Access to a variety of AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2017 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity. question patterns.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper May 2017
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
What is B.O.D.?
Answer:
The amount oxygen used by suitable micro organism present in water during five days at 20°C is called Bio Chemical Oxygen Demand (B.O.D.).
Question 2.
Write any one strategic adopted in green chemistry to avoid environmental pollution.
Answer:
Strategy adopted in green chemistry to avoid environmental pollution : In the dry cleaning of clothes earlier tetrachloro ethene is as used. This compound contaminates the ground water and is carcinogenic. Therefore it was replaced by liquid CO2 with a suitable detergent. This would not pollute the ground water.
![]()
Question 3.
What happens when Mg burns in air? Give equations also.
Answer:
When Mg metal burnt in air it reacts with O2 and N2 of air and forms MgO and Mg3N2.
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO
3 Mg + O2 → Mg3N2
Question 4.
What is Plaster of Paris ? Give two uses.
Answer:
Plaster of Paris is the hemi-hydrate of calcium sulphate. It’s 1
formula is CaSO4 \(\frac{1}{2}\) H2O.
Uses :
- It is used in making statues, monuments.
- It is used by dentists in treatment.
- It is used in setting fractured bones.
Question 5.
Among N2, O2, CH4 which gas diffuses fast, why?
Answer:
Among N2, O2, CH4 gases CH4 gas diffuse faster, because of it’s low molecular weight (16) where as N2 and O2 has 28 and 32 molecular weight. According to Graham’s law
Rate of diffusion ∝ \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\text { Molecular } w t}}\)
Question 6.
How many moles of glucose are present in 540 gms of glucose?
Answer:
No. of moles n = \(\frac{\text { Weight }}{\text { Gram molecular wt }}\)
= \(\frac{540}{180}\)
= 3
GMW (C6H12O6) = 180
Question 7.
What are extensive and intensive properties?
Answer:
Extensive properties:
The properties which depends on the amount of substance present in the system are called extensive properties. E.g. : Internal energy, mass, volume etc.
Intensitve Properties:
The properties which are independent on the amount of substance present in the system are called intensive properties. E.g. : Pressure, Temperature etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Define Third Law of Thermodynamics.
Answer:
The entropy of a pure and perfectly crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero temperature .

Question 9.
What is pH? Calculate the pH of 0.001 M HCl solution.
Answer:
pH : The negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration base ten expressed in moles / lit is called pH.
pH = – log10[H+]
Given 0.001M HCl solution
pH = – log10[H+]
= – log 0.001
= – log 10-3
= 3 log 10
= 3
∴ pH = 3
Question 10.
Write the structures of the following compounds.
a) 3, 3, 4, 5 – tetramethyl Heptane
b) 2 – methyl pent-1-ene
Answer:
a) 3, 4, 4, 5 – Tetramethyl heptane :
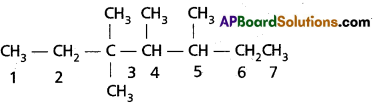
b) 2 – methyl pent-1-ene
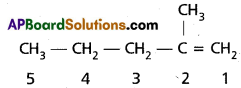
Question 11.
Deduce : (a) Boyle’s law and (b) Charle’s law from kinetic gas equation.
Answer:
a) Deduction of Boyle’s law :
Kinetic gas equation is
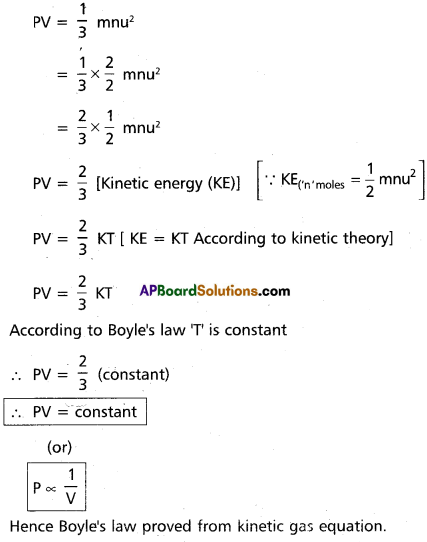
b) Deduction of Charle’s law :
Kinetic gas equation is PV = \(\frac{1}{3}\) mnu2
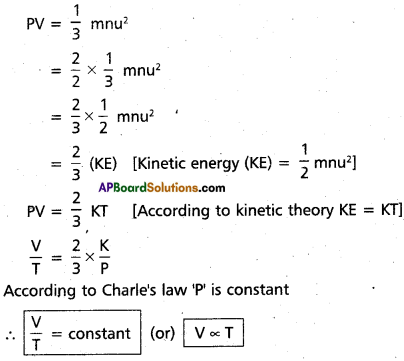
Hence Charle’s law proved from kinetic gas equation.
Question 12.
A carbon compound on analysis gave the following percentage composition. Carbon – 14.5%, Hydrogen – 1.8%, Chlorine – 64.46% and Oxygen – 19.24%. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound.
Answer:
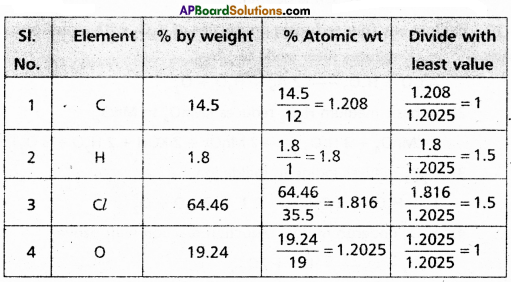
∴ The formula of the compound = C1H15Cl1.5 O1
Emperical formula of the compound = C2 H3 Cl3 O2
Question 13.
What is salt hydrolysis? Write the nature of the following salt solutions :
a) CH3 COONa
b) NH4 Cl
c) NaCl
Answer:
Salt hydrolysis:
The process of reacting the anion or cation or both of a salt with water to produce excess of H+ or OH- or both is called salt hydrolysis.
a) CH3 COQNa :
It is a salt obtained from weak acid and strong base. So it undergo anionic hydrolysis. In this hydrolysis of salt [OH–] > [H+] So pH > 7
∴ CH3COONa aq. solution is basic in nature.
b) NH4Cl : It is a salt obtained from strong acid and weak base. So, it undergo cationic hydrolysis. In this hydrolysis salt [H+] > [OH–]. So pH < 7.
NH4a aq. solution is acidic in nature.
c) NaCl : It is a salt obtained from strong acid and strong base. So it does not undergo hydrolysis.
∴ [H+] = [OH–] pH = 7
So, the nature of salt is neutral.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain any four reducing properties of H2O2 with equations.
Answer:
1) H2O2 reduces silver oxide to silver.
Ag20 + H202 > 2 Ag + H20 + 02
2) In basic medium H2O2 reduces KMnO4 to Mn02
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2O2 → 2 MnO2 + 2 KOH + 2 H2O + 3 O2↑
3) H2O2 reduces iodine to iodide ion
I2 + H2O2 + 2 OH2 → 2I–– + 2H2O + O2
4) H2O2 undergo mutual reduction reaction with ozone
H2O2 + O3 → H2O + 2O2
Question 15.
Explain any two methods for the preparation of Diborane.
Answer:
1. In industries diborane is prepared by the reaction between boron trr fluoride and lithium hydride.
![]()
2. Boron trichloride and hydrogen mixture subjected to silent electric discharge at low pressure to from diborane.
2BCl3 + 6H2 → B2H6 + 6HCZ
Boron trichloride undergo reduction with LiAlH4 to form diborane.
![]()
Question 16.
What is Hybridization? Explain Hybridization involved in PCl5 molecule?
Answer:
Hybridization: The inter-mixing of atomic orbitals of identical energy of an atom to form equal number of new identical orbital is called hybridization.
Answer:
1) In PCl5 the electron configuration of phosphorus is
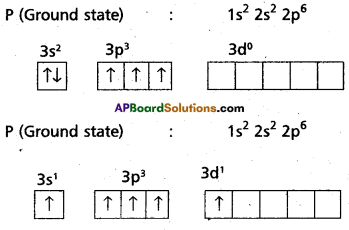
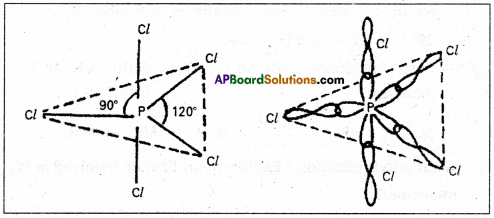
2) Phosphorus undergoes sp3d – hybridization by intermixing of one s – orbital [3s], three p – orbitals [3px, 3py, 3pz and one d – orbital.
These five hybrid orbitals overlap. The pZ orbitals of chlorine atoms forming five σsp3d-s bonds. Out of these five p – Cl bonds three are coplanar and the remaining two are in the axial position. There by PCl5 acquires the trigonal bipyramidal shape. The molecule contains two bond angles 90° and 120°.
Question 17.
Define Dipole Moment. Why the Dipole Moment of BeF2 is zero?
Answer: Dipole moment : The product of magnitude of the charge and the distance between the two poles (bond length) is called dipole moment.
Dipole moment μ p = q × d
q = change
d = bond length
Units :
Debye (D),1 Debye = 3.34 × 10-30 Coulombs metres.
Applications :
- Dipole moment is used to calculate the percentage of ionic character in a moiecufe.
- It is used to know the shape of the molecule.
- Symmetry (symmetrical (or) non symmetrical) of the molecule can be known by dipole moment.
- Even though Be – F bonds in BeF2 are polar, the dipole moment of BeF2 molecule is zero. Because BeF2 has linear shape.

- Here the vectrorial sum of the dipole moment of two Be – F bonds is zero. Flence dipole moment (μ) = 0.
Question 18.
Write the properties of Diamond and Graphite on the basis of their hybridization.
Answer:
| Properties of Diamond: | Properties of Graphite : |
| a) Each carbon is sp3 hybridised. | a) Each carbon is sp2 hybridised. |
| b) Each carbon is bonded to 4 other carbons tetrahedrally. | b) Each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings. It has sheet like structure. |
| c) It has a 3 dimensional structure. | c) It has a 2 dimensional structure. |
| d) C – C bond length is 1.54 A° and bond angle is 109° 28′. | d) C – C bond length in hexagonal rings is 1.42 A° and bond angle is 120°. |
| e) Carbon atoms are firmly held with strong covalent bonds. | e) The distance between two adjacent layers is 3.35 A°. These layers are held by weak Vander Waal’S forces. |
| f) Diamond is very hard. . | f) Graphite is soft. |
| g) Density = 3.5 g / cc. | g) Density – 2.2g/cc. |
| h) Diamond is an insulator due to the absence of free electrons. | h) Graphite is a conductor due to the presence of free electrons. |
| i) It is transparent, to light and X-rays. It has high refractive index (2.45). | i) It has layer lattice. The layers are slippery. Hence it is greasy. |
Section – C
Question 19.
Explain four quantum numbers and write their significance.
Answer:
- In general a large no.of orbitals are posible in an atom.
- These orbitals are distinguished by their size, shape and orientation.
- An orbital of smaller size means there is more chance to find electron near the nucleus.
- Atomic orbitals are precisely distinguished by quantum numbers. Each orbital is designated by three major quantum numbers.
- Principal quantum number (n)
- Azimuthal quantum number (l)
- Magnetic quantum number (m)
1) Principal quantum number:
The principal quantum number was introduced by Neils Bohr. It reveals the size of the atom (main energy levels). With increase in the value of ‘n’ the distance between the nucleus and the orbit also increases.
It is denoted by the letter ‘n’. It can have any simple integer value 1, 2, 3, but not zero. These are also termed as K, L, M, N etc. The radius and energy of an orbit can be determined basing on “n” value.
The radius of nth orbit is rn = \(\frac{n^2 h^2}{4 \pi^2 m e^2}\)
The energy of nth orbit is En = \(\frac{-2 \pi^2 m e^4}{n^2 h^2}\)
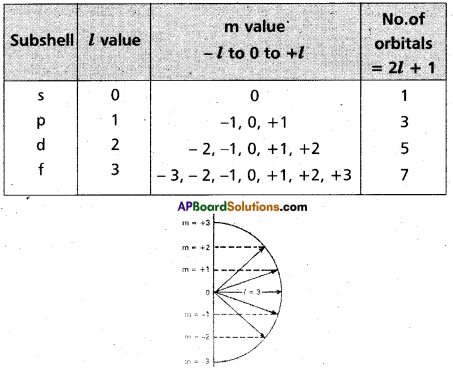
2) Azimuthal quantum number: It was proposed by Sommerfeld. It is also known as angular momentum quantum number or subsidiary quantum number.
it indicates the shapes of orbitals. It is denoted by T. The values of T depend on the values of ‘n’, T has values ranging from ‘O’ to (n-1) i.e., 1 = 0,1,2, ………(n-1). The maximum number of electrons present in the subshells s, p, d, f are 2, 6, 10, 14 respectively
| l – value | Shape | Shape |
| s | l = 0 | spherically symmetric |
| p | l = 1 | dunb – bell |
| d | l = 2 | double dumb – bell |
| f | l = 3 | four fold dumb – bell |
3) Magnetic quantum number:
It was proposed by Lande. It shows the orientation of the orbitals in space, ‘p’ – orbital has three orientations. The orbital oriented along the x-axis is called px orbital, along the y-axis is called py – orbital and along the z-axis is called pz orbital. In a similar way d – orbital has five orientations. They are dxy, dyz , dzx , dx2 – y2 and dz2. it is denoted by’m’. Its values depends on azimuthal quantum number, ‘m’ can have all the integral values from -l to +1 including zero. The total number of’m’ values are (2l + 1).
Spin quantum number:
- It was proposed by Ulhenbeck and Goud Smith.
- It is denoted by ‘S’.
- ‘S’ values are + \(\frac{1}{2},-\frac{1}{2}\)
Significance :
- It gives the information about spin of the electron.
- S = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (↑) represents the clock-wise spin of the electron.
- S = – \(\frac{1}{2}\) (↓) represents the anti clock-wise spin of the electron.
![]()
Question 20.
What is periodic property ? How are the following properties vary in a group and in a period ? Explain.
a) I.E.
b) Meatllic property
c) Atomic radius
Answer:
Recurrence of similar properties of elements at definite regular intervals with increasing atomic number i.e., according to their electronic configurations is known as periodicity. Any property which is periodic in nature is called periodic property.
a) IE : In groups and periods of the periodic table the ionization enthalpy values are periodically change depend upon the electronic configuration and size of elements.
In a group of elements ionization energy decreases from top to bottom because atomic radius increases.
In general, in a period the atomic size decreases. Because of this, the ionization energy increases across a period.
b) Metallic property :
Variation in group : Metallic nature in groups from top to bottom increases. This is due to increase of atomic size in groups.
Variation in period :
In periods from left to right metallic nature decreases. This is due to the decrease of atomic size in periods.
c) Atomic radius :
The atomic radius decreases from left to right in a period. With an increase in the atomic number in a period the nuclear charge increases. As a result the effective nuclear charge over the outermost electrons increases, due to this the orbitals are pulled closer to the nucleus causing in a decrease in the atomic radius.
The atomic radius increases from top to the bottom in a group because- with an increase in the atomic number the electrons are added to new shells resulting an increase in the number of inner
Question 21.
Explain any two preparation methods and two chemical properties of ethane.
Answer:
Methods of preparation of ethane :
1. Decarboxylation:
Ethane is prepared by heating sodium propionate with sodalime.
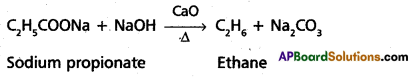
2. Kolbe’s electrolysis:
Ethane is obtained by the electrolysis of potassium acetate solution.
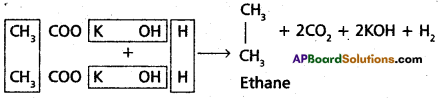
H2 gas evolves at cathode.
Ethane and CO2 are formed at anode Chemical properties of ethane:
1. Halogenation:
Ethane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight. Hydrogen atoms arjs substituted by halogen atoms successively. The final product is Hexachloro ethane.
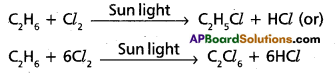
2. Nitration :
Ethane reacts with nitric acid at 400° C and gives nitro ethane.

3. pyrolysis:
When ethane is heated in the absence of oxygen it decomposes giving ethylene and hydrogen.
