Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 5th Lesson Respiration in Plants which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 5th Lesson Respiration in Plants
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Energy is released during the oxidation of compounds in respiration. How is the energy stored and released as and when it is needed?
Answer:
- Energy is released during respiration. This energy is stored in the form of ATP, in the bonds of carbohydrates like glucose, sucrose and starch.
- The energy released is not used directly but is used to synthesize ATP, which is broken down whenever energy needed.
Question 2.
Explain the term ‘energy currency’ which substance acts as energy currency in plants and animal cells?
Answer:
- Every function of cell requires energy. ATP( Adenosine triphosphate) acts as ‘energy currency’ in plants and animals.
- Because ATPs ‘stores and releases’ whenever energy needs to be utilised.
![]()
Question 3.
Different substrates get oxidised during respiration. How does respiratory quotient(RQ) indicate, which type of substrate i.e. carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidised?
R.Q. = A/B. What do A and B stand for?
What type of substrates have RQ of 1, <1, >1?
Answer:
1) Respiratory quotient is the ratio of the volume of CO2 liberated to the volume of O2 absorbed during respiration.

A: stands for volume of CO2 absorbed during respiration.
B: stands for volume of O2 liberated during respiration.
2) If RQ is 1, the carbohydrates are used as respiratory substrate.
If RQ is less than 1, fats are used as respiratory substrate.
If RQ is more than 1, organic acids are used as respiratory substrate.
Question 4.
What is the specific role of F0-F1 particles in respiration?
Answer:
- F0 is an integral membrane protein complex that forms the channel through which protons cross the inner membrane.
- F1 is the head piece, which is a peripheral membrane protein complex and contains the site for synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Question 5.
When docs anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Answer:
- In animal cells like muscle cells of man, during exercise, when oxygen is inadequate for cellular respiration, anaerobic respiration occurs.
- In yeast cells, during the process of fermentation, anaerobic respiration occurs.
Question 6.
Distinguish between obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes
Answer:
| Obligate Anaerobes | Facultative Anaerobes |
| 1) They cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. 2) They die in the presence of oxygen Ex: Clostridium, Actinomycetes |
1) They survive and make ATP in the presence of oxygen. 2) But if oxygen is absent they undergo fermentation. Ex: Yeast, E.Coli. |
Question 7.
Explain the economic importance of fermentation.
Answer:
- Fermentation is used in making of bread, yogurt, lactic acid etc in food industry.
- Fermentation is used in alcoholic industries the production of beverages like wine, beer.
- Many drugs and derivatives are also produced by fermentation.
Question 8.
What is the common pathway for aerobic and anaerobic respirations? Where does it take place?
Answer:
- Glycolysis
- It takes place in Cytoplasm of cell
Question 9.
Why mitochondria are termed as ‘power houses’ of the cell?
Answer:
- During cellular respiration, food is oxidized and converted into energy in form of ATP.
- This process happens in mitochondria.
- Hence mitochondria are called as power houses of cell.
Question 10.
What is the reason for describing ATP synthesis in F0-F1 particles of mitochondria as oxidative phosphorylation?
Answer:
- Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH 2 to O2 by a series of electron carriers.
- This process, which takes place in mitochondria, is the major source of ATP in aerobic organisms
- So ATP synthesis in F0-F1 particle of mitochondria is described as Oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 11.
Which substance is known as connecting line between glycolysis and kreb’s cycle? How many carbons does it have?
Answer:
- Acetyl coenzyme A
- It has two carbons.
Question 12.
What cellular organic substances are never used as respiratory substrates?
Answer:
Fats and Proteins.
Question 13.
Why is the RQ of fats less than that of carbohydrates?
Answer:
Fats require more oxygen for complete oxidation than carbohydrates.
Question 14.
What is meant by ‘Amphibolic pathway’?
Answer:
- Pathway involved in both catabolism and anabolism, is called Amphibolic pathway.
- Ex: Respiration pathway.
Question 15.
Name the mobile electron carriers of the respiratory electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Answer:
Ubiquinone and Cytochrome ‘c’.
![]()
Question 16.
What is the final acceptor of electrons in aerobic respiration? From which complex does it receive electrons?
Answer:
- Oxygen is the final acceptor of electrons in aerobic respiration.
- It receives electrons from Complex IV.
Question 17.
Do you know of any step in Krebs cycle where there is a substrate level phosphorylation? Explain.
Answer:
- In Kreb’s cycle Succinyl Co A splits into succinic acid and Co.Answer: by the catalytic activity of enzyme thyokinase.
- The substrate releases the phosphate ion directly. ADP accepts it and form ATP. This is the substrate level phosphorylation.

Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by the statement ’Aerobic respiration’ is more efficient?
Answer:
- Aerobic respiration is the process that leads to a complete oxidation of organic substance in the presence of oxygen.
- In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely oxidised in the presence of O2 and releases CO2, water and larger amounts of energy i,.e 686Kcal.
- It occurs in all higher plants, in four steps. ATP output is 36 molecules.
C6H12O6+ 6O2 + 6H20 → 6CO2 + 12H2O + 686 Kcals. - As the energy output is more, it is more efficient than anaerobic respiration.
Question 2.
Pyruvic acid is end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic fates of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions?
Answer:
The metabolic fate of pyruvic acid depends on the cellular need ie., the availability of O2 & type of organism.
There are three major ways in which different cells handle pyruvic acid formed by glycolysis.
- Under aerobic conditions, aerobic transpiration takes place. Here complete oxidation of pyruvic acid through kreb’s cycle takes place in the presence of O2.
- Under anaerobic conditions (absence of O2) fermentation takes place in many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes.
(i) Lactic acid fermentation (ii) Alcoholic fermentation
Question 3.
The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than during anaerobic respiration. Why there is anaerobic respiration even in organisms that live in aerobic conditions like human beings and angiosperms?
Answer:
1) During the scarcity of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place in organisms that live in aerobic conditions.
2) Muscle tissue under intense use, demands too much energy (ATP) and consumes much more oxygen to produce that energy. This high consumption leads to oxygen scarcity and the muscle cell begins to produce lactic acid by anaerobic respiration to fulfill their energy needs.
3) The first cells on this planet lived in an atmosphere are lacked O2. Even today all living organisms retain the enzymatic machinery to partially oxidize glucose without the help of oxygen during glycolysis.
Question 4.
Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration but it enters the respiratory process at the end. Discuss.
Answer:
- Although the aerobic process of respiration takes place only in the presence of oxygen, the role of oxygen is limited to the terminal stage of process.
- Oxygen presence is vital because it drives the whole process by removing hydrogen from the system.
- Oxygen acts as final hydrogen acceptor.
- O2 accepts 2H+ from complex 1V & from 2e– cytochrome C to induce 1 H2O molecule.
Question 5.
Respiration is an energy-releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process that involves a stepwise oxidative break down of organic substances inside living cells. In this statement about respiration, explain the meaning of (i) stepwise oxidative break down (ii) organic substance (used as substrate)
Answer:
(i) The oxidation of glucose is not a single-step reaction.
It occurs in a step wise manner to release energy in the form of ATP.
- Glycolysis – Glucose is converted to pyruvic acid in the cytoplasm (almost 9 biochemical reaction)
- Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid in mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle occurs in mitochondrial matrix.
- Electron transport which occurs in inner mitochondrial membrane Hence respiration is a series of stepwise biochemical reactions.
(ii) Respiratory substrates are organic molecules which are oxidized during respiration. Most common respiratory organic substrate is glucose.
Question 6.
Comment on the statement – Respiration is an energy-producing process but ATP is used in some steps of the process.
Answer:
Though ATP is released at the end of respiration, ATP is utilized in two steps during glycolysis.
- In glycolysis, ATP is utilized in the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP - ATP is utilized in the conversion of Fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1-6-biphosphate
Fructose -6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose -1,6- diphosphate + ADP
![]()
Question 7.
Explain briefly the process of glycolysis.
Answer:
- Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the first step of respiration in all living organisms.
- It occurs in cytoplasm of cells.
- During Glycolysis, Glucose molecules break down to release energy.
- Glycolysis is the partial oxidation of one glucose molecule to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.
- In glycolysis a chain of ten reactions under the control of different enzymes takes place.
- The end products of Glycolysis are pyruvic acid (PA), ATP, NADPH + H+
Question 8.
Why is the respiratory pathway referred to as an amphibolic pathway? Explain.
Answer:
- Glucose is the most favoured substrate for respiration.
- If the fats want to become a respiratory substrate, they have to break down into fatty acids, and they have to degrade into Acetyl Co. A and then only they have to enter into the respiratory pathway.
- But when the organism needs to synthesize fatty acids, acetyl Co. A. would be with draw from the pathway and has to synthesize fatty acids.
- Hence respiratory pathway comes into the picture both during the breakdown and synthesis of fatty acids.
- Similarly during the breakdown and synthesis of proteins also respiratory intermediates form a link.
- The break down of respiratory substrates is called catabolism.
- The synthesis of the substrates like proteins and fats is called anabolism.
- As the respiratory pathway is involved in both catabolism and anabolism, it is known as amphibolic pathway.
Question 9.
We commonly call ATP the energy currency of the cell. Can you think of some other energy carriers present in a cell. Name any two.
Answer:
- NADH and FADH2
- Oxidation of one molecule of NADH gives rise to 3 molecules of ATP.
- Oxidation of one molecule of FADH2 gives rise to 2 molecules of ATP.
- This takes place in electron transport system for mitochondria.
Question 10.
ATP produced during glycolysis is a result of substrate-level phosphorylation. Explain.
Answer:
ATP is formed from two substrates by dephosphorylation during glycolysis.
- 1,3 biphospho glyceric acid + ADP → 3-phosphoglyceric acid + ATP
- Phosphoenol pyruvic acid + ADP → Pyruvic acid + ATP
Question 11.
Do you know any step in Kreb’s cycle where there is a substrate-level phosphorylation. Explain.
Answer:
- During conversion of succinyl Co.A to succinic acid, a molecule of GTP is synthesized.
- This is a substrate-level phosphorylation.
- In a coupled reaction, GTP is converted to GDP with the simultaneous synthesis of ATP from ADP.
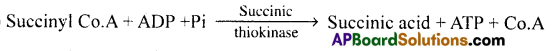
Question 12.
When a substrate is being metabolized, which doesn’t all energy produced get released in one single step? Instead, it is released in multiple steps what is the advantage of step wise release of energy?
Answer:
- The process of aerobic respiration is divided into four phases (glycolysis, kreb’s cycle, ETS and oxidative phosphorylation).
- The process of respiration takes place in step wise manner to release ATP.
- The product of one pathway forms substrate for another pathway.
- The respiratory substrates enter and withdraw’ from pathway on necessity ATP gets utilized whenever required and enzymatic rates are generally controlled
- Various molecules produced in respiration are involved in other biochemical processes.
- Thus, the stepwise release of energy makes the system more efficient in extracting and storing energy.
Question 13.
Respiration requires O2. How did first cells on earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked oxygen?
Answer:
- For early organisms, the source of energy must have been either fermentation or Anaerobic respiration.
- O2 is required for oxidation of food materials and release of energy.
- When a cell performs photosynthesis, O2 is released within the cell.
- This released O2 can be utilised for oxidation of food and release of energy.
- Primitive cells must have survived by this method.
Question 14.
The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than during anaerobic respiration. Explain.
Answer:
- In aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid is ‘completely oxidised’ in the presence of oxygen.
So the energy release1 is more - C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20 → 6CO2 + 12H2O + 686 Kcals.
- In anaerobic respiration, pyruvic acid is ‘partially oxidised’ in the absence of oxygen to ethyl alcohol. So the ‘energy release’ is less.
- C6H12O6 → 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH + 56Kcal.
Question 15.
RuBPcarboxylase, PEPase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactic dehydrogenase.
Select the enzymes from the list above which are involved in (a) Photosynthesis (b) Respiration (c) Both photosynthesis and respiration
Answer:
(a) Enzymes in Photosynthesis: RuBP carboxylase, PEP ase
(b) Enzymes in respiration: Cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Lactic dehydrogenase (Anaerobic respiration),
(c) Enzymes in Photosynthesis & Respiration : ATP ase.
Question 16.
How does a tree trunk exchane gases with the environment although it lacks stomata?
Answer:
- The older tree trunk is covered by dead woody tissue called cork.
- Lenticels openings are present in the bark of the trunk.
- They never close.
- The exchange of gases between trunk and outside an takes place through these lenticels.
Question 17.
Write about two energy-yielding reactions of glycolysis.
Answer:
The two energy-yielding reactions of glycosis are DephosphoryIation(Step 7) and the final dephosphorylation (Step 10).
1) In the seventh bio chemical reaction of Glycolysis 1,3 biphospho glyceric acid is converted into 3- Phospho glyceric acid. The inorganic phosphate released in this process is accepted by ADP and utilised in the formation of ATP mole. This is a substrate level phosphorylation. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme phosphoglycero kinase.
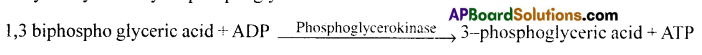
2) In the final step of Glycolysis. Phosphoenol pyruvic acid is converted into pyruvic acid. The inorganic phosphate released in this reaction is accepted by ADP and forms an ATP mole. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme pyruvic kinase. This is also a substrate level phosphorylation.
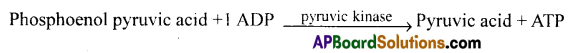
![]()
Question 18.
Name the site(s) of Pyruvate synthesis. Also write the chemical reaction wherein pyruvic acid dehydrogenase acts as a catalyst.
Answer:
- Pyruvic acid is synthesized in cytoplasm.
- Pyruvic acid enters into mitochondrial matrix undergoes oxidative decarboxylation by pyruvic dehydrogenase and several coenzymes including NAD+ and coenzyme A.
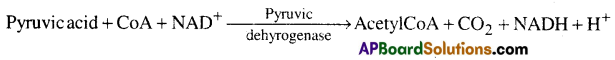
Question 19.
Mention the important series of events of aerobic respiration that occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion as wella as the one that takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Answer:
1) The important series of aerobic respiration that occurs in the mitochondrian matrix, is TCA cycle or Kreb’s cycle.
2) During citric acid cycle, complete oxidation of pyruvate takes place by step wise relese of hydrogen atoms leving 3 molecules of CO2 eight molecules of NADH + H+ and two molecules of ATP are formed.
3) The important series of events that takes place is in the inner membrane of the mitochondria is Electron transport system (ETS) and oxidative phosphorylation.
4) NADH + H+ and FADH2 are oxidised and releases energy through electron transport system and electrons are passed on to O2 releasing in the formation of H2O.
5) When electrons pass from ofre carrier to another through’ complex I to IV, they are coupled to ATPsynthetase for the porduction of ATP from ADP and Pi.
Question 20.
The respiratory pathway is believed to be a catabolic pathway. However, the nature of TCA cycle is amphibolic. Explain
Answer:
- Glucose is the most favoured substrate for respiration.
- If the fats want to become a respiratory substrate, they have to break down into fatty acids, and they have to degrade into Acetyl Co. Answer: and then only they have to enter into the respiratory pathway.
- But when the organism needs to synthesize fatty acids, acetyl Co. Answer: would be with drawn from the pathway and has to synthesize fatty acids.
- Hence respiratory pathway comes into the picture both during the break down and synthesis of fatty acids.
- Similarly during the breakdown and synthesis of proteins also respiratory intermediates form a link.
- The break down of respiration substrates is called catabolism.
- The synthesis of the substrates like proteins and fats is called anabolism.
- As the respiratory pathway is involved in both catabolism and anabolism, it is known as amphibolic pathway.
Question 21.
The net gain of ATP for the complete aerobic oxidation of glucose is 36. Explain.
Answer:
The balance sheet of ATP production in aerobic oxidation of Glucose:
A) Glycolysis:
1) ATP produced by substrate-level phosphorylation:
Biphosphoglyceric acid to Phospho glyceric acid : 2 x 1 = 2 ATP
Phosphoenol Pyruvic acid to Pyruvic acid : 2 x 1 = 2 ATP
ATP consumed for the phosphorylation of Glucose and fructose -6 phosphate : -2 ATP
Net gain of ATP : +2ATP
2) ATP from NADH generated in Glycolysis:
G-3-P to BPGA(2 NADH, each worth 2 ATP) : 2 x 2 = 4 ATP
ATP gain from glycolysis in the presence of O2 : 6 ATP(a)
B) Oxidative de carboxylation of pyruvic acid:
Pyruvic acid to acetyl Co.A (2 NADH, each worth 3 ATP) : 2 x 3 = 6 ATP(b)
C) Kreb’s Cycle:
1) ATP produced in substrate-level phosphorylation succinyl Co.A to Succinic acid: 2 x 1 = 2 ATP
2) ATP from NADH: Isocitric acid to Oxalosuccinic acid : 2 x 3 = 6 ATP
α-Keto glutaric acid to Succinyl Co.A : 2 x 3 = 6 ATP
Malic acid to Oxalo acetic acid: 2 x 3 = 6 ATP
3) ATP from FADH2:Succinic acid to fumeric acid : 2 x 3 = 6 ATP
ATP value of Kreb’s cycle: 2 x 2 = 4 ATP
Net gain of ATP in aerobic respiration per one mole of Glucose (a+b+c) = 36 ATP
Question 22.
Define RQ. Write a short note on RQ. [TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
1) Respiratory Quotient(RQ): The ratio between the volume of CO2 given out and O2 taken in a given period of time at standard temperature and pressure during respiration is called RQ.

A- stands for volume of CO2 absorbed during respiration.
B- stands for volume of O2 liberated during respiration.
2) RQ for fats will always be less than one.
3) Ex: Triolein
C57H104O6 + 80 O2 → 57 CO2 + 52 H2O
RQ for Triolein (Fat) = 57/80 = 0.7
4) If RQ is 1, the carbohydrates are used as respiratory substrate.
5) If RQ is less than 1, fats are used as respiratory substrate.
6) If RQ is more than 1, organic acids are used as respiratory substrate.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a,b,c and d with appropriate terms. Breitly explain the process and give any two applications of it.
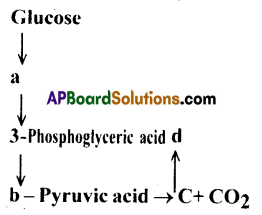
Answer:
a) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
b) Phosphoenol pyruvic acid
c) Ethanol
d) Lactic acid
![]()
Explanation:
- The given fermentation process refers to anaerobic respiration. ‘
- In this, glucose is partially oxidised to 2 pyruvic acid molecules which are converted to into ethanol and CO2 in the presence of Pyruvic acid, decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
- Lacto bacillus bacteria produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid.
- In this process, the reducing agent is NADH + H+ which is reoxidised to NAD+
Applications of Anaerobic respiration:
- Alcoholic fermentation and Anaerobic digestion.
- Biological treatment of waste water.
Question 2.
Explain Mitchell’s chemiosmosis in relation to oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer:
- The synthesis of ATP in respiration is associated with the consumption of oxygen, hence it is called as oxidative phosphorylation.
- Peter Mitchell proposed that the difference in concentration of protons on either side of the inner membrane (proton concentration gradient) is the main driving force for ATP Synthesis in mitochondria.
- This process is proposed by Mitchell is called chemiosmotic hypothesis.
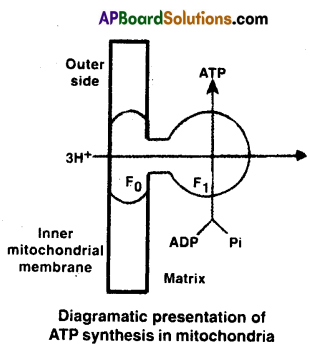
- Chemiosmotic hypothesis states that the energy of electrons harvested from glucose is used to transport protons out of the mitochondrial matrix.
- The return of the H+ back in to the matrix by diffusion through channels is coupled to ATP production.
- The energy released during the electron transport system is utilized in synthesizing ATP with help of ATP synthetase (complex -V) . This complex consists of two major components F1 and F0.
- F1 head piece is peripheral membrane protein complex and contains the site for synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
- F0 is an integral protein membrane complex that forms the channel protein membrane complex that forms the channel through which protons cross the inner membrane.
- The passage of protons through the channel is coupled to the catalytic site of F1 component for production of ATP.
- For each ATP produced, 3H+ pass through F0 from the intermembrane space to the matrix
down the electro chemical proton gradient. - Number of ATP molecules synthesized depends on nature of electron donor.
- Oxidation of mitochondrial NADH + H+ gives rise to 3 molecules of ATP while that lof cytosolic NADH + H+ or FADH2 produces two ATP molecules each.
Mitochondrial NADPH + H+
NADPH + H+ + ½ O2 + 3 ADP + 3Pi → NADP + 3ATP + 1H2O
Clvcolvtic NADPH + H+ or FADH2:
NADPH + H+ / FADH2 + ½ O2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi → NAD / FAD + 2ATP + 1H2O
Question 3.
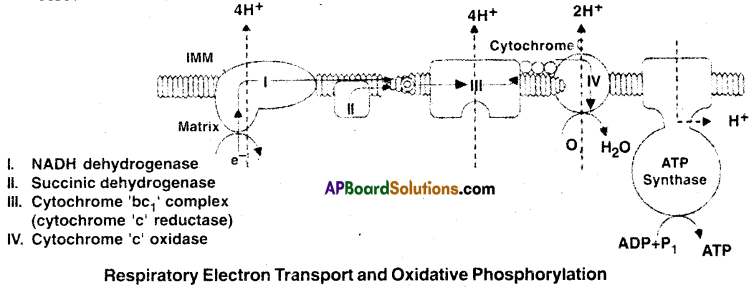
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration . Explain its role with respect to ETS.
Answer:
- NADPH + H+ or FADH2 formed in glycolysis and mitochondrial matrix are oxidised through
the electronic transport system and the electrons are passed on to O2 resulting in the formation of H2O. - The metabolic pathway through which an electron passes from one earner to another is called electron transport system.
- NADPH + H+ is oxidised and electrons are released in presence of NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) which are transferred to ubiquinone located within the inner membrane.
- Ubiquinone also receives reducing equivalents via FADH2 (Complex II).
- The reduced Ubiquinone (Ubiquinol) is oxidised and releases electrons which are accepted by cytochrome C1, Cytochrome (Complex III).
- Cytochrome C is a small protein acts as a mobile carrier for the transfer of electrons between complex III and IV to cytochromes ‘a’ and ‘a3‘, finally reaches 1/2 O2 along with 2H+ , produce 1 H2O molecule.
- During this electron flow, 10H+ moves from matrix to inner mitochondria membrane (4H+ at complex I, 4H+ at complex III and 2H+ at complex IV).
- As a result H+ concentration increases towards inner membrane of mitochondria.
- So the H+comes back to the matrix side through ATPase (F0, F1) involves in the synthesis of ATP.
Question 4.
Enumerate the assumptions that we undertake in making the respiratory balance sheet.
Are the assumptions valid for a living system? Compare fermentation and aerobic respiration in this context.
Answer:
a) It is possible to make calculations of the net gain of ATP for every glucose oxidised.
These calculations can be made only on the following assumptions.
- There is sequential orderly pathw ay functioning with one substrate forming the next artd with glycolysis, TCA Cycle, ETS pathway following one after another.
- The NADH synthesised in glycolysis in transferred into the mitochondria and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation
- None of the intermediates in the pathway are utilised to synthesize any other compound.
- Only glucose is being transferred no other alternative substrates are entering in the pathway at any of the intermediary stages.
b) But these kind of assumptions are not really valid in a living system. All pathways work simultaneously and do not take place one after another.
c) Comparison between Fermentation and Aerobic Respiration
| Fermentation | Aerobic Respiration |
| 1) Partial break down of glucose. | 1) Complete oxidation of glucose. |
| 2) End products are C02 and Ethyl alcohol. | 2) End products are C02 & H20 |
| 3) 2 ATP are formed | 3) 36 ATP are formed. |
Question 5.
Give an account of glycolysis. Where does it occur? What are the end products?
Trace the fate of these products in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. or
Describe the process of various biochemical reactions that occur during Glycolysis.
[AP, TS MAR-15], [AP, TS MAY-17] [AP, TS 20]
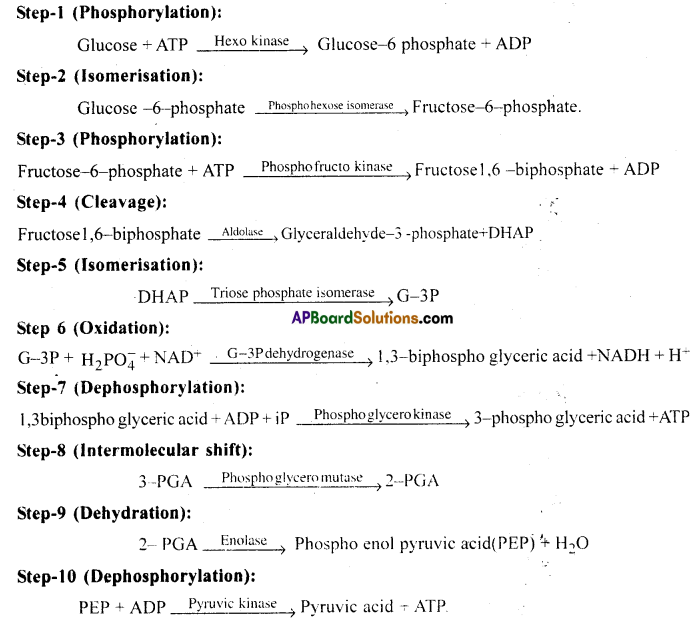
Answer:
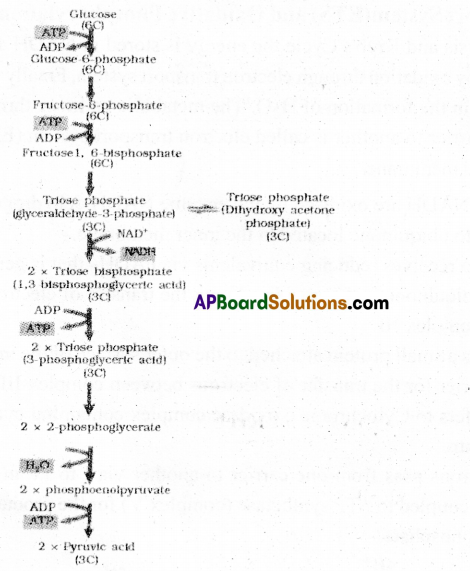
1) Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the first step of respiration in all living organisms. It occurs in cytoplasm of cells. During Glycolysis, Glucose molecules break down to release energy. Glycolysis is the partial oxidation of one glucose molecule to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.The end products of Glycolysis are pyruvic acid (PA), ATP, NADPH + H+
![]()
2) Fate of Pyruvic acid: In aerobic respiration, where oxygen is available, pyruvic acid will be completely oxidised into CO2 and H2O by Krebs cycle.
In anaerobic respiration, where oxygen is not available, pyruvic acid will be converted into Ethylalcohol or Lactic acid by Fermentation.
Glycolysis involves a chain of’10- step catalysed reactions’ by various enzymes.
3) Process of Glycolysis:
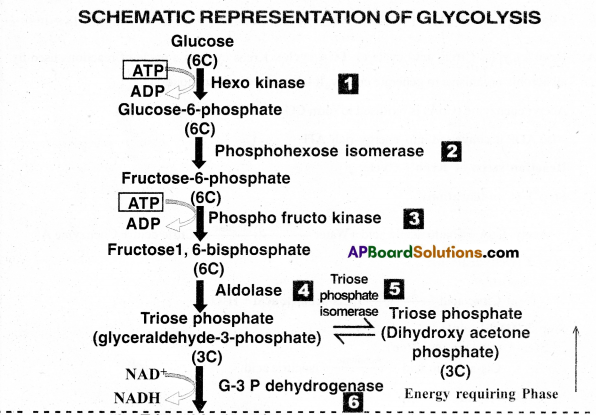

Question 6.
Explain the reactions of Kreb’s cycle. (AP,TSMAY-22] [APMAR-19,17,16] [TS MAR-17,19]
Answer:
Kreb’s Cycle( Citric acid cycle or TCA cycle): Krebs cycle is a cycle of reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy. It takes place in mitochondria.
Acetyl coenzyme (CoA ) is oxidised to form CO2 and H2O.
Also ADP is converted into ‘energy-rich’ ATP.
Reaction steps of Kreb’s Cycle:

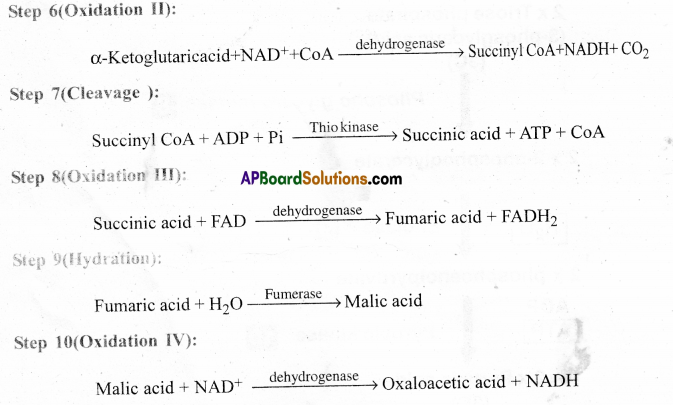
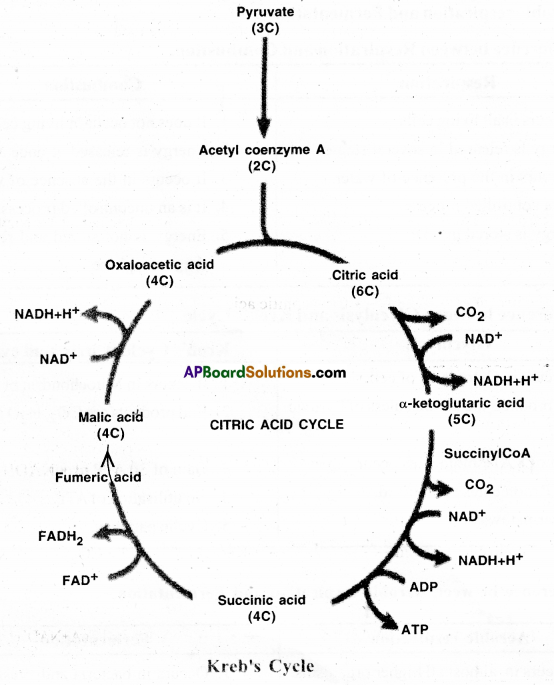
Exercise
Question 1.
Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation
Answer:
(a) Difference between Respiration and Combustion.
| Respiration | Combustion |
| 1. It occurs in all living cells. 2. Energy is released in several stages. 3. It occurs in the presence of water. 4. It is a controlled process. 5. Energy is stored in ATP |
1. it does not occur in living cells. 2. Energy is released at once as heat. 3. It occurs in the absence of water. 4. It is an uncontrolled process. 5. Energy is not stored and released into the atmosphere. |
b) Difference between Glycolysis and Kreb’s Cycle
| Glycolysis | Kreb’s Cycle (Citric acid cycle) |
| 1. It occurs in Cytoplasm of cell. | 1. It occurs in Mitochondria of cell. |
| 2. End products are 2 moleculess of Pyruvic acid. | 2. End products are CO2, H2O and Energy. |
| 3. Gain of 8 ATP molecules occur. | 3. Gain of 30 ATP occur. |
| 4. 2 ATP molecules are utilised. | 4. No utilisation of ATP. |
| 5. Linear pathway | 5. Cyclic pathway. |
c) Difference between Aerobic respiration and Fermentation
| Aerobic respiration | Fermentation |
| 1. It occurs in almost all higher organisms. 2. Occurs in the presence of oxygen. 3. Complete oxidation of glucose occurs. 4. End products are CO2 and water. |
1. Occurs in bacteria and yeast. 2. Occurs in the absence of oxygen 3. Partial oxidation of Glucose occurs. 4. End products are CO2 and Ethanol. |
Question 2.
What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
Answer:
The organic substances which are oxidised during respiration and liberate energy are called respiratory substrates.
The most common respiratory substrate is glucose.
Under certain circumstances proteins, fats are also used as respiratory substrates.
Question 3.
Give the schematic representation of glycolysis?
Answer:
Question 4.
What are the main steps in aerobic respiration? Where docs it take place?
Answer:
The main steps in aerobic respiration are – Glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, Electron transport system and Oxidative phosphorylation.
- Glycolysis – Occurs in Cytoplasm of the cell.
- Kreb’s cycle – Occurs in matrix of mitochondria
- ETS and oxidative phosphorylation – Occurs in the inner membrane of mitochondria.
![]()
Question 5.
Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Kreb’s cycle.
Answer:
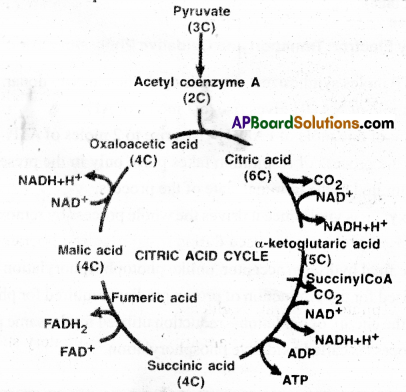
Question 6.
Explain ETS.
Answer:
Electron Transport System(ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation:
During Glycolysis and Kreb’s Cycle the energy is stored in NADH + H+ and FADH2. This energy is released by oxidation through electron transport system. Finally the electrons are passed on to O2 resulting in the formation of H2O. The metabolic pathway through which an electron passes from one carrier to another is called electron transport system (ETS). It is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Electrons from NADH are oxidised by the enzyme NADH dehydrogenase and the electrons are transferred to ubiquinone located in the inner membrane.
- Ubiquinone also receives reducing equivalents via FADH2 that is generated in Kreb’s cycle.
- The reduced Ubiquinone is then oxidised with the transfer of electron to Cytochrome c via Cyt b, Cyt c , complex III.
- Cytochrome c is a small protein attached to the outer surface of the inner membrane and acts as a mobile carrier for the transfer of electrons between complex III and IV.
- Complex IV refers to Cytochrome c oxidase complex containing cytochrome a and a3, and two copper centre.
- When the electrons pass from one carrier to another via I to IV in the electrons transport chain, they are coupled to ATP synthetase (complex V) for the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
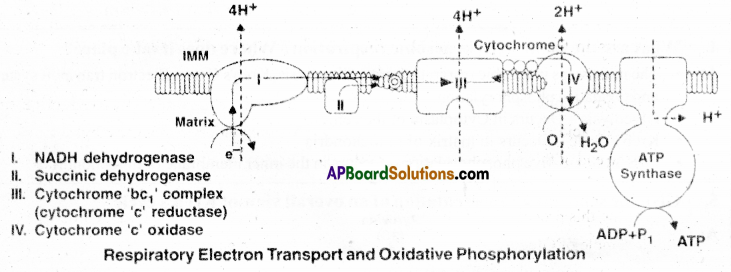
The number of ATP moles synthesized depends upon the electron donar. - Oxidation of one mole of NADH gives rise to 3 moles of ATP.
- While the oxidation of one mole of FADH2 gives rise to 2 moles of ATP.
- Although the aerobic process of respiration takes place only in the presence of oxygen, the role of oxygen is limited to the terminal state of the process.
- The presence of oxygen is vital, since it drives the whole process by removing hydrogen from the system.
- Oxygen acts as the final hydrogen acceptor, unlike photophosphorylation where it is the light energy that is utilised for the production of proton gradient required for phosphorylation.
- In respiration it is the energy of oxidation – reduction utilised for the same process. It is for this reason that the process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 7.
Distinguish between the following:
a. Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
b. Glycolysis and Fermentation
c. Glycolysis and Critic acid cycle
Answer:
a) Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respirs Gn.
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| 1. It occurs in the presence of oxygen. | 1. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. |
| 2. It includes Glycolysis, Kreb’s Cycle, ETS and oxidative phosphorylation. | 2. It includes Glycolysis and Fermentation. |
| 3. C6H12O6 +6O2 → 6CO2+6H2O +Energy | 3. C6H12O6 → 2CO2+2C2H5OH +Energy |
| 4. Complete oxidation of glucose takes place. | Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place. |
| 5. During this process 38 ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose. | During this process 2 ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose. |
b) Difference between glycolysis and Fermentation.
| Glycolysis | Fermentation |
| 1. Occurs in the Cytoplasm of all living organisms. | 1. Occurs in yeast cells. |
| 2. Glucose is converted into 2 molecules of Pyruvic acid. | 2. Pyruvic acid undergoes reduction and carboxylation to produce ethyl alcohol. |
| 3. At the end of this process a gain of 8 ATP occurs. | 3. Energy released is 2 ATP. |
| 4. During this process 2 ATP are utilised. | 4. CO2 is released.during this process. |
| 5. One mole of Glucose → 2 molecules of Pyruvic acid | Pyruvic acid → Ethyl alcohol + CO2 + Energy |
c) Difference between glycolysis and citric acid cycle
| Glycolysis | Kreb’s Cycle (Citru acid cycle) |
| 1. It occurs in Cytoplasm of cell. | 1. It occurs in Mitochondria of cell. |
| 2. End products are 2 molecules of Pyruvic acid. | 2. End products are CO2, H2O and Energy. |
| 3. Gain of 8 ATP moles occur. | 3. Gain of 30 ATP molecules occur. |
| 4. 2 ATP molecules are utilised. | 4. No utilisation of ATP. |
| 5. Linear pathway | 5. Cyclic pathway. |
Question 8.
What are the assumption made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
Answer:
The calculations made on the net gain of ATP during aerobic respiration is purely based on some assumptions. They are.
- The pathways are operating in an orderly manner one after another.
- The pathways are Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, Electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Only glucose is respired – no other alternative substrates entering this pathway at any of the intermediate stage.
- No intermediates in this pathway are utilised to synthesize any other compound.
- The NADH synthesized in Glycolysis is transferred to the mitochondria and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 9.
Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.”
Answer:
- Glucose is the most favoured substrate for respiration.
- If the fats want to become a respiratory substrate, they have to break down into fatty acids, and they have to degrade into Acetyl Co. Answer: and then only they have to enter into the respiratory pathway.
- But when the organism needs to synthesize fatty acids, acetyl Co. Answer: would be with drawn from the pathway and has to synthesize fatty acids.
- Hence respiratory pathway comes into the picture both during the break down and synthesis of fatty acids.
- Similarly during the breakdown and synthesis of proteins also respiratory intermediates form a link.
- The break dow n of respiration substrates is called catabolism.
- The synthesis of the substrates like proteins and fats is called anabolism.
- As the respiratory pathway is involved in both catabolism and anabolism, it is known as v amphibolic pathway.
![]()
Question 10.
Define RQ. What is its value for fats?
Answer:
Definition: The ratio between the volume of CO2 given out and O2 taken in a given period of time at standard temperature and pressure during respiration is called RQ.
RQ for fats: will always be less than one.
Ex: Triolein
C57H104O6 + 80 O2 → 57 CO2 + 52 H2O
RQ for Triolein (Fat) = 57/80 = 0.7
Question 11.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Answer:
- Synthesis of ATP from ADP and iP is called Phosphorylation.
- If this process is coupled to electron transport from substrate to molecular oxygen is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 12.
What is the significance of step-wise release of energy in respiration?
Answer:
- The breaking of C-C bonds of complex organic substances in respiration leads to release considerable amount of energy.
- All the energy is not released free into the cell or in a single step.
- It is released in a slow stepwise reactions controlled by enzymes and trapped in the form of ATP.
- It is broken down when ever energy needs to be utilised.
- Hence ATP acts as the energy currency of the cell.
- The step wise release of energy keeps the temperature of cell low.
- It minimises the wastage of energy.
- The activities of enzymes at different steps can be controlled.
- Thus stepw ise release of energy makes the system more efficient in extracting and storing energy.
Question 13.
Find the correct ascending sequence of the following, on the basis of energy released in respiratory oxidation.
a. 1 gm of fat
b. 1 gm of protein
c. 0.5gm of protein + 0.5 gm of glucose
d. 1 gm of glucose
Answer:
Ascending order-
a) 1 gm of fat
b) 1 gm of protein
c) 0.5 gm of protein + 0.5 gm of glucose
d) 1 gm of glucose
Question 14.
Name the products, respectively, in aerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle and anaerobic- fermentation in yeast.
Answer:
a) The product in aerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle is – Pyruvic acid.
b) The product of anaerobic respiration in yeast is – CO2 and Ethanol.
Question 15.
If a person is feeling dizzy, glucose or fruit juice is given immediately but not a cheese sandwich, which might have more energy. Why?
Answer:
Glucose is a simple sugar, so that it can be easily absorbed into the blood. It is the same situation
in the case of glucose present in the fruit juice. So the people feeling dizzy are to be provided with glucose or fruit juice, but not sandwich.
Question 16.
In a way green plants and cyanobacteria have synthesised all the food on earth. Comment.
Answer:
- Green plant and Cyanobacteria-contain chlorophyll pigment. .
- Can prepare food and supply it to consumers directly or indirectly.
- Plants prepare food but not all the food on the earth.
Question 17.
It is known that red muscle fibres in animals can work for longer periods of time continuously. How is this possible?
Answer:
Muscle fibres of striated muscles contain large number of mitochondria. They work with more speed and active for longer period. Smooth muscles can work still more longer periods than striated muscles.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The number of reduced coenzymes that are formed in one turn of Krebs cycle is
1. 2
2. 3
3. 4
4. 8
Answer:
3. 4
Question 2.
In anaerobic respiration. pyruvic acid is converted into ethyl alcohol by
1. decarboxylation and reduction
2. decarboxylation and oxidation
3. reduction and decarboxylation
4. oxidation and reduction
Answer:
1. decarboxylation and reduction
Question 3.
The last 6C compound of TCA cycle is
1. α-ketoglutaric acid
2. Oxalosuccinic acid
3. Isocitric acid
4. Cis-aconitic acid
Answer:
2. Oxalosuccinic acid
![]()
Question 4.
Total number of ATP molecules formed when citric acid molecule is oxidized in aerobic respiration is
1. 12
2. 14
3. 15
4. 19
Answer:
1. 12
Question 5.
Common phase for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration is
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs cycle
3. ETS
4. Fermentation
Answer:
1. Glycolysis
Question 6.
The compound that is regenerated in Krebs cycle is
1. Citric acid
2. Acetyl Co-A
3. OAA
4. Malic acid
Answer:
3. OAA
Question 7.
GTP formation is seen during substrate level phosphorylation of mitochondrial Kreb’s cycle in
1. Animal cells
2. Plant cells
3. Bacteria
4. Blue green Algae
Answer:
1. Animal cells
Question 8.
The number of steps of Kreb’s cycle involved in \ADH formation is (are)
1. One
2. Two
3. three
4. Four
Answer:
3. three
Question 9.
The enzyme helping in dehydration step of Kreb’s cycle is
1. Fumarase
2. Aconitase
3. Dehydrogenase
4. Synthetase
Answer:
2. Aconitase
Question 10.
Identify the incorret statement regarding g lycolysis
1. It is hexose diphosphate pathway
2. It is common for aerobic and anaerobic respiration
3. It releases CO2
4. It does not use oxygen
Answer:
3. It releases CO2
Question 11.
Anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration in
1. having glycolysis
2. lacking glycolysis
3. involving oxidation
4. not involving mitochondria
Answer:
4. not involving mitochondria
Question 12.
The only co-enzyme involved in glycolysis is
1. NADP+
2. FAD
3. FMN
4. NAD+
Answer:
4. NAD+
Question 13.
Which of the following is NOT the end product of fermentation?
1. Acetic acid
2. Lactic acid
3. Ethyl alcohol
4. G-3-P
Answer:
4. G-3-P
Question 14.
Products of cleavage reaction in Krebs cycle is
1. Succinyl CoA+ATP/GTP
2. Succinic Acid + ATP/GTP+CoA
3. Succinic acid + NADH+ + H+ + COA
4. Succinyl CoA + NAD+
Answer:
2. Succinic Acid + ATP/GTP+CoA
Question 15.
RQ value of sucrose is
1. 2.0
2. 1.6
3. 1.0
4. 4.0
Answer:
3. 1.0
Question 16.
In glycolysis, water molecule is removed from
1. PEP
2. G-3-P
3. 3-PGA
4. 2-PGA
Answer:
4. 2-PGA
Question 17.
Role of oxygen in respiration
1. Conversion of complex substances into simple substances
2. Oxidation cf simple substances
3. Behaves as an electron acceptor
4. Accepts both electron and protons
Answer:
4. Accepts both electron and protons
Question 18.
Plants which exhibit anaerobic respiration are
1. Green plants
2. Bacteria and Yeasts
3. Saprophytes
4. Parasites
Answer:
2. Bacteria and Yeasts
![]()
Question 19.
Substances that are mostly used in the oxidation during cellular respiration
1. Proteins
2. Fats
3. Organic acids
4. Carbohydrates
Answer:
4. Carbohydrates
Question 20.
Site of glycolysis is
1. Cytoplasm
2. Mitochondria
3. Matrix
4. Cristae
Answer:
1. Cytoplasm
Question 21.
Energy liberated during glycolysis is in the form of
1. Pyruvic acid
2. Carbon dioxide and water
3. ADP & NADH
4. ATP & NADH
Answer:
4. ATP & NADH
Question 22.
The connecting link between glycolysis and Kerb’s cycle is
1. PGA
2. Acetyle CoA
3. PEP
4. Acetaldehyde
Answer:
2. Acetyle CoA
Question 23.
Enefgy currency of the cell is
1. NADP
2. ADP
3. NADH
4. ATP
Answer:
4. ATP
Question 24.
One glucose molecule through EMP pathway forms
1. 2NADH & 4 ATP
2. 2NADH & 2ATP
3. 4NADH & 2 ATP
4. 4NADH & 4ATP
Answer:
1. 2NADH & 4 ATP
Question 25.
Direct use of oxygen is found in the following process
1. Glycolysis
2. Kreb’s cycle
3. Electron transport system
4. Fermentation
Answer:
3. Electron transport system
Question 26.
Glycosis yields more energy in
1. Aerobic respiration
2. Anaerobic respiration
3. Fermentation
4. Photorespiration
Answer:
1. Aerobic respiration
Question 27.
During glycolysis glucose splits into
1. 2 Acetic acid molecules
2. 2 Triose molecules
3. 2 pyruvic acid molecules
4. 2 Latic acid molecules
Answer:
3. 2 pyruvic acid molecules
Question 28.
Respiration is considered as
1. Catabolic process
2. Anabolic proces
3. Amphibolic process
4. Endergonic process
Answer:
3. Amphibolic process
Question 29.
Complete oxidation of glucose molecule occurs during
1. Anaerobic respiration
2. Fermenration
3. Aerobic respiration
4. Glycolysis
Answer:
3. Aerobic respiration
Question 30.
Anaerobic respiration requires
1. ATP
2. FADH2
3. CO2
4. ATP and NADH
Answer:
4. ATP and NADH
Question 31.
Carbon dioxide released is more than oxygen absorbed when
1. Sucrose is used as respiratory substrate
2. Glucose is used as respiratory substrate
3. Fats are used as respiratory substrate
4. Organic acids are used as respiratory substrates
Answer:
4. Organic acids are used as respiratory substrates
Question 32.
Glycolysis consists of a chain of
1. 6 reactions
2. 8 reactions
3. 10 reactions
4. 4 reactions
Answer:
3. 10 reactions
![]()
Question 33.
In plants, more energy is produced during the process of
1. Glycolysis
2. Kreb’s cycle
3. Electron Transport system
4. Fermentation
Answer:
3. Electron Transport system
Question 34.
Both respiration and photosynthesis require
1. Glucose
2. Cytochromes
3. Sun light
4. Oxygen
Answer:
2. Cytochromes
Question 35.
Energy rich compound formed during Kreb’s cycle
1. ATP
2. ADP
3. GDP
4. CTP
Answer:
1. ATP
Question 36.
Pyruvic acid enter into the Kreb’s cycle in the form of
1. Citric acid
2. Succinyl CoA
3. Acetyl CoA
4. Isocitric Acid
Answer:
3. Acetyl CoA
Question 37.
Enzyme required for conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose is
1. Hexokinase
2. Isomerase
3. Invertase
4. Enolase
Answer:
3. Invertase
Question 38.
The compound that is regenerated in Krebs cycle is
1. Citric acid
2. Acetyl co.A
3. OAA
4. Enolase
Answer:
3. OAA
Question 39.
Aerobic respiration involves
1. Oxidation
2. Catabolism
3. Anabolism
4. All of these
Answer:
4. All of these
Question 40.
Decarboxylation is involved in
1. Electron transport system
2. Glycolysis
3. Kreb’s cycle
4. Lactic acid fermentation
Answer:
3. Kreb’s cycle
Question 41.
The enzymes involved in glycolysis are
1. Hexokinase, enolase
2. Fumarase, enolase
3. Enolase, alcoholic dehydrogenase
4. Enolase, succinic dehydrogenase
Answer:
1. Hexokinase, enolase
Question 42.
The site of oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid is
1. Cell sap
2. Mitochondrion
3. Ribosomes
4. Golgi complex
Answer:
2. Mitochondrion
Question 43.
Respiration is
1) catabolic and exergonic process
2) catabolic and endergonic process
3) anabolic and endergonic process
4) anabolic and exergonic process
Answer:
1) catabolic and exergonic process
Question 44.
The path of ‘glucose breakdown to pyruvic acid’ was discovered by
1) Embden, Meyerhof and Pamas
2) Warburg and Dickens
3) Sir Hans Krebs
4) Calvin
Answer:
1) Embden, Meyerhof and Pamas
Question 45.
In which of the following reactions, substrate level phosphorylations doesn’t occur
1) 1,3- bits PGA → 3PGA
2) Glucose 6P → fructose – 6.P
3) Succinyl Co A → succinic acid
4) PEP → Pyruvic acid
Answer:
2) Glucose 6P → fructose – 6.P
![]()
Question 46.
The reduced coenzyme that is oxidised in fermentation is
1) NA DPH + H+
2) NADH + H+
3) NADH + H+
4) FADH
Answer:
3) NADH + H+
Question 47.
The triose suitable for biological oxidation is
1) glyceradehyde 3-P
2) DHAP
3) 2 Phospho glyceraldehyde
4) Fructose 6-P
Answer:
1) glyceradehyde 3-P
Question 48.
End product of glycolysis is the substrate for
1) Krebs cycle
2) fermentation
3) electron transport
4) oxidative phosphory lation
Answer:
2) fermentation
Question 49.
The connecting link reaction and Krebs cycle occurs in
1) cytosol
2) cristae
3) peroxisomes
4) Mitochondrial matrix
Answer:
4) Mitochondrial matrix
Question 50.
Product of first biological oxidation in Kreb cycle is
1) Isocitric acid
2) Oxalo succinic acid
3) °o keto glutaric acid
4) Succinic acid
Answer:
2) Oxalo succinic acid
Question 51.
In Krebs cycle, the substrate for final oxidation step is the product of the following biochemical reaction
1) Condensation
2) Decarboxylation
3) Dehydrogenation
4) Hydration
Answer:
3) Dehydrogenation
Question 52.
The only enzyme of Krebs cycle having prosthetic group as cofactor is
1) Succinic thiokinase
2) Succinic dehydrogenase
3) Isocitric dehydrogenase
4) a-ketoglutaric dehydrogenase
Answer:
2) Succinic dehydrogenase
Question 53.
The ratio of oxidation reactions in cytoplasm and mitochondria during aerobic respiration is
1) 1:5
2) 2:4
3) 1:4
4) 2:3
Answer:
1) 1:5
Question 54.
The last or ultimate reaction in aerobic respiration is
1) Formation of Acetyl CoA
2) Conversion of malic acid to oxaloacetic acid
3) Reduction of Cytochrome oxidase
4) Reduction of atmospheric O2
Answer:
4) Reduction of atmospheric O2
Question 55.
Complete oxidation of pyruvic acid results in the formation of ……………. end products
1) CO2 & H2O
2) CO2 & Malic acid
3) CO2 & C2H5OH
4) CO2 & Succinic acid
Answer:
1) CO2 & H2O
Question 56.
Cytochromes a and a3, and two copper centres are found in
1) Cytochrome C reduction
2) Cytochrome C oxidiase
3) Succinic dehydrogenase
4) NADH dehydrogenase
Answer:
2) Cytochrome C oxidiase
Question 57.
Conversion of pyruvic acid to ethanol includes
1) Dehydrogenation and oxidation
2) Decarboxylation and reduction
3) Decarboxylation (only)
4) Dehydrogenation and carboxylation
Answer:
2) Decarboxylation and reduction
Question 58.
Which of the following process makes direct – use of oxygen ?
1) Glycolysis
2) Fermentation
3) Electron transport
4) Citric acid cycle
Answer:
3) Electron transport
Question 59.
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvic acid enters into
1) Anaerobic respiration
2) Krebs cycle
3) M itochondrial matrix
4) Cristae
Answer:
1) Anaerobic respiration
Question 60.
Oxidative decarboxylation occurs in
1) Mitochondrial membrane
2) Cytosol of cell
3) Mitochondrial matrix
4) Perimitochondrial membrane
Answer:
3) Mitochondrial matrix
Question 61.
The number of complexes and mobile carriers are involved in the electron transport system and oxidative phosphorylation:
1) 5 and 2
2) 4 and 3
3) 5 and 1
4) 4 and 2
Answer:
1) 5 and 2
![]()
Question 62.
Proteins are converted into before they enter into respiratory pathway
1) Glucose
2) Amino acids
3) Glycerol
4) Fatty acids
Answer:
2) Amino acids
Question 63.
Glycolysis occurs in
1) an animal cell
2) all living cells
3) plant cells only
4) Protista cells only
Answer:
2) all living cells
Question 64.
In muscles during exercise, when oxygen is inadequate for cellular respiration, pyruvic acid is reduced to
1) Acetyl coenzyme A
2) Ethyl alcohol
3) Lactic acid
4) Acetic acid
Answer:
3) Lactic acid
Question 65.
65. A single turn of Krebs cycle yields
1) 1FADH2, 2NADH2 and 1ATP
2) 2FADH2, 1NADH2 and 1 ATP
3) 1FADH2, 3NADH2 and 1 ATP
4) 1FADH2, 1NADH2 and 1 ATP
Answer:
3) 1FADH2, 3NADH2 and 1 ATP
Question 66.
The ultimate electron acceptor and last electron donor of FTS which on mitochodrial cristae respectively, are
1) Cytochrome -a3 and Cyt-c
2) Ubiquinone and Cyt-a3
3) H20 and Cyt-a3
4) Oxygen and Cyt-a3
Answer:
4) Oxygen and Cyt-a3
Question 67.
Before entering into respiration, fats should be broken down into
1) Fatty acid + Amino acid
2) Fatty acid + Glucose
3) Fatty acid + Glycerol
4) Glycerol + Glucose
Answer:
2) Fatty acid + Glucose
Question 68.
Respiratory pathway is called amphibolic pathway because it is involved in both
1) Catabolism & Anabolism
2) Protein synthesis and photosynthesis
3) Respiraion & Lipid metabolism
4) Fat & Lipid metabolism
Answer:
1) Catabolism & Anabolism
Question 69.
RQ is maximum in
1) Fats
2) Oxalic acid
3) Glucose
4) Protein
Answer:
2) Oxalic acid
![]()
Question 70.
Number of NADH + H+, CO2 and FADH2 formed in two turn of Krebs cycle is
1) 3, 2 & 1
2) 6, 4 & 2
3) 1, 2 & 3
4) 2, 2 & 1
Answer:
2) 6, 4 & 2