Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 7 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
State the advantages and disadvantages of Hindu Undivided Family business organisation.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Hindu Undivided Family business organisation:
- Centralised management: The management of Joint Hindu Family firm centralised in the hands of one man known as Karta. He is being the eldest and most experienced person gives a very displined management.
- Quick decisions : In Joint Hindu Family firm, as Karta is the only decision maker, he can take quick decisions which is profitable to the business.
- Credit facilities : In Joint Hindu Family firm, the credit facilities are more, the reason being the liability of Karta is unlimited.
- Continuity : It is not dissolved by the death or insanity of a co-parcener.
- Work according to capacity : Unlike other business organisations, the work is assigned to members according to their capacity.
- Natural love and affection : Due to natural love and affection among the members, they ignore the short comings each other and help them to run the business more smoothly and efficiently.
- Economy : If a business is to be successful, economy is a must. It is well balanced and maintained in Joint Hindu Family firm.
Disadvantages :
- No reward for efficiency: The members who work more efficiently and dedicatedly are not rewarded for their work. So efficient persons are tempted to work less. If encourages laziness on the part of members.
- Limited capital : The investments are limited only upto the resources of one family. They may not be sufficient to meet business requirements.
- Limited managerial skill: Only the eldest member of the family is to manage the business. He is performing all the functions of the management. He may not be well conversant with the knowledge of business skill and other problems of management.
- Suspicion : The Karta is empowered with vast power of secrecy and he can keep a thing secret even from its members. But there is no restriction on him that he cannot disclose anything to any person with whom he is having more love. This gives raise to suspicion among the members themselves which is not good for the business.
Question 2.
Distinguish between Partnership and a Joint Stock Company.
Answer:
The following are the differences between Partnership and a Joint Stock Company.
| Partnership | Joint Stock Company |
| 1. Governing status: A Partnership firm is governed by Indian Partnership Act, 1932. | 1. Governing status: Joint Stock Company is governed by the Companies Act, 1956. |
| 2. Formation: It is formed by mutual agreement. | 2. Formation: It is formed by the Companies Act, 1956. |
| 3. Registration: Registration is not compulsory. It is optional. | 3. Registration: Registration is compulsory. |
| 4. Number of members: The minimum number of members in the partnership is 2 and maximum number of members is 10 in the case of banking business and 20 members in other business. | 4. Number of members: In case of Private Company the minimum number of members is 2 and maximum number of members is 50. In case of Public Company, the minimum number of members is 7 and maximum number of members is unlimited. |
| 5. Legal status: A partnership has no separate legal entity. | 5. Legal status: A company has a separate legal entity. |
| 6. Continuity: A partnership concern is dissolved on the death or insolvency of the partner. | 6. Continuity: The continuity of the company is not affected by death or insolvency of a member. |
| 7. Transfer of shares: A partner can transfer his share with the consent of all other partners. | 7. Transfer of shares: In Public Company, the shareholders are free to transfer their shares. |
| 8. Liability: The liability of the partners is unlimited, joint and several. | 8. Liability: The liability of the shareholders is limited to the value of shares held by them. |
| 9 . Management and control: Every partner has a right to participate in the management of the business. | 9. Management and control: A company is managed by elected Board of Directors. Members cannot participate in day-to-day business. |
| 10. Mobilising capital: A partnership concern cannot secure huge capital. | 10. Mobilising capital: A company can mobilise huge amount of capital by issuing shares to the public. |
| 11. Statutory obligations: A partnership firm is not under any statutory obligations for compliance of any rules and regulations. | 11. Statutory obligations: A company is required to maintain prescribed books and submit periodical reports. |
| 12. Audit: Audit of accounts is not compulsory. | 12. Audit: Audit of the accounts is compulsory. |
| 13. Flexibility: A partnership firm can change the business according to changing conditions. | 13. Flexibility: A company cannot change its business objects easily. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the process involved in incorporation of a company.
Answer:
Incorporation involves registration of the company under the companies act. The promoters of a company must prepare and file the following documents with the Registrar of companies of the state in which the registered office of the company is started to be submitted.
- Application for approval of name: An application is to be submitted to the Registrar of companies of the state and obtain approval of name. A company may adopt any name which is not prohibited by Emblems and names act, 1950. The Registrar is ex-pected to approve the .name within 14 days of the receipt of the application.
- Memorandum of association: It is the constitutior; of the company which describes its objects, scope and relation with out-side world. The document is carefully drafted, stamped and signed by 2 members in the case of private company and 7 memebers in the case of public company.
- Articles of association: It is the document which contains rules and regulations relating to the internal management and also capital structure. A private company is required is submit articles duly signed by signatories. However, a public limited company may adopt model articles prescribed in Table A, Schedule I of the Act.
- A list of persons who have consented to become directors of the company.
- The promoters should execute a power of attorney in favour of one of them or an advocate who is to carryout the formalities required for registration.
- When the location of the registered office is finalised prior to incorporation, the notice of it is to be filed.
- Where the company names first directors in its articles, their particulars are to be submitted to the Registrar within 30 days of its registration or appointment of such directors.
- A declaration stating that all the requirements of the com-panies act and other formalities relating to registration are duly complied within Form 1 and is to be filed with the Registrar.
- In addition to filing with the above documents, the pre-scribed fees has to be paid for registration of the company.
If the Registrar is satisfied with all the statutory requirements stated above are duly complied with under the act, issues a certifi-cate called “Certificate of Incorporation”. The date mentioned in the certificate is the date of Incorporation of the company.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Discuss the social responsibility of business.
Answer:
Every business operates within a society. It uses the resources of the society and depends on the society for its functioning. This creates an obligation on the part of the business to look after the welfare of the society. Therefore, all the activities of the business should be that they will protect and contribute to the interest of the society. Social responsibility of business refers to ail such duties and obligations of business directed towards welfare of the society.
The concept of social responsibility: People engage in business to earn profits. But earning profits is not only the sole objective of the business. It has to perform number of social functions, as it is a part of the society. A business man should not do anything harmful to the society. Thus the concept of social responsibility discourages business’men from adopting unfair means like black marketing, smuggling, adulteration, tax evasion etc., to earn profits. It encourages them to earn profits by proper management of the business, by providing better working conditions to employees, by providing better products to consumers and control pollution and conserve natural resources.
Question 5.
Explain the procedure of registration of partnership firm.
Answer:
For registering a partnership, the partners must prepare a statement containing the following particulars and submit the same to the Registrar along with the registration fees.
- Name of the firm.
- Name of the head office and branches, if any
- The names and addresses of partners.
- Dates on which the partners joined the firm.
- Duration of the business.
- Date of opening the firm, type of business.
The statement must be stamped, dated and signed by all the partners. Along with this statement, a copy of the partnership deed should be submitted to the Registrar. If everything is in order, the Registrar shall record an entry in the Register of Firms and will issue a Certificate of Registration.
Question 6.
What are the features of public company ?
Answer:
According to Section 3 of the companies (Amendment) Act, 2000, the public company has the following features.
- It can be started with a minimum number of 7 members and no maximum limit for number of members.
- The minimum paid up capital is ₹ 5,00,000.
- It can issue prospectus for inviting the public for subscrip-tion of its shares and debentures.
- The shares are freely transferable.
- It must secure minimum subscription.
- It cannot commence business unless it gets certificate of commencement of business.
- The minimum number of directors is 3.
- Directors should possess qualification shades.
- It must hold statutory meeting and file a statutory report.
- Five members form a quorum for meetings.
- The word ‘Limited’ must be added at the end of the name.
- It can grant loans to directors with the consent of the central government.
- One-third of the directors should retire by rotation every year.
- A separate resolution is necessary for electing each di-rector.
Question 7.
What are the sources of short-term finance ?
Answer:
The following are the sources of short-term finance :
1. Bank credit: Commercial banks extend the short term financial assistance to business in the form of loans, cash credits, overdrafts and discount of bills. Bank loans are provided for a specific short period. Such advance is credited to a loan account and the borrower has to pay interest on the entire amount of loan sanctioned. Bank grants cash credits upto a specific limit. The firm can withdraw any amount within the limit. Interest is charged on the actual amount withdrawn. In overdraft, the customer can overdraw his current account. The agreement is for short period only. Banks also finance the firms by discounting their bills of exchange.
2. Trade credit: Just as the firm grants credit to customers, so it often gets credits from suppliers. It is known as trade credit. It does not make available of funds in cash but it facilitate the purchase of goods without immediate payment of cash.
3. Instalment credit : Business firms get credit from equipment suppliers. The supplier may allow the purchase of equipment with payments extended for a period of 12 months or more: Some portion of the cost price is paid on delivery and the balance is paid in number of instalments. The supplier charges interest on unpaid balance.
4. Customers advance : Many times, the manufacturer of goods insist on advance by customers in case of big orders. The customer advance represent a part of the price of the product which will be delivered at a later date.5. Commercial paper : Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for short period, varying from 90 to 365 days. It is issued by one firm on another and the amount raised by C.P. is large.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the significance of MSMEs.
Answer:
Significance of MSMEs : Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises contributes nearly 8% of the country’s GDP. 45% of the manufacturing output and 40% of exports. They provide large share of employment after agriculture. They are nurseries for entrepreneurship and innovation. They are widely dispersed across the country and produce a diverse range of products and services to meet the needs of local markets, the global market, the national and international value chains.
- 90% of MSMEs in India are unregistered, out of which 80% are sole proprietorship firms.
- 40% of exports in India are through MSME channel.
- 40% employment opportunities in India are provided by MSME sector.
- MSMEs provides opportunities in building entrepre-neurship by providing various channels of investment opportunity according to their class of investments.
- MSMEs provides a good market for foreign companies to start venture capital business in India.
Question 9.
Explain any five opportunities of business enterprises in 21st century.
Answer:
The following are the opportunities of Business enterprises in 21st Century.
1) LPG : The economic reforms initiated in the form of Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation led to the Indian economy with world economics. It resulted in improved access to technology, growth of international trade, increase in production and employment opportunities and free flow of capital.
2) Increase in size and diversification : The 21st century business organisations are large in size and highly diversified. Increase in size results in increased output, reduction of cost and increase in profits.
3) Increase in percapita income : India has emerged as the fourth largest economy with high growth rate and improved percapita income. As Indian percapita income is increasing, the business opportunities are also increased.
4) E-Commerce : Business enterprises acorss the globe are discovering the benefits of E-Commerce such as improved cash flow, customer relation and service satisfaction.
5) Market economies : India being the largest economies in the world attracting industrial, trade and service sectors around the world with changes in the international economic order. India is converted into market economy and resulted in more business opportunities.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Industry
Answer:
Industry is concerned with making or manufacturing goods. It is that part of production which is involved in changing form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product.
Ex : Weaving yarn into cloth. Thus industry creates form utility in goods.
Question 11.
Mitakshara
Answer:
This school of Hindu Law prevails in entire India except in Assam and West Bengal. Family members of male line and their wives, unmarried daughters are its members. By birth, a member gets a share in common property, it continues till his death. In this way shares in the property gets fluctuates in accordance with the number of co-parceners.
Question 12.
Partner by estoppel.
Answer:
When a person is not a partner, but posses himself as partner by words or in writing or by his acts, he is called Partner by Estoppel. He neither contributes the capital nor participate in profits or losses. But he is liable to any creditor like any other partner.
Question 13.
Co-operative credit society.
Answer:
The people with moderate’means are formed with the object of extending short term credit to their members. They also develop thrift among members. The funds are contributed by the members. These societies are divided into rural credit co-operative societies and urban credit co-operative societies.
Question 14.
Define promotion.
Answer:
L.H. Haney defines “Promotion is the process of organising and planning the finances of a business enterprise under the corporate form”.
Grenstenberg says “Promotion may be defined as the discov-ery of business proposition and the subsequent organisation of funds, property and managerial ability into the business concern for the purpose of making profits thereon”.
Question 15.
Fixed capital
Answer:
The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such land and buildings and plant and machinery etc., is called fixed capital. Capital utilised by the business for the long term requirements is called fixed or block capital. The amount of fixed capital required depends on the size and nature of business.
Question 16.
Debenture
Answer:
A company may invite persons to lend their money as loan and this must be recorded and acknowledged. This document is called debenture. So, debenture is a acknowledge of debt by a company. It is issued under common seal, secured by floating charge or fixed charge on the assets of the company
![]()
Question 17.
E-trade
Answer:
E-trading is also known as online trading or E-broking. It is used for buying and selling stocks in the stock exchange.
Part – II
(50 Marks)
Section – D
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
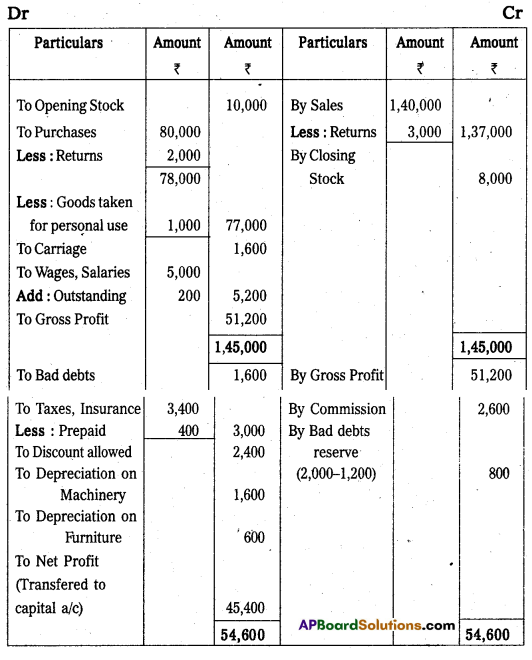
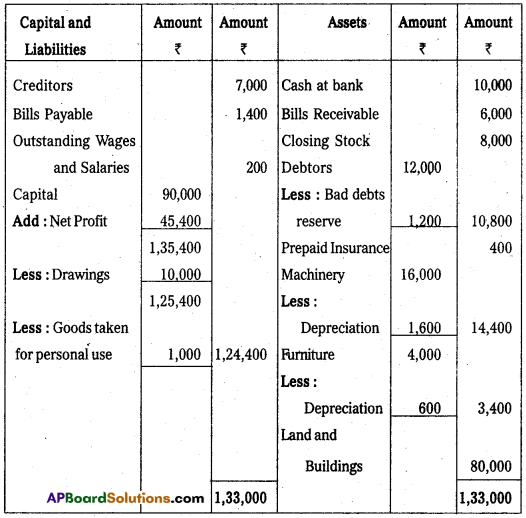
From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Sarat, prepare Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet for the year ending 31.03.2013.
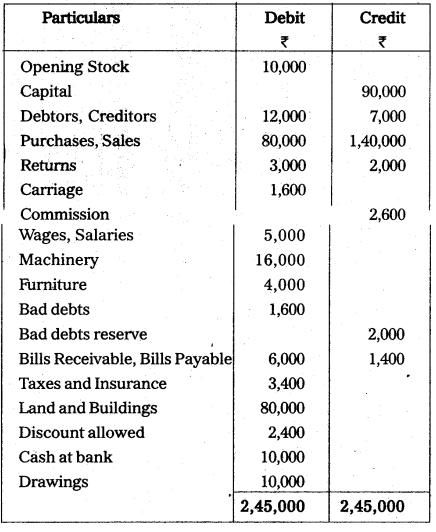
Adjustments:
- Stock as on 31.12.2009 ₹ 8,000.
- Prepaid insurance ₹ 400,
Outstanding Wages and Salaries ₹ 200. - Provide 10% for bad debts reserve on debtors.
- Depreciate Machinery and Furniture by 10% and 15%.
- Goods taken by the proprietor for personal use ₹ 1,000. The transaction was not recorded in the books.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss Account of Sarath for the year ended 31-03-13
Balance Sheet of Mr. Sarath as on 31-03-2013
Section – E
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare double column cash book with cash and discount columns.
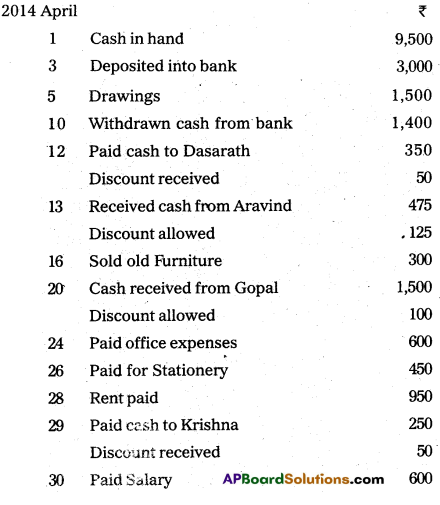
Answer:
Question 20.
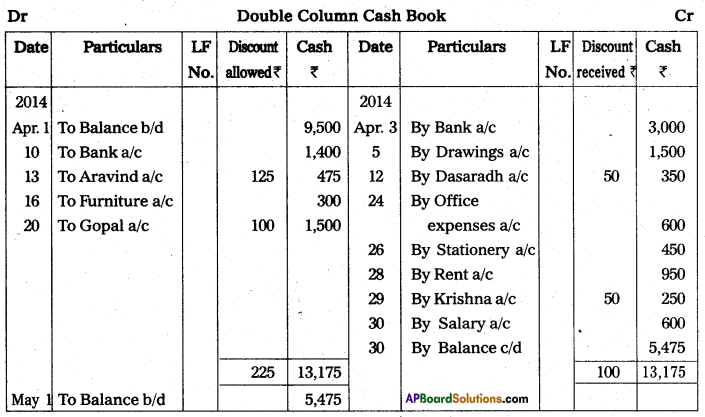
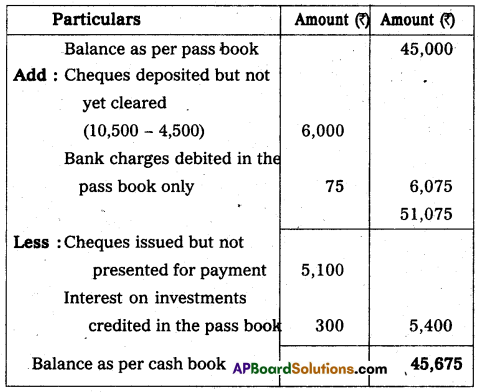
On 30th April 2013, the pass book of M/s PosinaBros. showed a credit balance of ₹ 45,000.
a) Cheques amounting to ₹ 10,500 were deposited in the bank but only cheques of ₹ 4,500 were cleared upto 30th April.
b) Cheques amounting ₹ 15,000 were issued but cheques worth ₹ 5,100 were not presented for payment in the bank upto 30th April.
c) In the pass book there was a credit of ₹ 300 for interest on investments and debit of ₹ 75 for bank charges.
Prepare a bank reconciliation statememnt showing the balance as per cash book.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation statement of M/s Posina Bro.s as on 30.04.2013
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Give the advantages of subsidiary books.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of subsidiary books.
- No need for writing journal entries. The transactions are entered directly into their respective journals.
- Ledger accounts can be prepared on the basis of subsidiary books.
- Recording of transactions is easy and fast.
- By entrusting different subsidiary books to different persons, division of work principle can be implemented.
- Accounting work will be done efficiently by allotting work to different experts who prepare the special books.
- Labour involved and time can be saved.
- Since separate books are maintained to record a particular set of transactions, errors can be easily detected.
- Information relating to similar types of transactions will be available at one place. Ex. Relating to sales, purchases, cash etc.
![]()
Question 22.
Prepare Swami’s account from the following.

Answer:
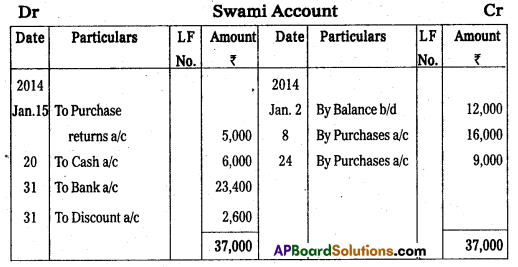
Question 23.
From the following transactions prepare sales book and sales returns book.

Answer:
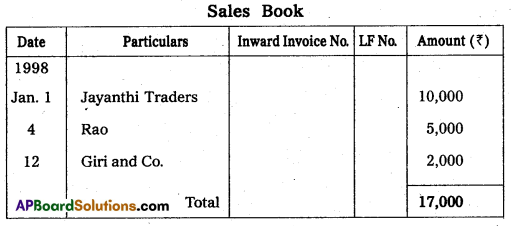
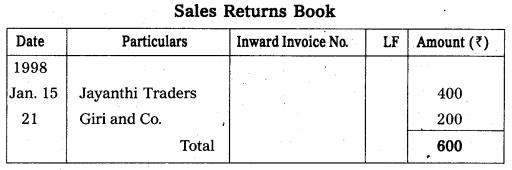
Question 24.
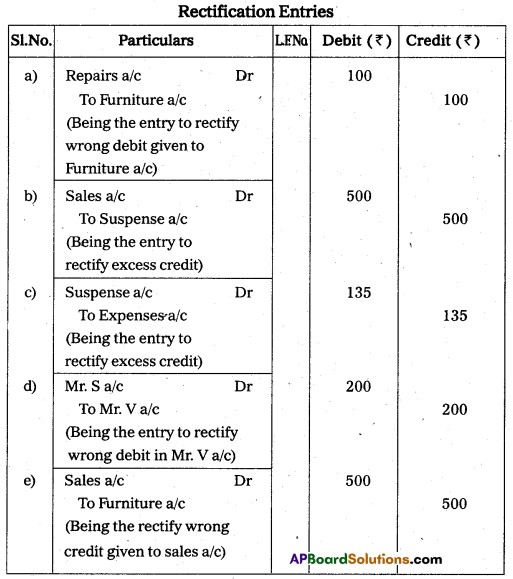
Rectify the following errors.
a) An amount of ₹ 100 paid for the repairs of furniture debited to Furniture a/c.
b) Sales book total was overcast by ₹ 500.
c) A sale of ₹ 200 to Mr. S was wrongly debited to the account of Mr. V
d) Expenses ₹ 15 was posted to the ledger as ₹ 150.
e) Old furniture sold has been credited to sales account ₹ 500.
Answer:
Section – G
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Voucher
Answer:
It is a written document is support of a transaction. It is a proof that a particular transaction has taken place for the value stated in the voucher. It may be in the form of cash receipt, bank pay-in-slip, invoice etc., voucher is necessary to audit the accounts.
Question 26.
Accounting cycle
Answer:
An accounting cycle is a complete sequence of accounting process that begins with recording of business transactions and ends with preparation of final accounts. These include journal, ledger, trial balance and financial statements such as trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Question 27.
Double entry book-keeping system.
Answer:
According to J.R. Batliboi “Every business transaction has a two-fold effect and that it affects two accounts in opposite direction and if a complete record were to be made of each such transaction, it would be necessary to debit one account and credit another account. This recording of two fold effect of every transaction has given rise to the term Double entry system of book-keeping is that “for every debit there must be corresponding value of credit”.
Question 28.
What is journal entry ?
Answer:
The process of recording business transactions in chronological order in Journal after analysing, classifying and identifying as debit and credit is called Entry. All the transactions recorded in the Journal are in the form of entries. Hence, they are called as Journal entries.
![]()
Question 29.
Debit note
Answer:
It is a document sent to the supplier while returning the goods purchased on credit from him, intimating that his account is debited to the extent of goods returned and the reasons for returning them. It is prepared by the purchaser.
Question 30.
Pass the necessary journal entries.

Answer:
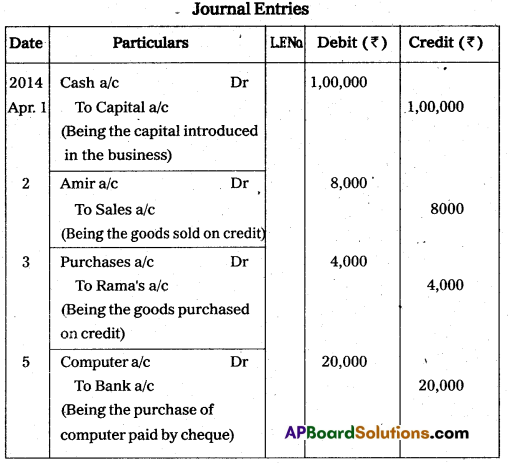
Question 31.
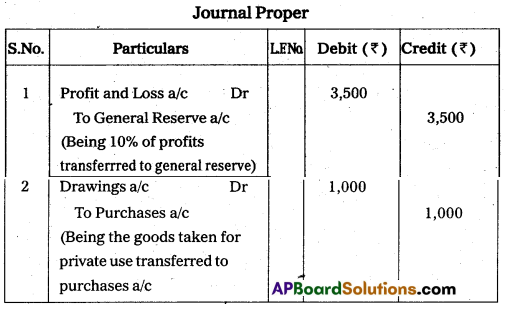
Write the necessary journal entries for the following transa-ctions.
i) The profit earned is ₹ 35,000 and decided to transfer 10% of the profit to general reserve.
ii) Goods taken by the proprietor for his personal use ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
Question 32.
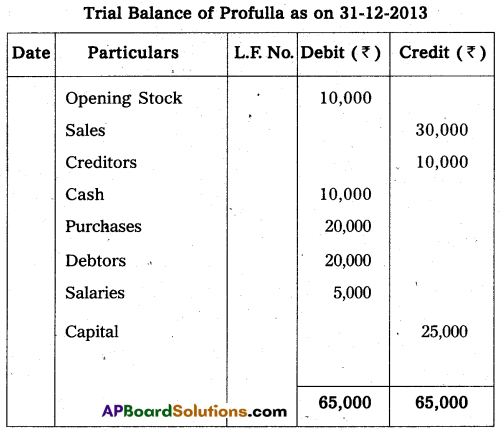
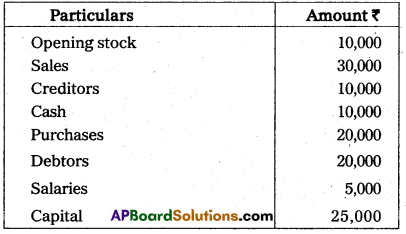
Prepare trial balance of Profulla from the following balances on 31.12.2013.
Answer: