Successful navigation through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Botany Question Paper April 2022 builds students’ confidence in their exam-taking abilities.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Question Paper April 2022
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 60
General Instructions:
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all the questions of Section – A. Answer any six questions in Section – B and answer ANY TWO questions in Section – C.
- In Section – A, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very short answer type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 5 lines. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section – B, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of”Short answer type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section – C, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long answer type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 Words.
- Draw labelled diagrams, wherever necessary for questions in Section – B and C.
Section – A (10 × 2 = 20)
Note:
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Each answer may be limited to 5 lines.
Question 1.
What is the basic unit of classification ? Define it.
Answer:
The basic unit of classification is species. A group of plants with similar characters is called species.
Question 2.
Give the main criteria used for classification by Whittaker.
Answer:
The main criteria for classification proposed by Whittaker include cell structure, thallus organisation, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationships.
Question 3.
What is Palaeobotany ? What is its use ?
Answer:
Study of fossil plants is called palaeobotany. It helps in understanding the course of evolution in plants.
Question 4.
Differentiate between Racemose and Cymose inflorescences.
Answer:
| Racemose Inflorescence | Cymose inflorescence |
| 1) Peduncle grows indefinitely. | 1) Peduncle grows definitely. |
| 2) Flowers are arranged in acropetal manner on the peduncle. | 2) Flowers are arranged in Basipetal manner on the peduncle. |
| 3) Flowers open in a centripetal manner. | 3) Flowers open in a centrifugal manner. |
![]()
Question 5.
What is meant by epipetalous condition ? Give an example.
Answer:
When the statements are attached to the petals, which is called epipetalous condition. Ex : Datura.
Question 6.
Explain the scope and significance of ‘Numerical Taxonomy’.
Question 7.
What is the significance of Vacuole in a plant cell ?
Answer:
Vacuoles play an important role in osmoregulation.
Question 8.
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysacdharides found among the following. Choose the one appropriate and write against each.
a) Cotton fibre ________
b) Exoskeleton of Cockroach ________
c) Liver ________
d) Peeled Potato ________
Answer:
a) Cotton fibre : Cellulose
b) Exoskeleton of cockroach : Chitin
c) Liver : Glycogen
d) Peeled potato : Starch
Question 9.
If a tissue has at a given time 1024 cells. How many cycles of mitosis had the original parental single cell undergone ?
Answer:
10 mitotic divisions.
Question 10.
Hydrophytes show reduced xylem. Why ?
Answer:
All submerged organs are capable of absorbing water. So hydrophytes show reduced xylem.
![]()
Section – B (6 × 4 = 24 )
Note :
- Answer any SIX questions.
- Each answer may be limited to 20 lines.
Question 11.
What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids ?
Answer:
- Most of the organisms are fresh water organisms found in stagnant water.
- They have a protein rich layer called pellicle which makes the body flexible.
- They have two flagella, a short and along one.
- The anterior part of the cell bears an invagination consisting of cytostome, cytopharynx and reservoir.
- Eye spot or photosensitive stigma is presentin the membrane of reservoir.
- They behave as heterotrophs by predating on other small organisms when deprived of light.
- They reproduce by longitudinal binary fission.
Question 12.
What is meant by homosporous and heterosporous pteridophytes ? Give two examples.
Answer:
The condition where only one type of spores are produced is called Homosporous pteridophytes.
Ex : Psilotum, Lycopodium
The condition where different types of spores are pro-duced is called Heterosporous pteridophytes.
Ex : Selagenella, Salvinia.
Question 13.
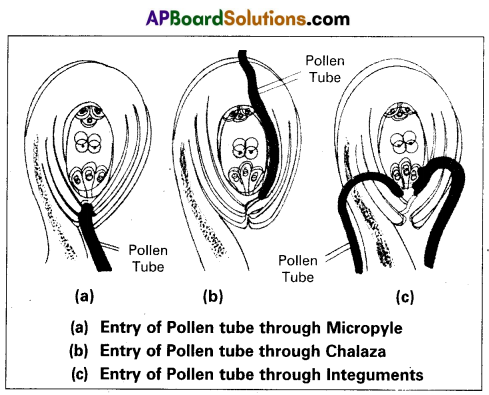
Discuss the various types of pollen tube enty into ovary with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
Pollen tube enters into the ovule from ovary by three ways.
They are
a) Porogamy : Pollen tube enters into the ovule through Micropyle.
Ex : Ottelia, Hibiscus.
b) Chalazogamy : “Pollen tube enters into the ovule through Chalaza”.
Ex : Casuarina.
c) Mesogamy: “Pollen tube enters into the ovule through the integuments”.
Ex : Cucurbita.
Question 14.
Write a brief account on the class of Dicotyledanae of Bentham and Hooker’s classification.
Answer:
In Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification, the class Dicotyledonae was divided into three sub-classes namely Polypetalae, Gamopetalae and Monochlamydae. Polypetalae, sub class is again divided into three series namely Thalamiflorae (6 orders), Disciflorae (4 orders) and Calyciflorae (5 orders). Gamopetalae, sub class is again divided into three series namely Inferae (3 orders), Heteromerae (3 orders) and Bicarpellatae (4 orders). Monochlamydae, sub class was divided into 8 series.
Question 15.
Briefly describe the cell theory.
Answer:
Mitochondria is termed as power houses of the cell. It is 0.2 to 1.0 μm in diameter, 1.0 to 4.1 μm in length, appears in cylindrical shape.
Each Mitochondria is a double membrane bound structure with outer smooth membrane and inner membrane with infoldings towards inside called cristae. The space inner to inner membrane is called matrix, which consists of single, circular DNA, few RNA molecules, 70s type of ribosomes and the components required for the synthesis of proteins. The cristae shows several stalked particles called F<sub>1</sub> particles or oxysomes.
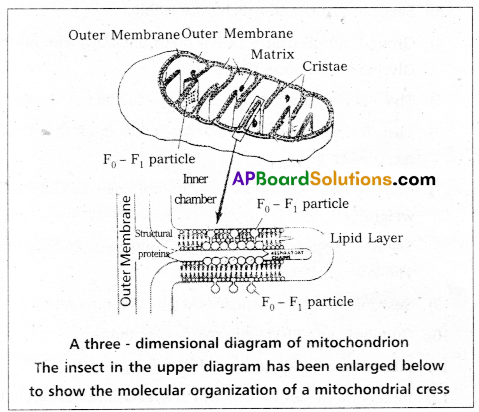
Function : Food materials undergo oxidation and releases energy in the form of ATP so called power houses of the cell.
![]()
Question 16.
Schematically represent Primary, Secondary and Tertiary structures of a hypothetical polymer using protein as an example.
Answer:
Metabolites which have identifiable functions and play known roles in normal physiological processes are called primary metabolites. E.g. : Amino acids, sugars. Metabolites which have no identifiable function in host organisms are called secondary metabolites.
E.g. : Rubber, drugs, scents and pigments.
Question 17.
Though redundantly described as a resting phase, interphase does not really involve rest. Comment.
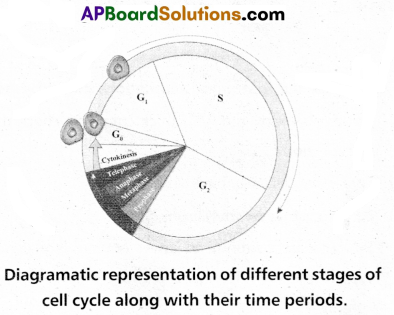
Answer:
The interphase, also called phase of non apparent division though called the resting phase, is the time during which the cell is preparing for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA Replication. The
interphase is divided into three further phases. They are
A) G1 phase : It is the interval between mitosis and Initiation of DNA replication. In this cell is metabolically active and continuously grows.
B) ‘S’ phase : In this, DNA replication occurs. The amount of DNA per cell doubles. However three is no increase in the number of chromosomes.
C) G2 phase: Proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while ceil growth continues. So Interphase is not a resting phase.
Question 18.
Enumerate the morphological adaptations of Xerophytes.
Answer:
- Roots are long with extensive branching spreading over wide areas.
- Root hairs and root caps are well developed.
- Mostly stems are stunted, woody, hard and covered with thick bark.
- Stems are usually covered by hairs or waxy coatings.
- Leaves are very much reduced to small, scale like and sometimes modified into spines to reduce the rate of transpiration.
- Lamina may be long, narrow, needle like or divided into many leaflets as in Acacia.
Section – C (2 × 8 = 16)
Note :
- Answer any TWO questions.
- Each answer may be limited to 60 lines.
Question 19.
Explain how stem is modified variously to perform different functions.
Answer:
Stems are modified in several ways to perform different functions. They are :
1) Tendrils : Slender, spirally coiled structures which may develop either from auxiliary bud (cucumber) or from terminal bud (grapes) are called tendrils. They help in climbing.
2) Thorns : Buds are modified into woody, straight pointed thorns which protect plants from grazing animals.
Ex : Citrus, Bougain villaea.
3) Phylloclade : In some plants of acid zones, leaves are modified into scales or spines to reduce the rate of transpiration. In such plants, stems are modified into flattened, green structure which carryout photosynthesis. Such stems are called phylloclades.
Ex : In euphorbia stem is cylindrical, in casuarina needle like, and in opuntia – flattened, fleshy green.
4) Bulbils : In some plants, the vegetative buds or floral buds store food materials. At maturity, may detach from the parent plants, develop.adventitious roots, grow as new plants thus help in vegetative reproduction. Ex : Diascoria.
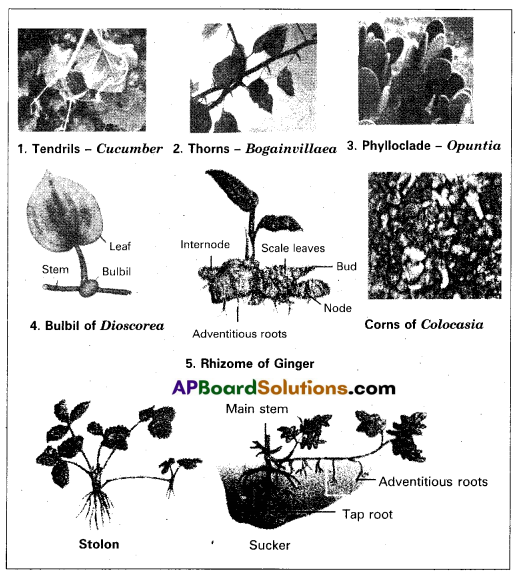
5) Underground stems : In some plants, stem grows into soil, store food materials, show perennation, to resist unfavourable conditions and also help in vegetative reproduction. Such stems are called underground stems.
Ex : Rhizome – Ginger, com – colacacia.
6) Sub aerial stems : In some plants, some part of the stem is underground and some part is aerial. Such stems are called sub aerial stems. In such plants, slender, lateral branches arises from the base of the main axis, grow vertically, arches downwards, produce adventitious roots when touches the ground. When they separates from the parent plant, they develop into new plants they help in vegetative reproduction.
Ex : Stolons – Nerium, Jasmine
Suckers – Chrysanthemum, Mertha.
![]()
Question 20.
Draw the diagram of a microsporangium and label its wall layers. Write briefly about the wall layers.
Answer:
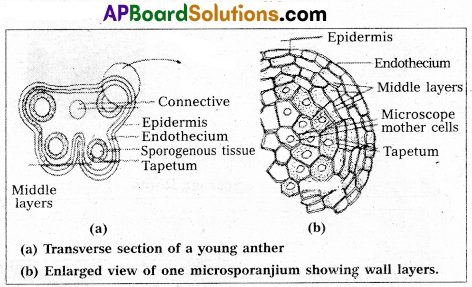
A typical angiospermics anther is bilobed with each lobe having two theca. The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four microsporangia located at the comers, two in each lobe.
In a transverse section, a typical microsporangium is circular in out line and is surrounded by four wall layers, the
(a) epidermis
(b) endothecium
(c) wall layers
(d) tapetum.
a) Epidermis : The epidermis is one celled thick, the cells present between the pollen sacs are th thin walled and their region is called as stomium which is useful for the dehiscence of pollen sacs.
b) Endothecium : It is present below the epidermis and expands radically with fibrous thickenings, at maturity these cells loose water and contract and help in. the dehiscence of pollen sacs.
c) Wall layers : Beneath the Endothecium, there are thin walled cells, arranged in one to five layers, which also help in dehiscence of Anther.
d) Tapetum : The innermost wall layer is Tapetum, the cells are large, with thin cell walls, abundant cytoplasm and have more than one nuclei. Tapetum is a nutritive tissue which nourishes the developing pollen grains.
Question 21.
Describe the internal structure of a dicot root.
Answer:
A thin transerverse section of dicot root shows three parts namely
(i) Epidermis
(ii) Cortex and
(iii) stele.
(i) Epidermis – It is the outer most layers made of thin walled cells. Some cells protrude in the form of unicelluler root hairs. So called Epiblema. it protects the inner parts. Root hairs help in absorption of water from the soil.
(ii) Cortex – It consists of several layers of thin walled parenchyma cells with inter cellular spaces. The Innermost layer of cortex is called Endodermis. It comprises a single layer of barrel shaped cells without intercellular spaces. The tangential as well as the radial walls of Endoderm cells show suberin thickenings called casparian strips. Some cells opposite to protoxylem lack these strips. Some cells opposite to protoxylem lack these strips called passeage cells. They help in the movement of water and dissolved salts from cortex into xylem.
(iii) Stele : – It is the central part, consists of 4 layers.
(d) Pericycle : It is single layered, made of thin walled parenchyma cells, present next to endodermis. It produces lateral roots and become vascular cambium during secondary growth.
(e) Vascular Bundle : Xylem and phloem constitutes vascular Bundle. They are arranged on different radius (in alternate manner) so called Radial vascular Bundle, Xylem is exarch, where protoxylem is towards periphery and metaxylem is towards the center. Xylem is diarch to tetrach condition. Xylem helps in conduction of water and minerals and phloem helps in conduction of food materials.
(f) Medulla : It is absent or small, made of parenchyma cells. When present, it helps in the storage of food and water.