridisation
Answer:
3. Mutations
Question 12.
The chemical basis of heredity in majority of organisms is
1. RNA
2. DNA
3. Protein
4. Enzyme
Answer:
2. DNA
Question 13.
The genetic information is stored in DNA rather than RNA because
1. DNA has very high molecular weight
2. DNA is doulbe stranded
3. DNA is more stable
4. DNA can replicate
Answer:
3. DNA is more stable
Question 14.
Genomics is a modern branch {hat deals with
1. Transfer of genetic information from one generation to another
2. Synthesis of genes artificially
3. Study of the nucleotide sequence of the human genome
4. Study of genes
Answer:
3. Study of the nucleotide sequence of the human genome
![]()
Question 15.
Identify the correct statement
1. Hereditary material in all organisms is DNA
2. RNA is a highly stable nucleic acid
3. Genes are present randomly in a chromosome
4. Variations are caused by mutations only
Answer:
1. Hereditary material in all organisms is DNA
Question 16.
The unit of inheritance is
1. Nucleus
2. Chromosome
3. Gene
4. DNA
Answer:
3. Gene
Question 17.
Mutations cause changes in
1. Phenotype only
2. Genotype only
3. Both genotype and phenotype
4. Chromosomes only
Answer:
3. Both genotype and phenotype
Question 18.
Mutations do not lead to
1. Variations
2. Cancer
3. Denaturation of DNA molecule
4. Changes in gene sequences
Answer:
3. Denaturation of DNA molecule
Question 19.
Transgenic crops are produced by
1. Inducing mutations
2. Hybridisation
3. Gene transfer
4. Gene sequencing
Answer:
3. Gene transfer
Question 20.
The cause of variations and recombinations is
1. Synapsis
2. Disjunction of genomes
3. Crossing over
4. cytokinesis
Answer:
3. Crossing over
Question 21.
Linked genes can be seperated naturally by
1. Mutation
2. crossing over
3. genetic engineering
4. Genomics
Answer:
2. crossing over
Question 22.
One of the following is not a character of the genetic material
1.It is stable
2. It should replicate itself
3. It should be able to mutate
4. It is chemically more reactive
Answer:
4. It is chemically more reactive
Question 23.
Which among the following is the genetic material
1. protein
2. DNA
3. Histone
4. Non-histone
Answer:
2. DNA
![]()
Question 24.
Mutations are
1. heritable changes in characters
2. non inheritable changes
3. change in chromosome numbers only
4. changes in chromosomes shapes only
Answer:
1. heritable changes in characters
Question 25.
Parental characters occur in the progeny due to
1. Mutation
2. Crossing
3. Linkage
4. Recombinations
Answer:
3. Linkage
Question 26.
A true breeding plant is
1) Breeds on its own
2) Produced by selfing – homozygous
3) Produced by selfing – heterozygous
4) Always homozygous recessive
Answer:
2) Produced by selfing – homozygous
Question 27.
A gamete normally contains
1) Two alleles of a gene
2) Many alleles of a gene
3) All alleles of a gene
4) One allel of a gene
Answer:
4) One allel of a gene
Question 28.
Mendel proposed certain things which were being stably passed down unchanged from parents to offspring are called
1) genes
2) genotype
3) factors
4) alleles
Answer:
3) factors
![]()
Question 29.
In a dihybrid cross, the maximum number of phenotypes would be
1) 8
2) 4
3) 2
4) 16
Answer:
2) 4
Question 30.
Types of genoty pes and phenotypes obtained in F2 generation of mcndclian dihybrid cross
1) 9 & 16
2) 4 & 9
3) 9 & 12
4) 9 & 4
Answer:
4) 9 & 4
Question 31.
What is the phenotypic ratio of dihybrid test cross?
1) 1:1: 1:1
2) 1:1
3) 9: 3:3:1
4) 1 : 2 : 2 : 4 : 1 :2 : 1 : 2 : 1
Answer:
1) 1:1: 1:1
Question 32.
A cross between two pea plants with round seeds produced some plants with wrinkled seeds. What will be the genotype of parents?
1) RR & RR
2) RR & rr
3) Rr & Rr
4) RR & Rr
Answer:
3) Rr & Rr
Question 33.
Change in single base pair of DNA is called
1) Frame shift mutation
2) Point mutation
3) Silent mutation
4) Lethal mutation
Answer:
2) Point mutation
Question 34.
A classical example for point mutation is
1) Sickle cell anemia
2) Turners syndrome
3) Down’s syndrome
4) Acquired Immuno Defficiency Syndrome
Answer:
1) Sickle cell anemia
Question 35.
Lens culinaris ssp etilinaris is
1) Ornamental plant of South America
2) Pulse crop of North America
3) Medicinal plant of Eastern India
4) Fibre yielding plant of Western Ghats
Answer:
2) Pulse crop of North America
![]()
Question 36.
If F1 generation has all tall plants and ratio of F2 generation 3 tall : 1 dwarf, it proves
1) Law of segregation
2) Law of independent assortment
3) Incomplete dominance
4) Law of dominance
Answer:
1) Law of segregation
Question 37.
The phenotypic & genotypic ratios in F2 generation progeny are 1:2:1 in
1) Incomplete dominance
2) Codominance
3) Test cross
4) 1 & 2
Answer:
4) 1 & 2
Question 38.
In monohybrid cross, the Ft hybrid produces two kinds of gametes each with only one character. It is explained as
1) Inherited factor
2) Purity of gametes
3) Alleles
4) Heterozygous
Answer:
2) Purity of gametes
Question 39.
When a heterozygous tall plant is crossed with homozygous dwarf plant, the progeny shows
I) 1 : 1 phenotypic ratio
II) 1 : 1 genotypic ratio
III) No recessive individuals
IV) No dominant individuals
1) I & II
2) I & IV
3) I & III
4) III & IV
Answer:
1) I & II
Question 40.
The geometrical device that helps in visualizing all the possible combinations of male and female gametes is called
1) Mendel square
2) Bateson square
3) Morgan square
4) Punnet square
Answer:
4) Punnet square
Question 41.
A cross between an organism of dominant phenotype with an unknown genotype and a known recessive phenotype is called
1) Test cross
2) Progeny testing
3) Back cross
4) Reciprocal cross
Answer:
1) Test cross
Question 42.
In a typical monohybrid, cross % of F2, resembling the dominant parent phcnotypically is
1) 100
2) 75
3) 50
4) 25
Answer:
2) 75
![]()
Question 43.
Mendelian ratio 9:3:3: I is due to
1) Law of segregation
2) Law of purity of gametes
3) Law of independent assortment
4) Law of dominance
Answer:
3) Law of independent assortment
Question 44.
How many types of gametes arc produced by a plant having the genotype: Yy rr Tt
1) One
2) Two
3) Four
4) Eight
Answer:
3) Four
Question 45.
The paper “Experiments on plant hybrids” was published in
1) 1856
2) 1863
3) 1866
4) 1906
Answer:
2) 1863
Question 46.
Gene → (x) → Character. Identify ‘X’.
1) Hormone
2) Toxin
3) Enzyme
4) Vitamin
Answer:
3) Enzyme
Question 47.
The proportion of 3:1 at the F2 generation is explained by the
1) Law of Dominance
2) Law of Segregation
3) Law of Independent assortment
4) Test cross
Answer:
2) Law of Segregation
Question 48.
When both alleles express their effect on being present together, the phenomenon is called
1) Dominace
2) Codominance
3) Pseudodominance
4) Amphidominance
Answer:
2) Codominance
Question 49.
Which one of the following is test cross?
1) YYRRXyyrr
2) YyRrXYyRr
3) YYRR X YYRR
4) YyRrXyyrr
Answer:
4) YyRrXyyrr
Question 50.
Test cross is mainly performed to find out the
1) Phenotype of hybrid
2) Genotype of recessive parent
3) Genotype of dominant parent
4) Genotype of hybrid
Answer:
3) Genotype of dominant parent
![]()
Question 51.
There will be no change in phenotype when an altered gene produces
1) No enzyme
2) Non functional enzyme
3) Functional enzyme
4) Less efficient enzyme
Answer:
2) Non functional enzyme
Question 52.
Pleotropy is correctly represented as
1) One gene → different phenotypes
2) One gene → one phenotype
3) One phenotype → different genotypes
4) Many genes → one phenotype
Answer:
1) One gene → different phenotypes
Question 53.
Phenotypic and genotypic ratios are different in
1) Monohybrid cross
2) Monohybrid Test Cross
3) Codominance-F2
4) Incomplete dominance -F2
Answer:
1) Monohybrid cross
Question 54.
Stage of meiosis in which seggregation of chromosomes occurs is
1) Prophase – I
2) Prophase – II
3) Anaphase -I
4) Anaphase – II
Answer:
3) Anaphase -I
Question 55.
Crossing over in diploid organisms is responsible for
1) Dominance of genes
2) Linkage between genes
3) Recombination of linked genes
4) Segregation of alleles
Answer:
3) Recombination of linked genes
Question 56.
According to Mcndclism, which character shows dominance?
1) Terminal position of flower
2) Green colour in seed coat
3) Wrinkled seeds
4) Green pod colour
Answer:
4) Green pod colour
Question 57.
In hybridisation, Ttxtt gives rise to the progeny of ratio
1) 2:1
2) 1:2:1
3) 1:1
4) 1:2
Answer:
3) 1:1
Question 58.
Multiple alleles control inheritance of
1) Phenylketonuria
2) colour blindness
3) sickle cell anaemia
4) blood groups
Answer:
4) blood groups
Question 59.
The mechanism that causes a gene to move from one linkage group to another is called
1) Inversion
2) Duplication
3) Translocation
4) Crossing-over
Answer:
3) Translocation
![]()
Question 60.
Fruit colour in squash is an example of
1) recessive epistasis
2) dominant epistasis
3) complementary genes
4) inhibitory genes
Answer:
2) dominant epistasis