Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers Set 4 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Paper Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
PART – I (50 MARKS)
(Section – A)
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define business. What are its characteristics ?
Answer:
In the words of Haney “Business may be defined as human activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. “According to Whealer” Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services to the society under the incentive of private gain.
The following are the characteristics of business.
1) Economic activities : All those activities relating to the production and distribution of goods and services are called economic activities. Business is carried on with profit motive. Any activity undertaken without economic considerations are not business.
2) Deals with goods and services : Every business concern produces or purchase goods and services with a view to selling them for profit. Goods may be consumed goods or producer goods. Consumer goods like coffee, bread or shoes are meant for direct use by the consumers. Producer goods are used for production of consumer or capital goods like raw materials, machinery etc., services like transport, warehousing etc., may be considered as invisible goods.
3) Exchange of goods and services : A business must involve exchange of goods and services with a profit motive. Production or purchasing goods and services for personal consumption do not constitute business. The purchase of goods should be to sell them again. If a person cooks food at his home, it is not business, but if the same person cooks at a restaurant it is business because he exchanges his services for money.
4) Continuity of transactions : In business only those transactions are included which have regularity and continuity. An isolated transaction is not called business, even if the person earns profit from the deal.’ A person builds a house for himself and later on sells it for a profit, it is not business. On the other hand, if a house building society builds houses and sells them, this will be called business.
5) Profit motive: The profit motive is an important element of business. Profits are essential for survival as well as the growth. Profits must, however, be earned with legal and fair means. Business should not exploit society to make money.
6) Risk and uncertainity : The business involves a large element of risk and uncertainity. The factors on which business depends are never certain, so the business opportunities will also be uncertain. There may be shift in demand, strike by employees, floods, war, fall in prices etc.
7) Creation of utility : Business creates various types of utilities in goods so that consumers may use them. The utility may be form utility, place utility and time utility. When raw materials are converted in finished goods it creates form utility. When the goods are transported from the places of production to the ultimate consumers, it creates place utility. The process of storing goods when they not required and supplying them at a time when they needed is called creation of time utility.
Question 2.
What is Articles of Association ? Explain its contents.
Answer:
Articles bf Association is another important document to be registered with the Registrar at the time of incorporation. Some rules and regulations are necessary for conducting the internal affairs of the company efficiently. Articles contain only those rules and regulations and guide the management in day-to-day administration. It defines the relationship between the members and the company. It defines clearly the rights, duties and liabilities of shareholders, directors and chief executives. According to Section (2) of the Companies Act “Articles of Association of the company as originally framed or as altered from time to time in pursuance of any previous companies law or of this Act”.
The private companies limited by shares, limited by guarantee and unlimited companies must have their articles of association. A public company limited by shares may not have own articles. If the company not prepared articles, it may adopt all or any regulations contained in Table A Schedule I of the Act.
The articles must be printed, divided into paragraphs, numbered consecutively, stamped and signed by each subscriber of memorandum. It is duly witnessed and filed along with memorandum.
Contents: The Articles of Association contain the following details.
- Share capital – Division, number of shares, value of shares, rights of the shareholders.
- Calls on shares.
- Rights of underwriters.
- Transfer and transmission of shares.
- Forfeiture of shares and reissue.
- Lien on shares.
- Conversion of shares into stock and stock into shares.
- Alteration of share capital.
- Issue of share warrants.
- Company meetings and resolutions.
- Borrowing powers of the company.
- Reserves, dividends, conversion of reserves into capital.
- Company common seal.
- Approval of preliminary contracts.
- Quorum for the meeting.
- Voting procedure for members.
- Directors rights, duties, liabilities and remuneration.
- Appointment, rights and remuneration of secretary and managing director.
- Minimum subscription.
- Company accounts and audit.
- Arbitration.
- Winding up of the company.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the differences between shares and debentures ?
Answer:
The following are the differences between shares and debentures
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A debenture is an acknowledgement of debt. |
| 2. c Shareholders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debentureholders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Dividend on shares is a charge against profit and loss appropriation account. | 4. Interest on debentures is a charge against profit and loss account. |
| 5. Shareholders have voting rights. They have control over the management of the company. | 5. Debenture holders are only creditors of the’ company. They cannot participate in management. |
| 6. Shares are not redeemable except redeemable preference shares during the life time of the company. | 6. The debentures are redeemed after a certain period. |
| 7. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all outside liabilities. | 7. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital. |
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Brief explanation of economic activities.
Answer:
Economic activities are broadly divided into business, profession and employment.
Business : The word business literally means a state of being busy. Every person is engaged in some kind of occupation or other work. The business is an activity which is primarily pursued with the object of earning profits. So, a business activity involves production, exchange of goods and services to earn profits or a living.
Profession : Profession is an occupation involving the provision of personal services of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc. The specialised service is provided for professional fees charged from the clients. For example, a doctor helps his patients through his expert knowledge of science of medicine and charges a fees for the service.
Employment: Employment involves working under a contract of employment for or under some one known as employer in return for a salary. The person engaged under employment works as per the directions of the employer.
Question 5.
Discuss the registration procedure of partnership.
Answer:
For registering a partnership, the partners must prepare a statement containing the following particulars and submit the same to the Registrar along with the registration fee.
- Name of the firm.
- Name of head office and branches, if any.
- The names and addresses of partners.
- Dates on which the partners joined the firm.
- Duration of the business.
The statement must be stamped, dated and signed by all the partners. Along with this statement, a copy of the partnership deed should be submitted to the Registrar. If everything is in order, the Registrar shall record an entry in the Register of firms and will issue a Certificate of Registration.
Question 6.
Explain the functions of promoters.
Answer:
A promoter conceives an idea for setting up a particular business at a given place and performs various formalities required for starting a company. A promoter may be an individual, a firm, association of persons or a company. Promoter takes lead for bringing money, men, machinery and material together for establishing an enterprise.
Promoter performs the following functions.
- A promoter conceives an idea for the setting up of a business.
- He makes preliminary investigations and ensures about the future prospects of the business.
- He brings together various persons who agree to associate with him and share the business responsibilities.
- He prepares various documents and gets the company incorporated.
- He raises the required finances and gets the company going.
Question 7.
What are the various types of capital required for business enterprises ?
Answer:
Depending upon the nature and purpose, capital may be divided into fixed capital and working capital.
Fixed Capital : The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such as land and buildings, plant and machinery etc., is called fixed capital. Capital used by the business organisations to meet the long term requirements is called fixed capital or block capital. The amount of fixed capital required by the business concern depends on the size and nature of business. Ex : A trading concern may require small amount of fixed capital than a manufacturing concern.
Working Capital : The capital required by business enterprises to run its day- to-day operations such as payment of wages, purchase of raw materials and holding current assets like stock of materials, bills receivable is called working capital. Current assets are those which are converted into cash within a period of one year. The amount of working capital required varies from business to business. Ex : If a business unit selling goods on credit or having a slow turnover would require more working capital as compared to firm selling its goods and services on cash basis or having a high turnover.
Question 8.
State any four merits of MNCs to host country.
Answer:
The following are merits of Multi National Corporations to host country.
- Provide Capital: MNCs bring in much needed capital for the development of industries. These corporations make direct foreign investment and speed up the process of economic development.
- Transfer of Technology : Developing countries are technically backward. They lack resources to carry research and development. MNCs serve as a vehicles for the transfer of advanced technology.
- Generate Employment : It creates large scale employment opportunities in host countries. They offer excellent pay scales and career opportunities to managers, technical and clerical staff.
- Foreign Exchange : MNCs help the host countries to increase their exports. They reduce their dependence on imports. MNCs enable host countries to improve their balance of payments position.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the benefits of E-business to society.
Answer:
The following are the benefits of E-business to the society.
- Availability products : E-business enables the people in developing countries and particularly to the people living in rural areas to enjoy the products and services which otherwise not available to them.
- Public welfare : E-business allows some of the goods and services to be sold at lower prices. It will benefit the poor people.
- Environmental benefits : E-business enables people to do shopping and less travelling for shopping. It results in less traffic on the roads and reduces air pollution.
Section – C
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Commerce
Answer:
Commerce is concerned with exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to transfer of goods from the places of production to the ultimate consumer. Commerce enables all these processes which helps to break the barriers between producers and consumers. It is sum of those processes which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of persons, place and time in exchange.
Question 11.
Co-Parcener
Answer:
The members of the Joint Hindu Family are called co-parceners. Co-parcener is a person who has a share in common property formed either through inheritance or conversion of assets by members. The liability of the co-parceners is limited to their share of interest in the common property.
Question 12.
Statutory Company
Answer:
The companies which are established by special acts of Parliament or state legislature are called Statutory Companies. Ex : Reserve Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation of India, Unit Trust of India.
Question 13.
Minimum subscription
Answer:
The minimum amount of capital to be collected by the company before the allotment of shares is known as minimum subscription. A public company cannot commence business unless the minimum subscription is received. It is fixed by the amount required for the purchase of property, payment of preliminary expenses and the working capital requirement.
Question 14.
External source of finance
Answer:
External sources of funds are those sources which lie outside the business organisation. These sources include shares, debentures, borrowings from commercial banks, financial institutions, lenders, suppliers and investors.
Question 15.
Financial institutions.
Answer:
Another important source of raising finance is from the financial institutions like Industrial Finance Corporation of India, Industrial Development Bank of India, Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India. Such institutions provide long-term and medium on easy installments to big industrial houses. Such institutions help in promoting new companies and expansion and development of existing companies.
Question 16.
Define FDI.
Answer:
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is the control of production in one country (host country) by a firm based in other country (home country) FDI is the defining features of Multi National Corporation. Foreign Direct Investment occurs when a firm invest its resources in business activities outside its home country.
![]()
Question 17.
E-Banking.
Answer:
Electronic banking is one of the most successful online business. E-Banking allows customers to access their accounts and execute orders through website. Online banking allows the customers to get their money from an Automatic Teller Machines instead of walking upto the cash desk in the bank. The customers can view their accounts, transfer funds and can pay bills.
Ex: Internet banking.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
Prepare final accountsof Praveen Traders for the year ending 31.032014.
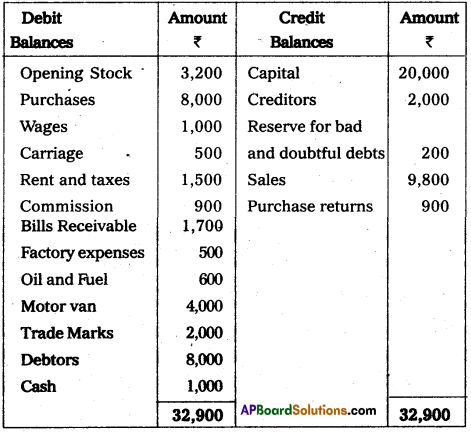
Adjustments:
1) Closing stock : ₹ 5,800
2) Depreciation on Motor van 10%.
3) Reserve for bad and doubtful debts 5%
4) Outstanding Rent: ₹ 500
5) Prepaid taxes: ₹ 200
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Praveen Traders for the year ended 31-03-2014
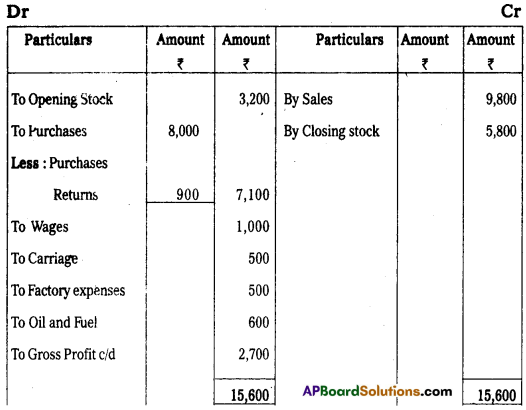
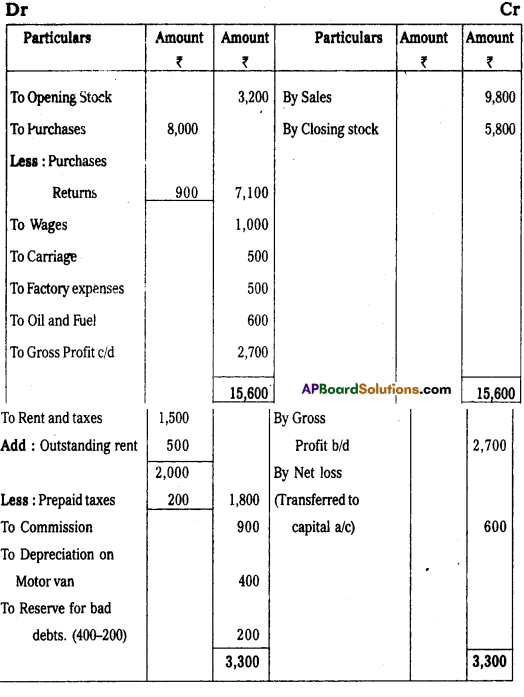
Balance Sheet of Praveen Traders as on 31-03-2014
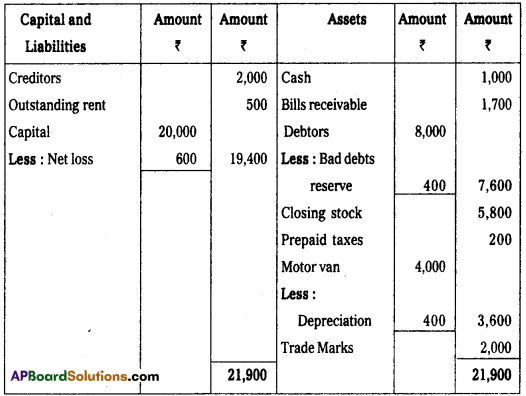
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
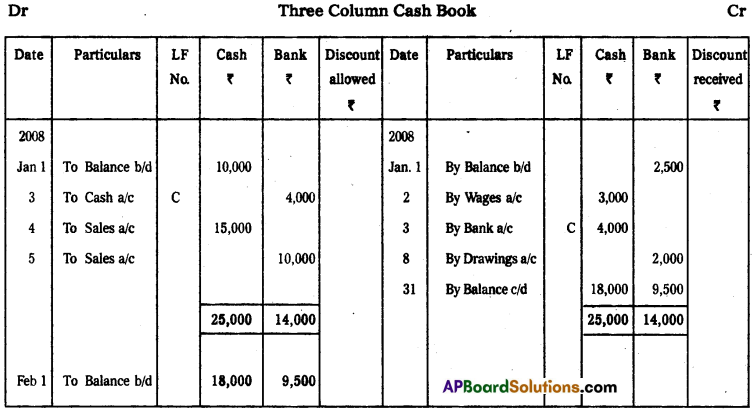
Prepare Three column cash book from the following particulars.

Answer:
Question 20.
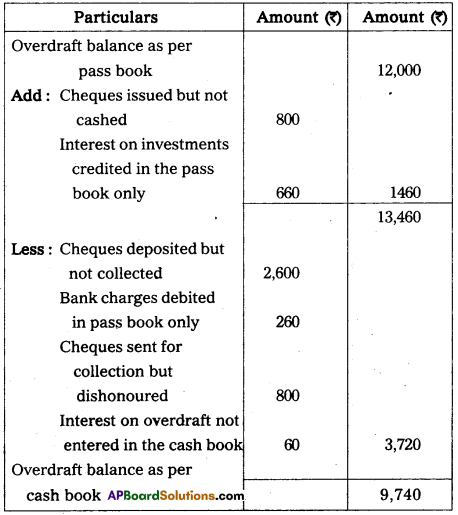
Mr. Balu, a trader found ₹ 12,000 overdraft balance in his pass book on 31.12.2006. Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement from the following information.

Answer:
Bank Reconciliation statement of Balu as on 31.12.2006
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain the advantages and limitations of accounting.
Answer:
- Accounting provides permanent and complete record of all business transactions. Thus it facilitates to replace human memory.
- It helps in ascertaining profit or loss for the financial year.
- It facilitates to ascertain financial position of the business.
- Accounting provides the facility of comparative study of various aspects such as profits, sales, expenses etc., with that of previous year and helps to take necessary decisions.
- It facilitates to excercise better control over the assets management.
Limitations:
- Accounting considers monetary transactions only. Non-monetary aspects like quality managerial skill, organisation culture completely ignored.
- The financial statements are prepared on historical cost basis. It ignores price level changes.
- Transactions relating to future estimates and fore casts are not considered in Accountancy.
- It is not free from personal bias when exercising choice out of alternative available. They may not realistic information which affects the overall results of the business concern.
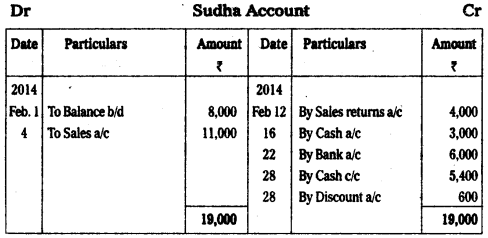
Question 22.
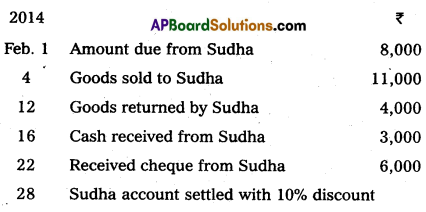
Prepare Sudha account from the following.
Answer:
Question 23.
Record the following transactions in proper subsidiary books.

Answer:
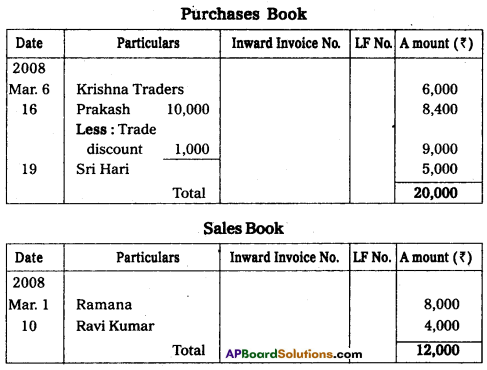
![]()
Question 24.
Rectify the following errors with suspense account.
a) Received cash from Ravi ₹ 200 has been posted to his account as ₹ 120
b) Goods sold to Rakesh ₹ 100 was omitted to be entered his account.
c) Credit side of Hari’s account was overcast by ₹ 20
d) Goods returned from Ramesh ₹ 35 was not posted to his account.
e) Sales book undercast by ₹ 350.
Answer:
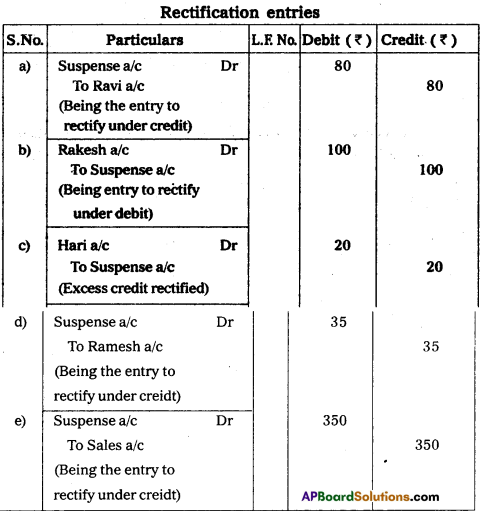
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
Accounting equation
Answer:
Accounting equation is based on the duel aspect concept, (i.e. debit and credit). The accounting equation shows the relationship between the economic resources of the business and claims against these resources.
Economic resources = claims
The economic resources are assets, claims consists of liabilities and owners claim or equity.
Assets = Equities or capital + Liabilities
Question 26.
Stock
Answer:
Stock includes goods unsold on a particular date. Stock may be opening or closing stock. The term opening stock means goods unsold at the being of the accounting period and closing stock includes goods unsold at the end of the accounting period.
Question 27.
Journal
Answer:
The book in which the business transactions are recorded in chronological order after analysing them and classifying the benefits according to principles of debit and credit is called ‘Journal’.
Question 28.
Record the following transactions into the journal.

Answer:
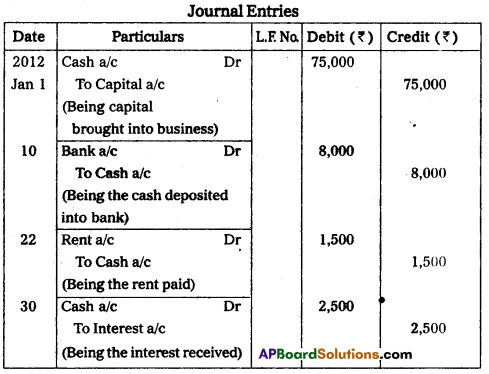
Question 29.
Record the opening journal entry from the following particulars.

Answer:
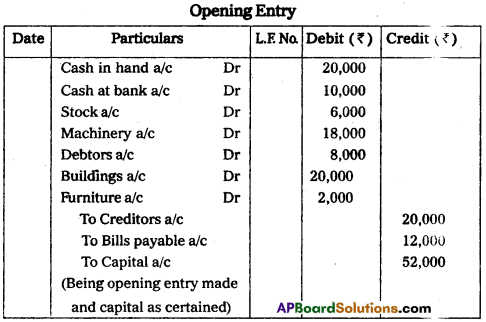
![]()
Question 30.
Error of omission
Answer:
These errors arise in the books due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books or posting into ledger.
Ex : When no entry is made for a transaction in any subsidiary book or journal.
Omission of posting an entry in ledger.
Question 31.
Prepare a trial balance from the following balances.

Answer:
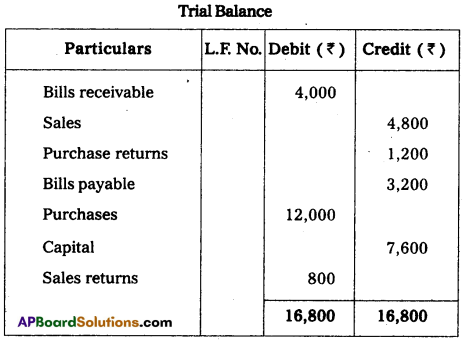
Question 32.
Depreciation
Answer:
The value of fixed assets like Machinery, Plant and Buildings will decrease year after year due to reasons like wear and tear, obsolescence etc. Such decline is called depreciation. It is considered as an expense and generally calculated as a percentage on the value of the asset. It is debited to profit and loss account and again deducted from the asset on the Balance Sheet.