Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2019 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2019
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is Joint Hindu Family Business ? Discuss its main features.
Answer:
Meaning:
- “A business, which continues from one generation to another generation is known as “Joint Hindu Family Business”. This is special form of business organization, which now exists only in India. And the business is within the family.
- The head of the family is the head of the business also. He is . also known as “Karta” and the members are known as “co-parceners”.
Features of Joint Hindu Family Business : The essential fea-tures of the Joint Hindu Family Business are as follows.
a) Formation : In Joint Hindu Family business there must be atleast two members in the family, having some ancestral property. It is not created by an agreement but by operation of law.
b) Governed by Hindu Law : The JHF business is a jointly owned business. The management and control of the JHF business is done according to Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
c) Membership: The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. Unlike other business, outsiders are not allowed to become the coparceners in the JHF business. However, by adoption and Marriage with male member also confers membership.
d) Management: The business is managed by the senior most member of the family known as ‘Karta’ or ‘Manager’. Other members do not have the right to participate in the management. The Karta has the authority to manage the business as per his own will. His ways of managing cannot be questioned.
e) Profit Sharing : The Joint Hindu Family business is jointly owned by all the members. All the coparceners have equal share in the profits of the business.
f) Liability : All the members in a Joint Hindu Family have limited liability to the extent of property. The self acquired property of any member cannot be taken to pay the liabilities of the’family. But the liability of the Karta is unlimited. His personal property can also be utilised to meet the business liability.
g) Continuity : Death of any coparceners does not affect the continuity of business. Even on the death of the Karta, it continues to exist as the eldest of the coparceners takes position of Karta.
h) Accounts : The accounts are maintained by Karta. Karta is not accountable to any member and no member is supposed to ask what are the profits and losses of business.
Question 2.
Distinguish between a Private Company and a Public Company.
Answer:
| Private Company | Public Company |
| 1. To form a Private Company the minimum number of members is 2 and maximum number of members is 50. | 1. Minimum number of members is 7 and maximum number of members is unlimited. |
| 2. It cannot issue prospectus. | 2. Public Company can issue prospectus. |
| 3. The transferability of shares is generally restricted by its articles. | 3. The shareholders can freely transfer their shares. |
| 4. It can commence its business as soon as it obtains certificate of incorporation from the Registrar. | 4. The business can be started only after getting the certificate of commencement of the business. |
| 5. It need not conduct statutory meeting and file copy of statutory report to the Registrar of Joint Stock Companies. | 5. A statutory meeting must be held within 6 months from the date of receiving the certificate of commencement of business. Statutory report is to be submitted to the Registrar. |
| 6. A Private Company can proceed with the allotment of shares before minimum subscription is received. | 6. Shares cannot be allotted before minimum subscription is received. |
| 7. The word private limited at the end of the name. | 7. The word Limited at the end of the name. |
| 8. The minimum number of directors is 2. The maximum number of directors is no limit. | 8. The minimum number of directors is 3. The maximum number of directors is 20. |
| 9. The directors need not take qualification shares. | 9. Qualification shares are necessary to become a director. |
| 10. The directors need not retire by rotation. | 10. 1/3 of the directors must retire by rotation every year. |
| 11. There is no age limit to become a director. | 11. Age limit for the directors is 65 years. |
| 12. The directors need not sent their consent to act as directors. | 12. The directors must send their consent to act as directors. |
| 13. There is no restriction on the remuneration to the directors and managing directors. | 13. The remuneration payable to the directors and others shall not exceed 11% of the net profits. |
| 14. It can grant loans to the directors without the consent of the central government. | 14. Permission from the central government is necessary to grant loans to the directors. |
| 15. Quorum for the meeting is 2. | 15. Quorum for the meeting is 5. |
| 16. All the directors can be appointed by single resolution. | 16. A separate resolution is required for the appointment of every director. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain various sources of business finance available to Indian businessmen.
Answer:
A businessman can raise funds from various sources. On the basis of period, they are classified into three :
1. Long term sources
2. Medium term sources
3. Short term sources.
1) Long term sources: These sources include
i) Issue of equity and preference shares
ii) Issue of debentures
iii) Retained earnings.
i) Shares : A company is able to get large amount of capital primarily by the issue of shares. A company generally issues various types of shares, preference shares, equity shares and deferred-shares. The object of issuing different kinds of shares is to appeal investors with different temperments. Preference shares carry preferrential right with regarding to payment of dividend and repayment of capital at the time of winding up of the company. Equity shares do not cany such rights. Issue of shares is the most important method of raising long-term finance because the raising from the share-holders remain in the company till the time of winding up.
ii) Debentures: A company may not wish to possess more share capital. Instead it may invite persons to lend their money. Money so lent must be acknowledged. The document which the lender receives is called debenture. So, debenture is an acknowledge of debt by a company. It is usually issued Under common seal, secured by fixed or floating charge on the assets of the company. A company inorder to secure long term finance for initial needs and more of ten for develop-ments, to suppliment its capital may issue debentures. Money raised through debentures remain in the company for long period.
iii) Retained earnings : The ploughing back of earning is an important source of financing the business. Instead of distributing the entire profits, some portion of the profits are retained in the business as reserve. The undistributed earnings are used to finance long term needs.
2) Medium term finance: These sources include
i) Public deposit
ii) Loans from banks
iii) Lease financing
i) Public deposits: Industries receive deposits from the public. These deposits are called as public deposits. The period of public deposits used to be short (i.e., For three years) so public deposits have been a very important source for working capital requirements.
ii) Loans from banks: Commercial banks occupy a vital position as they provide funds for different purposes and for different periods. They extend loans in the form of cash credits, overdrafts, purchase/ discounting bills and term loans. The borrower is required to provide some security or to create a charge on the assets of the firm before a loan is sanctioned.
iii) Lease financing: A lease is a contractual agreement whereby the lesser or owner grants lesser the right to use the asset in return for a periodic payment known as lease rent. At the end of the lease period, the asset goes back to lessor. Lease finance is an important means for modernisation and diversification in the firm. Such financing is resorted to in acquiring assets like computers and electronic equipment.
3) Short-term sources : These sources include
i) Bank Credit
ii) Trade credit
iii) Installment credit
iv) Advances
v) C.E
i) Bank credit : Commercial banks extend the short-term fi-nancial assistance to business in the form of loans, cash credits, over-draft and discount of bills.’Bank loans are provided for a specific short period. Such advance is credited to loan account and the borrower has to pay interest on the entire amount of loan sanctioned. Bank grants the cash credit upto a specific limit. The firm can withdraw any amount within the limit. Interest is charged on the actual amount withdrawn. In overdraft, the customer can overdraw his current account. This arrangement is for a short period only. Commercial banks finance the business houses by discounting the bills of exchange or promissory notes.
ii) Trade credit: Just as firm grants credit to customers, so it often gets credit from suppliers. It is known as trade credit. It does not make available of funds in cash but it facilitate the purchase of goods without immediate payment.
iii) Installment credit: Business firm gets credit from equipment suppliers. The supplier may allow the purchase of equipment with payments extended over a period of 12 months or more. Some portion of the cost price is paid on delivery and the balance is paid in a number of installments. The supplier charges interest on unpaid balance.
iv) Customers advance : Many times, the manufacturer of goods insist on advance by the customers, incases of big orders. The cus-tomers advance represent a part of the price of the product that has been ordered which will be delivered at a later date.
vi) C.P or Commercial Paper : Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for shorter period, varying from 90 days to 365 days. It is issued by one firm to another firm. The amount raised by CP is generally large. As the debt is totally unsecured, firms having good credit rating can issue commercial paper.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each :
Question 4.
Define business. What are its characteristics ?
Answer:
In the words of L.H.Haney “Business may be defined as human activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buy-ing and selling of goods”. According to Wheeler “Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services to the society under the incentive of private gain”. Spriegal considers all activities concerned with production and sale of goods are business activities.
An analysis of the above definitions brings out the following characteristics of business.
1) Economic activities : All those activities relating to the pro-duction and distribution of goods and services are called economic activities. Business is carried on with a profit motive. Any activity undertaken without economic considerations will not be part of busi-ness.
2) Deals with goods and services: Every business concern pro-duces or purchases goods and services with a view to selling them for profit. Goods may be consumer goods or producer goods. Consumer
goods like coffee, bread or shoes are meant for direct use by the con-sumers. Producer goods are used for the production of consumer or capital goods like raw materials, machinery etc. Services like trans-port, warehousing etc., may be considered as intangible and invisible goods.
3) Exchange of goods and services : A business must involve exchange of goods and services with a profit motive. Production or purchasing of goods and services for personal consumption do not constitute business. The purchase of goods should be to sell them again. If a person cooks his food at home, it is not business, but if the same person cooks at a restaurant it is business because he exchanges his services for money.
4) Continuity of transactions : In business only those transac-tions are included which have regularity and continuity. An isolated transaction will not be called business, even if the person earns profit from the deal. A person builds a house for himself but later on sells it for a profit, it is not business. On the other hand, if a house building society builds houses and sells them, this will be called business.
5) Profit motive : The profit motive is an important element of business. Profits are essential for the survival as well as the growth. Profit must, however, be earned through legal and fair means. Busi-ness should never exploit society to make money.
6) Risk and uncertainly : The business involves a large element of risk and uncertainity. The factors on which business depends are never certain, so the business opportunities will also be uncertain. There may be shift in demand, strike by employees, floods, war, fall in prices etc. A business man can reduce risks through correct forecasting and insurance. But all risks cannot be eliminated.
7) Creation of utility : Business creates various types of utilities in goods so that consumers may use them. The utility may be form utility, place utility and time utility. When rato materials are converted into finished goods it creates form utility. When the goods are transported from the places of production to the ultimate consumers, it creates place utility. The process of storing goods when they are not required and supplying them at a time when they are needed is called creation of time utility.
8) Art as well as science: Business is an art because it requires personal skills and experience. It is also a science because it is based on certain principles and laws.
Question 5.
Explain the limitations of sole trader.
Answer:
The following are the limitations of sole trading business.
1. Limited resources : The resources of sole trader are limited. He has only two sources of securing capital, personal savings and borrowing on personal security. Hence, he can raise very limited amount of capital.
2. Instability: It has no separate legal status. The business and the owner are inseparable from one another. The business comes to an end on the death, insolvency, insanity of the owner.
3. Unlimited liability: The liability of the sole trader is unlim-ited. The creditors can recover the loan amounts not only from the business but also from his private property.
4. Not suitable for large scale operations : The resources are limited. Therefore, it is suitable only for small business and not large scale operations.
5. Limited managerial skill: The managerial ability is limited. A person may not be an expert in all matters. Sometimes wrong deci-sions may be taken.
6. Restricted growth : The limitations of capital and manage-rial ability will restrict the growth development and expansion of the business.
7. Dependence on paid employees : When the business ex-pands, the sole trader has to depend on the paid employees. They may not work hard and show interest. Hence the efficiency suffers.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Business finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organizations.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called “Business finance”.
Finance is considered as the life blood of any organization. The success of any organization depends on the availability of adequate finance.
Definition :
According to B.O. Wheeler: “Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of a business enterprise”.
Need and Significance :
1) To meet fixed capital requirement of business :
Business requires finance to meet fixed capital require-ments such as purchase fixed assets like land and building, plant and Machinery, furniture and fixtures etc.
2) To meet working capital requirements :
Working capital is used for holding current assets such as purchase of material, payment of wages, transportation expenses etc. business requires finance.
3) For growth and expansion :
For growth and expansion activities, a business requires finance. It may be required increase production, to install more machines, to set up a R & D centre, etc.
4) For diversification :
Entering into new business and new lines of activities is known as diversification. The Business finance is needed to start any new activity in business.
5) For Survival:
Without the required finance, organizations can not survive for long time. To carry out the various business operations in continuity, business finance is needed.
6) Liabilities :
To meet liabilities of business, may be long-term or short, a business requires sufficient finance, e.g. for payment of loan installments, creditors etc.
7) For payment of expenses
Business finance is needed for payment of expenses like paying salaries, wages, taxes, rent, advertisements etc.
Question 7.
What are the various types of capital required for business en-terprises ?
Answer:
Depending up on the nature and purpose; capital may be divided into fixed capital and working capital.
1) Fixed capital:
- The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such as land and buildings, plant and machinery etc, is called “fixed capital”.
- Business organizations used fixed capital to meet the long term requirements.
- The amount of fixed capital required by the business concern depends on the size and nature of the business.
- The need for fixed capital investment would be greater for a large business as compared to a small business. Ex: A trading concern require small amount of fixed capital than a manufacturing concern.
2) Working capital:
- The capital required by a business enterprise to run its day to day operations is called ‘Working capital”.
- Working capital is used for holding current assets such, as stock of material, bills receivables and for meeting expenses like salaries, wages, taxes and rent.
- The amount of working capital requirement is various from one business enterprises to another depending on various factors.
- For Example : A business unit selling goods on credit or having a slow sales turnover, would require more working capital as compared to a business unit selling its goods on cash basis or having a high turnover.
Question 8.
Discuss the previleges enjoyed by MSMEs.
Answer:
MSMED Act, 2006 provides the following privileges to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
1. Buyers liability to make timely payment : Section 15 envisages to ensure timely receipt of payment for their goods and services by Micro and Small Enterprises. It casts an obligation upon the buyer of any goods or services, to make payment to the supplier, by the specified date as follows.:
a) When there is an agreement in writing : On or before the date agreed upon between them in writing. Further, in no case the period so agreed shall exceed 45 days from the day of acceptance.
b) When there is no agreement : Before the appointed day, which means the day following immediately after the expiry of 15 days from the day of acceptance or day of deemed acceptance.
The terms buyer, supplier, day of acceptance has been defined by Act as under.
Buyer means a person buying goods or receiving any service from a supplier for consideration.
Supplier means a Micro or Small Enterprise.
Day of acceptance means the day of acutal delivery of goods or rendering service.
2) Interest for delayed payment by buyer: Where a buyer fails to make payment as required above, he shall be liable to pay interest on the -outstanding amount. The interest shall be payable for the period of delay from the date immediately following the agreed date. The interest shall be payable at a rate three times the bank rate and compounded at monthly rests.
3) Reference of dispute : Any dispute relating to the payment for any goods or services and any interest thereon, may be referred by any party to the Micro and Small Enterprises. Facilitation council, which shall conduct conciliation in the matter.
Question 9.
Explain merits of MNCs to home country.
Answer:
Merits of MNCs to home country:
- Availability of resources : The country can obtain raw materials, land and labour at comparatively low cost.
- Develop exports: They can export commodities and finished
products for assembling or for distribution in foreign markets. Thereby market in widened. - Generate income : They can earn huge income from dividends, licencing fees, royalty and management contracts. They can acquire technical and managerial expertise of foreign countries.
- Provides employment : They can increase job and career opportunities at home and abroad in connection with overseas operations.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each :
Question 10.
Entrepot Trade.
Answer:
- Importing of goods with the intention to export the same to other country is called as entrepo trade.
- Example : England imports, Tea from India and Exports to Europe.
Question 11.
Transport.
Answer:
There is a vast distance between centres of production and cen-tres of consumption. Goods are to be moved from the places of production to the place where they are demanded.
- The activity which is concerned with movement of goods is called transportation. Transport create place utility.
- There are several kinds of transport such as air, water and land transport. The geographical distance between produc-ers and consumers is removed with the help of transport.
Question 12.
Partnership deed.
Answer:
- Partnership Deed: Partnership deed is a document contain-ing the terms and conditions of a partnership. It is an agreement in writing signed by all the partners duly stamped and registered.
- The partnership deed defines certain rights, duties and obligations of partners and governs relations among them in the conduct of business affairs of the firm.
Question 13.
Mitakshara system of Hindu law.
Answer:
This school of Hindu lawprevails in entire India except in Assam and West Bengal. Family members of male line and their wives, un-married daughters are its members. By birth, a member gets a share in common property, it continues till his death. In this way shares in the property gets fluctuates in accordance with the number of co-parceners.
Question 14.
Define Promotion.
Answer:
- Promotion is the first state in the formation of a company. It involves identification of a business opportunity or idea, analysis of its prospects, gathering the relevant information and taking steps to implement it.
- L.H. Haney “Promotion is the process of organizing and planning the finance of a business enterprise under the corporate form”.
![]()
Question 15.
Statement in liev of Prospectus.
Answer:
- If the public company is able to raise capital on its own, it need not issue prospectus. In such case, a statement is pre-pared and filed with the registrar. This statement is called “Statement in lieu of prospectus”.
- Statement in lieu of prospectus is a substitution of prospec-tus.
Question 16.
Short – term finance.
Answer:
- The finance required for a period of not exceeding one year is called short-term finance. Short-term finance is utilised for meeting working capital requirements of the business.
- The amount required for short-term funds depends on nature of business order and delivery time, volume of business and operating cycle. The sources of short-term finance are trade credit, bank credit, installment credit, customer advance etc.
Question 17.
e-Banking.
Answer:
- Performing all banking operations by using internet is known as “E-banking”. It is also called “Online Banking”.
- Online banking allows the customers to get their money from an Automated Teller Machine (ATM). They can view their accounts, transfer funds, deposit amount and can pay bills.
Section – D (50 MARKS)
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Trading profit and loss account and Balance Sheet as on 31.12.2017 of M/s Praveen Traders.
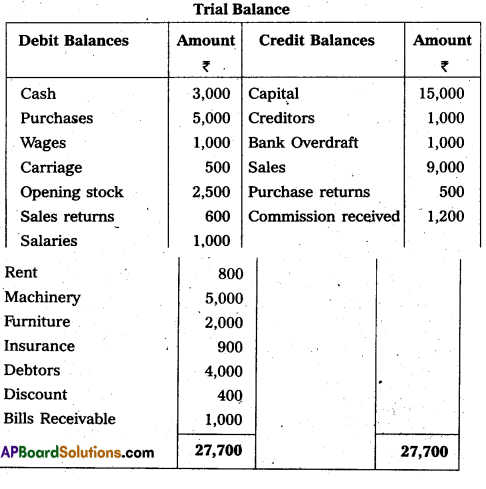
Adjustments :
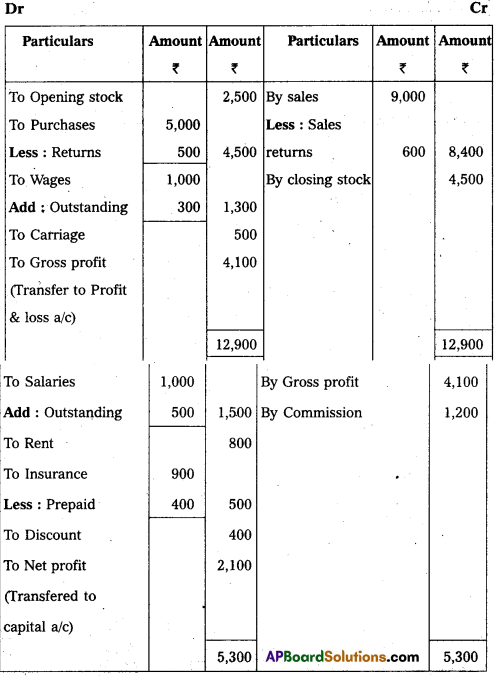
(1) Closing Stock value ₹ 4,500.
(2) Outstanding Wages ₹ 300.
(3) Outstanding Salaries ₹ 500.
(4) Prepaid Insurance – ₹ 400.
Answer:
Trading, Profit & Loss Account of Mr. Praveen Traders for the year ended 31-12-2017
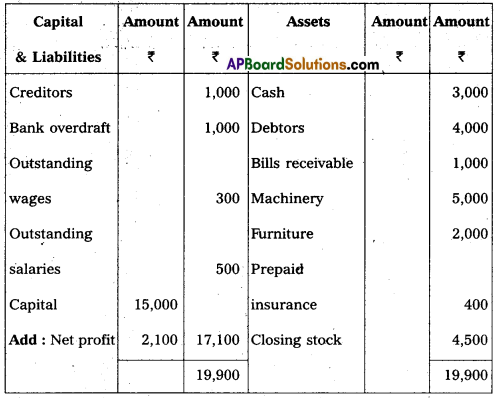
Balance sheet of Praveen Traders, as on 31-12-2017
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer ANY ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare Three Column Cash Book from the following particulars :

Adjustments :
(1) Closing Stock value’ ₹ 4,500.
(2) Outstanding Wages ₹ 300.
(3) Outstanding Salaries ₹ 500.
(4) Prepaid Insurance – ₹ 400.
Answer:
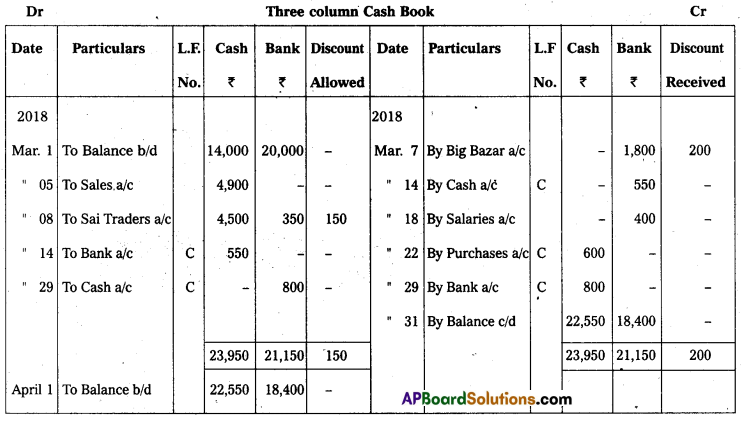
Question 20.
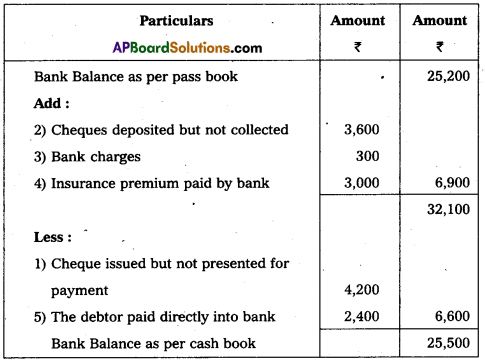
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement of M/s Naidu Ltd. as on 31.12.2017. Balance as per Passbook ₹ 25,200 :
(1) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 4,200.
(2) Cheques deposited but not collected ₹ 3,600.
(3) Bank charges ₹ 300.
(4) Insurance premium paid by bank ₹ 3,000.
(5) The debtor paid directly into Bank Account ₹ 2,400.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation statement of Ms. Naidu Ltd. as on 31.12.2017
Section – E
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer ANY TWO of the following questions :
Question 21.
Explain different types of Accounts along with their debit and credit rules.
Answer:
Accounts are classified into 3 types. Which are :
1) Personal Accounts
2) Real Accounts and
3) Nominal Accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : The accounts which are related to persons, films and companies are called “personal accounts”.
Ex : Ramu a/c , State Bank of India a/c etc.
Rule : Debit The receiver
Credit the giver.
2) Real Accounts : Accounts related‘to properties and assets of business are called “Real accounts”.
Ex : Cash a/c, Furniture a/c, land & building a/c ; goodwill a/c etc
Rule: Debit what comes in
Credit what goes out.
3) Nominal Accounts: The accounts related to expenses, losses, incomes and gains are called as “Nominal Accounts”.
Ex : Wages a/c , salaries a/c, commission a/c, rent a/c, discount received a/c etc.
Rule : Debit all expenses and losses
Credit all incomes and gains.
Question 22.
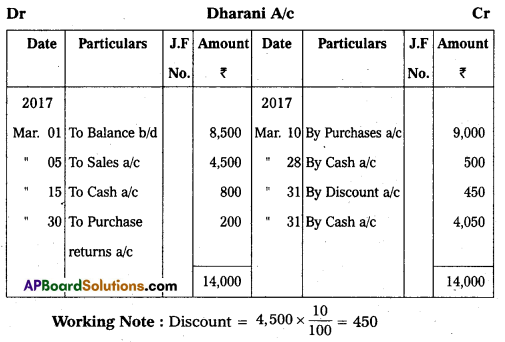
From the following information, prepare Dharani Account as on 31.3.2017.

Answer:
Question 23.
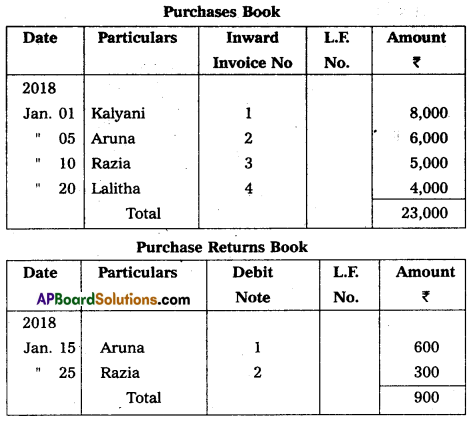
From the following particulars, prepare purchase and purchase return Journal :

Answer:
Question 24.
What is a Suspense Account? Why is it opened?
Answer:
When the trial balance does not agree, an effort is made to locate the errors and rectify them. But if the errors cannot be located easily and quickly and at the same time, if the final accounts are to be prepared urgently, the difference in the trial balance is made good by writing it to smaller side of the tried balance under the name ‘suspense account’ such temporary suspense account is closed later when once errors are located and rectified.
The suspense account is an imaginary account opened tempo-rarily for the purpose of just tallying trial balance. Ex: if the debit side of the trial balance exceeds credit side, then the difference put on the credit side and the suspense account shows credit balance. If the credit side of the trial balance exceeds debit side, then the difference is put on the debit side and suspense account shows debit balance. The difference in trial balance are due to one side errors and not due to other errors. The errors which involve both the accounts permits the trial balance to agree and therefore they do not give rise to suspense ac-count. The balance of suspense account is shown on the balance sheet either on liabilities or assets side, depending upon whether the suspense account has a credit or debit balance.
Section – G (6 × 2 = 10)
Answer ANY FIVE of the following questions :
Question 25.
Money measurement concept.
Answer:
- Only those transactions are recorded in accounting which can be expressed interms of money. The transactions which cannot be expressed in money is beyond the scope of ac-counting.
- Receipt of income, payment of expenses, purchase of assets , etc., are monetary transactions that are recorded in the books of account. Where as in the event of breakdown of machinery is not recorded because it has no monetary value.
![]()
Question 26.
What is an Account ?
Answer:
Every transaction has two aspects and each aspect has an ac-count. An account is a summary of relevant transactions at one place relating to a particular head. An account has three parts.
- A title describes the name of the account.
- A left side or debit side.
- A right side or credit side.
The form of an account is called T account because of the similarity to the letter T.

Question 27.
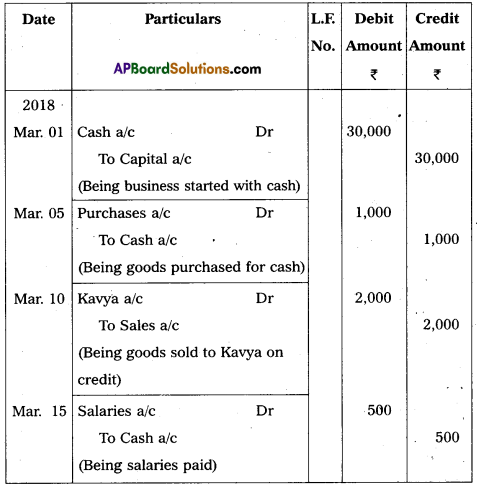
Journalise the following transactions :

Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Anitha
Question 28.
Journal Proper.
Answer:
- Journal proper is also known as “Journal Residual” or “General Journal”.
- This book is used to record only those transactions which cannot recorded in purchase book or sales book or cash book, purchase returns or sales return book, Bills Receivable or Bills Payable book.
- E.g. When a firm purchased machinery on credit.
Question 29.
Write the opening Journal Entry as on 1.1.2018 :

Answer:
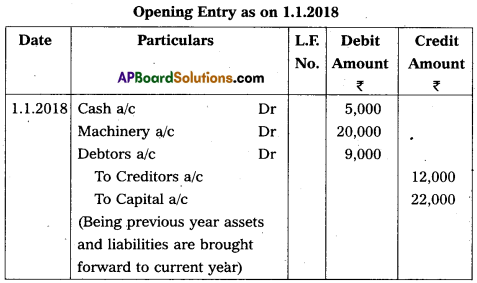
Question 30.
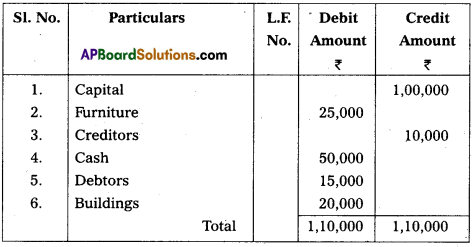
Prepare Trial Balance of Susmita as on 31.3.2018 :

Answer:
Trial Balance of Susmitha as on 31.3.2018
Question 31.
Compensating Errors.
Answer:
- If two or more errors are committed and, one error nullifieds the another error, they are called “compensating errors”.
- Example : amount of ₹ 100 excess in sales will compensate the amount of excess ₹ 100 in purchases.
Question 32.
Bad Debts.
Answer:
The debts which are not collected and irrecoverable are knowns as “Bad Debts”.
Baddebts are treated as loss to the business.